Presynaptic inhibition of dopamine neurons controls optimistic bias
Figures
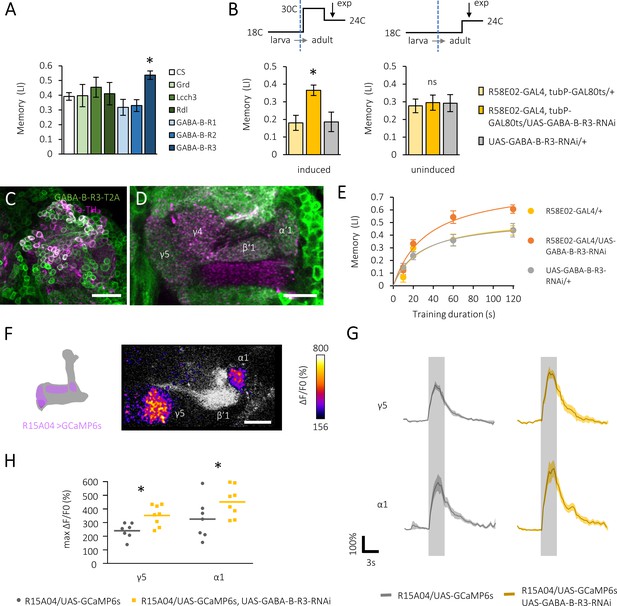
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-B-R3 suppresses sugar reward.
(A) Cell type-specific GABA receptor silencing in the protocerebral anterior medial (PAM) neurons directed by R58E02-GAL4, showing GABA-B-R3-specific memory increment. *q < 0.008 (Benjamini and Hochberg method, N = 8, 23). Mean ± SEM are shown hereafter. (B) Acute silencing of GABA-B-R3 in the PAM neurons using Tub-GAL80ts and heat-induced inactivation. *p<0.05 (Sidak’s test, N = 10, 12; Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, N = 7, 8). (C, D) A substack projection image and a single optical slice showing endogenous GABA-B-R3 expression in somata of PAM neurons (C) and their axon terminal profiles in the mushroom body (MB) (D) by using GABA-B-R3-T2A-GAL4. Anti-tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) antibody signal (magenta) for labeling PAM neurons. Scale bars, 100 μm (C), 20 μm (D). (E) Memory acquisition curves of knock-down and control flies. Hyperbola curve fitting and subsequent permutation tests (Figure 1—figure supplement 1E–F) reveal an altered plateau level but not the acquisition speed in knock-down flies. N = 12. (F) Superimposed and color-coded sugar-evoked calcium signal (ΔF/F0) in a subset of PAM neurons measured in R15A04-GAL4/UAS-GCaMP6s, UAS-mCD8::RFP flies. (G) Time course of the calcium transients in defined compartments of the MB in control (left) and GABA-B-R3 knock-down (right) flies. Gray shades indicate sugar stimulation for 3 s. Mean ± SEM, N = 7, 8. (H) GABA-B-R3 knock-down significantly increases sugar-evoked peak calcium transients in γ5 and α1 neurons. *p<0.05 (Holm-Sidak’s test, N = 7, 8).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
GABA receptor silencing in the PAM neurons and the effects on appetitive memory.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Acute suppression of GABA-B-R3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig1-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 1—source data 3
Memory acquisition curve in control and GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig1-data3-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 1—source data 4
Sugar response in the PAM neurons in control and GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig1-data4-v1.xlsx
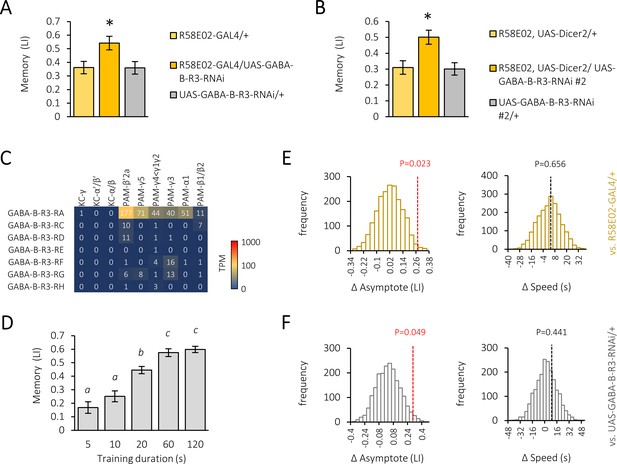
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-B-R3 knock-down in the protocerebral anterior medial (PAM) neurons increases memory strength.
(A) Appetitive memory score in R58E02-GAL4/UAS-GABA-B-R3-RNAi flies compared with parental controls. Mean ± SEM hereafter. *p<0.05 (Sidak’s test, N = 12). (B) Appetitive memory score in R58E02-GAL4/UAS-Dicer2, UAS-GABA-B-R3-RNAi #2 flies compared with parental controls. *p<0.05 (Sidak’s test, N = 11–12). (C) Mean TPM of GABA-B-R3 splicing isoforms in subtypes of the Kenyon cells and PAM cluster dopamine neurons. Data from Aso et al., 2019. (D) Memory acquisition curve of CS flies. Significant statistical differences between different alphabet groups (Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, N = 8–16.). (E–F) Null distributions of memory asymptote difference (left) and acquisition speed difference (right) between R58E02-GAL4/UAS-GABA-B-R3 and R58E02-GAL4/+ (E) or UAS-GABA-B-R3/+ (F) flies generated by permutation test. Broken lines indicate observed differences with respective p-values.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Appetitive memory score in control and GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Appetitive memory score in control and GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies with a second RNAi line.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig1-figsupp1-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 3
Memory acquisition curve in wild-type flies.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig1-figsupp1-data3-v1.xlsx
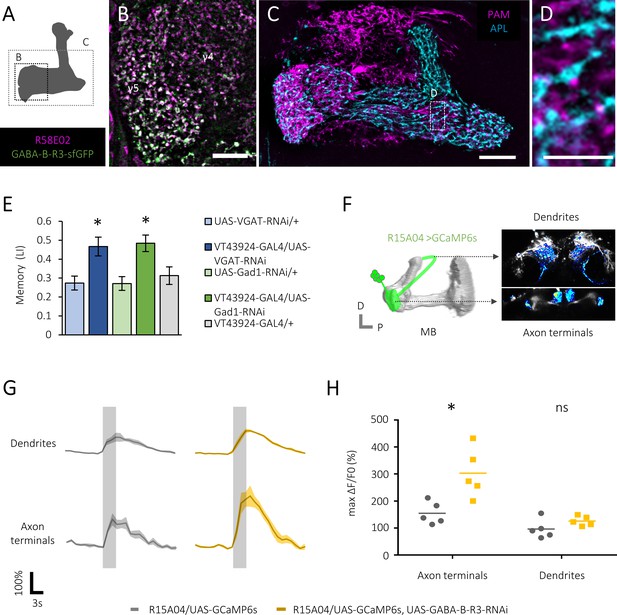
Presynaptic GABAergic inhibition of the protocerebral anterior medial (PAM) neurons.
(A) A schematic showing brain regions visualized in subsequent figures. (B) A substack projection image of double labeling of GFP-tagged GABA-B-R3 protein and PAM neurons using GABA-B-R3-sfGFP-TVPTBF, R58E02-GAL4/UAS-mCD8::RFP fly. Presynaptic localization of GABA-B-R3 protein in the γ5 and α1 (Figure 2—figure supplement 1A) compartments of the mushroom body (MB). Scale bar, 10 μm. (C–D) A substack projection image showing double labeling of the PAM and anterior paired lateral (APL) neurons visualized by VT43924-GAL4/UAS-mCD8::RFP, R58E02-LexA/LexAop-rCD2::GFP. These axonal profiles co-localize at close proximity in the MB. A single optical slice of the inset in C is magnified in D. Scale bars, 10 μm (C), 2 μm (D). (E) Increased appetitive memory score by shRNA-mediated silencing of GABA neurotransmission-related genes in the APL neurons. *p<0.05 (Sidak’s test, N = 11–13). (F) A cartoon depicting volumetric imaging from axon terminals and dendritic fields of PAM neurons using a z-objective piezo actuator. (G) Time course of calcium transients (ΔF/F0) near-simultaneously recorded from axon terminals and dendrites of PAM-γ5 neurons (Figure 2—figure supplement 1) of control (left) and GABA-B-R3 knock-down (right) flies. Gray shades indicate sugar stimulation for 3 s. Mean ± SEM, N = 5. (H) Significantly increased sugar-evoked peak calcium transients of GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies in axon terminals. *p<0.05 (Dunn’s test, N = 6, 7).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Inhibition of GABA neurotransmission in APL neurons.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Sugar response in the axon terminals and dendrites of the PAM neurons.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig2-data2-v1.xlsx
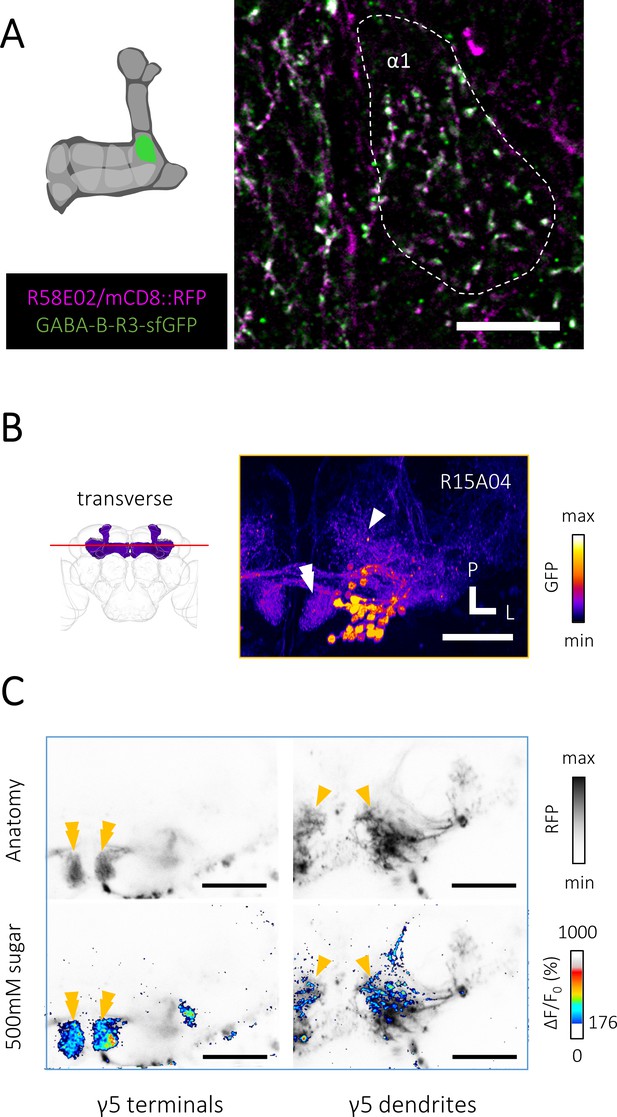
Presynaptic gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-B-R3 localization and volumetric Ca2+ imaging from a defined protocerebral anterior medial (PAM) cell class.
(A) A substack projection image of double labeling of GFP-tagged GABA-B-R3 protein and PAM neurons using GABA-B-R3-sfGFP-TVPTBF, R58E02-GAL4/UAS-mCD8::RFP fly. Presynaptic localization of GABA-B-R3 protein in the α1 compartment of the mushroom body (MB). Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) A transverse section showing dendrites and axon terminals of PAM neurons visualized by fixed brain sample of R15A04-GAL4/UAS-mCD8::GFP flies, the depth of which approximately matches to that of C. The arrowhead and double arrowhead indicate the dendritic field and axon terminals of PAM-γ5 neurons, respectively. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) Volumetric Ca2+ imaging of activities from axon terminals (left, double arrowhead) and dendrites (right, arrowhead) of PAM-γ5 neurons. Thresholded Ca2+ activities in response to 500 mM sucrose superimposed on the anatomy of PAM neurons (lower row). Scale bar, 50 μm.
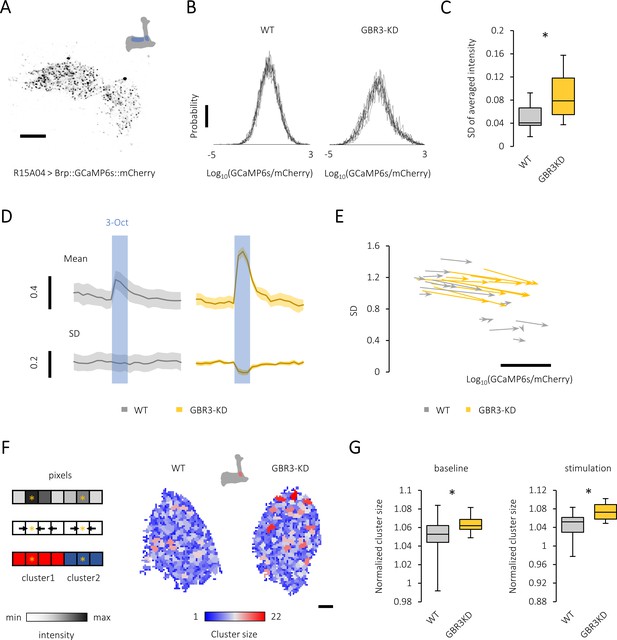
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-B-R3 controls presynaptic activity patterns in the protocerebral anterior medial (PAM) neurons.
(A) A single optical slice showing punctate sensor localization in the mushroom body (MB) lobe of R15A04-GAL4/UAS-Brp::GCaMP6s::mCherry flies. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) The histograms of GFP/RFP signals from nine different time points (PAM-α1 terminals) reveal a large calcium diversity among active zones and the temporal instability in the knock-down fly (right). The probability distribution of the active-zone calcium mostly followed the Gaussian distribution, characteristics of which are well represented by the mean and standard deviation (SD). Scale bar, 0.01. (C) The temporal variance of spatially averaged intensities is larger in the GABA-B-R3 knock-down PAM neurons. *p<0.001 (Mann-Whitney test, N = 24, 17). (D) Time course of odor-evoked calcium transient (mean) and the variance (SD) of PAM-α1 terminals in control (left) and GABA-B-R3 knock-down (right) flies. The blue shade indicates odor stimulation for 3 s. Mean ± SEM, N = 6–8. (E) Map of the probability distribution of active-zone calcium intensity in the PAM-α1 terminals for each individual. The abscissa and ordinate represent the mean and SD of the signal distribution, respectively. The clear inverse correlation between the mean and the variance in wild-type terminals (r = −0.82, p<10−6) may represent individually defined unique set points of activity levels. This structured individual difference is disrupted by GABA-B-R3 RNAi (r = 0.53, p=0.03). The start and end of an arrow represent the probability distribution of active-zone calcium before and during the odor stimulation, respectively. Scale bar, 0.5 in Log10(GCaMP6s/mCherry). (F) Local peaks in the PAM terminals are color-coded for their cluster sizes (right). Schematic example of the algorithm finding the cluster structure applied to a one-dimensional system (Left). Spatial distribution of calcium intensity (Left upper). Finding steepest paths from each pixel to local peaks by computing the gradient (i.e., the difference of the intensity values between neighboring pixels)(Left middle). Note that in two-dimensional systems we analyzed, each pixel had four neighboring pixels. Clustering based on the paths to local peaks (Left lower). Pixels having the same destination (i.e., local peak) are clustered together. (G) The average area per peak is significantly larger in the GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies during baseline activity (*p<0.05, Mann-Whitney test, N = 22, 17) and odor stimulation (*p<0.05, t-test, N = 15, 11).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Temporal variance of spatially averaged intensities in control and GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Probability distribution of active-zone calcium intensity before and during odor stimulation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig3-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 3
Average cluster size in control and GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig3-data3-v1.xlsx
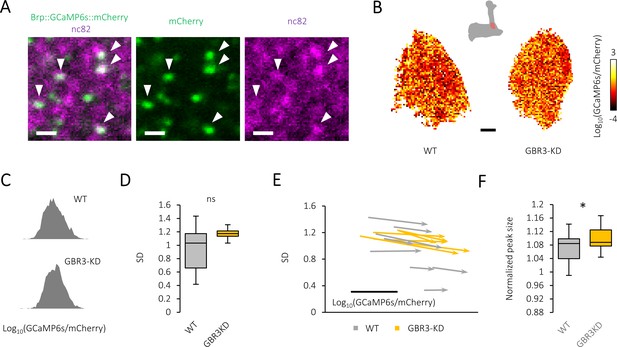
Spatial and temporal characteristics of active-zone calcium signal in the presynapses of protocerebral anterior medial (PAM) neurons.
(A) Brp::GCaMP6s::mCherry (green) expressed by R15A04-GAL4 co-localizes with native Brp detected by nc82 (magenta). Scale bar, 1 μm. (B) Pseudo-color-coded distribution of active-zone calcium signals of PAM-α1 neurons at the baseline activity in control (left) and GABA-B-R3 knock-down (right) flies. Scale bar, 3 μm. (C) The histogram of active-zone calcium intensity at single representative frames of baseline activity of control (upper) and GABA-B-R3 knock-down (lower) flies, which typically follow log-normal distribution. (D) Standard deviation (SD) of the active-zone calcium intensity calculated individually. Silencing GABA-B-R3 did not alter the heterogeneity (t-test, N = 16, 11). (E) Map of the probability distribution of active-zone calcium intensity for each individual. The start and end of an arrow represent the probability distribution of active-zone calcium before and during sugar stimulation. The abscissa and ordinate represent the mean and SD of the distribution, respectively. Scale bar, 0.5 in Log10(GCaMP6s/mCherry). (F) Significantly increased peak size in GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies. See Materials and methods for details. *p<0.05 (t-test, N = 17, 22).
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Standard deviation of the active-zone calcium intensity.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 2
obability distribution of active-zone calcium intensity before and during sugar stimulation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig3-figsupp1-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 3
Normalized peak size in control and GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig3-figsupp1-data3-v1.xlsx
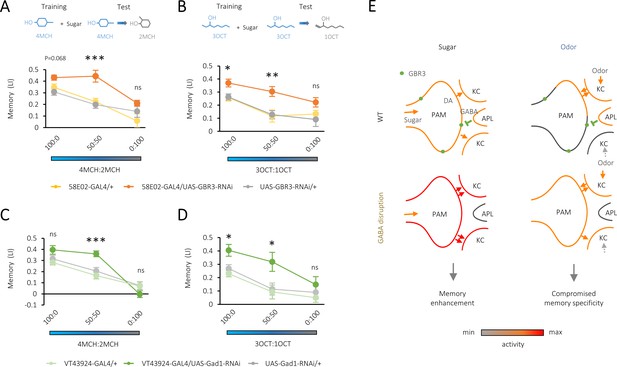
Compromised odor specificity in the rewarded memory by attenuating local gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) signaling in the mushroom body.
(A–D) Olfactory generalization of appetitive memory depends on the blend ratio of a contaminant to a trained odor 4-methylcyclohexanol (4MCH) (A, C) or octan-3-ol (3OCT) (B, D). Significantly broader generalization in R58E02-GAL4/UAS-GABA-B-R3-RNAi flies (A, B) and VT43924-GAL4/UAS-Gad1-RNAi flies (C, D) compared to the respective parental controls. *p<0.05; ***p<0.001 (Sidak’s test across genotypes at each blend ratio, N = 8–20 [A, B], N = 9–12 [C, D]). (E) A model for dual behavioral roles of GABA-B-R3 in the protocerebral anterior medial (PAM) terminal in the mushroom body (MB). GABA-B-R3 controls the overall gain (left) and localization (right) of sugar- and odor-evoked terminal activity of PAM neurons, respectively. Note that input sources of sugar and odor response are different. In an odor response, reciprocal PAM-KC (Kenyon cell) synapses serve as KC activity-dependent local enhancers for reward signaling from the PAM synapses. In wild-type flies, this local modulation is restricted to the PAM synapses onto the odor-activated KCs, which laterally inhibit activities of surrounding ones via KC-APL (anterior paired lateral) feedback. GABA-B-R3 knock-down in the PAM neurons eliminates this negative feedback from the APL, reducing the activity contrast within presynaptic terminals of the PAM neurons and the selectivity of memory to the rewarded odor.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Olfactory generalization of appetitive memory in control and GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies (4MCH).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Olfactory generalization of appetitive memory in control and GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies (3OCT).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig4-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 3
Olfactory generalization of appetitive memory in control and Gad1 knock-down flies (4MCH).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig4-data3-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 4
Olfactory generalization of appetitive memory in control and Gad1 knock-down flies (3OCT).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-fig4-data4-v1.xlsx
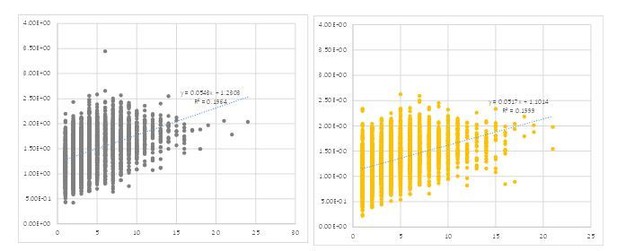
Scatter plots showing dependency between the size (abscissa) and intensity (ordinate) of each peak calculated by the method we described.
Each circle represents a single cluster in the 9 frames before stimulation of a single representative fly.
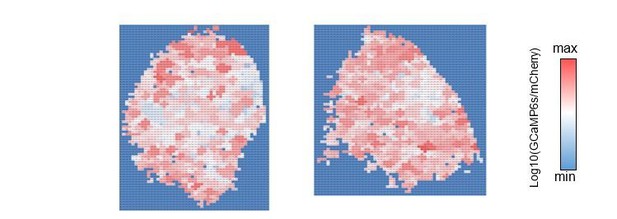
The cluster value map.
Each cluster is color-coded by the averaged intensity of associated pixels. Left: control, right: GABA-B-R3-KD.
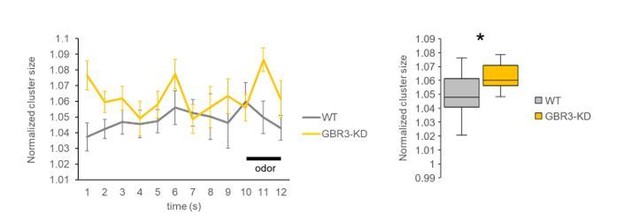
Time courses of normalized cluster size (left) and the comparison between genotypes using all frames from pre- and during-stimulation phases (frames 1-12, right).
The averaged cluster size was consistently higher in the GABA-B-R3 knock-down flies compared to wild-type flies. * P < 0.05, Mann Whitney test. N=15, 11.
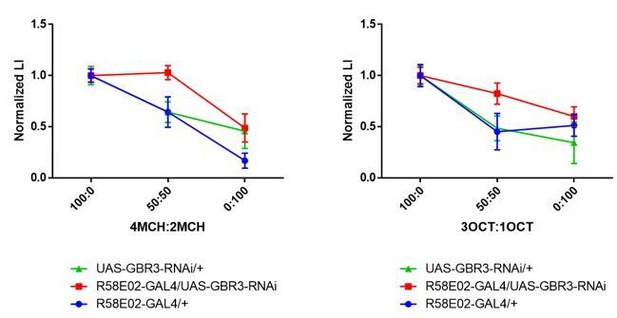
Normalized generalization curves using 4MCH:2MCH (left) and 3OCT:1OCT (right) mixtures.
Statistics suggest experimental group exhibit altered memory specificity to learned odors when compared with its parental control groups. (4MCH:2MCH) R58E02-GAL4/+, p = 0.030; UAS-GBR3-RNAi/+, p = 0.006; R58E02-GAL4/UAS-GBR3-RNAi, p = 0.972. N = 8-17. (3OCT:1OCT) R58E02-GAL4/+, p = 0.002; UAS-GBR3-RNAi/+, p = 0.006; R58E02-GAL4/UAS-GBR3-RNAi, p = 0.500. N = 8-20. Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | GMR58E02-GAL4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 41347; FLYB: FBal0253714; RRID:BDSC_41347 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | GMR15A04-GAL4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 48671; FLYB: FBtp0057752; RRID:BDSC_48671 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | VT043924-GAL4 | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | VDRC: v201194; FLYB: FBtp0105273; | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-GABA-B-R3-RNAi | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 50622; FLYB: FBti0157477; RRID:BDSC_50622 | FlyBase symbol:P{TRiP.HMC02989}attP40 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-mCD8::GFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 32194; FLYB: FBti0131936; RRID:BDSC_32194 | FlyBase symbol: P{20XUAS-IVS-mCD8::GFP} |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-GCaMP6s | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 42746; FLYB: FBti0151344; RRID:BDSC_42746 | FlyBase symbol: P{20XUAS-IVS-GCaMP6s} |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | GABA-B-R3-sfGFP-TVPTBF | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | VDRC: v318614; FLYB: FBst0491638; | FlyBase symbol: PBac{fTRG00613.sfGFP-TVPTBF} |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-GCaMP6s.brpS.mCherry | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 77131; FLYB: FBtp0125966; RRID:BDSC_77131 | |
| Antibody | (Rabbit polyclonal) anti-GFP | Invitrogen | Cat# A11122; RRID:AB_221569 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | (Mouse monoclonal) anti-TH | ImmunoStar | Cat# 22941; RRID:AB_1267100 | (1:100) |
| Antibody | (Rabbit polyclonal) anti-DsRed | Clontech | Cat# 632496; RRID:AB_10013483 | (1:200) |
| Antibody | (Mouse monoclonal) anti-Brp | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat# nc82; RRID:AB_2314866 | (1:20) |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 5 | GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, 2007 | https://www.graphpad.com/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | MPI-CBG | https://fiji.sc/ |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of fly strains and crosses for experiments, and the statistical results.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-supp1-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64907/elife-64907-transrepform-v1.docx





