Exosomes mediate horizontal transmission of viral pathogens from insect vectors to plant phloem
Figures
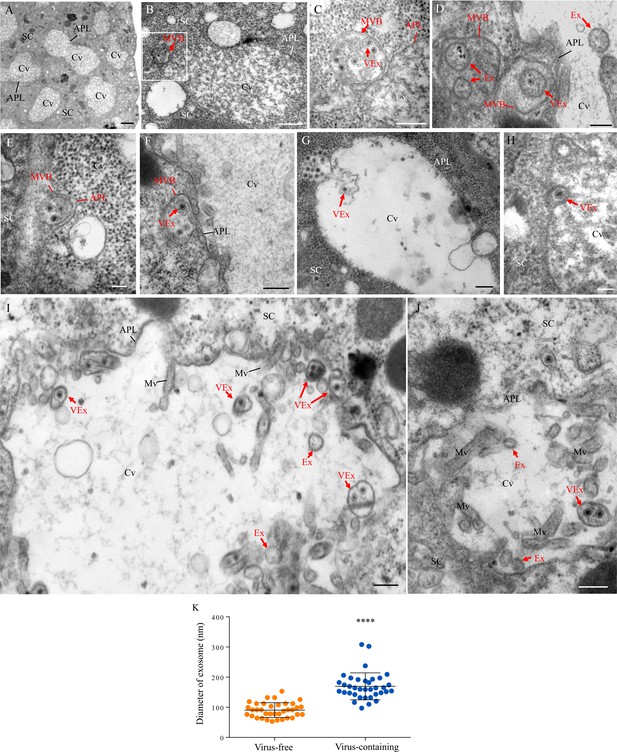
Transmission electron micrographs showing that RDV traverses the apical plasmalemma into the salivary cavities via the exosomal release pathway.
At 14 days padp, virus-infected salivary glands of N. cincticeps were examined by transmission electron microscopy. (A) Salivary cavities in type III cells. (B–C) Virus-containing MVBs at the periphery of salivary cavities attached to the apical plasmalemma. Panel C showing an enlarged image of the boxed area in panel B. (D–E) The propulsion of MVBs led to the enation of the apical plasmalemma toward the cavity. (F–H) Virus-containing MVBs fused with the apical plasmalemma of cavities. (I–J) Virus-containing exosomes were released into the cavities. SC, salivary cytoplasm; APL, apical plasmalemma; Cv, cavity; Ex, exosome; VEx, virus-containing exosome; MVB, multivesicular body; Mv, microvilli. Bars, 2 μm (A), 500 nm (B, F), 200 nm (C, D, G, I and J), and 100 nm (E and H). (K) The mean diameters of exosomes within the salivary cavities, as measured from more than 30 virus-free or virus-containing exosomes. The diameters of exosomes are shown in a dot plot, with the middle line representing the mean value and the top and bottom lines representing the SD. ****p<0.0001.
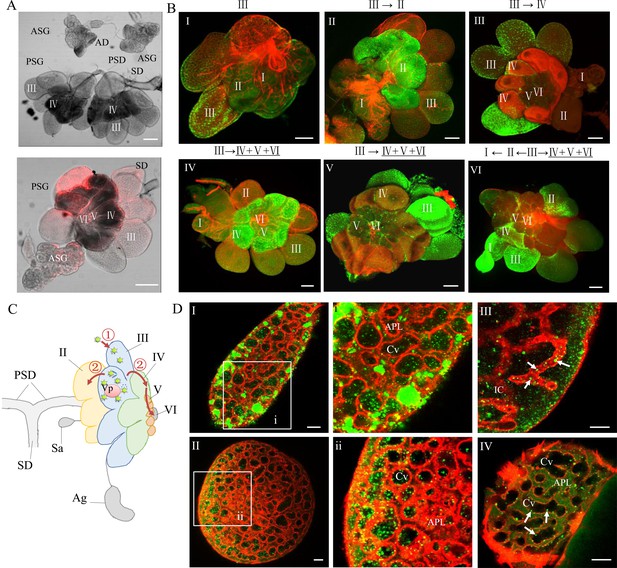
RDV dissemination into the salivary cavities in the PSG.
(A) Transmission light micrographs of salivary glands of the leafhopper vector N. cincticeps. Leafhopper salivary glands consist of a pair of PSGs, each containing six types of cells (I to IV), and an accessory salivary gland (ASG). (B) RDV infection immunolabeled with virus-FITC in different types (I to VI) of salivary cells. The Roman numerals in the panels indicate the five different types (I to V) of salivary cells. Roman numerals above the panels indicate the possible viral infection route among the types of cells indicate the five different types (I to V) of salivary cells. (C) Proposed model for the RDV infection route in salivary glands. RDV initially infects type III cells and then spreads to type II, IV, V, or VI cells. (D) The distribution of RDV antigens immunolabeled with virus-FITC in the cavities of type III (image I and II), IV (image III), and V (image IV) cells. Virus-infected salivary glands of leafhoppers were immunostained with virus-FITC (green) and the actin dye phalloidin-rhodamine (red) and then examined by immunofluorescence microscopy. Arrows indicate released viruses. Panels i and ii are enlarged images of the respective boxed areas in panels I and II. PSD, principal salivary duct; SD, salivary duct; AD, accessory salivary duct; Sa, spherical appendage; Vp, viroplasm; APL, apical plasmalemma; Cv, cavity; IC, intracellular canaliculi. Bars, 100 μm (A), 50 μm (B), 10 μm (D).
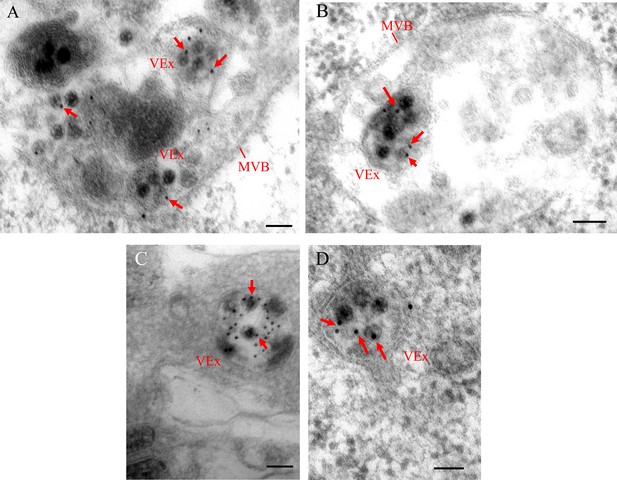
Immunogold labeling of RDV antigens on viral particles within the MVBs or exosomes in the leafhopper salivary glands or cultured cells.
Virus-infected salivary glands (A–C) or cultured cells (D) were immunolabeled with virus-specific IgG as primary antibodies, followed by treatment with 15 nm gold particle-conjugated goat antibodies against rabbit IgG as secondary antibodies. MVB, multivesicular body; VEx, virus-containing exosome. Arrows indicate gold particles. Bars, 100 nm.
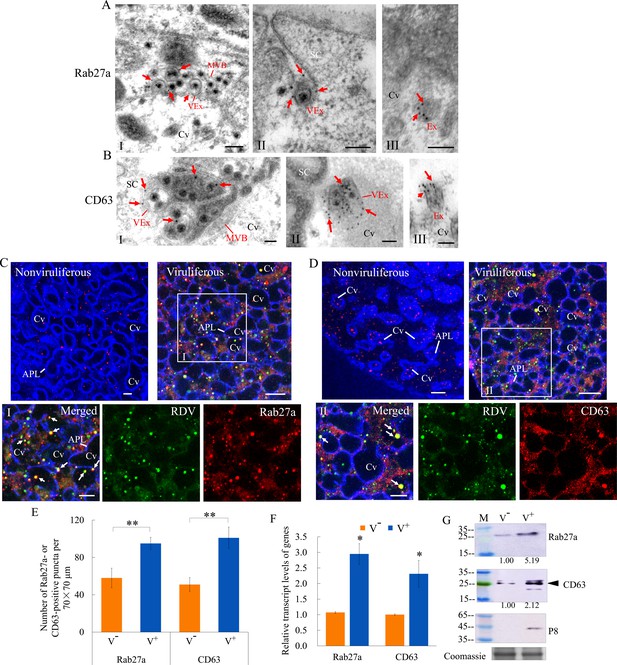
RDV dissemination into the salivary cavities via Rab27a-involved exosomal release pathway.
(A–B) Immunogold labeling of Rab27a (A) or CD63 (B) on virus-containing MVBs or exosomes in the salivary glands of N. cincticeps. Virus-infected (panels I and II) or uninfected (panels III) salivary glands of N. cincticeps were immunolabeled with Rab27a-specific IgG or CD63-specific IgG as primary antibody, followed by treatment with 15 nm gold particle-conjugated goat antibody against rabbit IgG as secondary antibody. SC, salivary cytoplasm; MVB, multivesicular body; Cv, cavity; Ex, exosome; VEx, virus-containing exosome. Arrows indicate gold particles. Bars, 100 nm. (C–D) Immunofluorescence assay of the distribution of Rab27a (C) or CD63 (D) during viral infection of the salivary glands of N. cincticeps. Salivary glands of nonviruliferous or viruliferous N. cincticeps were fixed, immunostained with virus-FITC (green), Rab27a- rhodamine (red) or CD63-rhodamine (red), and actin dye phalloidin-Alexa Fluor 647 carboxylic acid (blue). Then, immunostained salivary glands were processed for immunofluorescence microscopy. Panels I and II (merged) are the enlarged images of the boxed areas in C and D. Arrows show the colocalization puncta in the salivary cavities. APL, apical plasmalemma; Cv, cavity. Bars, 5 μm. (E) The mean number of Rab27a- or CD63-positive puncta in infected or uninfected salivary glands. Twenty random 70 × 70 μm fields of type III cell samples from infected or uninfected salivary glands were examined. (F) RT-qPCR assay showing the transcript levels of Rab27a and CD63 in the salivary glands of viruliferous or nonviruliferous leafhoppers. RT-qPCR results were normalized against the actin expression level, and the transcript levels of Rab27a or CD63 in the salivary glands of nonviruliferous leafhopper were normalized as 1. (G) Western blot assay showing the expression levels of Rab27a and CD63 in the salivary glands of viruliferous or nonviruliferous leafhoppers. The relative intensities of bands in the analyses of Rab27a and CD63 are shown below. Coomassie-blue-stained gels demonstrate the loading of equal amounts of proteins. Data shown here are representative of three biological replicates. Means (± SD) from three biological replicates are shown in E and F. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. V-, nonviruliferous; V+, viruliferous.
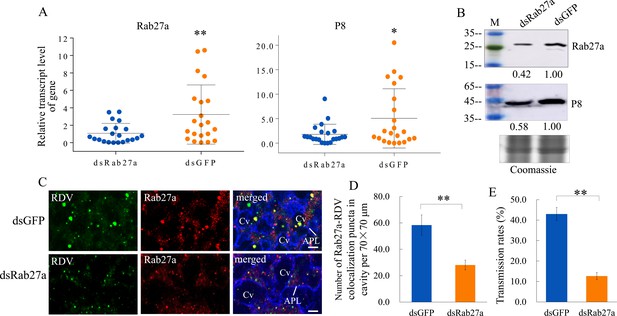
Knockdown of Rab27a expression reduces viral dissemination from salivary glands via the exosomal release pathway.
(A) RT-qPCR assay showing the transcript levels of RDV P8 and Rab27a expression in the salivary glands of dsRab27a- or dsGFP-treated insects. Results were normalized against the actin expression level. Means (± SD) from three biological replicates are shown. The relative expression levels of the genes in individual insects are shown in a dot plot, with the middle line representing the mean value and the top and bottom lines representing the SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (B) Western blot assay showing the expression levels of RDV P8 and Rab27a in the salivary glands of dsRab27a- or dsGFP-treated insects. The relative intensities of bands in the analyses of Rab27a or RDV P8 are shown below. Coomassie-blue-stained gels demonstrated the loading of equal amounts of protein. Data shown here are representative of three biological replicates. (C) Immunofluorescence microscopy showing the distribution of Rab27a during viral infection in the salivary glands of dsRab27a- or dsGFP-treated insects. Salivary glands were fixed, immunolabeled with virus-FITC (green), Rab27a-rhodamine (red) and actin dye phalloidin-Alexa Fluor 647 carboxylic acid (blue), and processed for immunofluorescence microscopy. APL, apical plasmalemma; Cv, cavity. Bars, 5 μm. (D) The mean number of Rab27a–RDV antigen colocalization puncta in the cavities of dsGFP- and dsRab27a-treated salivary glands. Twenty random 70 × 70 μm fields in type III cell samples from infected or uninfected salivary glands were examined, and means (± SD) from three biological replicates are shown. **p<0.01. (E) The transmission rates by viruliferous dsGFP- or dsRab27a-treated leafhoppers. Means (± SD) from three biological replicates are shown. **p<0.01.
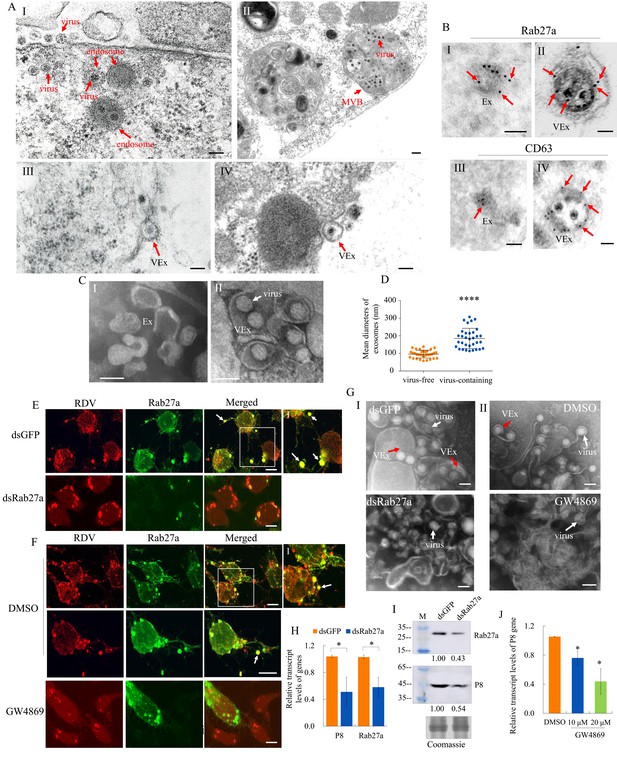
The secretion of RDV from cultured insect vector cells via the exosomal release pathway.
(A) At 48 hpi, virus-infected cultured leafhopper cells were examined by transmission electron microscopy. RDV virions were sequestered in the endosomal compartments (I), which then developed into MVBs (II). Finally, virus-containing exosomes were secreted from cultured cells (III-IV). Bars, 100 nm (I, III, IV) and 200 nm (II). (B) Immunogold labeling of Rab27a or CD63 in virus-free (I, III) or virus-containing (II, IV) exosomes. Arrows indicate gold particles. At 48 hpi, cultured cells were immunostained with Rab27a-specific IgG or CD63-specific IgG as primary antibody, followed by treatment with 15 nm gold particle-conjugated goat antibody against rabbit IgG as secondary antibody. Bars, 100 nm. (C) Negative staining electron microscopy showing the purified exosomes from the extracellular media of uninfected (I) or virus-infected (II) cultured cells. Bars, 100 nm. (D) The diameters of purified exosomes are shown in a dot plot, with the middle line representing the mean value and the top and bottom lines representing the SD. ****p<0.0001. (E–F) Virus-infected cultured cells treated with dsRab27a (E) or 20 μM GW4869 (F) were immunostained with virus-rhodamine (red) and Rab27a-FITC (green) and examined by immunofluorescence microscopy. Treatments with dsGFP (E) or DMSO (F) served as the controls. Arrows indicate the colocalization puncta of virus-rhodamine and Rab27a-FITC on the cell surface or outside of cells. Panels I show the enlarged images of the boxed areas in panels E or F. Bars, 5 μm. (G) Negative staining electron microscopy showing the purified exosomes from the extracellular media of dsGFP-, dsRab27a-, DMSO-, or 20 μM GW4869-treated virus-infected cultured cells. Panel I, dsGFP- and dsRab27a-treated cells; Panel II, DMSO- and GW4869-treated cells. Bars, 100 nm. (H) RT-qPCR assay showing the transcript levels of RDV P8 and Rab27a in dsRab27a- or dsGFP-treated cells. Results were normalized against the actin transcript level; the expression levels of Rab27a or P8 in dsGFP-treated cells were normalized as 1. Means (± SD) from three biological replicates are shown. *p<0.05. (I) Western blot assay showing the expression levels of RDV P8 and Rab27a in dsRab27a- or dsGFP-treated cells. The relative intensities of bands in the analyses of Rab27a and P8 are shown below. Coomassie-blue-stained gels demonstrated the loading of equal amounts of protein. Data shown here are representative of three replicates. (J) RT-qPCR assay showing the transcript levels of RDV P8 in GW4869 (10 or 20 μM)- or DMSO-treated cells. Means (± SD) from three biological replicates are shown. *p<0.05. Ex in A–C, exosome; VEx in A–C and G, virus-containing exosome; MVB in A, multivesicular body.
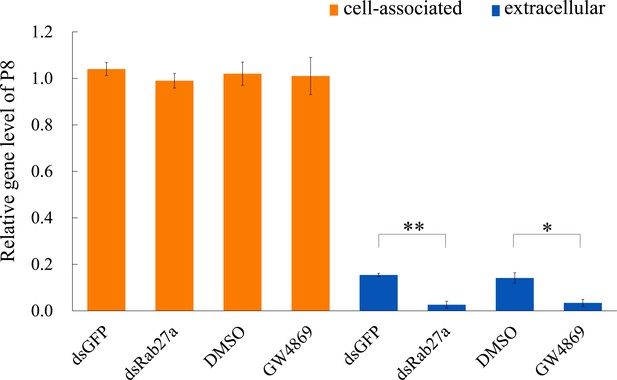
Effects of treatment with dsRab27a, dsGFP, GW4869 (20 μM), or DMSO on the accumulation of cell-associated and extracellular viruses in cultured leafhopper cells infected with RDV (MOI of 10) at 48 hpi.
The relative transcript levels of RDV P8 were examined in the cell-associated and extracellular viruses after different treatments. Results were normalized against the actin expression level; the expression levels of P8 in dsGFP- or DMSO-treated cells were normalized as 1. Means (± SD) from three biological replicates are shown. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
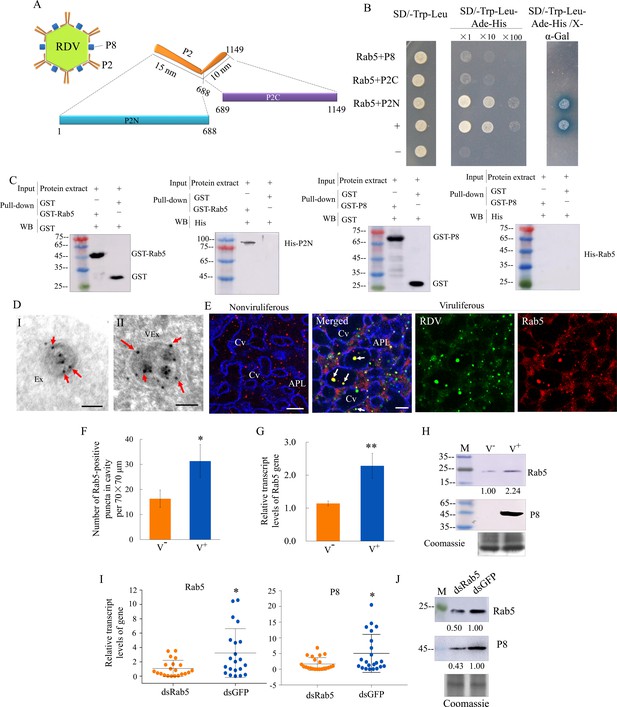
RDV P2 interacts with endosomal Rab5 of leafhopper.
(A) Schematic representation of the structures of RDV particle and P2 protein. P2 is composed of an L-shaped flexible structure with a 15 nm domain (aa 1–688, P2N) toward the exterior, and a 10 nm domain (aa 689–1149, P2C) on the viral envelope. (B) RDV P2N, but not RDV P2C or P8, specifically interacted with Rab5 in a yeast two-hybrid assay. Transformants on SD/-Trp-Leu-Ade-His plates are labeled as follows: +, positive control, i.e., pGBKT7-53/pGADT7-T; –, negative control, i.e., pGBKT7-Lam/pGADT7-T; Rab5 +P8, pGADT7-Rab5/pGBKT7-P8; Rab5 +P2C, pGADT7-Rab5/pGBKT7-P2C; Rab5 +P2N, pGADT7-Rab5/pGBKT7-P2N. Yeast cultures appeared blue in the β-galactosidase assay. (C) GST pull-down assay demonstrating the interaction of P2N with Rab5. Rab5 or RDV P8 fused with GST served as the bait, and GST alone served as the control. P2N or Rab5 fused with His served as the prey. The bait protein or the GST control were incubated with cell lysate expressing the His-fused protein. Input and pull-down samples were probed with antibodies against GST or His for western blot assays. (D) Immunogold labeling of Rab5 on exosomes in the salivary cavities. The salivary glands from nonviruliferous (panel I) or viruliferous (panel II) leafhoppers were immunostained with Rab5-specific IgG as primary antibody, followed by treatment with 15 nm gold particle-conjugated goat antibody against rabbit IgG as secondary antibody. Arrows indicate gold particles. Ex, exosome; VEx, virus-containing exosome. Bars, 100 nm. (E) Immunofluorescence assay showing the distribution of Rab5 during virus infection in the salivary glands of N. cincticeps. Virus-infected or uninfected salivary glands of N. cincticeps were fixed, immunostained with virus-FITC (green), Rab5-rhodamine (red), and actin dye phalloidin-Alexa Fluor 647 carboxylic acid (blue). Immunostained salivary glands were then processed for immunofluorescence microscopy. Arrows show the colocalization puncta in the salivary cavities. APL, apical plasmalemma; Cv, cavity. Bars, 10 μm. (F) The mean number of Rab5-positive puncta in infected or uninfected salivary glands. Twenty random 70 × 70 μm fields of type III cell samples from infected or uninfected salivary glands were examined. (G) RT-qPCR assay showing the transcript levels of Rab5 in the salivary glands of viruliferous or nonviruliferous leafhoppers. RT-qPCR results were normalized against the actin expression level, and the transcript levels of Rab5 in the salivary glands of nonviruliferous leafhopper were normalized as 1. Means (± SD) from three biological replicates are shown in F and G. *p<0.05; **p<0.01. (H) Western blot assay showing the expression levels of Rab5 in the salivary glands of viruliferous or nonviruliferous leafhoppers. The relative intensities of bands in the analyses of Rab5 and RDV P8 are shown below. Coomassie-blue-stained gels demonstrated the loading of equal amounts of proteins. Data shown here are representative of three biological replicates. (I) RT-qPCR assay showing the transcript levels of RDV P8 and Rab5 in the salivary glands of dsRab5- or dsGFP-treated insects. Results are normalized against the actin expression level. The relative expression levels of the genes in individual insects are shown in a dot plot, with the middle line representing the mean value and the top and bottom lines representing the SD. *p<0.05. (J) Western blot assay showing the expression levels of RDV P8 and Rab5 in the salivary glands of dsRab5- or dsGFP-treated insects. The relative intensities of bands are shown below. Coomassie-blue-stained gels demonstrated the loading of equal amounts of protein. Data shown here are representative of three replicates. V-, nonviruliferous insects; V+, viruliferous insects.
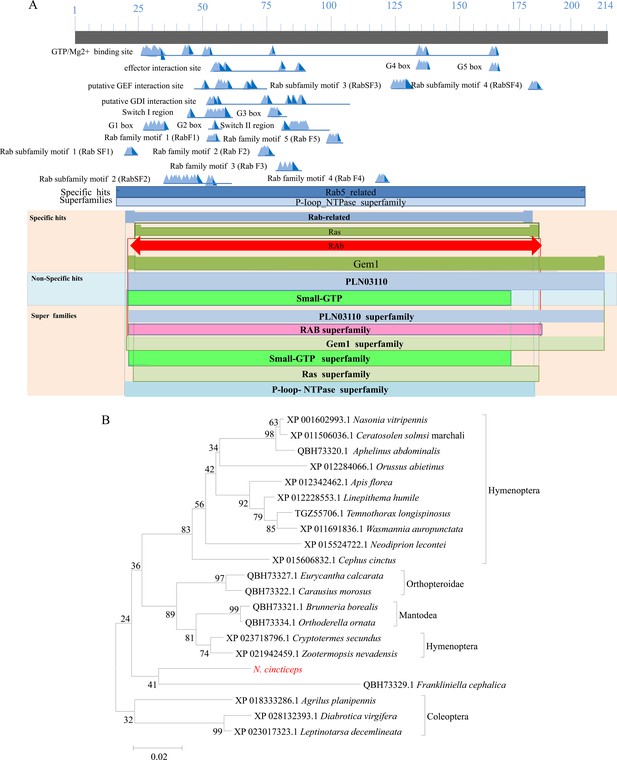
Bioinformatic analyses of Rab5 of N. cincticeps.
(A) Schematic representation of N. cincticeps Rab5. (B) Phylogenetic relationships of N. cincticeps Rab5 (in red) with its counterparts. The available sequences were aligned using ClustalW, and a phylogenetic tree was reconstructed using the neighbor-joining analysis method with P-distance using MEGA 5.0. The reliability of the phylogenetic tree was estimated by calculating bootstrap confidence limits based on 1000 replicates.
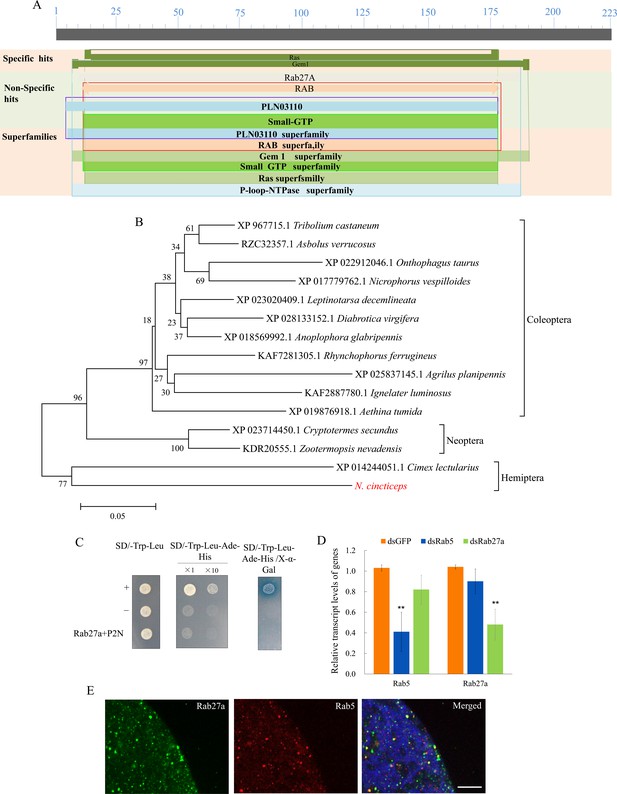
Bioinformatic analyses of Rab27a of N. cincticeps.
(A) Schematic representation of N. cincticeps Rab27a. (B) Phylogenetic relationships of N. cincticeps Rab27a (in red) with its counterparts. The available sequences were aligned using ClustalW, and a phylogenetic tree was reconstructed using the neighbor-joining analysis method with P-distance using MEGA 5.0. The reliability of the phylogenetic trees was estimated by calculating bootstrap confidence limits based on 1000 replicates. (C) Test of the possible interaction between P2N and Rab27a in a yeast two-hybrid assay. Transformants on SD/Trp-Leu-His-Ade plates are labeled as follows: +, positive control, i.e., pGBKT7-53/pGADT7-T; –, negative control, i.e., pGBKT7-Lam/pGADT7-T; Rab27a + P2N, pGADT7-Rab27a/pGBKT7-P2N. Positive clones appear blue in the β-galactosidase assay. (D) RT-qPCR assay showing the transcript levels of Rab5 and Rab27a in salivary glands treated with dsRab5 or dsRab27a. Means (± SD) from three biological replicates are shown. **p<0.01. (E) Immunofluorescence microscopy showing the localization of Rab27a and Rab5 in the salivary glands of nonviruliferous leafhoppers. Salivary glands of nonviruliferous leafhoppers were immunostained with Rab5-rhodamine (red) and Rab27a-FITC (green) and then examined by immunofluorescence microscopy. Bars, 10 μm.
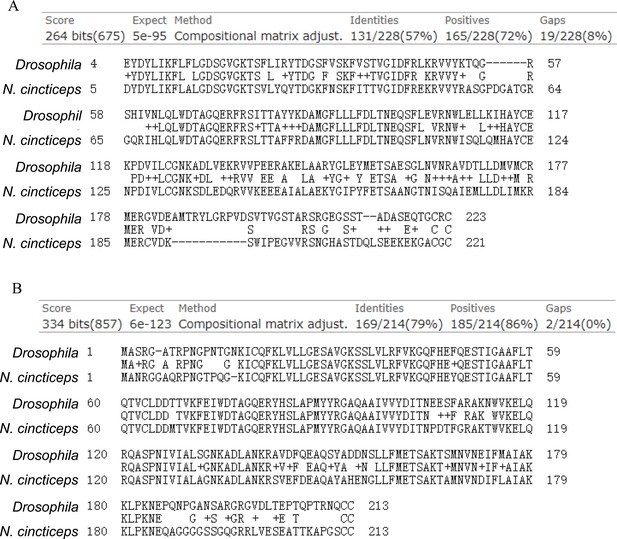
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool of Protein Databases (BLASTP) showing the similarity of Rab27a (A) or Rab5 (B) from N. cincticeps with homologues from Drosophila.
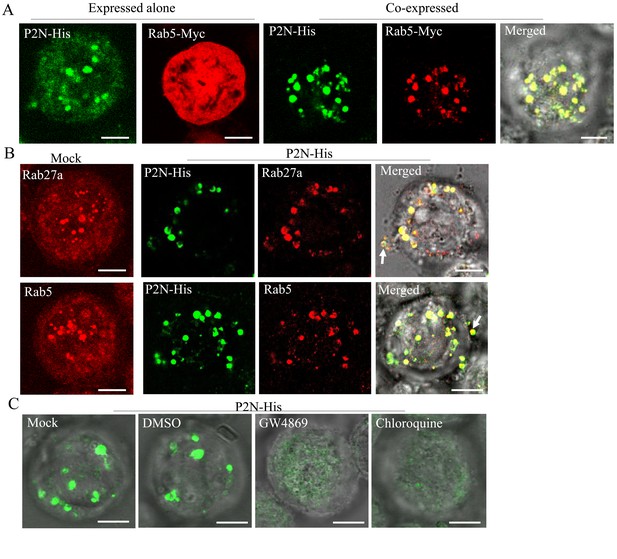
RDV P2N is associated with the endosomal compartments in Sf9 cells.
(A) Immunofluorescence assay showing the colocalization of RDV P2N with Rab5 of N. cincticeps in Sf9 cells. RDV P2N-His and Rab5-Myc were expressed alone or co-expressed. Sf9 cells were fixed at 48 hpi and immunolabeled with His-Alexa Fluor 488 (green) and Myc-Alexa Fluor 555 (red). (B) The association of RDV P2N with the endosomal compartments labeled by Rab5- or Rab27a-specific IgG in Sf9 cells. The control or P2N-expressing cells were immunostained with Rab5- or Rab27a-rhodamine and His-Alexa Fluor 488. Arrows indicate the release of P2N-specific endosomal compartments into the extracellular medium. (C) Endosomal inhibitors inhibited the association of P2N with the endosomal compartments. Sf9 cells were infected with recombinant baculovirus encoding P2N-His. At 48 hpi, cells were treated with GW4869 (20 μM) or chloroquine (280 μM). Cells were immunostained with His-Alexa Fluor 488 prior to examination by immunofluorescence microscopy. Bars, 5 μm.
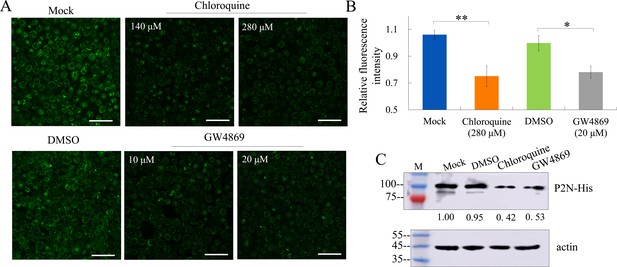
The effects of chloroquine or GW4869 on the expression of P2N-His in Sf9 cells.
(A) Immunofluorescence microscopy showing the expression of P2N-His in Sf9 cells treated with chloroquine or GW4869 at different concentrations. Each panel is representative of three independent biological experiments. Bars, 50 μm. (B) The mean fluorescence intensity of each treatment was analyzed using ImageJ. Means (± SD) from three biological replicates are shown. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (C) Western blot assay of P2N-His in Sf9 cells treated with chloroquine (280 μM) or GW4869 (20 μM). Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected with His-specific antibody. The relative intensities of bands in analyses of P2N-His are shown below the bands. Actin detected with actin-specific IgG is shown to demonstrate the loading of equal amounts of protein. Data shown here are representative of three biological replicates.
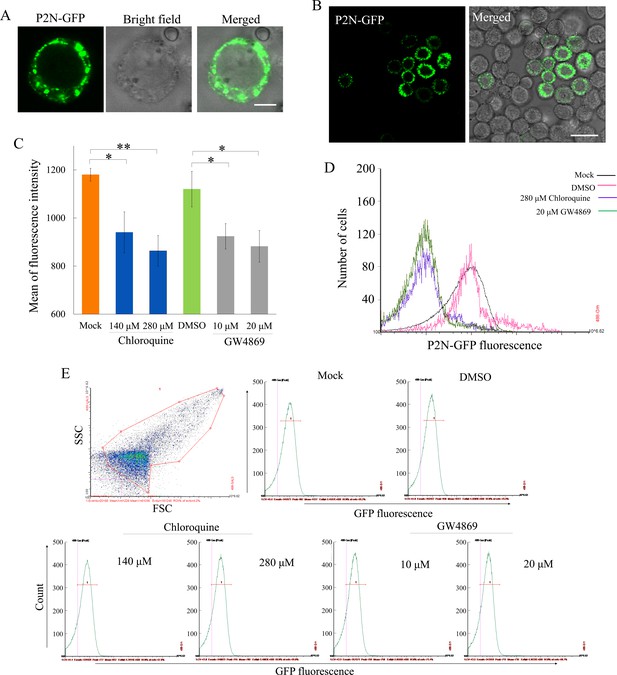
The effects of chloroquine or GW4869 on the expression of P2N-GFP in Sf9 cells.
(A–B) Immunofluorescence microscopy showing the expression of P2N-GFP in Sf9 cells. Bars, 10 μm (A) and 50 μm (B). (C) The fluorescence intensity of P2N-GFP in cells treated with chloroquine or GW4869 at different concentrations. The fluorescence intensity was analyzed using ImageJ. Means (± SD) from three biological replicates are shown. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (D) Flow cytometry assay of the fluorescence intensity of P2N-GFP expressing cells treated with chloroquine or GW4869. Each curve is representative of three independent biological experiments. (E) Fluorescence of P2N-GFP in each treatment. SSC, side scatter; FSC, forward scatter. Each panel is representative of three independent biological experiments.
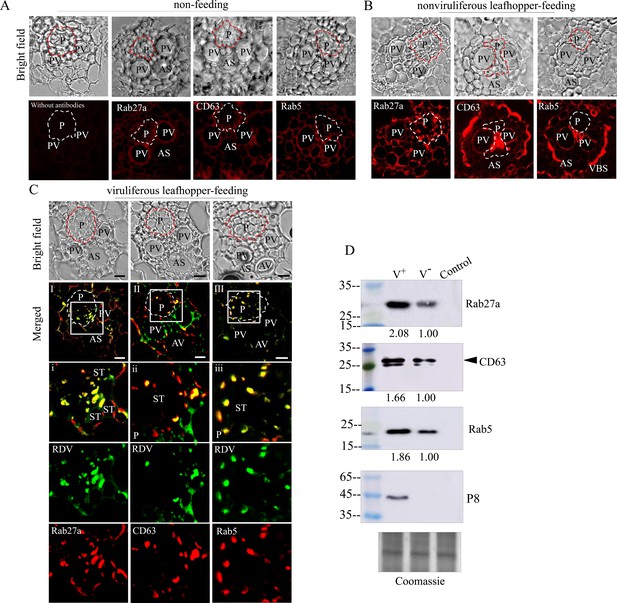
Exosome-mediated RDV delivery to the phloem of rice plants via leafhopper feeding.
(A–C) Immunofluorescence microscopy showing the distribution of RDV antigens, Rab27a, CD63 or Rab5 in the phloem of rice plants after 2 day feeding of viruliferous or nonviruliferous leafhoppers. Rice plants without leafhopper feeding (A) and fed on by nonviruliferous (B) or viruliferous (C) leafhoppers were immunolabeled with virus-FITC (green) and Rab27a, CD63, or Rab5-rhodamine (red) and then examined by immunofluorescence microscopy. Panels i to iii are enlarged images of the boxed areas in panels I to III, respectively. The green and red panels show the separate green (RDV antigens) or red fluorescence (Rab27a, CD63, or Rab5 antigens) of the merged images in panels i to iii. Areas enclosed with a dotted line indicate phloem. AS, air space; P, phloem; PV, pitted vessel; AV, annular vessel; ST, sieve tube; VBS, vascular bundle sheath. Bars, 10 μm. (D) Western blot assay of RDV P8, Rab27a, CD63, or Rab5 in rice plants that had been fed on by viruliferous or nonviruliferous leafhoppers. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected with P8-, Rab27a-, CD63-, or Rab5-specific antibody. V-, rice plants that had been fed on by nonviruliferous leafhoppers; V+, rice plants that had been fed on by viruliferous leafhoppers; Control, rice plants without leafhopper feeding. The relative intensities of bands in analyses of Rab5, Rab27a, and CD63 are shown below. Coomassie-blue-stained gels demonstrated the loading of equal amounts of protein. Data shown here are representative of three biological replicates.
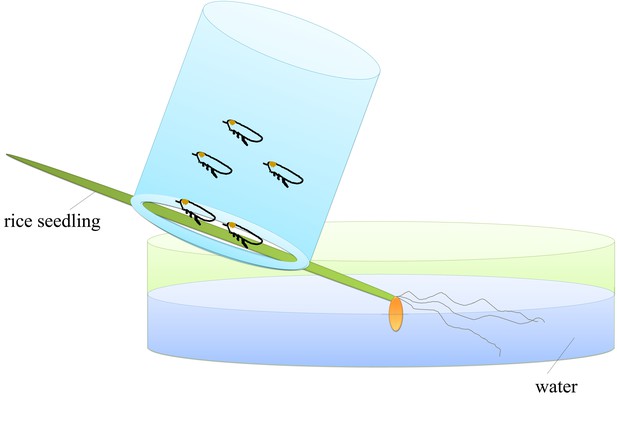
Schematic illustration of the feeding cage used for collecting components released from leafhopper salivary glands.
Fifteen viruliferous leafhoppers were confined for 2 days, respectively, in pipe-like cages (2.5 cm in diameter by 4 cm in height), in which one end was covered by mesh and the other end was fixed to a rice seedling. The root of the rice seedling was immersed in water in a plate to keep the plant alive.
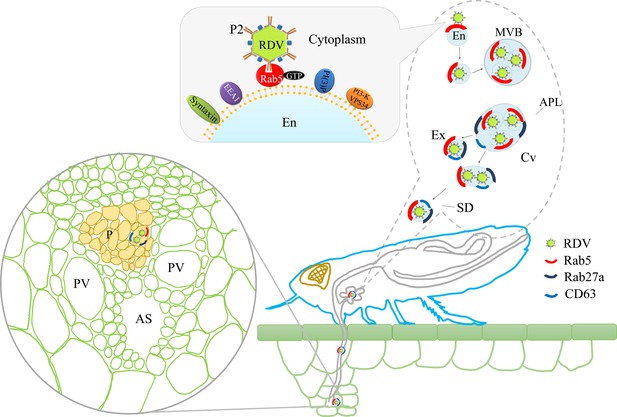
Proposed model of RDV hijacking the exosomal release pathway to be released from salivary glands of leafhopper vectors into rice phloem.
In the proposed model, the specific interaction of RDV P2N and Rab5 causes the internalization and delivery of viruses to endosomes. Then, these virus-containing endosomes are engulfed in the MVBs in the cytoplasm. The attachment of MVBs with the apical plasmalemma drives the enation of the apical plasmalemma toward the cavity. The fusion of MVBs with apical plasmalemma leads to the release of virus-containing exosomes to the cavities. This exosomal release pathway is mediated by Rab27a. Exosomes are secreted with the salivary flow from the salivary cavities into the stylets and are then injected into the plant phloem as leafhoppers feed on rice plants. The virus released into the phloem establishes the initial replication within plant cells. APL, apical plasmalemma; MVB, multivesicular body; Cv, cavity; SD, salivary duct; En, endosome; Ex, exosome; P, phloem; AS, air space; PV, pitted vessel.





