Science Forum: Nanoscape, a data-driven 3D real-time interactive virtual cell environment
Figures
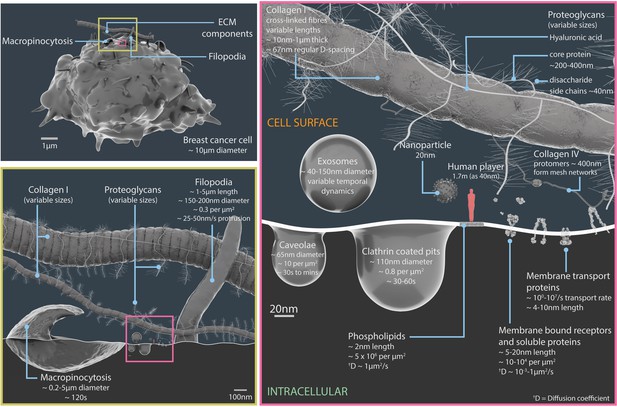
Relative scales and temporal dynamics of the cell surface components featured in Nanoscape.
A 3D model of a breast cancer cell (upper left panel). The region inside the yellow box is shown in more detail in the lower left panel, and region inside the pink box is shown in more detail in the panel on the right. The lower left panel details the components of the extracellular matrix (such as collagen I and proteoglycans), filopodia and macropinocytosis structures (which engulf extracellular material and fluid). The right panel details extracellular vesicles (exosomes), pits in the plasma membrane (caveolae and clathrin coated pits), plasma membrane lipids, surface proteins, components of the extracellular matrix (proteoglycans, collagens I and IV), and a 20 nm nanoparticle. The light red figure in the right panel is 40 nm tall. See Video 1 for animations of some of these processes. ECM: extracellular matrix.
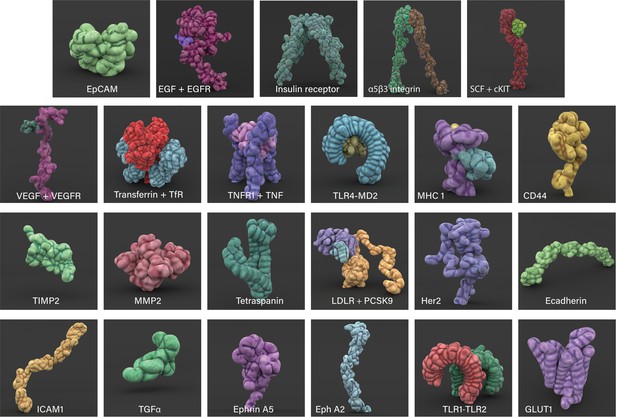
3D modelled cell surface receptors and ligands featured in Nanoscape.
Stylized 3D meshes modelled from structures retrieved from the RSCB Protein Data Bank (PDB). Most proteins are depicted as monomers; see Appendix 1 for details.
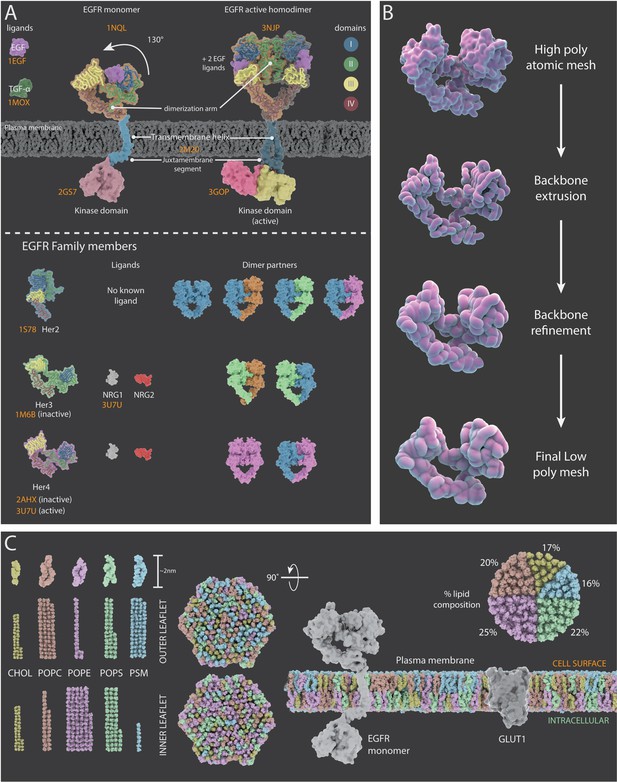
Representations of surface receptors and plasma membrane lipids.
(A) Structural and dynamic information about the four proteins in the ErbB family of proteins (EGFR, Her2, Her3, and Her4) and their ligands. Top: Mechanism of action for EFGR which, upon ligand binding, undergoes a conformational change (130° movement) into the active extended conformation; it can also form a dimer with another active EGFR protein. Bottom: PDB structures, ligands and dimer partner combinations for Her2, Her3 and Her4. (B) The creation of stylized protein meshes starts with structures sourced from the PBD (top); the backbone is extruded and the structure is then refined to produce the mesh (bottom). (C) A 3D model of a lipid bilayer in a cancer cell, highlighting an asymmetric distribution of 400 lipids (data adapted from Shahane et al., 2019). The bilayer components include cholesterol (CHOL), 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC), 1-palmatoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (POPE), 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-L-serine (POPS), and palmitoylsphingomyelin (PSM). The proportion of each lipid species within the outer and inner leaflets is shown on the left; the percentage of each species in the bilayer is shown on the right. The two hexagonal shapes are side views of a model cancer plasma membrane with proteins EGFR and GLUT1.
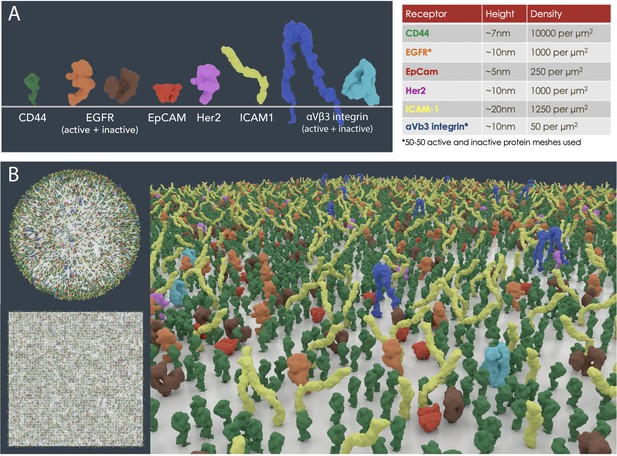
Cell surface receptor density modelling from experimental data.
(A) PDB meshes of 6 well-known surface biomarkers (CD44, EGFR, EpCAM, Her2, ICAM1 and αVβ3 integrin) on MDA-MB-231 cells from flow cytometry data (Cahall et al., 2015). (B) Scaled receptor meshes were distributed onto a 1 µm2 surface area sphere and plane using the autoPACK plugin in Blender.
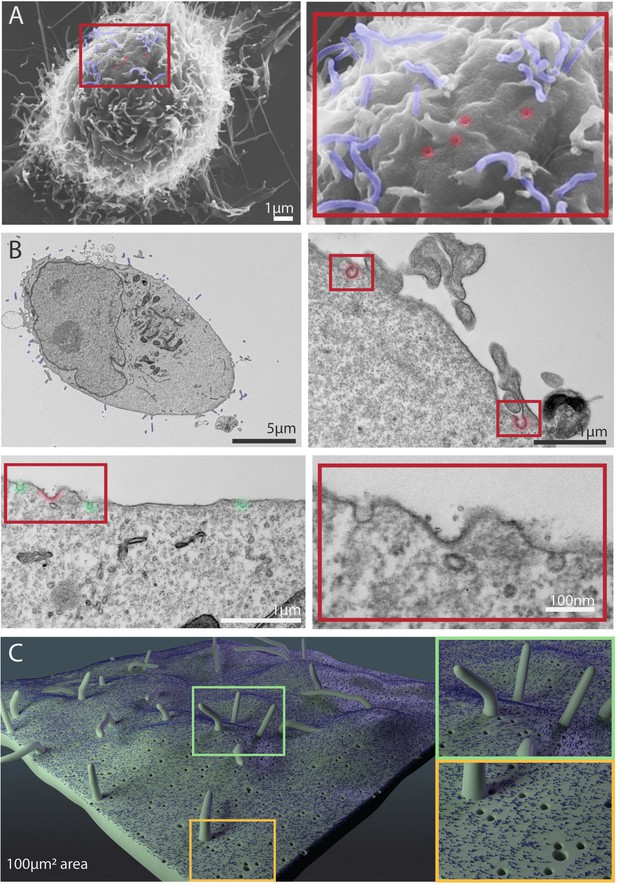
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) images of MDA-MB-231 cells showing cellular features used in Nanoscape.
(A) Representative SEM images of MDA-MB-231 cells. The boxed area shows a higher magnification of filopodia (pseudocoloured blue) and putative pits (caveolae, clathrin coated pits) in red. (B) Representative TEM images of sections of MDA-MB-231 cells. Filopodia are visible in the upper left panel (pseudocoloured blue). Clathrin coated pits are visible in the upper right and lower left panels (red) and right. Caveolae are visible in the lower left panel (green). The lower right panel shows the region inside the red box in the lower left panel at higher magnification. (C) 3D depiction of filopodia, caveolae, clathrin coated pits, and a representative receptor on a 100 µm2 patch on the cell membrane.
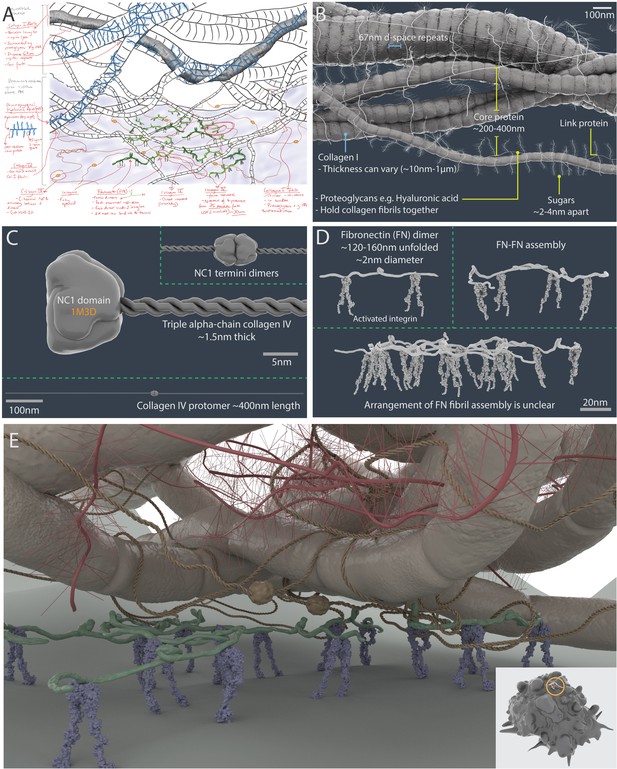
A 3D artistic impression of the extracellular matrix in a tumour microenvironment.
A pre-production sketch (A) and a 3D model (B) of collagen I fibrillar bundles and proteoglycans (such as hyaluronic acid). (C) Collagen IV protomers and dimers. (D) Fibronectin dimers bound to active αVβ3 integrin. (E) Artistic interpretation of the extracellular matrix in a tumour microenvironment. The insert shows the scale of the modelled area (circle) relative to a breast cancer cell model (which has a diameter of ~10 µm).
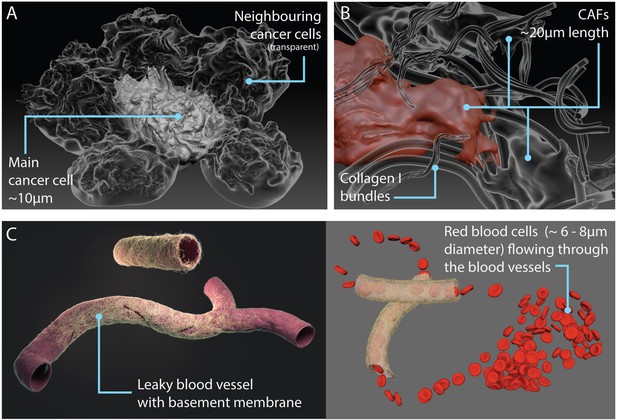
Models of components in the tumour microenvironment.
(A) Additional neighbouring cancer cells (transparent) surrounding the central or main cancer cell. (B) Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) entangled in collagen fibres. (C) Leaky blood vessel surrounded by basement membrane mesh (left); snapshot of animation with red blood cells flowing through the vessel (right; see also Video 2).
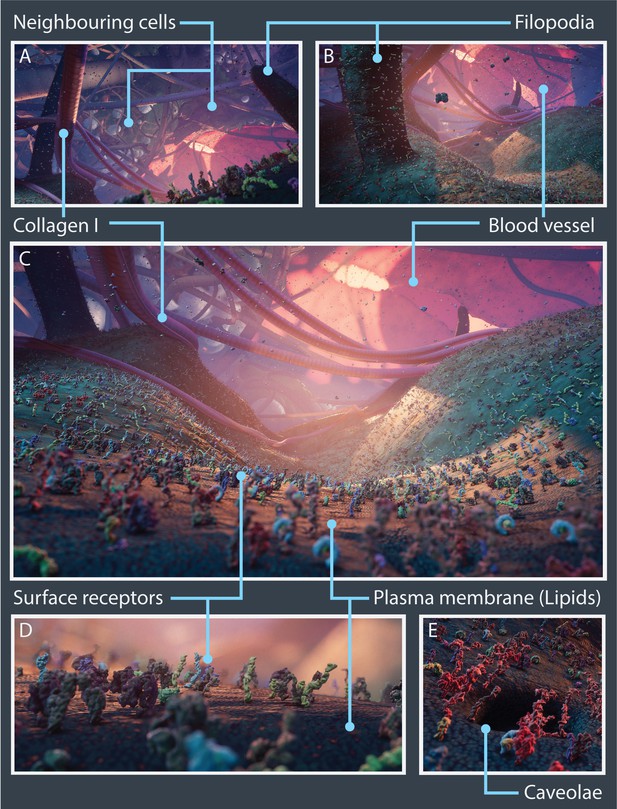

Nanoscape real-time open-world experience.
Vistas from the Nanoscape real-time open-world experience with key cellular features and microenvironment components highlighted. (A–C) Panoramic views showing surface receptors on the plasma membrane along with neighbouring cancer cells, filopodia, collagen I fibres, and blood vessels. Close-up views of surface receptors and lipids (D) and a caveolae (E).
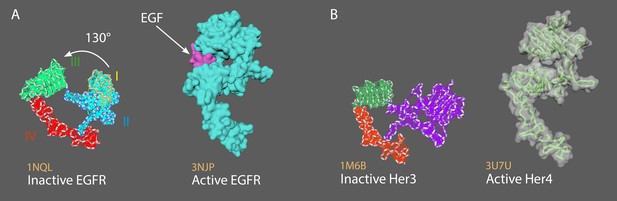
Two members of the ErbB family of surface receptors.
(A) Inactive (left) and active (right) EGFR. (B) Inactive Her3 (left) and active Her4 (right).
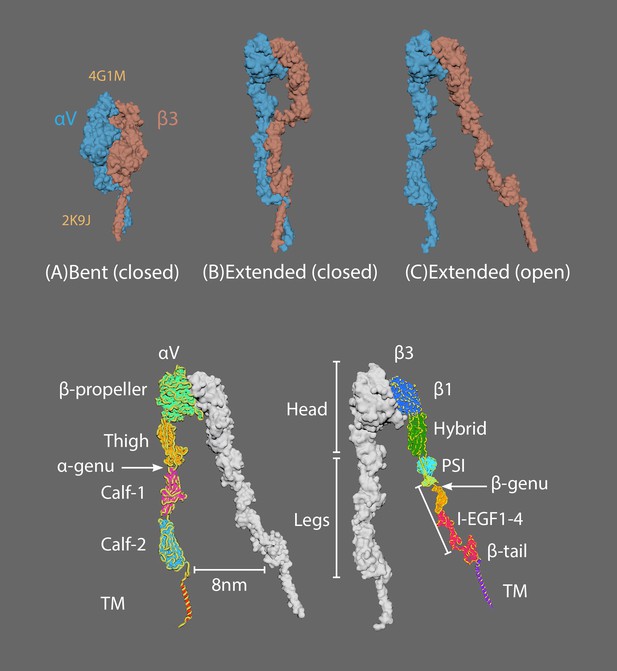
The three major conformational states of integrin.
(A) Bent with closed headpiece; (B) extended with a closed headpiece; (C) extended with an open headpiece. Extracellular domains in alpha chains (lower left) and beta chains (lower right).
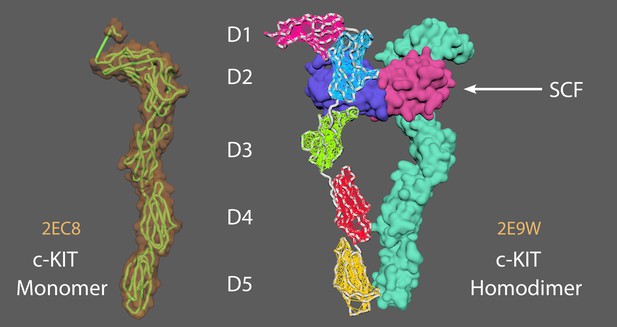
A c-KIT monomer (left) and a c-KIT homodimer (right) after binding by a Stem Cell Factor (SCF) protomer.
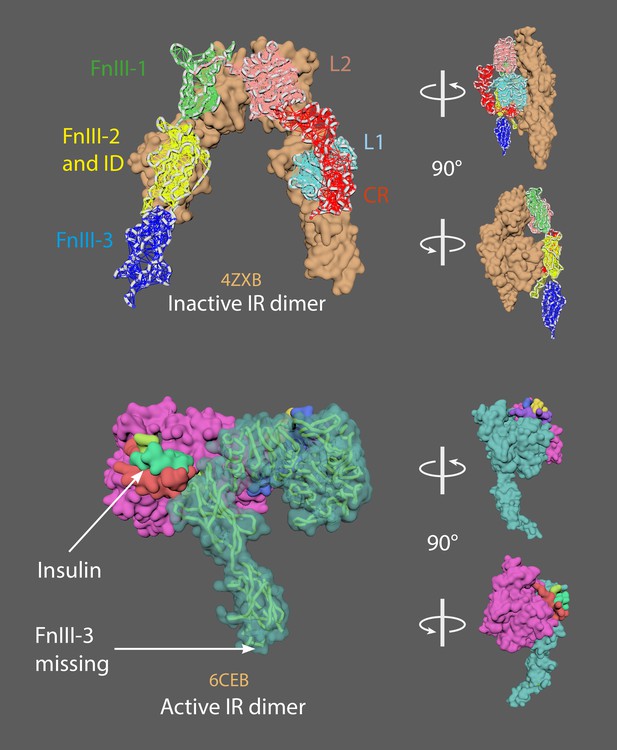
The inactive insulin receptor dimer has an inverted U shape (upper panel).
The active insulin receptor dimer has a T shape (lower panel); the insulin ligand is shown in green.
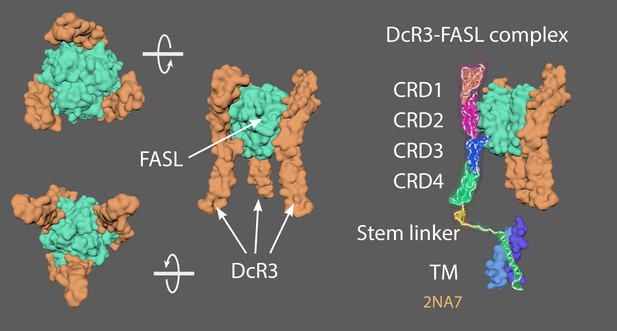
Different views of the DcR3-FASL complex, which consists of a trimeric ligand (green) bound to three upright decoy receptors (orange/purple).
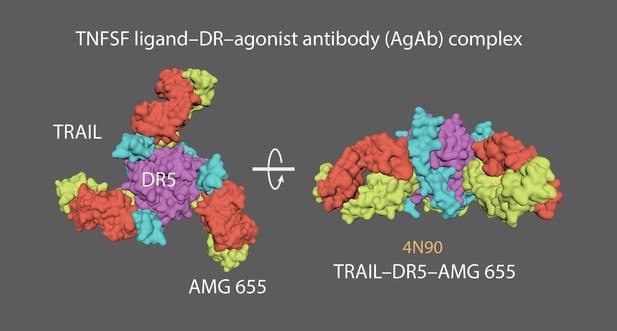
Top and side views of a TNFSF protein complex featuring DR5 ligand (purple), TRAIL (blue) and antibody Fab fragments (orange/yellow).
Videos
Animated models of five cellular processes – macropinocytosis (upper right), caveolae (middle left), clathrin coated pits (middle right), exosomes (lower left) and filopodia (bottom lower) – created in Maya.
Animation showing red blood cells flowing through a leaky blood vessel surrounded by basement membrane mesh in the Nanoscape tumour microenvironment (see also Figure 7).
Animation strategy for EGFR.
1NQL = inactive EGFR (monomer; Ferguson et al., 2003). 3NJP = active EGFR (dimer; Lu et al., 2010). Rigged 1NQL with mMaya rigging kit, created elastic networks for each domain: I + II combined, III, and IV. Set 3NJP as a target for 1NQL to morph into, and cached the animation. See ‘Surface protein simulations’ in Materials and methods for more details.
Animation strategy for Her3.
1M6B = inactive Her3 (monomer; Cho, 2002). 3U7U = active Her4 (dimer; Liu et al., 2012). Rigged 1M6B with mMaya rigging kit, created elastic networks for each domain: I + II combined, III, and IV. Set 3U7U as a target for 1M6B to morph into, and cached the animation. See ‘Surface protein simulations’ in Materials and methods for more details.
Animation strategy for αVβ3 integrin.
4G1M = αVβ3 inactive bent conformation (Dong et al., 2012). 2K9J = transmembrane domain of integrin αIIb-β3 (Lau et al., 2009). Connected 2K9J to the C-term of αVβ3 integrin (4G1M) using the mMaya modelling kit. New PDB created was rigged and elastic networks made for all extracellular domains. As no extended structures are available artistic licence was used to create hypothetical structures. Handles were created for the head portion of αV and β3 to manually open the mesh into the extended closed conformation, and a second handle created for the I-EGFR1-4 and β-tail to move ~8 nm into the extended open conformation.
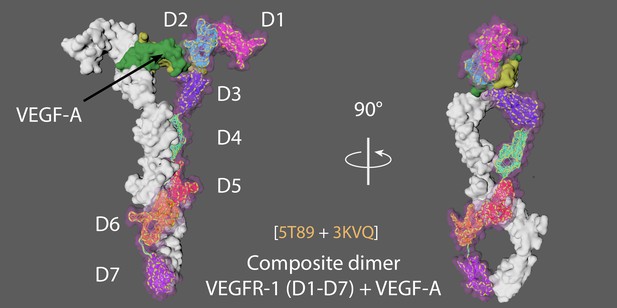
Animation strategy for VEGFR1.
The composite VEGFR1 dimer was built from 5T89 and 3KVQ (see Appendix 4—figure 1) and rigged using mMaya rigging kit. Elastic networks were created for each domain (D1 to D7). Handles were made for the entire CA backbone and individual domains to manually pull the rig away from the dimer conformation, artistic licence was used to create a hypothetical monomer conformation (as no monomer structure is currently available). The hypothetical monomer was simulated to conformationally morph into the target composite VEGFR dimer for the cached animation.
Animation strategy for c-KIT.
2EC8 = c KIT monomer (Yuzawa et al., 2007). 2E9W = c KIT homodimer with SCF (Yuzawa et al., 2007). Aligned chain A from 2E9W (dimer conformation) to 2EC8 (monomer conformation). Saved a new PDB version of chain A 2E9W (now as a monomer conformation). Created elastic networks for each domain (D1-5). Set it to target morph to the original 2E9W dimer position, cached animation.
Animation strategy for the insulin receptor.
4ZXB = inactive model (– ligands; Croll et al., 2016). 6CEB = active model (+ligands; Scapin et al., 2018). The missing FnIII-3 domain in 6CEB chain A was added using the mMaya modelling kit to get the whole ectodomain structure (FnIII-3 domain taken from 4ZXB); a new PDB was created. A mMaya rig was made for 4ZXB and elastic networks created for L1, CR, L2, FnIII-1, FnIII-2 and ID, and FnIII-3 domains. Rig was target morphed to the new version of 6CEB, mesh animation was cached. Binding animation of insulin ligands on 4ZXB were key-framed manually and was approximated based on their position relative to 6CEB.
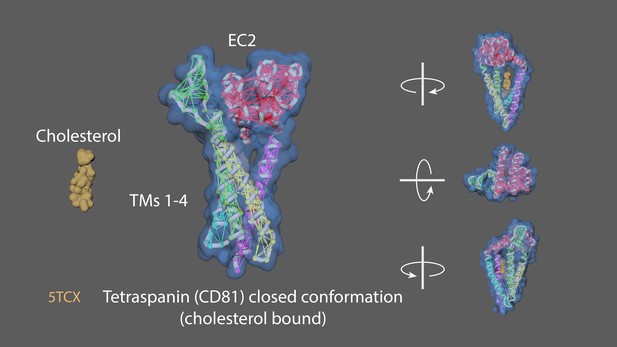
Animation strategy for Tetraspanin.
5TCX = Tetraspanin (closed conformation (i.e. cholesterol-bound); Zimmerman et al., 2016). Rigged 5TCX, created elastic networks for EC2 (residues 34–55 and 113–201), TM1 (6–33), TM2 (56–84), TM3 (86–112), TM4 (202–232). Created a handle for the residues 113–201 of the EC2 extracellular domain, manually key-framed to form the open conformation (apoprotein/unbound to cholesterol).
Animation strategy for TNFR1.
4MSV = Decoy receptor 3 (DcR3)(chain A) and FasL (chain B; Liu et al., 2016). 2NA7 = Transmembrane domain of human Fas/CD95 death receptor (Fu et al., 2016). 4N90 = Crystal structure of TRAIL-DR5 with the agonist antibody (Graves et al., 2014). As no complete structures of the active state or resting/non-signalling state structures exist, a ‘hybrid’ TNFRSF molecule was made. Created a stem linker (PQIEN VKGTE DSGTT) taken from TNFR1 (1EXT4, residues 197–211) with mMaya modelling kit to connect the CRD4 of DcR3 (4 MSV) and a TM domain trimer (2NA7). New PDB created named ‘Hybrid TNFRSF’ and rigged with mMaya rigging kit. Elastic networks of CRD1-4, stem linker and TM domain were created. Handles were created (CD1 +2; CD3, and CD4) to manually move the rig into a hypothetical resting state. Movement was key-framed, animation cached and meshes extracted. Alembic cached meshes were positioned in a hexagonal lattice and ligand binding was key-framed for the final animation. 4N90 [Crystal structure of TRAIL-DR5 with the agonist antibody (Fab fragments)] was used as a reference to get the correct spacing of the hexagonal array when the trimers become active (from their antiparallel dimer conformation in the resting state).
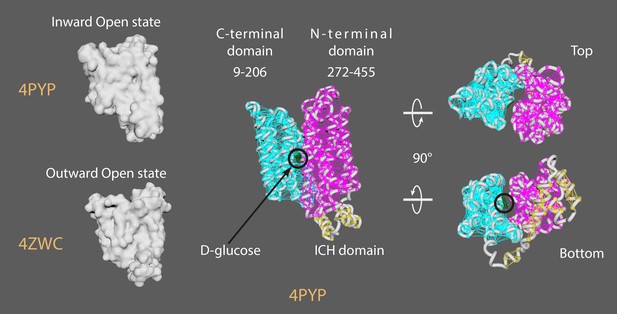
Animation strategy for GLUT1.
4PYP = GLUT1; inward-open state (Deng et al., 2015). 4ZWC = GLUT3; outward-open state (Deng et al., 2014). Rigged 4PYP (chain A) (inward-open state) was targeted to conformationally morph ‘backwards’ into 4ZWC (outward-open state), and the alembic cache was reversed. Created elastic networks of N-terminal domain (9-206), C-terminal domain (272-455), and ICH domain (211-264). Downloaded Het atoms for D-glucose structure and manually key-framed glucose uptake.
Tables
Cellular structures and processes in Nanoscape.
| Feature | Examples | Dimensions | Density | Temporal dynamics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structures | Membrane bound receptors1 | EGFR, Integrins, VEGFR | ~5–20 nm length; ~1–5 nm diameter | Protein specific ~10–104 per µm2 | Protein specific D ~ 10−3–1 µm2/s [see note 10]; Transitions between protein states ~ 1–100µs |
| Soluble proteins1 | EGF, TNF, MMPs | ||||
| Membrane transport proteins2 | GLUT4, K+ channel, Na+/K+ pump | ~4–10 nm length | ~104 per µm2 | ~100–107/s transport rate | |
| Extracellular matrix3 | Collagens, Fibronectin, Hyaluronic acid | Variable: from large fibres to smaller glycoproteins | Variable | Very low mobility relative to proteins | |
| Plasma membrane4 | Phospholipids | ~2 nm length;~0.25–0.5 nm2 cross-sectional area | ~5×106 per µm2 | †D ~ 1 µm2/s | |
| Processes | Protrusions | Filopodia5 | ~1–5 µm length; ~150–200 nm diameter | ~0.3 per µm2 | ~25–50 nm/s protrusion rate |
| Endocytosis | Caveolae6 | ~65 nm mean diameter; ~0.0067 µm2 area | ~10 per µm2 | ~30 s to minutes | |
| Clathrin mediated endocytosis7 | ~110 nm mean diameter; ~0.0190 µm2 area | ~0.8 per µm2 | ~30–60 s | ||
| Macropinocytosis8 | ~0.2–5 µm diameter | ? | ~120 s | ||
| Extracellular vesicles | Exosomes9 | ~40–150 nm diameter | ? | ? |
-
* Key features of cellular structures and processes in Nanoscape, with examples detailing properties such as dimensions, densities, temporal dynamics. See Figure 1 for 3D models.
Notes: 1 Membrane bound receptors and soluble proteins. Milo et al., 2010. 2 Membrane transport proteins. Milo et al., 2010. Chapter IV in Milo and Phillips, 2015. Page 9 (top paragraph) in Itzhak et al., 2016. Table 8.3 in Gennis, 1989. 3 Extracellular matrix. Frantz et al., 2010. Insua-Rodríguez and Oskarsson, 2016; Früh et al., 2015; Mouw et al., 2014; Pankov and Yamada, 2002. 4 Plasma membrane lipids. Milo et al., 2010. Chapter II in Milo and Phillips, 2015. Chapter 10 in Alberts et al., 2002. Table 1 in Rawicz et al., 2000. Page 2644 (right column, 2nd paragraph) in Brügger et al., 2006. 5 Filopodia density and dimensions. Measured from scanning electron micrographs, see Figure 5 in Mallavarapu and Mitchison, 1999. 6 Caveolae density, dimensions and temporal dynamics. Parton, 1994; Parton et al., 2020a; Parton et al., 2020b; Pelkmans and Zerial, 2005; Boucrot et al., 2011; Richter et al., 2008. 7 Clathrin mediated endocytosis density, dimensions and temporal dynamics. Cocucci et al., 2012; Doherty and McMahon, 2009; Edeling et al., 2006; Kirchhausen, 2009; McMahon and Boucrot, 2011; Merrifield et al., 2002; Parton, 1994; Saffarian and Kirchhausen, 2008; Taylor et al., 2011. 8 Macropinocytosis dimensions. Condon et al., 2018; Lim and Gleeson, 2011. 9 Exosome dimensions. Skotland et al., 2017. 10 Diffusion coefficient. D is microscopically determined by the velocity of the molecule and the mean time between collisions.