Excitation of medium spiny neurons by ‘inhibitory’ ultrapotent chemogenetics via shifts in chloride reversal potential
Figures
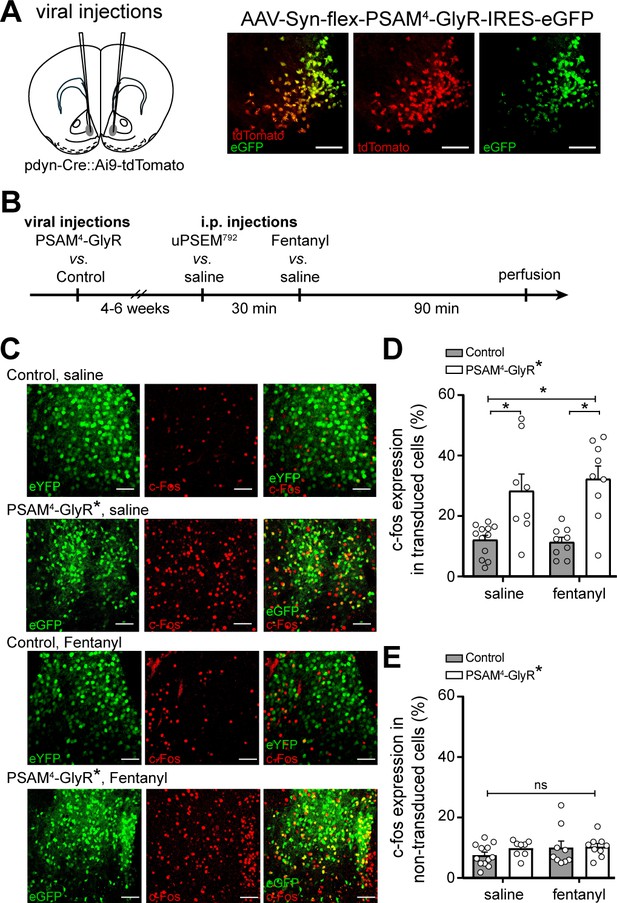
In vivo activation of PSAM4-GlyR enhances c-fos expression in D1-MSNs.
(A) Left, cartoon of viral injection site in the ventral striatum. Right, representative confocal images of Cre-dependent PSAM4-GlyR expression (eGFP) in Cre-expressing D1-MSNs (tdTomato). (B) Experimental design for measuring c-fos expression after activation of PSAM4-GlyR. (C) Representative maximum intensity Z-stack confocal images of c-fos immunostaining (red) in D1-MSNs with or without activation of PSAM4-GlyR, after saline vs. fentanyl injection (0.2 mg/kg, i.p.). PSAM4-GlyR* refers to PSAM4-GlyR activated with uPSEM792 (3 mg/kg, i.p.). The ‘Control’ group includes pooled data from mice with (control virus + uPSEM792 1st i.p. injection) and (PSAM4-GlyR virus + saline 1st i.p. injection). Scale bars: 50 µm. (D) Activation of PSAM4-GlyR with uPSEM792 increased c-fos expression in PSAM4-GlyR expressing D1-MSNs compared to control (two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). Data are presented as % colocalization of c-fos and eGFP/eYFP+ in transduced D1-MSNs. (E) Activation of PSAM4-GlyR did not increase c-fos expression in non-transduced cells (calculated as the number of c-fos expressing non-transduced cells/total number of non-transduced cells). Data represent mean ± SEM. * indicates statistical significance, ns denotes not significant.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
PSAM4-GlyR enhances c-fos expression in D1-MSNs in-vivo (source data).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64241/elife-64241-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
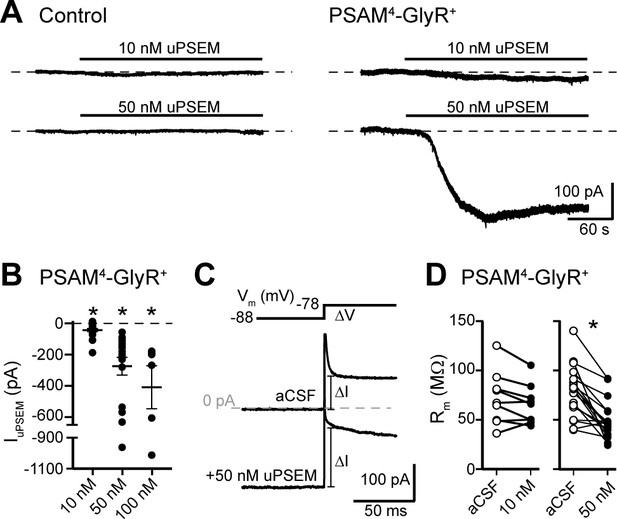
Activation of PSAM4-GlyR in D1-MSNs produces an inward current.
(A) Representative traces of whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings (Vhold −88 mV) demonstrate no effect of uPSEM792 (10 or 50 nM) in control neurons. In PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons, 10 or 50 nM uPSEM792 produced an inward current. Dashed line is baseline whole-cell current for ease of visualization. (B) Plot of the magnitude of the inward current produced by 10, 50, or 100 nM uPSEM792 in PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons. Line and error bars represent means ± SEM. (C) To measure membrane resistance (Rm), a 10 mV voltage step (−88 to −78 mV) was made in aCSF and during the uPSEM792-induced inward current, and the instantaneous change in current following the capacitive transient was measured (ΔI). Representative traces are shown below the voltage step command. Dashed line is 0 pA. (D) In PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons, 50 nM uPSEM792 significantly decreased Rm (paired t-test, p<0.0001) while 10 nM showed a trend toward lower Rm (paired t-test, p=0.08). * indicates statistical significance, ns denotes not significant.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
of PSAM4-GlyR depolarizes D1-MSNs (source data).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64241/elife-64241-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
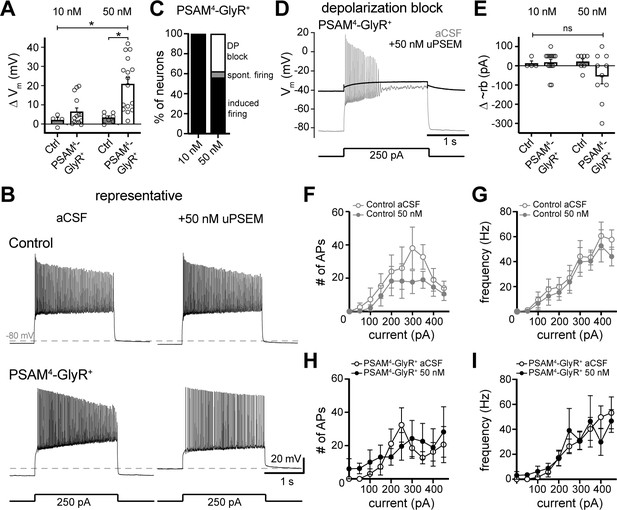
Activation of PSAM4-GlyR depolarizes D1-MSNs and does not inhibit firing.
(A) In PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons, activation of PSAM4-GlyR with uPSEM792 (10 and 50 nM) significantly depolarized the membrane potential (Vm) compared to control (non-PSAM4-GlyR) neurons, measured in current-clamp (two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). (B) Representative traces of current-clamp recordings from a control (top) or PSAM4-GlyR+ neuron (bottom). Action potential firing was evoked by somatic current injection (250 pA, 2 s) in aCSF (left) and 50 nM uPSEM792 (right). Dashed line is −80 mV. (C) Distribution of firing response of PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons after 10 or 50 nM uPSEM792 application. In 10 nM uPSEM792, 14/14 neurons continued to fire with current injection. In 50 nM, 9/16 neurons fired with current injection (induced firing), 1/16 fired spontaneously without a current injection (spont. firing), and 6/16 went into depolarization block (DP block). (D) Representative traces of current-clamp recordings from a PSAM4-GlyR+ neuron that went into depolarization block with uPSEM792. Response to somatic current injection (250 pA, 2 s) in aCSF (gray) and after uPSEM792 application (black). The membrane potential in uPSEM792 was more depolarized than the potential where the neuron entered depolarization block in aCSF. Dashed line is −80 mV. (E) Plot of change in the minimum current needed to induce firing (approximate rheobase: ~rb) induced by uPSEM792 (10 and 50 nM) in control (gray) and PSAM4-GlyR+ (black) in cells that continued to fire (10/16). No significant change of ~rb was observed. (F) Plot of number of action potentials (APs) fired versus injected current in control neurons in aCSF (open) and in uPSEM792 (closed). No significant difference was observed. (G) Plot of AP firing frequency versus injected current in control neurons in aCSF (open) and in uPSEM792 (closed). No significant difference was observed. (H) Plot of number of APs fired versus injected current in PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons in aCSF (open) and in uPSEM792 (closed). No significant difference was observed. (I) Plot of AP firing frequency versus injected current in PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons in aCSF (open) and in uPSEM792 (closed). No significant difference was observed. Line and error bars represent means ± SEM, * indicates statistical significance, ns denotes not significant.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
PSAM4-GlyR does not inhibit firing of D1-MSNs (source data).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64241/elife-64241-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
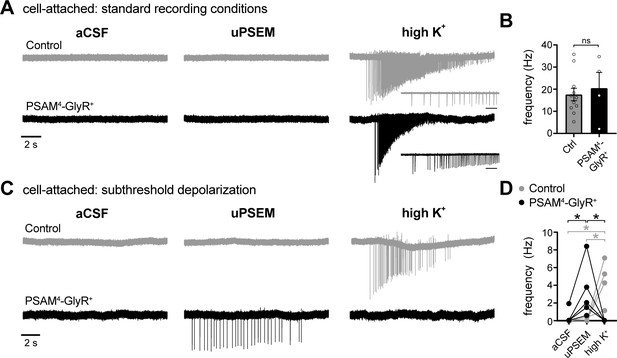
In cell-attached configuration, activation of PSAM4-GlyR triggers firing of D1-MSNs when the membrane is depolarized to subthreshold potentials.
(A) Representative traces of cell-attached recordings from a control (gray) or PSAM4-GlyR+ neuron in standard aCSF (4.5 mM [K+]). Action currents were evoked following uPSEM792 by applying a high external concentration of potassium (high K+, ~40 mM). The insets below the high K+ traces represent an expanded timescale at the beginning of firing; Inset scale bar = 200 ms. (B) In PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons, activation of PSAM4-GlyR with uPSEM792 had no effect on the frequency of action currents in response to high K+. (C) Representative traces of cell-attached recordings from a control (gray) or PSAM4-GlyR+ neuron in aCSF containing 10–13 mM [K+]. In PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons, activation of PSAM4-GlyR with uPSEM792 produced firing. There was no further firing with application of high K+. uPSEM792 had no effect on firing in control neurons. (D) Plot of the frequency of action currents in control and PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons in aCSF, uPSEM792 and high K+ (mixed effect two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). Line and error bars represent means ± SEM. * indicates statistical significance, ns denotes not significant.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
PSAM4-GlyR induces D1-MSN firing in cell-attached recordings (source data).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64241/elife-64241-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
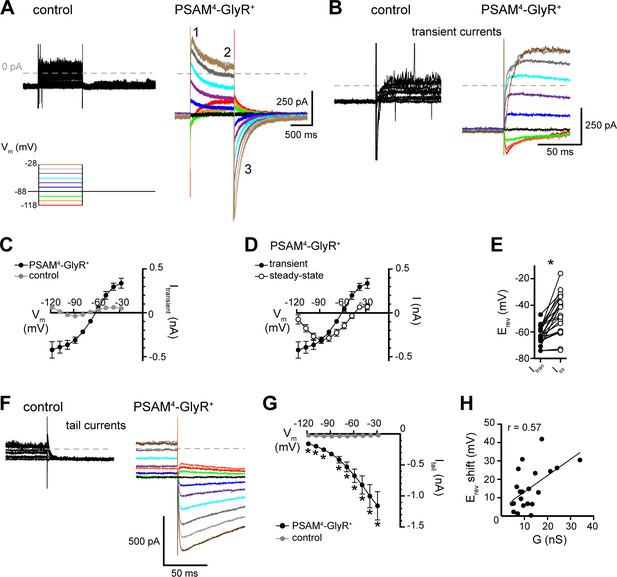
Current–voltage relationship of PSAM4-GlyR current shows rightward shift in reversal potential and transient or small outward currents at depolarized potentials.
(A) Current was recorded in response to voltage steps (1 s, −118 to −28 mV, 10 mV) from Vhold −88 mV in aCSF and after application of uPSEM792 (50 or 100 nM). uPSEM792-induced current was isolated by subtraction. Representative traces of uPSEM792-induced current during voltage steps in a control (left) and a PSAM4-GlyR+ neuron (right). Inset numbers by trace indicate transient (Roth, 2016), steady-state (Saloman et al., 2016), and tail (Gomez et al., 2017) currents. (B) Expanded timescale of transient currents (inset ‘1’ in A) in a control and a PSAM4-GlyR+ neuron. (C) Plot of current–voltage relationship of the transient current (Itransient) in control (n = 11) vs. PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons (n = 21). The reversal potential of transient current in PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons was −61 mV. (D) Plot of current–voltage relationship of the transient (inset ‘1’ in A, same as in C) vs. steady-state uPSEM792-induced (inset ‘2’ in A) currents in PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons. At steady state, the reversal potential of uPSEM792-induced current shifted to −44 mV. (E) Plot of the pairwise shift of reversal potential (Erev) between transient (Itran) and steady-state currents (Iss). (F) Expanded timescale of tail currents (inset ‘3’ in A) in a control and a PSAM4-GlyR+ neuron. (G) Plot of the amplitude of tail currents measured at Vhold −88 mV (Itail) versus holding potential of the preceding voltage step in control and PSAM4-GlyR+ neurons. uPSEM792-induced tail current at −88 mV demonstrated robust augmentation with prior depolarization and reduction with prior hyperpolarization. (H) The magnitude of the rightward shift in reversal potential between transient and steady-state current was positively correlated with the PSAM4-GlyR conductance (G in nS). Line and error bars represent means ± SEM, * indicates statistical significance.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Current-voltage relationship of PSAM4-GlyR current (source data).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64241/elife-64241-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
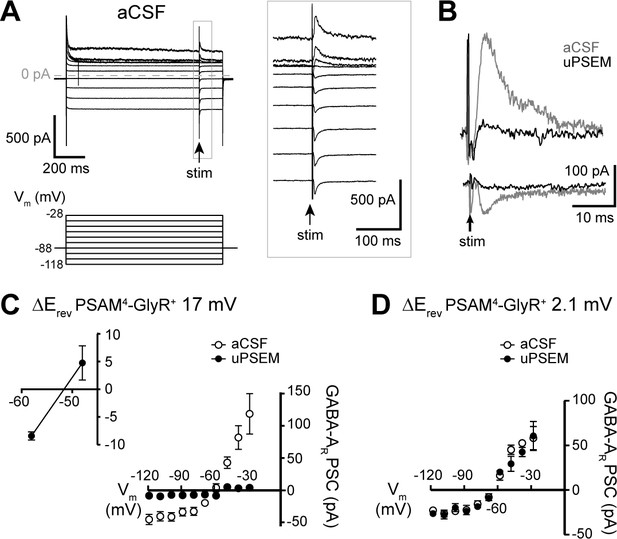
PSAM4-GlyR activation in D1-MSNs reduces GABAergic synaptic inhibition.
(A) Representative traces of GABA-A receptor-mediated synaptic currents in a PSAM4-GlyR+ neuron in aCSF, evoked during voltage steps from Vhold −88 mV (voltage steps: 1 s, −118 to −28 mV, 10 mV; electrical stimulation at 850 ms into voltage steps). Panel on the right shows the traces in expanded timescale corresponding to the gray rectangle on the left. (B) Representative traces of GABA-A receptor-mediated currents evoked in the same neuron from Vhold −28 mV (outward) and −118 mV (inward) in aCSF (gray) and uPSEM792 (black). (C) Plot of the current–voltage relationship of the GABA-A receptor synaptic currents in aCSF and uPSEM792 in neurons where the reversal potential of PSAM4-GlyR current shifted by >5 mV (n = 5, average shift of 17.0 mV). The reversal potential of GABA-A receptor-mediated current was −60.9 mV in aCSF and −51.6 mV in uPSEM792. Inset (top left) shows values of GABA-A receptor synaptic currents in uPSEM792 near the reversal potential in an expanded scale. (D) Plot of the current–voltage relationship of the GABA-A receptor-mediated synaptic current in aCSF and uPSEM792 in neurons where the reversal potential of PSAM4-GlyR current did not shift (n = 3, average shift of 2.1 mV). The reversal potential of GABA-A receptor-mediated synaptic currents was similar in aCSF (−64.7 mV) and uPSEM792 (−64.9 mV). Line and error bars represent means ± SEM, * indicates statistical significance.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Reduced GABAergic synaptic inhibition (source data).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64241/elife-64241-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx





