Nutrient dominance governs the assembly of microbial communities in mixed nutrient environments
Figures
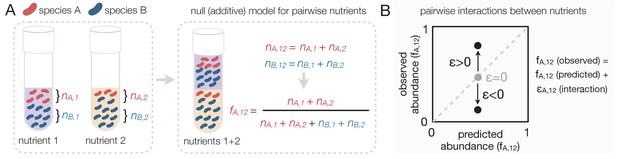
Predicting community composition in mixed nutrient environments.
(A) Community composition in a single nutrient (nutrient 1 or nutrient 2) vs a mixture of nutrients (nutrient 1 + nutrient 2). Assuming that nutrients act independently, the null model predicts that the abundance of each species in the mixture is the sum of its abundance in the single nutrients (i.e. additive). (B) Plotting the experimentally measured (observed) relative abundance in the mixed carbon sources against its predicted (from null model) relative abundance reveals the presence or absence of interactions. Any deviation from the identity line (predicted = observed) is the interaction effect (ε). When ε = 0, there is no interaction between nutrients. When ε is non-zero, community composition is affected by nutrient interactions. If ε > 0, the null model underestimates the abundance. If ε < 0, the model overestimates the abundance.
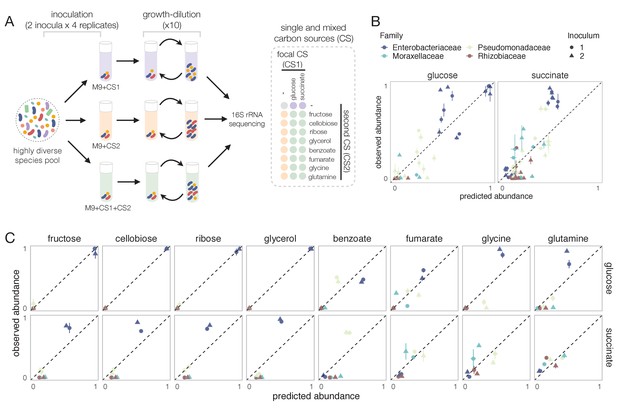
Systematic deviations from the null prediction reveals that some nutrients interact to shape community assembly.
(A) Schematic of experimental design. Two different soil samples were inoculated in minimal M9 medium supplemented with either a single carbon source (CS1 or CS2) or a mixture of two carbon sources (CS1 + CS2) (three to four replicates each). Communities were propagated into fresh media every 48 hr for 10 transfers and then sequenced to assess community composition. Carbon source mixtures consisted of a focal carbon source (CS1; glucose or succinate) mixed with a second carbon source (CS2). (B, C) For each pair of carbon sources, we show the experimentally observed and predicted (by the null additive model) relative abundance of each family in the mixture. Any deviation from the identity line (predicted = observed) reveals an interaction effect. Only the four most abundant families are shown. Error bars represent mean ± SE.
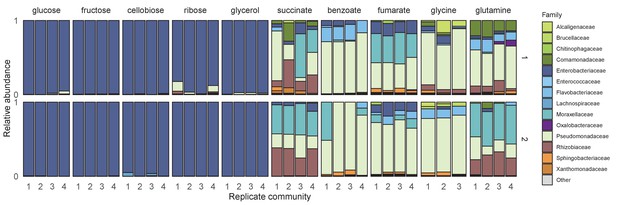
Community assembly in a single carbon source.
Two soil samples were inoculated in minimal M9 medium supplemented with a single carbon source (three or four replicates each) and propagated into fresh media every 48 hr for 10 transfers (Materials and methods). Shown is the family-level taxonomic composition at Transfer 10 for inoculum 1 (top) and inoculum 2 (bottom). Families with a relative abundance lower than 0.01 are shown as ‘Other’.
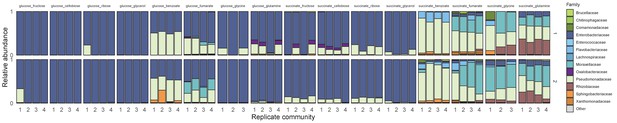
Community assembly in a mixture of two carbon sources.
Two soil samples were inoculated in minimal M9 medium supplemented with two carbon sources (glucose or succinate + another carbon source), and propagated into fresh media every 48 hr for 10 transfers (Materials and methods). There are three/four replicates per carbon source pair. Shown is the family-level taxonomic composition at Transfer 10 for the two inocula. Families with a relative abundance lower than 0.01 are shown as ‘Other’.
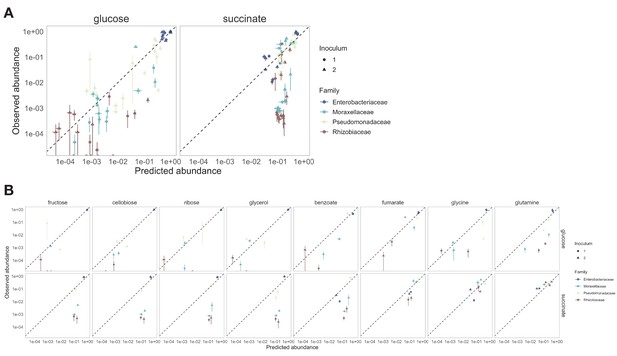
Systematic deviations from the null (additive) prediction reveal interactions between nutrients.

Comparison of the observed relative abundance and abundance predicted by the null model.
Shown is the observed vs predicted abundance for different taxonomic levels and focal carbon source (CS) (mean ± SE). Table shows the Pearson’s R and RMSE for each family-focal carbon source combination.
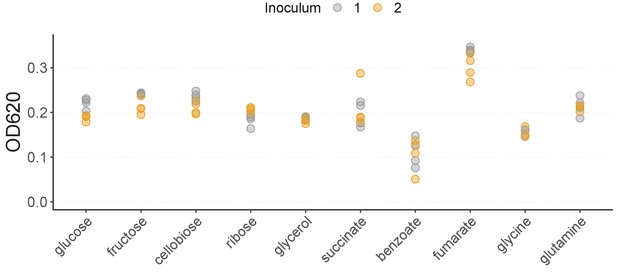
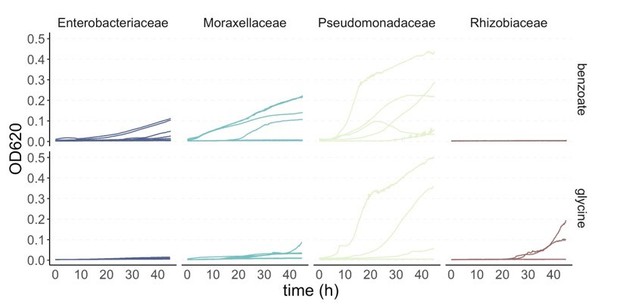
Community yield in each single carbon source.
Total community biomass (OD620) at the end of the 48 hr incubation period at Transfer 10. There are four biological replicates per carbon source per inoculum, except for glycine with three replicates.
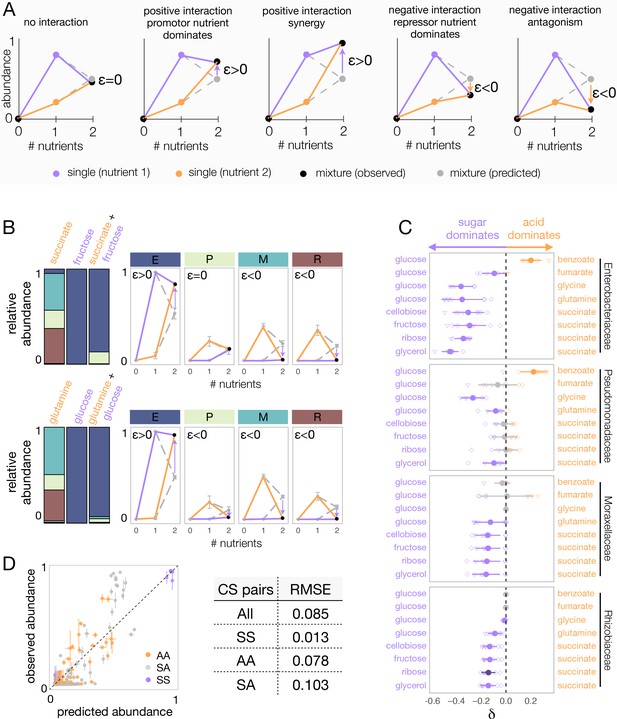
Sugars generally dominate over organic acids.
(A) Detecting interactions and hierarchies of dominance between nutrients on microbial community composition. Drawing the single and pairwise abundance landscapes for each species allows us to visualise interactions between nutrients. Multiple types of interactions are possible, including dominance, synergy, and antagonism. Interactions occur when ε is significantly different from 0 (Materials and methods). Synergy (antagonism) occurs when the abundance in the mixture is greater (lower) than the abundances in any of the single nutrients independently (Materials and methods). Dominance occurs when the abundance in the mixture is closer or similar to the abundance in one of the singles. The landscape also allows us to identify which carbon source has a dominating effect within the pair. When ε > 0, the growth-promoting nutrient dominates and has an overriding effect in the community composition. In contrast, when ε < 0, the growth-repressing nutrient dominates. (B) Two examples of nutrient interactions (succinate + fructose and glucose + glutamine) exhibiting sugar dominance. Barplots show a representative replicate from one of the inocula (Figure 2—figure supplements 1–2). For instance, the landscape for succinate-fructose shows that fructose overrides the effect of succinate by promoting Enterobacteriaceae (E), and repressing Moraxellaceae (M) and Rhizobiaceae (R) (purple arrows), whereas no interaction effect is observed for Pseudomonadaceae (P). Error bars represent mean ± SD of the four replicates. (C) Dominance index for the eight sugar–acid pairs and the four dominant families. Filled circles show the mean ± SD of the two inocula × four replicates for each pair of nutrients, and open symbols show all eight independent replicates (different shapes for different inocula), except for glycine pairs where N = 6. Purple indicates that the sugar dominates while orange indicates that the acid dominates. Lighter purple and orange indicate dominance, while darker purple and orange indicate super-dominance (synergy or antagonism). An interaction occurs when the abundance is greater (ε > 0) or lower (ε < 0) in the carbon source mixture than predicted by the null model (one-tailed paired t-test, p<0.05, N = 8, based on 1000 permutations; Materials and methods). In gray are shown cases where there is no interaction, or when dominance is undefined because the two inocula exhibit opposite dominant nutrient (in which case δ is shown as both –δ and +δ). (D) Predicted vs observed family-level abundance. For each pair of carbon sources (CS), shown is the experimentally observed and predicted (by the null model) relative abundance of each family in the mixed carbon sources. Any deviation from the identity line (predicted = observed) is the interaction effect. The colors show whether the carbon source pairs are sugar–sugar (SS), acid–acid (AA), or sugar–acid (SA). Error bars represent mean ± SE. Table shows RMSE for each carbon source pair type.
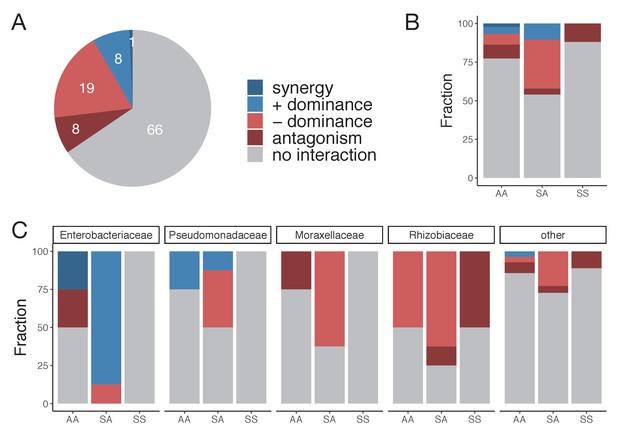
Dominance is the most common type of nutrient interaction, especially in the sugar–acid mixtures.
(A) Interaction type for each pair of carbon source and family. An interaction between nutrients occurs when the abundance in the mixture is significantly greater or lower than predicted by the null additive model (one-tailed paired t-test, p<0.05 based on 1000 permutations; only cases where N ≥ 6 unique pairs are considered) (Materials and methods). Multiple types of nutrient interaction are possible: dominance, synergy, and antagonism. Synergy (antagonism) occurs when the abundance in the mixture is greater (lower) than the abundances in any of the single nutrients independently (Welch two sample t-test, p<0.05) (Materials and methods). Dominance occurs when the abundance in the mixture is closer or similar to the abundance in one of the singles. (B) Interaction type by carbon source pair type. AA: mixture of two acids; SS: mixture of two sugars; and SA: mixture of a sugar and an acid. (C) Interaction type shown for the four most abundant families and ‘other’ families grouped together.
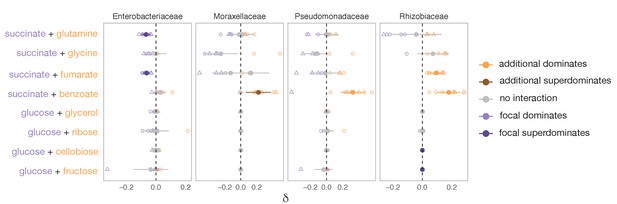
Family-level dominance for mixtures of acid–acid and sugar–sugar.
For each carbon source pair, the filled circles show the mean ± SD of N = 8 unique replicates (two inocula × four replicates each), and the open symbols show all eight replicates individually (except for glycine pairs where N = 6). The different shapes correspond to different inocula. When δ < 0, the focal carbon source (succinate or glucose) dominates. When δ > 0, the additional carbon source dominates (Materials and methods). Orange or purple corresponds to cases where nutrients interact, in which case there is dominance (or super-dominance). An interaction occurs when the abundance observed in the mixture is significantly greater (ε > 0) or lower (ε < 0) than predicted by the null additive model (one-tailed paired t-test, p<0.05, based on 1000 permutations; see Materials and methods). Gray corresponds to cases where nutrients do not interact or dominance is undefined because one carbon source dominates in one of the inocula and the paired carbon source dominates in the other inocula (in which case δ is shown as both −δ and +δ). Lighter orange or purple indicates dominance while darker orange or purple indicates super-dominance (synergy or antagonism) (Materials and methods). Only the four most dominant families are shown.
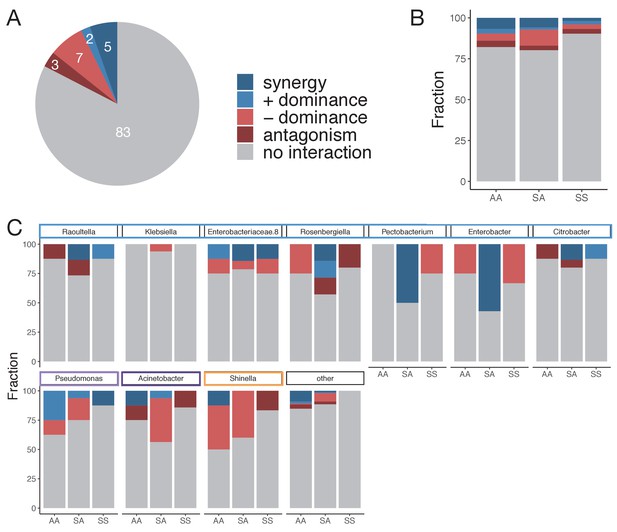
Patterns of nutrient interaction at the genus level.
(A) Multiple types of nutrient interactions are possible, including dominance, synergy, and antagonism (Figure 3A). An interaction occurs when ε is significantly greater or lower than 0 (one-sided paired t-test, p<0.05 based on 1000 permutations, Materials and methods). Inocula are considered separately, and only cases where N ≥ 3 unique pairs are considered. Synergy (antagonism) occurs when the abundance in the mixture is greater (lower) than the abundances in any of the singles separately. Dominance occurs when the abundance in the mixture is closer or similar to one of the single abundances but not above or below any of the single abundances independently (Materials and methods). (B) Interaction type by carbon source pair type. AA: mixture of two acids; SS: mixture of two sugars; and SA: mixture of a sugar and an acid. (C) Interaction type is broken down by the 10 most abundant genera spanning the Enterobacteriaceae family (blue), Pseudomonadaceae (light purple), Moraxellaceae (dark purple), and Rhizobiaceae (orange) families. Note that Enterobacteriaceae.8 is a non-identified genus belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family. The other genera are grouped together and shown as ‘other’.
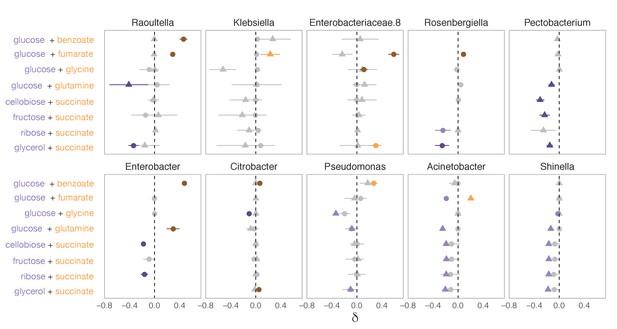
The systematic dominance of sugars observed at the family level does not apply to the genus level.
To determine the genus-level dominance, the two inocula are considered separately (different shapes) as the genera that are sampled in one inocula may not be sampled in the other inocula. Purple indicates that the sugar dominates while orange indicates that the acid dominates. Lighter purple and orange indicate dominance, while darker purple and orange indicate super-dominance (synergy or antagonism) (Materials and methods). No interaction is shown in gray. An interaction occurs when ε is significantly greater or lower than 0 (one-sided paired t-test, p<0.05 based on 1000 permutations, Materials and methods). Shown are the 10 most abundant genera (mean ± SD). Note that Enterobacteriaceae.8 is a non-identified genus of the Enterobacteriaceae family.
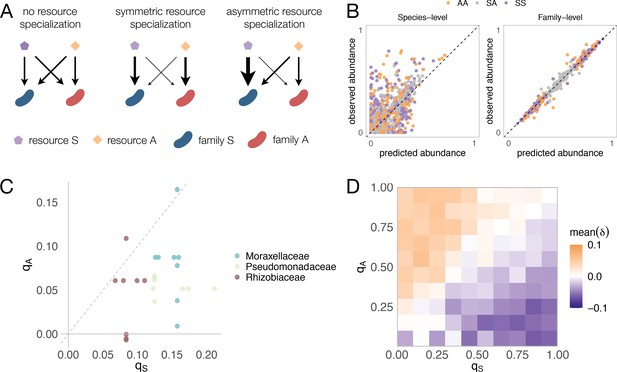
Family-level asymmetry in nutrient benefits can lead to dominance.
(A) Schematic illustrating different scenarios of nutrient preference. There are two families (FS and FA) and two resource classes (RS and RA). Without resource specialization, FS and FA have equal access to RS and RA. With symmetric specialization, each family prefers its own resource class with the same strength. With asymmetric specialization, one family (FS) has better access to its own resource class (RS) relative to that of the other family (FA) on its own resource class (RA). (B) A mechanistically explicit consumer-resource model that incorporates resource competition, resource specialization and nonspecific cross-feeding (Materials and methods) recovers the predicted additivity pattern at both the species (left) and family (right) level of taxonomic organization. The observed relative abundance of each species or family in 300 communities grown on a different pair of nutrients (100 AA, 100 SS, and 100 SA) is plotted against the abundance predicted from the same communities grown on each of the relevant single nutrients (S, A). Each family specializes equally on its preferred nutrient (qS = qA = 0.9) as in previous work (Marsland et al., 2020a). In Figure 4—figure supplement 4, we illustrate representative consumption matrices for different choices of qA and qS. (C) 22 strains were isolated from the assembled communities and their growth rates on minimal M9 media supplemented with one the 10 carbon sources were measured. qS represents the growth rate advantage of Enterobacteriaceae on sugars relative to the other dominant family (colored), while qA represents the growth rate advantage of the other family on the acids relative to Enterobacteriaceae (Materials and methods). When qS is positive, Enterobacteriaceae grow faster on the sugar than the other family, while when qS is negative, Enterobacteriaceae grow more slowly on the sugar than the other family. When qA is positive, the other family grows faster on the acid than Enterobacteriaceae, while when qA is negative, the other family grows more slowly on the acid than Enterobacteriaceae. Each dot corresponds to a sugar-acid pair for a Enterobacteriaceae-other family pair (n = 24). The growth rate advantage of Enterobacteriaceae on sugars is significantly greater than the growth rate advantage of the other families on acids (i.e. qS > qA, mean of differences = 0.069, paired t-test, n = 24, p-value<0.0001). (D) Here we repeat the same simulation as shown in (B), this time using different combinations of qA and qS (0.05, 0.15, 0.25, 0.35, 0.45, 0.55, 0.65, 0.75, 0.85, 0.95). Heatmap shows the mean dominance level (δ) for different combinations of qA and qS. When δ < 0, the sugar dominates (purple); when δ > 0, the acid dominates (orange).
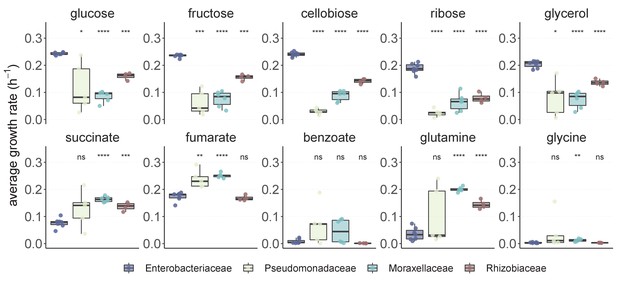
Enterobacteriaceae generally have a strong growth advantage in sugars.
Twenty-two strains belonging to the four dominant families, namely Enterobacteriaceae (7), Pseudomonadaceae (5), Moraxellaceae (6), and Rhizobiaceae (4) were isolated from the self-assembled communities and their growth rate on the 10 carbon sources was measured (Materials and methods, Supplementary file 1b). The average growth rate is measured as the mean cell divisions from 0.5 hr to 16 hr of growth (three or four replicates each) (Materials and methods). Thus, this approach takes into account both lag and growth rate, two growth traits that are important in determining the competitive ability of a strain. We use the first 16 hr of growth rather than a longer time window to better assess growth rate on the supplied nutrient and avoid potential artifacts from growth on secretions. Significance level (p-value) is measured by comparing the average growth rate between Enterobacteriaceae (reference) and each other family (paired t-test, ****p<0.0001; ***p<0.001; **p<0.01; *p<0.1).
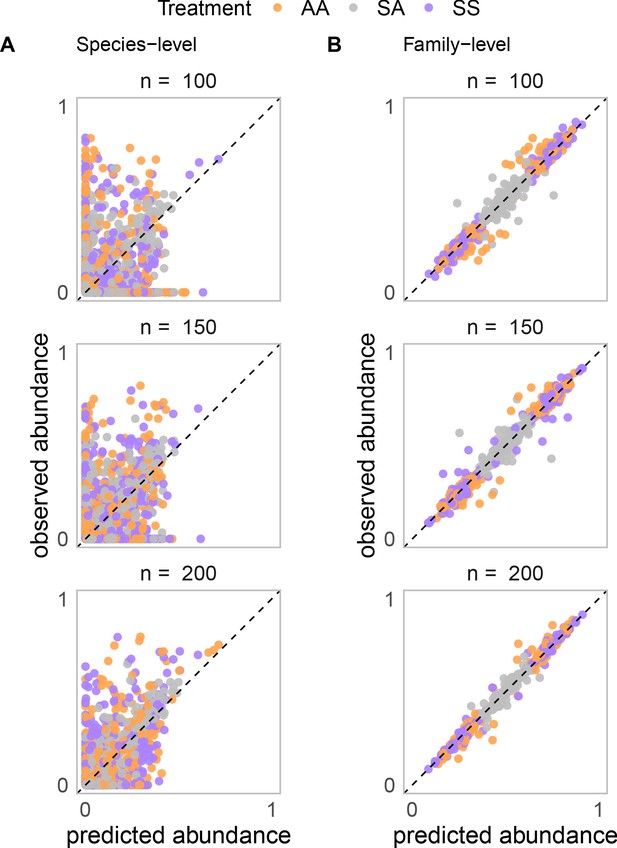
Stochastic colonization has no qualitative effect on the pattern of additivity found using a Microbial Consumer Resource Model.
Relative abundance of each species (A) or species grouped by family (B) in simulated communities grown in a mixture of nutrients plotted against the predicted relative abundance from simulated communities grown in single nutrients assuming that nutrients act independently (Materials and methods). Communities are colonized with n species, randomly sampled from a regional pool of 200 species, while keeping the number of families constant. When n = 200, all species are sampled. Decreasing n reduces the initial species variability of the community and also introduces stochastic colonization through the random sampling of the regional species pool. For each n, the result of 100 simulations for communities grown in three carbon source pairs is shown (1 SS pair, 1 AA pair, and 1 SA pair).
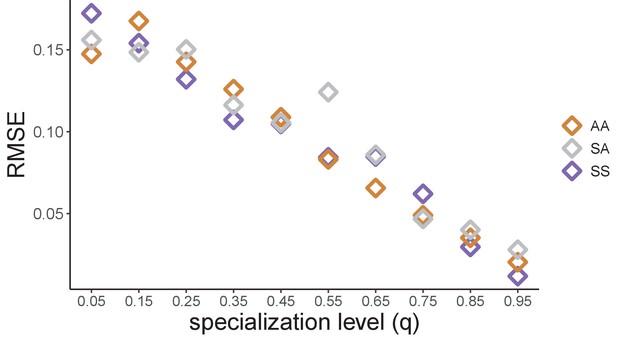
The predictive accuracy of the null model decreases with lower levels of resource specialization.
In Figure 4B (right-hand panel), we performed consumer-resource model simulations and plotted the observed and predicted relative abundance of each family in 300 communities grown on a different pair of nutrients (100 AA, 100 SS, and 100 SA). In those simulations, each family is specialized on its preferred nutrient (qS = qA = 0.9). Here, we repeat these exact simulations for different degrees of resource specialization (qS = qA ∈ [0.05, 0.15, 0.25, 0.35, 0.45, 0.55, 0.65, 0.75, 0.85, 0.95]). When qS = qA = 0.05, the two families are largely unspecialized whereas when qS = qA = 0.95 both families are largely specialized (Figure 4—figure supplement 4). The predictive accuracy of the null model is quantified using the RMSE calculated across n = 100 communities.
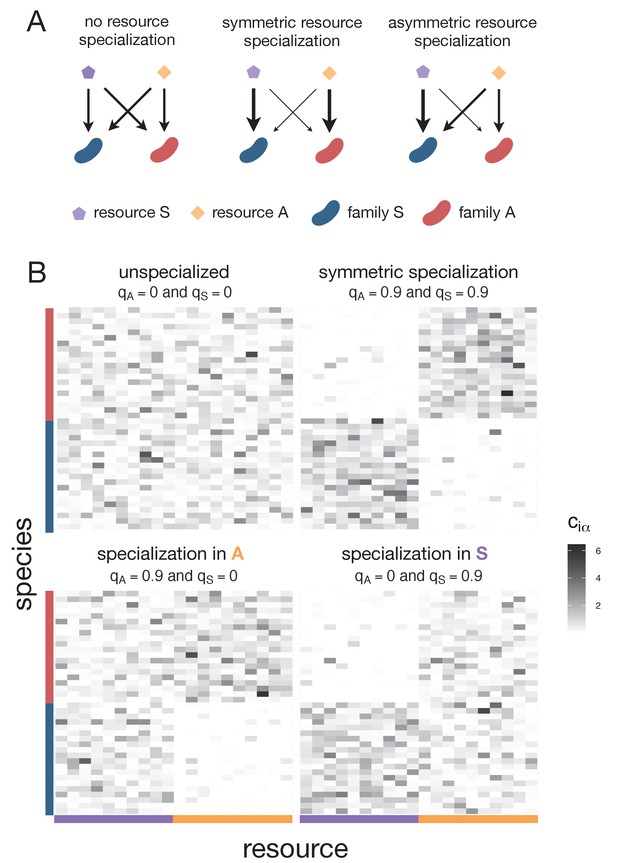
Consumption matrices for different patterns of nutrient preference between families used in the consumer-resource model simulations.
(A) The schematics illustrate different scenarios of nutrient preference for two families (FS and FA) and two resource classes (RS and RA). Without resource specialization, FS and FA have equal access to RS and RA. With symmetric specialization, each family prefers its own resource class with the same strength. With asymmetric specialization, one family (FS) has better access to its own resource class (RS) relative to that of the other family (FA) on its own resource class (RA). (B) Consumption matrices for two families (FA and FS coloured in orange and purple respectively) in two resource classes (RS and RA). Each row corresponds to a different species (for visualization purposes we show 30 species per family) and each column corresponds to a different nutrient within a resource class (10 nutrients per resource class). The value ciα corresponds to the uptake rate of species i in nutrient α. Four nutrient preference patterns are illustrated. Without family-level nutrient preference (specialization), species from the two families have equal access to resources in A (qA = 0) and resources in S (qS = 0). When each family has a strong and quantitatively similar preference for its own resource class, there is symmetric specialization (qA = qS > 0). When family FA has a strong preference for its own resource class A but both families have equal access to resources in S, then qA > 0 and qS = 0. When family FS has a strong preference for its own resource class S but both families have equal access to resources in A, then qS > 0 and qA = 0.
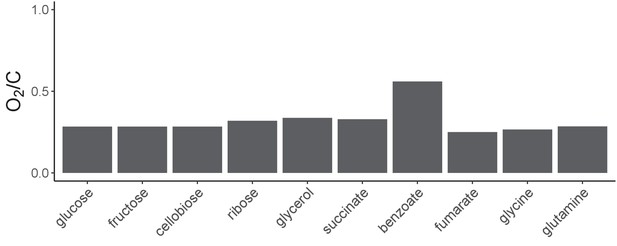
Oxygen demands are similar across the different carbon sources.
We carried out flux-balance analysis using a genome-scale metabolic model of E. coli to determine if different carbon sources are likely to exhibit large differences in oxygen demand (Materials and methods). On the y-axis, we plot the oxygen exchange flux/carbon flux for each of the 10 carbon sources used in this study.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical compound, drug | D-Glucose | VWR | 0188–500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | D-Cellobiose | Sigma | 22150–10G | |
| Chemical compound, drug | D-Fructose | Acros Organics | 161355000 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | D-Ribose | Acros Organics | AC132361000 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glycerol (80%, w/v) | Teknova | G8797 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium Succinate hexahydrate | Alfa Aesar | 419A3 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium hydrogen fumarate | Alfa Aesar | B24683 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium benzoate | Alfa Aesar | A15946 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | L-Glutamine 200 mM (29.23 mg/mL) | Sigma | G7513-100ML | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glycine | Sigma | G7126-100G | |
| Software, algorithm | R | R Development Core Team, 2017. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.r-project.org/ | RRID:SCR_001905 | R version 3.4.3 |
| Software, algorithm | DADA2 | Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods. 2016;13: 581–583. | Version 1.6.0 | |
| Software, algorithm | Community simulator | Marsland R, Cui W, Goldford J, Mehta P. The Community Simulator: A Python package for microbial ecology. PLoS One. 2020;15: e0230430. | Version 1.0 | |
| Software, algorithm | COBRApy | Ebrahim A, Lerman JA, Palsson BO, Hyduke DR. COBRApy: COnstraints-Based Reconstruction and Analysis for Python. BMC Syst Biol. 2013;7: 74. | RRID:SCR_012096 | Version 0.17.0 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Supplementary tables.
(a) Carbon sources used in this study. (b) Taxonomy of strains used in the growth rate assay and community they were isolated from.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/65948/elife-65948-supp1-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/65948/elife-65948-transrepform-v1.docx