Midbrain dopaminergic inputs gate amygdala intercalated cell clusters by distinct and cooperative mechanisms in male mice
Figures
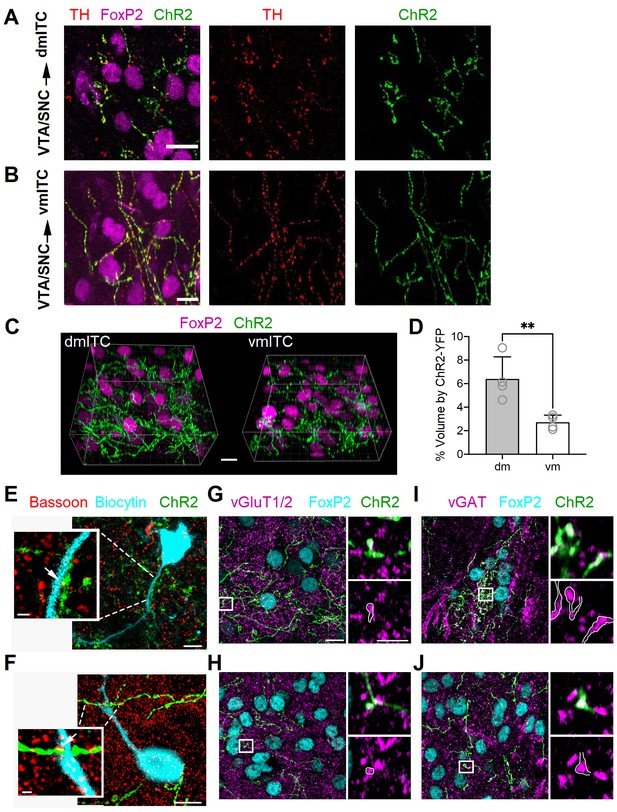
Dopaminergic fibers from VTA/SNC targeting dm- and vm-ITC clusters in the amygdala co-label with vGAT and vGluT1/2.
(A–B) Maximum intensity projection confocal images illustrating ChR2-YFP+ axons (green) originating from tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive dopaminergic neurons (TH, red) in the ventral tegmental area/substantia nigra pars compacta (VTA/SNC) targeting FoxP2-positive neurons (magenta) in the dorsomedial (dm)- and ventromedial (vm)-intercalated cell (ITC) clusters. Overlay (left), TH staining (middle), ChR2-YFP (right). Scale bars: 10 µm. (C) Representative image volumes of the dm- and vm-ITC clusters with FoxP2-labeled nuclei (magenta) and ChR2-YFP+ axons (green). Scale bar: 10 µm. (D) The volume fraction encompassed by ChR2-YFP+ axons was significantly higher in the dm-ITC (6.40 ± 0.94% of total image volume) compared to the vm-ITC cluster (2.72 ± 0.30% of total image volume; unpaired t-test, **p=0.0097). Histograms display the mean ± SEM and values from individual mice (empty circles, n=4 animals). The average dm- and vm-ITC cluster volume analyzed per animal was 138.15 ± 29.51 and 156.12 ± 10.29 µm3, respectively. (E–F) Overlay confocal images of ChR2-YFP+ axons (green) and biocytin-filled cells (turquoise) in dm-ITC and vm-ITC clusters immunostained for the presynaptic marker Bassoon to examine putative active zones (white arrows). Scale bars 5 and 1 µm (inset). (G–H) Confocal images of dm- and vm-ITC clusters, including FoxP2-positive neurons (turquoise) that contain ChR2-YFP+ fibers (green) co-labeled for the presynaptic markers vGluT1/vGluT2 (magenta). Right panels show a higher magnification of the boxed area containing an example of a bouton co-expressing ChR2-YFP and vGluT1/vGluT2 outlined in white. (I–J) Confocal images of dm- and vm-ITC clusters, including FoxP2-positive neurons (turquoise) that contain ChR2-YFP fibers (green) co-labeled for the presynaptic marker vGAT (magenta). Right panels show a higher magnification of the boxed area containing an example of a bouton co-expressing ChR2-YFP and vGAT outlined in white. Scale bars for (G–J): 10 µm for left panels, 3 µm for right panels. Thickness of confocal z-stacks: (A) 11.1 μM; (B) 12.5 μM; (E) 8.06 and 2.01 µm for the cell and synapse on dendrite, respectively; (F) 12.2 and 2.2 µm for the cell and synapse on dendrite, respectively; (G–J) left panels, 8.83 µm; right panels, single plane of 0.18 µm nominal thickness.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Data Figure 1D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx

Specific expression of ChR2-YFP in dopaminergic midbrain neurons.
(A) Experimental strategy: Targeting of dopaminergic midbrain neurons by injecting DAT-Cre mice with AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP. Subsequent examination of injection and projection sites using tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and FoxP2 immunostaining, as well as Neurotrace (NT), to delineate brain structures. (B) Single-plane confocal images (0.9 µm thickness) of ventral tegmental area/substantia nigra pars compacta (VTA/SNC) midbrain neurons expressing ChR2-YFP (green, left) immunolabeled for TH (red, middle), and overlay (right), including close-up of a TH-positive ChR2-YFP-expressing cell. Scale bars 100 µm (overview), 10 µm (close-up). (C) On average, 91.17 ± 1.37% of ChR2-YFP-expressing midbrain neurons were TH-positive (n=10 hemispheres from five animals).
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
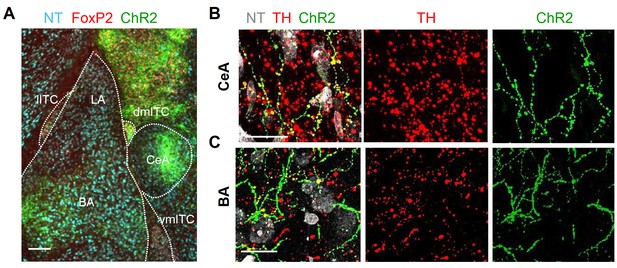
Labeling of TH-positive axons in the amygdala.
(A) Fluorescence microscopic overview image of the amygdala showing ChR2-YFP+ axons distributed in central amygdala (CeA), basal amygdala (BA), intercalated cell (ITC) clusters, and the amygdala-striatal transition zone. Scale bar 200 µm. (B–C) Maximum intensity projection confocal images of ChR2-YFP+ axons (green, right panel), punctate labeling with tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) (red) in the same area (middle panel), and overlay together with Neurotrace (NT) (grey, left panel), demonstrating that ChR2-YFP+ axons are decorated with TH-positive puncta (yellow) in CeA (B) and basolateral complex of the amygdala (BLA) (C). Thickness of confocal z-stacks: 12.9 and 11.7 µm for (B) and (C), respectively. Scale bars 10 µm.

Example of 3D analysis of axonal volumes in ITC clusters.
Left: Image volume showing FoxP2-labeled nuclei (magenta) of neurons in the dorsomedial-intercalated cell (dm-ITC) cluster and midbrain dopaminergic axons expressing ChR2-YFP (green). Right: Surface rendering of ChR2-YFP+ axons. Images are derived from processing of volumes with IMARIS 9.7.0 software.
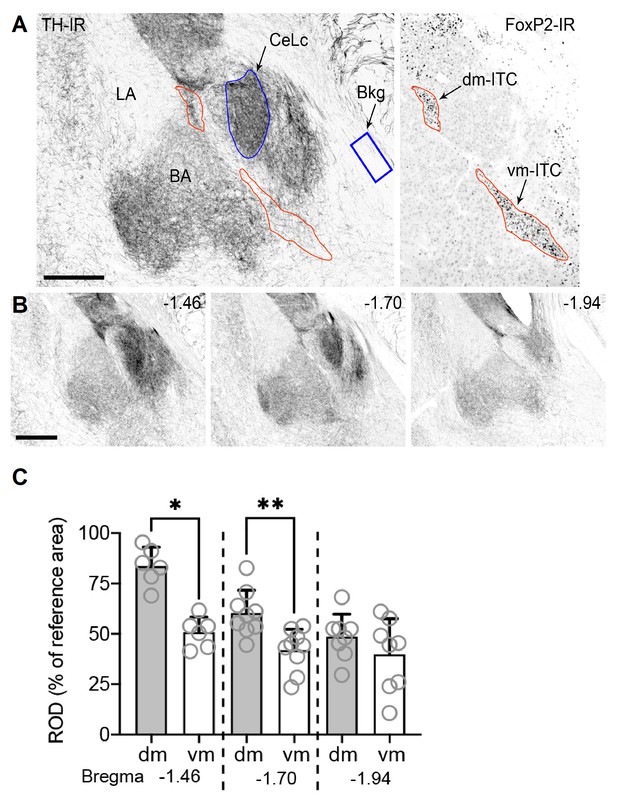
Quantitative analysis TH-staining reveals stronger labeling in dm- versus vm-ITC clusters.
(A) Representative images of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and FoxP2 immunoreactivity (IR) from consecutive amygdala sections of C57BL/6J adult male mice. FoxP2-IR, associated primarily with nuclei of intercalated cells (ITCs), was used to delineate the dorsomedial (dm)- and ventromedial (vm)-ITC clusters (outlined in red). The central component of the central lateral nucleus (CeLc) of the amygdala (outlined in blue) was used as a reference area for its very high density of TH-IR fibers. An area within the optic nerve (blue box) was used to calculate the background mean grey value (MGV). Scale bar 250 µm. (B) Representative images of three different amygdala rostro-caudal levels (bregma −1.46,–1.70, and −1.94) at which the TH-IR MGV within the dm- and vm-ITC clusters was analyzed. Scale bar 500 µm. (C) Significant changes in the TH-IR relative optical density (ROD) between dm- and vm-ITC clusters were observed at bregma −1.46 (Wilcoxon test, *p=0.031) and −1.70 (Wilcoxon test, **p=0.004), but not at −1.94 (Wilcoxon test, p=0.195). Higher TH-IR ROD was detected at different bregma levels in the dm-ITC clusters (one-way ANOVA, F(2,20)=18; p<0.0001), at bregma −1.46 vs. −1.70 (Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test, p=0.0015) and −1.46 vs. −1.94 (Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test, p<0.0001). Conversely, no differences were observed in the TH ROD at different bregma levels in the vm-ITC cluster (one-way ANOVA, F(2,20)=1.3; p=0.28). Histograms display the mean ± SEM and values from individual mice (empty circles, n=9 animals, not all bregma levels represented in all animals).
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 4—source data 1
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig1-figsupp4-data1-v1.xlsx
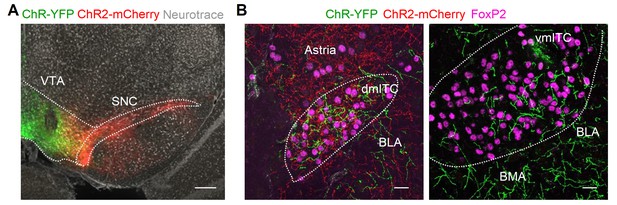
Dm-ITC and vm-ITC clusters receive differential inputs from VTA and SNC.
(A) Fluorescence microscopic overview image of the dopaminergic midbrain showing neurons transduced with ChR2-YFP (green) and ChR2-mCherry (red) in ventral tegmental area (VTA) and substantia nigra pars compacta (SNC), respectively. Neurotrace is shown in grey. Scale bar 200 µm. (B) Resulting projection patterns in intercalated cell (ITC) clusters upon viral injections shown in (A). Maximum intensity projection confocal images of ChR2-YFP+ (green) and ChR2-mCherry+ (red) axons within FoxP2-positive dorsomedial (dm)-ITC (left) and ventromedial (vm)-ITC clusters (right). Thickness of confocal z-stacks: 20 µm. Scale bar 20 µm. Representative data from n=2 animals.
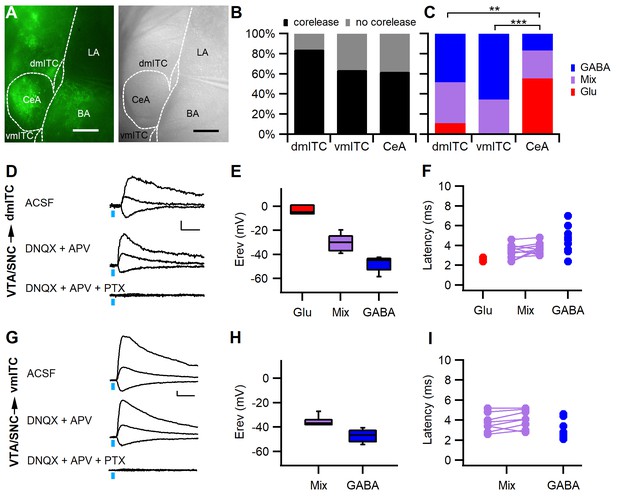
Stimulation of midbrain dopaminergic fibers evokes mainly GABAergic PSCs in dm- and vm-ITCs.
(A) Fluorescence (left) and infrared differential interference contrast image of an amygdala slice with patch recording pipette in the dorsomedial-intercalated cell (dm-ITC) cluster (right). ChR2-YFP-expressing axons from dopaminergic midbrain were observed in central amygdala (CeA), amygdalostriatal transition zone, basal amygdala (BA), and ITC clusters. (B) Fast postsynaptic currents (PSCs) were evoked by stimulation of dopaminergic fibers in a large fraction of recorded ITCs and CeA neurons (Fisher’s exact test=4.823, p=0.098; 84% for dm-ITCs, n=32 cells from 16 animals; 64% for ventromedial-intercalated cells (vm-ITCs), n=36 cells from 11 animals; and 62% for CeA, n=29 cells from 11 animals). (C) Distribution of fast PSCs in dm-ITCs, vm-ITCs, and CeA neurons by response type. ITCs show mostly GABAergic PSCs (dm-ITCs, n=27: GABA 48%, mixed 41%, Glu 11%; vm-ITCs, n=23: GABA 65%, mixed 35%), whereas CeA neurons (n=18) exhibited mostly glutamatergic PSCs (GABA 17%, mixed 28%, Glu 55%). Response types were significantly different between all regions (Fisher’s exact test=21.41, p<0.001). A pairwise comparison revealed differences between CeA and ITC clusters (CeA vs. dm-ITC, **p=0.005; CeA vs. vm-ITC, ***p<0.001). (D and G) Representative traces of light-evoked mixed PSCs recorded at −70, 0, and 40 mV from a dm-ITC (D) and a vm-ITC (G). Application of glutamate receptor blockers DNQX (20 µM) and APV (100 µM) had a small effect, whereas the GABAA-R channel blocker picrotoxin (PTX, 100 µM) abolished the PSCs entirely (n=5 cells from five animals for dm-ITC, n=3 cells from three animals for vm-ITC). Scale bars: 10 pA, 10 ms. (E and H) Box plot of PSC reversal potentials (Erev) for dm-ITCs (E) and vm-ITCs (H) by PSC type. (E) Erev in dm-ITCs was −3.49 ± 2.21 mV for glutamatergic PSCs, −48.15 ± 1.65 mV for GABAergic PSCs, and −30.21 ± 2.07 mV for mixed PSCs (one-way ANOVA, F(2, 24)=70.563, p<0.001). (H) Erev in vm-ITCs was −47.12 ± 1.31 mV for GABAergic PSCs and −35.57 ± 1.32 mV for mixed PSCs (unpaired t-test, p<0.001). (F and I) Latencies of PSCs were consistent with monosynaptic connections. (F) Latencies in dm-ITCs were 2.60 ± 0.12 ms (n=3) for pure glutamatergic, 3.45 ± 0.21 ms for the glutamatergic, and 3.67 ± 0.16 ms (n=11) for the GABAergic components of mixed PSCs, and 4.33 ± 0.35 ms (n=13) for pure GABAergic PSCs. (I) Latencies in vm-ITCs were 3.75 ± 0.32 ms for glutamatergic and 4.09 ± 0.32 ms (n=8) for GABAergic components of mixed PSCs, and 3.04 ± 0.25 ms (n=15) for pure GABAergic PSCs.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Data Figure 2C, E-F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Data Figure 2C, H-I.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig2-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 3
Data Figure 2C and Figure 2—figure supplement 2B-C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig2-data3-v1.xlsx
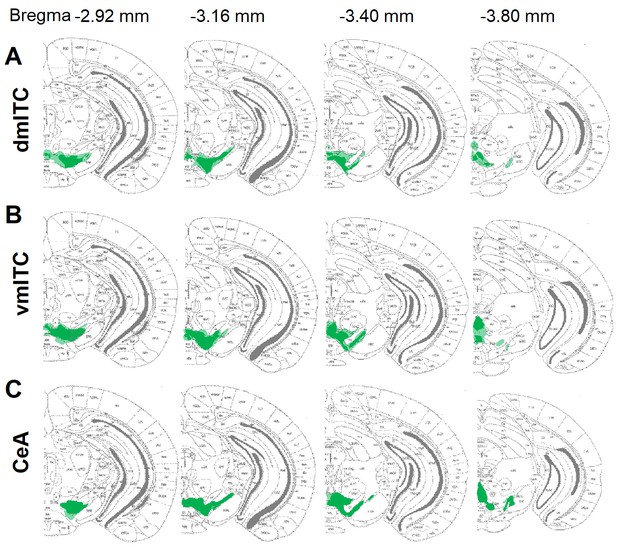
Overview of ChR2-YFP injection and expression sites in the midbrain for co-release experiments.
Brain atlas overlays of sites showing distribution of ChR2-YFP-labeled neuronal cell bodies in the dopaminergic midbrain for all animals in which fast postsynaptic currents (PSCs) were recorded. (A) Injection sites for dorsomedial-intercalated cell (dm-ITC) recordings (n=16 animals). (B) Injection sites for ventromedial-intercalated cell (vm-ITC) recordings (n=11 animals). (C) Injection sites for central amygdala (CeA) recordings (n=11 animals). Bregma levels are indicated at the top.
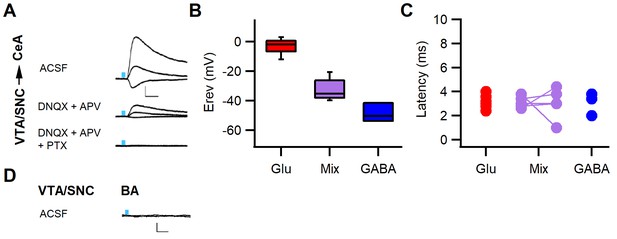
Fast PSCs onto CeA neurons are mainly glutamatergic.
(A) Example traces of mixed postsynaptic currents (PSCs) evoked by dopaminergic fiber stimulation recorded from a central amygdala (CeA) neuron at different holding potentials (−70, 0, and 40 mV). PSCs were largely blocked with glutamate receptor blockers (20 µM DNQX and 100 µM APV, middle traces) and completely abolished upon addition of the GABAA channel blocker picrotoxin (PTX, 100 µM, bottom traces, n=8 cells from seven animals). (B) Box plot of PSC reversal potentials (Erev) for CeA neurons. Erev for different response types were glutamatergic PSCs −2.98 ± 1.54 mV, mixed PSCs −32.75 ± 3.28 mV, and GABAergic −48.58 ± 3.62 mV (one-way ANOVA, F(2, 15)=90.495, p<0.001). (C) Similar latencies of evoked excitatory (glutamatergic 3.14 ± 0.19 ms, n=10), inhibitory (GABAergic 3.07 ± 0.55 ms, n=3), and mixed (glutamatergic component 3.12 ± 0.22 ms and GABA component 3.04 ± 0.57 ms, n=5) PSCs. Scale bars 40 pA, 10 ms. (D) Example traces recorded from a basal amygdala (BA) projection neuron at different holding potentials (−70, 0, and 40 mV) upon dopaminergic fiber stimulation yielding no response (n=10 neurons recorded from five animals showing co-release in either CeA or intercalated cells (ITCs)). Scale bars: 20 pA, 10 ms.

Locations of neurons receiving co-release and no co-release from DA midbrain afferents.
(A) Distribution of recorded dorsomedial (dm)- and ventromedial-intercalated cells (vm-ITCs), as well as central amygdala (CeA) neurons, at different bregma levels color-coded by co-release type. (B) Distribution of recorded dm- and vm-ITCs, as well as CeA neurons, at different bregma levels showing no co-release from the same animals shown in (A).
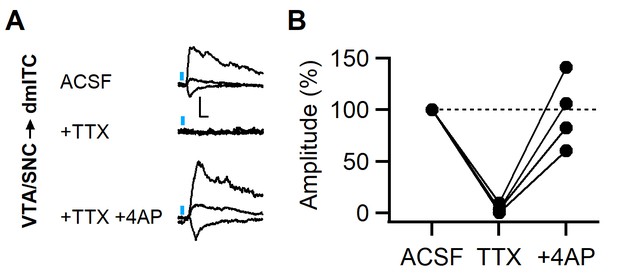
Fast PSCs from midbrain dopaminergic fibers onto dm-ITCs are monosynaptic.
(A) Example traces of postsynaptic currents (PSCs) evoked by dopaminergic fiber stimulation recorded from a dorsomedial-intercalated cell (dm-ITC) at different holding potentials (−70, 0, and 40 mV). The PSC was blocked by tetrodotoxin (TTX, 0.5 µM) and recovered with 4-aminopyridine (4-AP, 100 µM) in the presence of TTX, indicating its monosynaptic nature. Scale bars 20 pA, 5 ms. (B) Summary data of normalized PSC amplitudes for the experiment shown in (A). Repeated-measures ANOVA, F(2, 6)=14.88, p=0.013, reveals significant differences between drugs (n=4 cells from three animals).
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 4—source data 1
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig2-figsupp4-data1-v1.xlsx
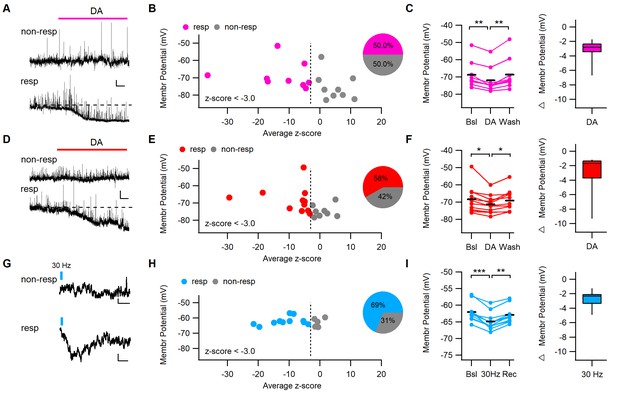
DA application or phasic stimulation of midbrain inputs hyperpolarizes a fraction of dm-ITCs.
(A, D) Representative traces of dorsomedial-intercalated cells (dm-ITCs) recorded at resting membrane potential in current clamp mode from young (postnatal day 20–28) and adult (8–10 weeks) mice. Dopamine (DA, 15–30 µM) was applied during the time indicated. Scale bars for (A): 3 mV, 30 s; and for D: 2 mV, 30 s. DA hyperpolarized some cells (responding), but not others (non-responding). (B, E) Distribution of recorded cells according to how DA affects their membrane potential represented as z-scores (x-axis) and their initial membrane potential (y-axis). Responding cells (z-score cut-off at −3) are shown in pink (young) or red (adult), non-responding cells in grey. Insets: fraction of DA-responsive neurons in young mice (n=18 cells from seven animals) and adult mice (n=19 cells from 10 animals). (C, F) Left: Absolute and relative changes in membrane potential in DA-responsive neurons recorded from young (C) and adult mice (F). DA significantly hyperpolarized responsive dm-ITCs in slices from young (n=9 cells from five animals, repeated-measures ANOVA: F(2, 16)=16.23, p<0.001; Bonferroni post-hoc test: Bsl vs. DA **p=0.001, DA vs. Wash **p=0.004) and adult animals (n=11 cells from eight animals, repeated-measures ANOVA: F(2, 20)=7.91, p=0.003; Bonferroni post-hoc test: Bsl vs. DA *p=0.016, DA vs. Wash *p=0.019). DA-induced hyperpolarization amounted to –3.18 ± 0.48 mV and –2.94 ± 0.83 mV in neurons from young and adult mice, respectively. (G) Representative traces of dm-ITCs recorded in current clamp mode from adult mice. Trains of 10 pulses at 30 Hz optogenetic stimulation of DA midbrain afferents were applied during the time indicated. Scale bars: 0.5 mV, 1 s. (H) Distribution of recorded cells according to 30 Hz stimulation of DA afferents affects their membrane potential represented as z-scores (x-axis) and their initial membrane potential (y-axis). Responding cells (z-score cut-off at −3) are shown in blue, non-responding cells in grey. Insets: Fraction of stimulation-responsive neurons (n=16 cells from three animals). (I) Absolute and relative changes in membrane potential in responsive neurons. 30 Hz stimulation significantly hyperpolarized responsive dm-ITCs (n=11 cells from two animals, repeated-measures ANOVA: F(2, 20)=49.01, p<0.001; Bonferroni post-hoc test: Bsl vs. Stim *p<0.001, Stim vs. Recovery *p=0.001). 30 Hz stimulation-induced hyperpolarization amounted to –2.84 ± 0.35 mV.
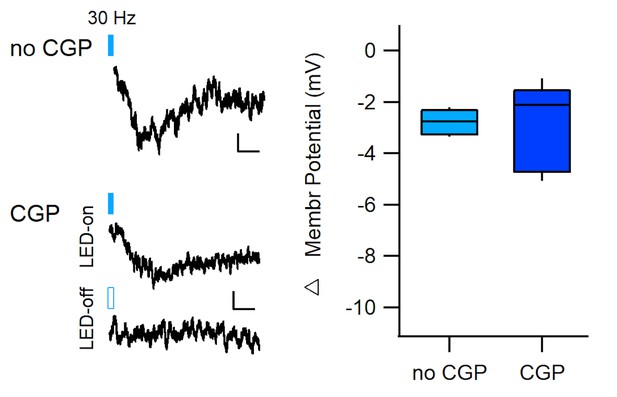
30 Hz stimulation hyperpolarizes dm-ITCs in the presence of a GABAB receptor blocker.
Left: Representative traces of dorsomedial-intercalated cells (dm-ITCs) recorded in current clamp mode from adult mice. Trains of 10 pulses at 30 Hz optogenetic stimulation of dopaminergic (DA) midbrain afferents were applied in the absence (top, Figure 3G) or in the presence of GABAB receptor antagonist CGP55845 (10 µM) with and without light stimulation (bottom) during the time indicated. Scale bars 0.5 mV, 1 s. Right: The relative changes in membrane potential in responsive neurons did not differ between neurons recorded in the absence (–2.77 ± 0.22 mV, n=6 cells from two animals) or presence of CGP55845 (–2.92 ± 0.76 mV, n=5 cells from one animal), unpaired t-test, p=0.836.

Distribution of dm-ITCs according to their response to DA and 30 Hz stimulation.
(A, B) Distribution of recorded dorsomedial-intercalated cells (dm-ITCs) at different bregma levels in young (A) and adult mice (B) color-coded according to their response to dopamine (DA) application. (C) Distribution of recorded dm-ITCs at different bregma levels in adult mice color-coded according to their response to 30 Hz afferent stimulation. Bregma levels are indicated at the bottom.
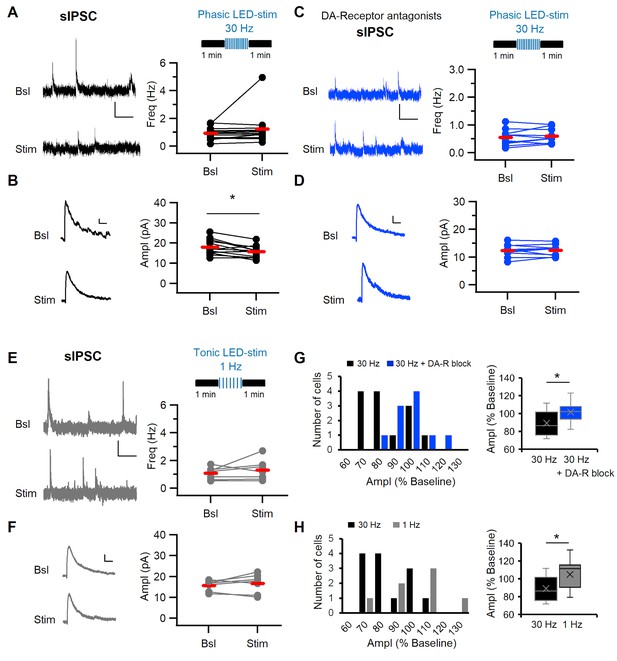
Phasic stimulation of midbrain dopaminergic fibers alters sIPSC amplitude in dm-ITCs in a DA-R-dependent manner.
(A, C, E) Top: Experimental protocol. Spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic current (sIPSC) frequency and amplitude were assessed before and after optogenetic stimulation of midbrain dopaminergic fibers in (A, C) with phasic (10 times 10 pulses at 30 Hz) and in (E) with tonic (100 pulses at 1 Hz) patterns. (A–F) Left: sIPSC example traces before (Bsl) and after stimulation (Stim). All sIPSCs were recorded at 0 mV. Right: Plots of sIPSC frequency and amplitude depict values for individual neurons (dots) and the average (red line). (A) Left: Example traces of sIPSC activity (scale bars: 10 pA, 1 s). Right: sIPSC frequency did not change upon 30 Hz stimulation (0.94 ± 0.12 Hz vs. 1.23 ± 0.32 Hz, n=13, paired t-test, p=0.278). (B) Left: Example traces of averaged sIPSCs (scale bars: 2 pA, 20 ms). Right: sIPSC amplitude decreased after 30 Hz stimulation (17.94 ± 1.06 pA vs. 15.74 ± 0.78 pA, n=13, paired t-test, *p=0.011). (C) Left: Example traces of sIPSC activity (scale bars 10 pA, 1 s). Right: sIPSC frequency did not change (0.55 ± 0.09 Hz vs. 0.60 ± 0.08 Hz, n=10, paired t-test, p=0.349) in the presence of DA-R blockers (D1: SCH23390 10 µM; D2: Sulpiride 20 µM; D4: L-745870 100 nM). (D) Left: Example traces of averaged sIPSCs (scale bars 2 pA, 20 ms). sIPSC amplitude did not change after 30 Hz stimulation in the presence of DA-R blockers (12.36 ± 0.72 pA vs. 12.43 ± 0.64 pA, n=10, paired t-test, p=0.857). (E) Left: Example traces of sIPSC activity (scale bars 10 pA, 1 s). sIPSC frequency did not change after 1 Hz stimulation (1.07 ± 0.17 Hz vs. 1.31 ± 0.28 Hz, n=7, paired t-test, p=0.348). (F) Left: Example traces of averaged sIPSCs (scale bars 2 pA, 20 ms). Right: sIPSC amplitude did not change after 1 Hz stimulation (15.71 ± 0.96 pA vs. 16.68 ± 1.74 pA, n=7, paired t-test, p=0.398). (G) Comparison of amplitude changes in sIPSCs after 30 Hz stimulation in the absence (black) and in the presence of DA-R blockers (blue). Left: Distribution of amplitudes (as % of baseline). Right: Box plots comparing relative amplitudes between the groups (Mann-Whitney U-test, *p=0.047), indicating that DA-R blockers prevent the effect of 30 Hz stimulation on sIPSCs. (H) Comparison of amplitude changes in sIPSCs after 30 Hz (black) and 1 Hz stimulation (grey) of dopaminergic fibers. Left: Distribution of amplitudes (as % of baseline). Right: Box plots comparing relative amplitudes between the groups (Mann-Whitney U-test, *p=0.043). Data were obtained from three to seven animals per experiment.

Overview of ChR2-YFP injection and expression sites in the midbrain for phasic and tonic stimulation experiments.
Brain atlas overlays of sites showing distribution of ChR2-YFP-labeled neuronal cell bodies for experiments related to Figure 4 and its supplements. (A) Injection sites for 30 Hz stimulation onto dorsomedial-intercalated cells (dm-ITCs) recorded in the absence of DA-R blockers (n=7 animals). (B) Injection sites for 30 Hz stimulation onto dm-ITCs recorded in the presence of DA-R blockers (n=3 animals). (C) Injection sites for 1 Hz stimulation onto dm-ITCs recordings (n=4 animals). Bregma levels are indicated at the top.
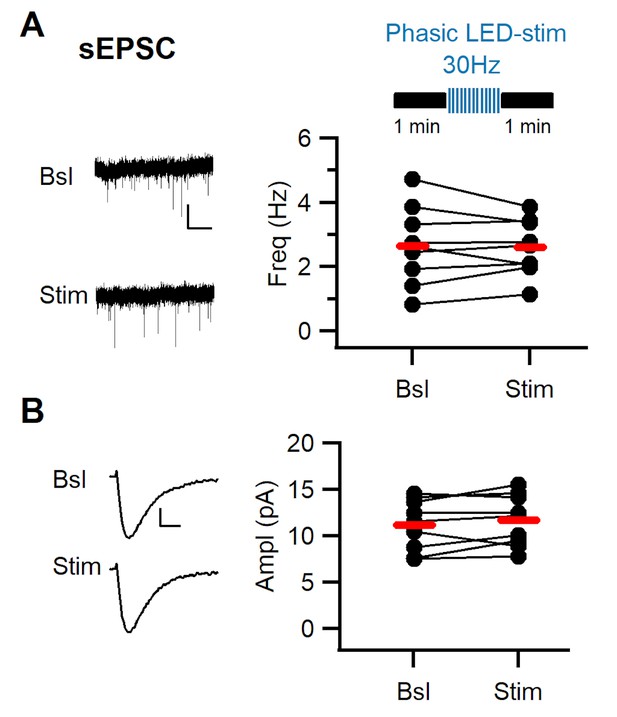
Phasic stimulation of midbrain dopaminergic fibers does not affect sEPSCs in dm-ITCs.
(A) Top: Experimental protocol. Spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) were assessed in dorsomedial-intercalated cells (dm-ITCs) before and after phasic stimulation of dopaminergic fibers (30 Hz, 10 pulses, 10 sweeps). Left: Example traces of sEPSC activity recorded at −70 mV in 100 µM picrotoxin (PTX) before (Bsl) and after stimulation (Stim). Scale bars: 20 pA, 10 s. Right: Plot of sEPSC frequency in individual neurons (dots) and average (red lines). sEPSC frequency remained stable (2.65 ± 0.40 Hz vs. 2.60 ± 0.29 Hz, n=9; paired t-test, p=0.759). (B) Left: Example traces of averaged sEPSCs before and after stimulation. Scale bars 3 pA, 3 ms. Right: Plot of sEPSC amplitudes in individual neurons (dots) and average (red lines). sEPSC amplitude was not affected by dopaminergic fiber stimulation (11.18 ± 0.92 pA vs. 11.68 ± 0.92 pA; n=9, paired t-test, p=0.217). Data were obtained from seven animals.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig4-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
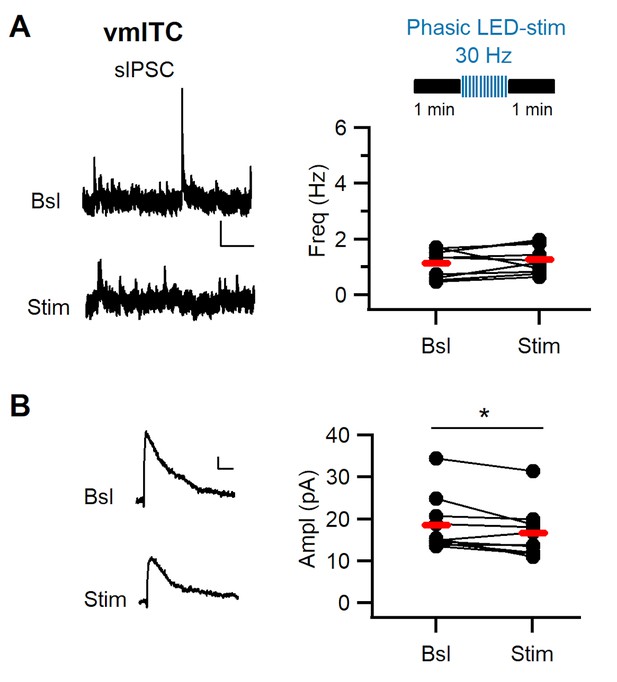
Phasic stimulation of midbrain dopaminergic fibers alters sIPSC amplitude in vm-ITCs.
(A) Top: Experimental protocol. sIPSCs were assessed in ventromedial-intercalated cells (vm-ITCs) before and after phasic stimulation of dopaminergic fibers (30 Hz, 10 pulses, 10 sweeps). Left: Example traces of sIPSC activity recorded at 0 mV (A) recorded from vm-ITCs before (Bsl) and after stimulation (Stim). Scale bars: 20 pA, 10 s. Right: Plot of sIPSC frequency in individual neurons (dots) and average (red lines). sIPSC frequency (1.14 ± 0.16 Hz vs. 1.28 ± 0.16 Hz, n=10, paired t-test, p=0.272) was not affected by dopaminergic fiber stimulation. (B) Left: Example traces of averaged sIPSCs before and after stimulation. Scale bars for sIPSC: 5 pA, 20 ms. Right: Plot of sIPSC amplitudes in individual neurons (dots) and average (red lines). sIPSC amplitude decreased after stimulation (18.50 ± 2.12 pA vs. 16.68 ± 1.92 pA, n=10, paired t-test, *p=0.034). Data were obtained from six animals.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 3—source data 1
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig4-figsupp3-data1-v1.xlsx
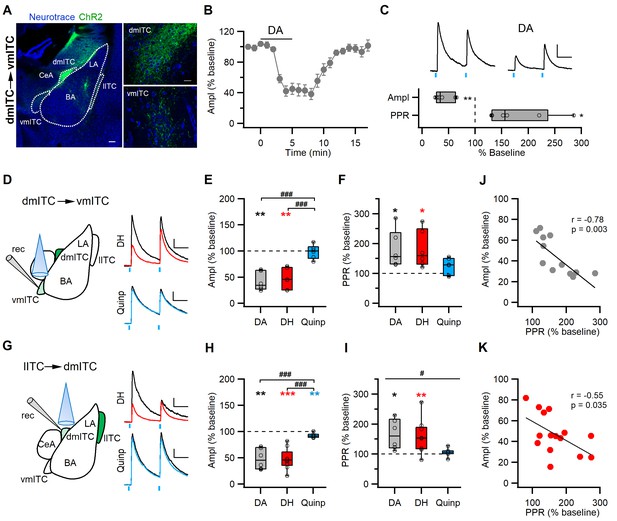
DA via DRD1 mediates presynaptic depression between ITC clusters.
(A) Confocal images of the amygdala showing ChR2-YFP-expressing neurons in the dorsomedial-intercalated cell (dm-ITC) cluster and their efferents targeting the ventromedial-intercalated cell (vm-ITC) cluster after injection of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP in FoxP2-Cre mice. Left: Overview of the amygdala. Right: Details of the dm-ITC injection site with YFP+ cells (top) and vm-ITC recording site with YFP+ fibers (bottom). Scale bars: 200 and 20 µm. (B) Time course of changes in inhibitory postsynaptic current (IPSC) amplitude upon bath application of dopamine (DA, 30 µM, 5 min) in the dm-ITC→vm-ITC pathway. DA decreased IPSC amplitude, which returned to near baseline levels upon washout. (C) Top: Representative IPSC traces recorded at 0 mV from the baseline period and during DA application (paired pulse interval 100 ms). Scale bars: 50 pA, 50 ms. Bottom: Relative change of IPSC amplitude and paired pulse ratio (PPR) during DA application (n=6 cells from three animals, amplitude 41.53 ± 7.25%, paired t-test, **p=0.003; PPR 180.00 ± 25.01%, paired t-test, *p=0.031). (D and G) Left: Schematics of experimental approach with infection, recording, and light stimulation sites. Right: Representative traces recorded at baseline (black) and during agonist application (colored). Dihydrexidine (DH, 10 µM), a DRD1 agonist, is shown in red, Quinpirole (Quinp, 1 µM), a DRD2 agonist, is shown in blue (paired pulse interval: 100 ms). Scale bars 50 pA, 50 ms. (E and H) Comparison of relative changes in IPSC amplitude during agonist application in the dm-ITC→vm-ITC pathway (E) and l-ITC→dm-ITC pathway (H). (E) DH (red, n=6 cells from four animals) suppressed IPSCs (amplitude 46.69 ± 8.14%, **p=0.010, paired t-test), whereas Quinp (blue, n=6 cells from three animals) had no effect (amplitude 98.45 ± 5.37, p=0.438, paired t-test). Between-group analysis revealed a significant drug effect on the dm-ITC→vm-ITC amplitude (one-way ANOVA, F(2, 15)=20.107, p<0.001) with Quinp differing from DA and DH (###p<0.001 each, Bonferroni post-hoc tests). (H) DH (red, n=9 cells from five animals) strongly suppressed IPSCs (amplitude 47.16 ± 6.67%, ***p<0.001, paired t-test), whereas Quinp (blue, n=7 cells from three animals) had a minor effect (amplitude 92.38 ± 1.63%, **p=0.006). Between-group analysis revealed a significant drug effect on the l-ITC→dm-ITC amplitude (one-way ANOVA, F(2, 19)=17.394, p<0.001) with Quinp differing from DA and DH (###p<0.001 each, Bonferroni post-hoc tests). (F and I) Comparison of relative change of PPR during drug application in the dm-ITC→vm-ITC pathway and l-ITC→dm-ITC pathway. (F) DH (red, n=6) increased PPR (181.37 ± 25.38%, *p=0.035, paired t-test), whereas Quinp (blue, n=6) had no significant effect on PPR (123.97 ± 11.25%, p=0.127, paired t-test). Between-group analysis revealed no significant drug effect on the dm-ITC→vm-ITC PPR (one-way ANOVA, F(2, 15)=2.304, p=0.134). (I) DH (red, n=9) increased PPR (158.46 ± 18.52%, **p=0.005, paired t-test), whereas Quinp (blue, n=7) had no effect on PPR (105.02 ± 4.98%, p=0.385, paired t-test). Between-group analysis revealed a significant drug effect on the l-ITC→dm-ITC PPR (one-way ANOVA, F(2, 19)=3.804, #p=0.041). (J and K) Combined data from both pathways show a significant correlation between change in PPR and change in amplitude upon application of DA (J: Pearson correlation, r=−0.78, p=0.003, n=12) and upon application of DH (K: Pearson correlation, r=−0.55, p=0.035, n=15).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Data Figure 5B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Data Figure 5C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig5-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 3
Data Figure 5E-F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig5-data3-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 4
Data Figure 5H–I.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig5-data4-v1.xlsx

An l-ITC→dm-ITC inhibitory pathway that is modulated by DA via a presynaptic mechanism.
(A) Experimental scheme. AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP was injected into the amygdala of FoxP2-Cre mice to specifically infect the lateral intercalated cell (l-ITC) cluster, and optically evoked postsynaptic currents (PSCs) were recorded in dorsomedial-intercalated cells (dm-ITCs). (B) PSCs recorded in a dm-ITC at different holding potentials (−70 mV to +40 mV) with a reversal potential of −41.44 mV. Application of the GABAA channel blocker picrotoxin (PTX) 100 µM) abolished the PSCs. Scale bars 200 pA, 20 ms. (C) Box plots and individual latencies (circles) for IPSCs evoked between different ITC clusters. Synaptic latencies were similar for the l-ITC→dm-ITC pathway (2.07 ± 0.10 ms, n=22 cells from 12 animals) and the dm-ITC→vm-ITC pathway (2.23 ± 0.09 ms, n=18 cells from 10 animals, unpaired t-test, p=0.268). (D) Confocal images showing ChR2-YFP-expressing neurons in the l-ITC cluster and their efferents targeting the dm-ITC cluster. Left: Overview of the amygdala. Right: Close-up of the injection sites with YFP+ cells in the l-ITC (top) and recording sites with YFP+ fibers in the dm-ITC cluster (bottom). Scale bars 200 and 20 µm. (E) Time course of changes in IPSC amplitude upon bath application of dopamine (DA, 30 µM, 5 min) in the l-ITC→dm-ITC pathway. DA decreased IPSC amplitude, which returned to near baseline levels upon washout. (F) Top: Representative IPSC traces recorded at 0 mV from the baseline period and during DA application (paired pulse interval 100 ms). Scale bars 50 pA, 50 ms. Bottom: Relative change of IPSC amplitude and paired pulse ratio (PPR) during DA application (n=6 cells from three animals, amplitude 48.05 ± 8.09%, paired t-test, **p=0.006; PPR 165.72 ± 20.46%, paired t-test *p=0.019).
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 2
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig5-figsupp1-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 3
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig5-figsupp1-data3-v1.xlsx
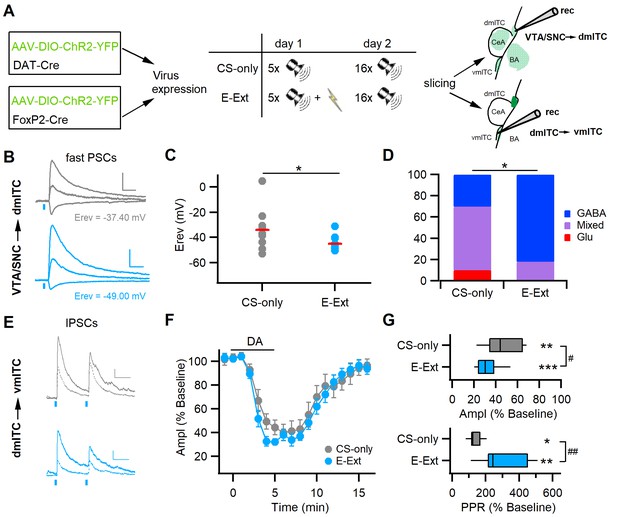
Early extinction enhances GABA release from midbrain terminals and DA-mediated depression of the dm-ITC→vm-ITC pathway.
(A) Experimental scheme: To investigate the VTA/SNC→dm-ITC pathway, ChR2 was transduced in dopaminergic midbrain neurons of DAT-Cre mice. To investigate dopamine (DA) modulation of the dm-ITC→vm-ITC pathway, ChR2 was transduced into the dorsomedial-intercalated cell (dm-ITC) cluster of FoxP2-Cre mice. The early extinction group (E-Ext) underwent fear conditioning on day 1 (5 conditioned stimulus-unconditioned stimulus (CS-US) pairings) and early extinction training on day 2 (16 CS presentations). The CS-only group received only CS presentations. (B) Left: Example traces of light-evoked postsynaptic currents (PSCs) by dopaminergic fiber stimulation recorded in dm-ITCs at −70, 0, and 40 mV from CS-only (grey traces) or E-Ext animals (blue traces). Scale bars: 50 pA, 50 ms. (C) Plot of PSC reversal potentials in individual dm-ITCs (dots) and average (red lines) from CS-only and E-Ext groups. Erev was significantly lower in the E-Ext (−45.09 ± 1.76 mV, n=11 cells from six animals) vs. the CS-only group (−34.06 ± 5.11 mV, n=10 cells from four animals, *p=0.047, paired t-test). (D) Summary graph comparing the type of fast PSCs in dm-ITCs recorded from CS-only and E-Ext animals (CS-only, n=10: GABA 30%, mixed 60%, Glu 10%; E-Ext, n=11: GABA 82%, mixed 18%). PSC types were significantly different between groups (Fisher’s exact test = 5.68, *p=0.041). (E) Example traces of light-evoked inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) recorded in a ventromedial-intercalated cell (vm-ITC) at 0 mV upon paired pulse stimulation (100 ms interstimulus interval) of the dm-ITC→vm-ITC pathway from CS-only (grey traces) or E-Ext (blue traces) animals before (solid) and during DA application (dotted). Scale bars 50 pA, 50 ms. (F) Time course of changes in IPSC amplitude upon bath application of DA (30 µM, 5 min) in dm-ITC→vm-ITC pathway in CS-only and E-Ext groups. Two-way ANOVA (1–9 min) revealed significant changes for time, F(8)=37.903, p<0.001, and group, F(1)=8.229, p=0.005, but no significant interaction, F(8, 144)=0.521, p=0.839. (G) Significant changes of IPSC amplitude (paired t-tests: CS-only, **p=0.002; E-Ext, ***p<0.001) and paired pulse ratio (PPR) (paired t-tests: CS-only, *p=0.040; E-Ext, **p=0.003) 4–5 min after DA application in both groups. IPSC amplitude was more depressed in neurons recorded from E-Ext vs. CS-only animals (32.42 ± 3.16%, n=11 cells from six animals, vs. 46.75 ± 6.14%, n=7 cells from four animals, unpaired t-test, #p=0.036). The PPR increase was larger in neurons recorded from E-Ext vs. CS-only animals (310.63 ± 42.64%, n=11, vs. 139.68 ± 15.43%, n=7, unpaired t-test, ##p=0.007).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Data Figure 6C–D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Data Figure 6F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig6-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 3
Data Figure 6G.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig6-data3-v1.xlsx

Behavioral data from DAT-Cre mice used for ex vivo recordings and viral injection sites.
(A) Experimental strategy for targeting of dopaminergic midbrain neurons by injecting DAT-Cre mice with AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP. (B) Freezing levels for behavioral paradigms shown in Figure 6A in virally transduced DAT-Cre mice used for recordings. A group of mice was subjected to only conditioned stimulus (CS) presentations (CS-only, grey, n=4 mice), and the other group was subjected to fear conditioning on day 1 and early extinction training with 16 CS presentations (E-Ext, blue, n=6 mice). Repeated-measures ANOVA, F(3, 15)=1.382, p=0.287, reveals no significant differences between time points for E-Ext. (C) Brain atlas overlays of sites showing the distribution of ChR2-YFP-labeled neuronal cell bodies in the dopaminergic midbrain of DAT-Cre mice in which fast postsynaptic currents (PSCs) were recorded. Top: CS-only (n=4 mice); bottom: E-Ext (n=6 mice). Bregma levels are indicated at the top.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
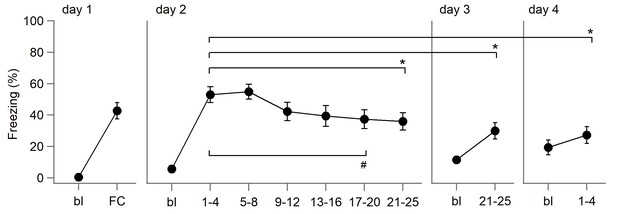
Behavioral data from mice trained with a long extinction protocol.
Another group of DAT-Cre mice was subjected to extinction training with 25 conditioned stimulus (CS) presentations on days 2 and 3, and extinction recall by four CS presentations on day 4 (n=10 mice). On days 2 and 3, freezing was averaged across four CSs for the first five time points and five CSs for the last one. Across days 2–4, a repeated-measures ANOVA, F(3, 27)=6.467, p=0.002, reveals significant differences between time points; Bonferroni-corrected pairwise comparisons: day 2 (CS1–4) vs. day 2 (CS21–25), *p=0.039; day 2 (CS1–4) vs. day 3 (CS21-25) and vs. day 4 (CS1-4), *p=0.015 and *p=0.018, respectively. For within-session extinction on day 2, a repeated-measures ANOVA, F(5, 45)=8.14, p<0.001, reveals significant differences between CS blocks; Bonferroni-corrected pairwise comparisons: (CS1–4) vs. (CS17–20), #p=0.045.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 2—source data 1
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig6-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
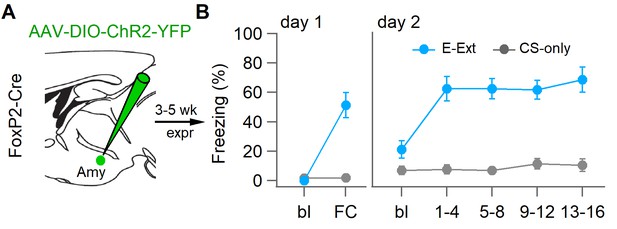
Behavioral data from FoxP2-Cre mice used for ex vivo recordings.
(A) Experimental strategy for targeting of dorsomedial-intercalated cell (dm-ITC) clusters by injecting FoxP2-Cre mice with AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP. (B) Freezing levels of virally transduced FoxP2-Cre mice used for recordings (conditioned stimulus (CS)-only group, grey, n=4 mice; E-Ext group, blue, n=6 mice) are displayed as described in Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Repeated-measures ANOVA, F(3, 15)=0.647, p=0.597, reveals no significant differences between time points for E-Ext.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 3—source data 1
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63708/elife-63708-fig6-figsupp3-data1-v1.xlsx
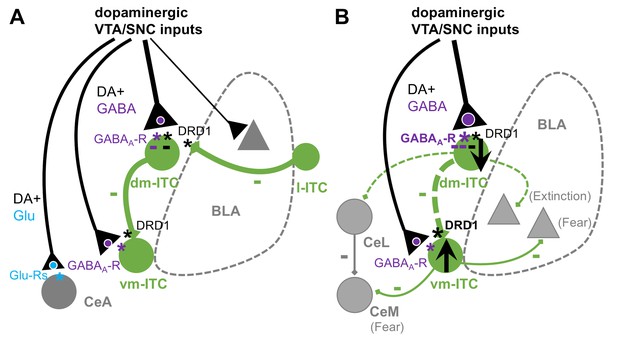
Summary scheme of results.
(A) Impact of dopaminergic midbrain inputs onto intercalated cell (ITC) clusters, central amygdala (CeA), and basal amygdala (BLA). Dopaminergic inputs from ventral tegmental area/substantia nigra pars compacta (VTA/SNC) target amygdala ITC clusters and, to a lesser extent, BLA and CeA. The dorsomedial-intercalated cell (dm-ITC) cluster is more densely and differentially innervated than the ventromedial-intercalated cell (vm-ITC) cluster. Co-release of glutamate is mainly observed in CeA, whereas GABA co-release is prominent onto dm- and vm-ITCs. Released dopamine (DA) directly hyperpolarizes some dm-ITCs, and DA depresses inhibitory interactions between ITC clusters via presynaptic DRD1. Dopaminergic midbrain inputs can thus regulate the ITC network by inhibitory and disinhibitory mechanisms acting on different time scales. (B) Effects of early extinction on dopaminergic regulation of ITC cluster activity and interactions. Early extinction training enhances both direct fast inhibition of dm-ITCs, by biasing midbrain inputs toward GABA co-release, and disinhibition of vm-ITCs, by altering DA-mediated suppression of the dm-ITC→vm-ITC pathway. Together, this may tip the activity balance toward decreased dm-ITC and increased vm-ITC activity. We speculate that this could impact behavioral outcome by decreasing inhibition onto dm-ITC targets (such as CeL and extinction-promoting neurons in BLA), while promoting inhibition onto vm-ITC targets (such as fear-promoting neurons in centro-medial amygdala [CeM] and BLA).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | Male C57BL/6J mice | Charles River or Envigo | Stock#: 000664, RRID:IMSR_JAX:000664 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Male heterozygousB6.SJL-Slc6a3tm1.1(cre)Bkmn/J mice | The Jackson Laboratory | Stock#: 006660, RRID:IMSR_JAX:006660 | Maintained on C57BL/6J background |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Male heterozygousB6.Cg-Foxp2tm1.1(cre)Rpa/J mice | The Jackson Laboratory | Stock#: 030541, RRID:IMSR_JAX: 030541 | Maintained on C57BL/6J background |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Male heterozygous ICR.Cg-Gad1tm1.1Tam/Rbrc mice | Tamamaki et al., 2003. J Comp Neurol 467(1):60–79. doi:10.1002/cne.10905 | RRID:IMSR_RBRC03674 | Maintained on C57BL/6J background |
| Strain, strain background (adeno-associated virus) | AAV2/1.EF1a.DIO.hChR2(H134R).eYFP | Addgene / U. Penn Vector Core | Cat# 20298-AAV1, RRID:Addgene viral prep # 20298-AAV1 | |
| Strain, strain background (adeno-associated virus) | AAV2/9.EF1a.DIO.hChR2 (H134R).eYFP | Addgene / U. Penn Vector Core | Cat# 20298-AAV9, RRID:Addgene viral prep # 20298-AAV9 | |
| Strain, strain background (adeno-associated virus) | AAV2/1.EF1a.DIO.hChR2 (H134R).mCherry | Addgene/Viral Vector Facility U. Zurich | Cat# 20297-AAV1, RRID:Addgene viral prep # 20297-AAV1 | |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (goat polyclonal) | GeneTex | Cat# GTX26673, RRID:AB_371426 | IF(1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (rabbit polyclonal) | Invitrogen | Cat# A11122, RRID:AB_221569 | IF(1:750 or 1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-FoxP2 (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# AB16046, RRID:AB_2107107 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-FoxP2 (mouse monoclonal) | Merck Millipore | Cat# MABE415, RRID:AB_2721039 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-FoxP2 (sheep polyclonal) | R and D Systems | Cat# AF5647, RRID:AB_2107133 | IF(1:200), IHC(1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-TH (rabbit polyclonal) | Millipore | Cat# AB152, RRID:AB_390204 | IF(1:1000), IHC (1:4000) |
| Antibody | Anti-TH (mouse monoclonal) | Merck Millipore | Cat# MAB318, RRID:AB_2313764 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Bassoon (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat# AB82958, RRID:AB_1860018 | IF(1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-VGAT (guinea pig polyclonal) | Synaptic Systems | Cat# 131 004, RRID:AB_887873 | IF(1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-VGLUT1 (guinea pig polyclonal) | Chemicon/ Millipore | Cat# AB5905, RRID:AB_2301751 | IF(1:3000) |
| Antibody | Anti-VGLUT2 (guinea pig monoclonal) | Chemicon/ Millipore | Cat# AB5907, RRID:AB_2301731 | IF(1:5000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Goat Alexa 488 (donkey polyclonal) | Invitrogen/Life Technologies | Cat# A-11055, RRID:AB_2534102 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Rabbit Alexa 555 (donkey polyclonal) | Invitrogen/Life Technologies | Cat# A-31572, RRID:AB_162543 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Mouse Alexa 555 (goat polyclonal) | Invitrogen/Life Technologies | Cat# A-21424, RRID:AB_141780 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Rabbit Alexa 647 (donkey polyclonal) | Invitrogen/Life Technologies | Cat# A-31573, RRID:AB_2536183 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Mouse Alexa 633 (goat polyclonal) | Invitrogen/Life Technologies | Cat# A-21052, RRID:AB_2535719 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Rabbit Alexa 633 (goat polyclonal) | Invitrogen/Life Technologies | Cat# A-21071, RRID:AB_2535732 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Rabbit Alexa 488 (donkey polyclonal) | Life Technologies | Cat# A21206, RRID:AB_2535792 | IF(1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Goat Cy5 (donkey polyclonal) | Jackson Immuno-research | Cat# 705-175-147, RRID:AB_2340415 | IF(1:400) |
| Antibody | Anti-Guinea pig DyLight 405 (donkey polyclonal) | Jackson Immuno-research | Cat# 706-475-148, RRID:AB_2340470 | IF(1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit (goat polyclonal) | Vector Laboratories | Cat# BA-1000, RRID:AB_2313606 | IHC(1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-goat/sheep (horse polyclonal) | Vector Laboratories | Cat# BA-9500, RRID:AB_2336123 | IHC(1:500) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tetrodotoxin citrate (TTX) | Alomone Labs | Cat# T-550 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 4-amino pyridine (4-AP) | Sigma Aldrich | Cat# 275875 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Picrotoxin (PTX) | Sigma Aldrich | Cat# P1675 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 6,7-dinitro quinoxaline-2,3-dione (DNQX) disodium salt | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 2312 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DL-2-Amino-5-phosphono pentanoic acid sodium salt (DL-AP5) | BioTrend | Cat# BN0086 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dopamine hydrochloride | Sigma Aldrich | Cat# H8502 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dihydrexidine hydrochloride (DH) | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 0884 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Quinpirole hydrochloride | Sigma Aldrich | Cat# Q102 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | CGP55845 hydrochloride | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 1248 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SCH23390 hydrochloride | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 0925 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sulpiride | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 0895 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | L-745870 trihydro- chloride | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 1002 | |
| Software, algorithm | SPSS | IBM | RRID:SCR_002865 | |
| Software, algorithm | Igor Pro | WaveMetrics | RRID:SCR_000325 | |
| Software, algorithm | NeuroMatic | NeuroMatic | RRID:SCR_004186 | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | NIH | RRID:SCR_003070 | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | Fiji | RRID:SCR_002285 | |
| Software, algorithm | pClamp 10 | Molecular Devices | RRID:SCR_011323 | |
| Software, algorithm | ZEN 2009 Software | Zeiss | RRID:SCR_013672 | |
| Software, algorithm | Huygens Suite 19.04 | Scientific Volume Imaging | RRID:SCR_014237 | |
| Software, algorithm | Imaris Software, versions 7.6.1 and 9.7.0 | Oxford Instruments, Bitplane | RRID:SCR_007370 | |
| Other | NeuroTrace stain 435/455 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# N21479 | |
| Other | Vectastain Elite ABC-Peroxidase kit | Vector Laboratories | Cat# PK-7100, RRID:AB_2336827 | |
| Other | CY3-Streptavidin | Dianova/ Jackson Immuno-Research | Cat# 016-160-084, RRID:AB_2337244 | |
| Other | Pacific Blue-Streptavidin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# S11222 |





