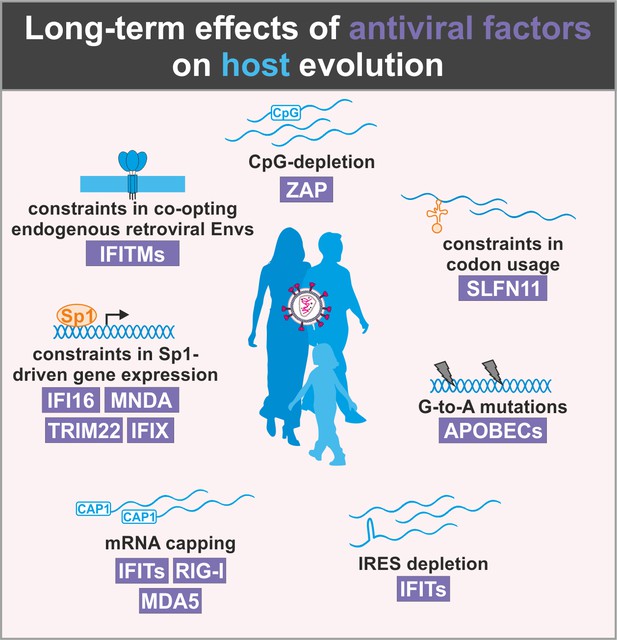
Evolutionary conflicts and adverse effects of antiviral factors
Figures
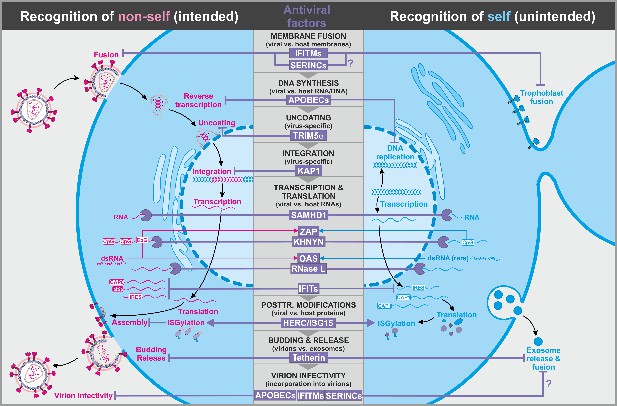
Antiviral factors targeting components of the virus.
The retroviral replication is exemplarily shown to illustrate antiviral host factors (violet) that directly target viral proteins, nucleic acids, and membranes during essentially all steps of the viral life cycle. While some factors successfully distinguish between self (blue, right panel) and non-self (pink, left panel), others may have unintended side effects on the host as they also target cellular factors. CpG: cytosine guanine dinucleotides; dsRNA: double-stranded ribonucleic acid; CAP0: 5′ mRNA cap with unmethylated ribose hydroxy-groups; CAP1: 5′ mRNA cap with methylated ribose hydroxy-group; IRES: internal ribosome entry site; PPP: 5′-triphosphate group without cap; abbreviations of protein names are explained in the text.
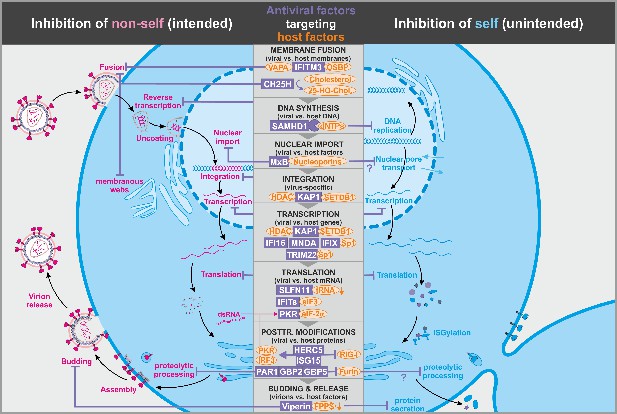
Antiviral factors modulating virus-dependency factors.
Several antiviral host proteins (violet) suppress viral replication (left panel) by modulating the stability, localization, or activity of cellular factors (orange) involved in the viral replication cycle. Since these host factors also play important roles in the cell, their inhibition may be associated with detrimental side effects (right panel). dsRNA: double-stranded ribonucleic acid; tRNA: transfer ribonucleic acid; 25-HO-Chol.: 25-hydroxy-cholesterol; abbreviations of protein names are explained in the text.
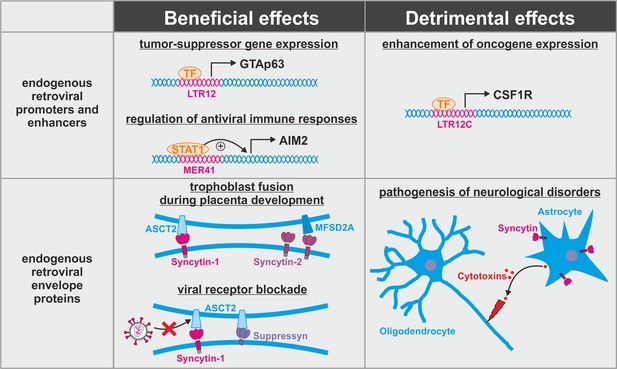
Dual role of endogenous retroviruses (ERVs).
ERV-derived regulatory elements (promoters, enhancers, repressors, insulators) and proteins (syncytin-1, syncytin-2, suppressyn, etc.) may have beneficial (left) or detrimental (right) effects on the host. Abbreviations are explained in the text.
Tables
Selection of antiviral factors directly targeting viral replication (abbreviations are explained in the text).
| Antiviral factor(s) | Target(s) | Discrimination between self and non-self | Effect on viral replication | (Potential) Unwanted effects on host cell | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate | Long term | ||||
| IFITMs | Fusing membranes | Membrane curvature, lipid composition | Impaired fusion of viral and host membranes | Impaired fusion of cellular membranes | Constraints in membrane fusion (e.g. Syncytin-mediated trophoblast fusion) |
| SERINCs | Fusing membranes | Not known (viral glycoprotein dependency?) | Impaired fusion of viral and host membranes | None (?) | |
| TRIM5α, Fv1 | Retroviral capsids | Specific protein-binding | Untimely uncoating | None (?) | Constraints in the co-option of endogenous retroviral capsid proteins |
| KAP1 | Retroviral integrase | Specific protein-binding | Inhibition of integration | None | |
| ZAP/TRIM25/ KHNYN | RNA | CpG content | Degradation of viral RNA | Degradation of host RNA | CpG depletion (?) |
| RNAse L | RNA | dsRNA-dependent, OAS-mediated activation | Degradation of viral RNA | Degradation of host RNA | Avoidance of dsRNA |
| SAMHD1 | RNA | Not known | Degradation of viral RNA | Degradation of host RNA (?) | |
| IFITs | RNA | IRES, modification of 5′ RNA ends (cap-1 vs. cap-0) | Inhibition of viral translation | Inhibition of cellular translation (?) | Depletion of IRES structures, constraints in mRNA capping |
| HERC5/ISG15 | Numerous viral proteins (e.g. HIV-1 Gag, HPV capsid) | Preferred ISGylation of newly translated proteins | Inhibition of viral protein function | Inhibition of host protein function | |
| Tetherin | Budding membranes | Localization in lipid rafts | Inhibition of virion release | Inhibition of exosome release, inhibition of cell division (?) | |
| APOBECs | ssDNA, RNA | Partially sequence dependent | Introduction of lethal hypermutations in the viral genome | Emergence of detrimental mutations | Depletion of specific dinucleotides |
Selection of antiviral factors indirectly targeting viral replication (abbreviations are explained in the text).
| Antiviral factor(s) | Target(s) | Discrimination between self and non-self | Effect on viral replication | (Potential) Unwanted effects on host cell | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate | Long term | ||||
| IFITM3 | VAPA, OSBP | Membrane curvature, lipid composition | Impaired fusion of viral and host membranes | Impaired fusion of cellular membranes | Constraints in membrane fusion (e.g. syncytin-mediated trophoblast fusion) |
| CH25H | Cholesterol | Not known | Impaired fusion of viral and host membranes, impaired membraneous web formation | Impaired fusion of host membranes (?) | |
| SAMHD1 | dNTPs | Not known | Limits reverse transcription/viral DNA replication | Inhibition of host DNA replication | Regulation of SAMHD1 activity in dividing cells |
| MxB | Nucleoporins | Simultaneous interaction with viral (capsid) proteins | Reduced nuclear import of subviral complexes | Impaired nuclear pore transport | Evolution of diverse nuclear pore variants |
| KAP1 | NuRD complex/HDACs, SETDB1, transcription factors | Not known | Suppression of viral gene transcription, latency | Suppression of host gene transcription | |
| TRIM22 | Sp1 | Not known | Reduced Sp1-driven expression of viral genes | Reduced Sp1-driven expression of host genes | Constraints in Sp1-driven gene expression |
| IFI16, MNDA, IFIX | Sp1 | Chromatinization status of the DNA | Reduced Sp1-driven expression of viral genes | Reduced Sp1-driven expression of host genes | Constraints in Sp1-driven gene expression |
| PKR | eIF-2α | Activation by dsRNA | Reduced translation of viral mRNA | Reduced translation of host mRNA | Avoidance of dsRNA |
| IFITs | eIF3 | IRES, modification of 5′ RNA ends | Inhibition of translation | Inhibition of translation (?) | Depletion of IRES structures, mRNA capping (methylated) |
| SLFN11 | tRNA | preferred targeting of tRNAs exploited by viruses | Reduced translation of viral mRNA | Reduced translation of cellular mRNA | Specific codon usage pattern |
| PAR1, GBP2, GBP5 | Furin | Not known | Impaired furin-mediated maturation of viral (glyco)proteins | Impaired proteolytic activation of host proteins | Constraints in furin-mediated protein cleavage |
| HERC5/ISG15 | Numerous host proteins (e.g. IRF3, RIG-I, PKR) | Preferred ISGylation of newly translated proteins | Several proposed inhibitory mechanisms | Modulation of host protein stability and function | |
| Viperin | FPPS, CTP | Not known | Inhibition of viral budding, inhibition of viral RNA polymerization | Inhibition of cellular protein secretion and potentially cellular RNA synthesis | |