Rampant tooth loss across 200 million years of frog evolution
Figures
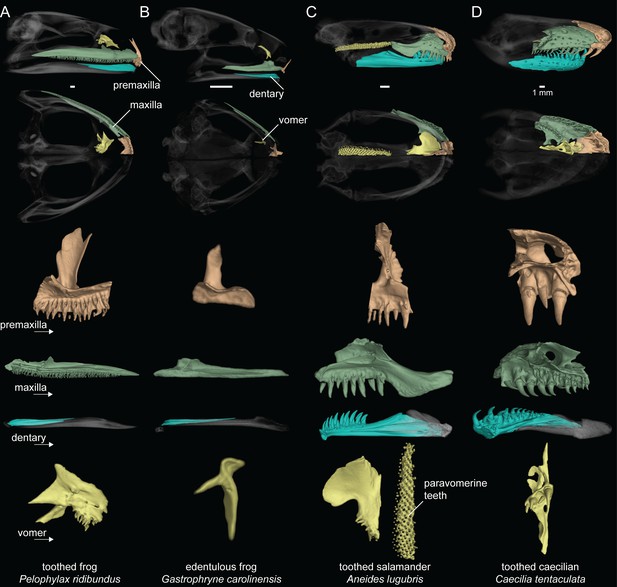
Dental diversity of amphibians.
(A) Toothed frog, Pelophylax ridibundus (CAS:Herp:217695), (B) edentulous frog, Gastrophryne carolinensis (UF:Herp:110645), (C) toothed salamander, Aneides lugubris (MVZ:Herp:249828), (D) toothed caecilian, Caecilia tentaculata (KU:Kuh:175441). Skulls in lateral and ventral views: dentigerous cranial elements are colored and the remainder of the skull is semi-transparent. Isolated premaxilla (orange), maxilla (green), dentary (blue), and vomer (yellow) in lingual views. Teeth are present on all colored elements except the dentary in P. ridibundus and those of G. carolinensis. Scale bars = 1 mm.
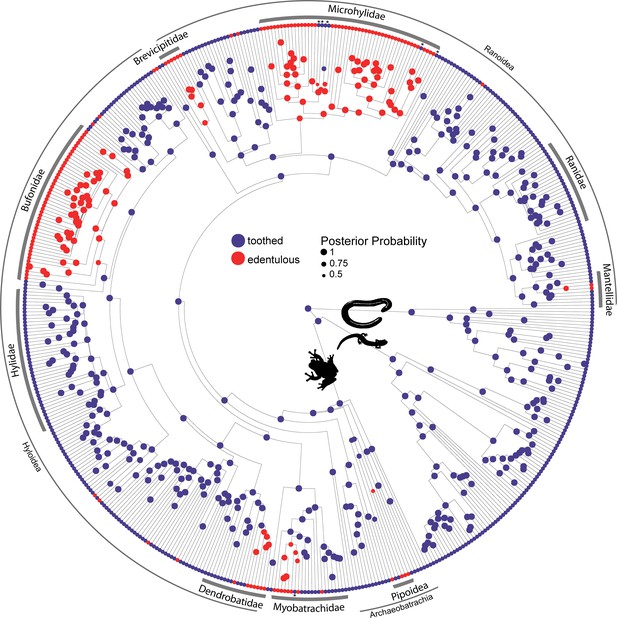
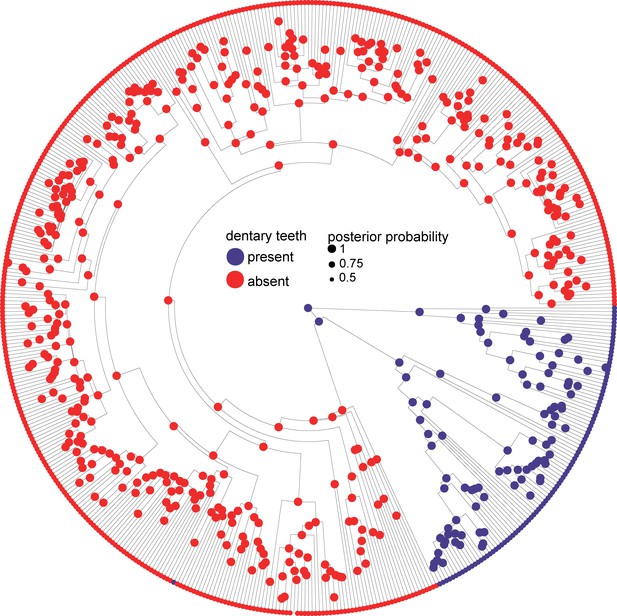
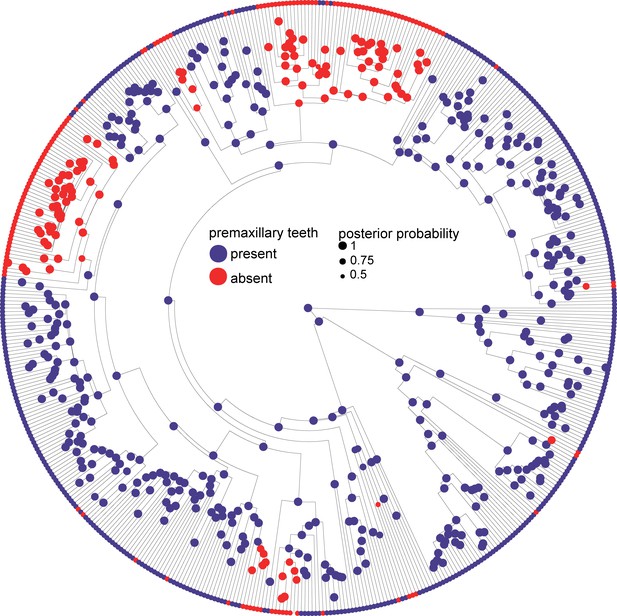
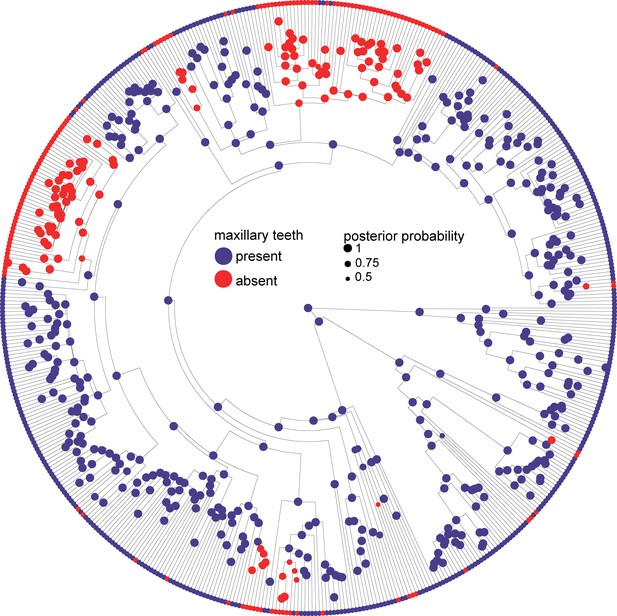
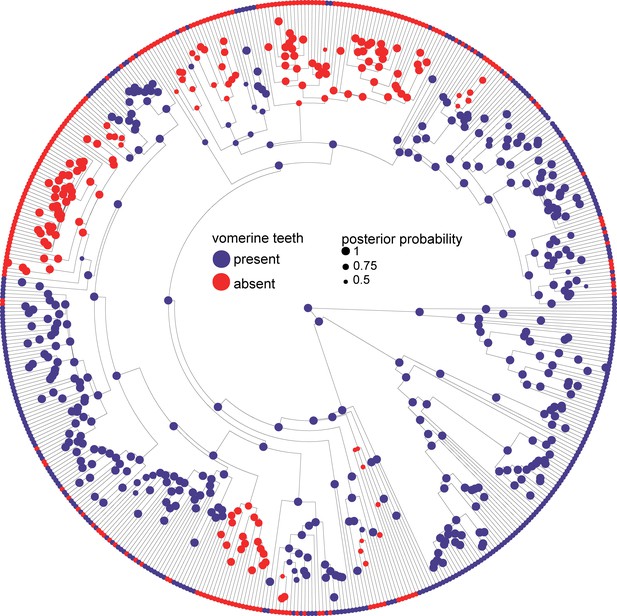
Phylogeny of 524 amphibians depicting the evolution of dentition.
Node point color corresponds to Bayesian model-averaged ancestral states of dentition: blue = toothed; red = edentulous. The size of each node point represents the posterior probability of the most probable ancestral state. Tip point colors correspond to dentition states for all species. Asterisks indicate inferred reversals. For species tip labels display Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Corresponding data are provided in Dataset S1.
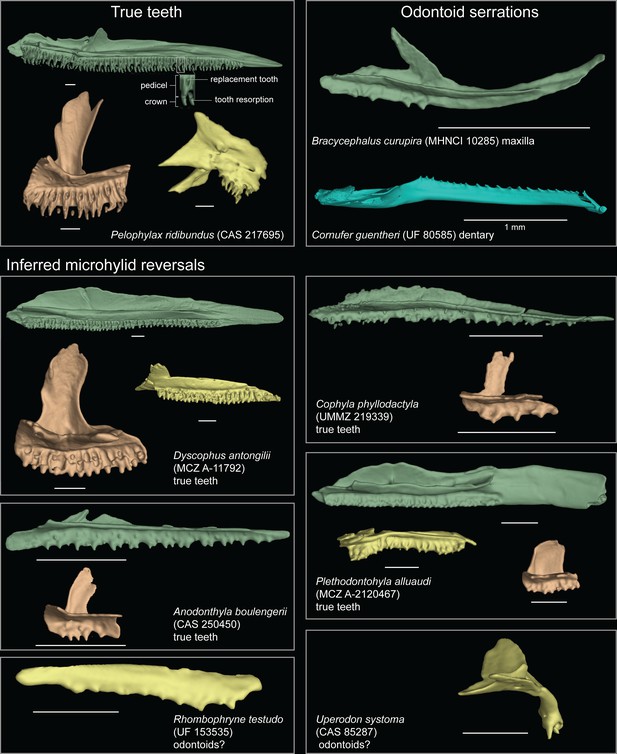
Comparison of true teeth, odontoids, and dental anatomy of the microhylid taxa with inferred evolutionary reversals.
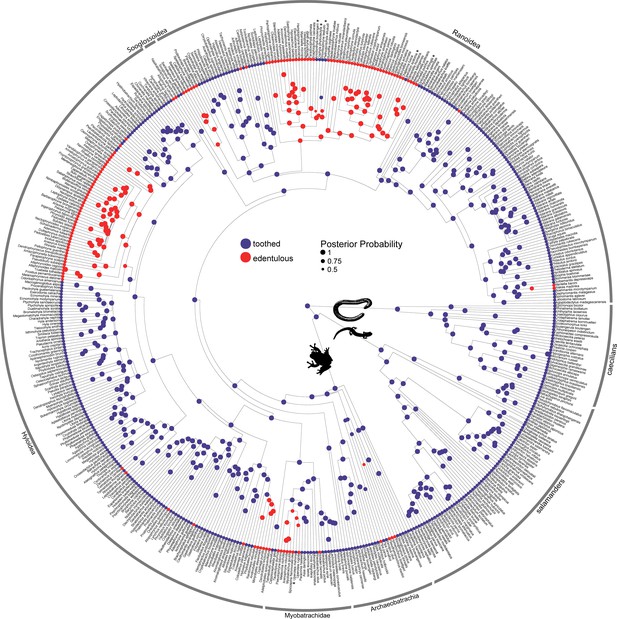
Phylogeny of 524 amphibians depicting the evolution of dentition with species tip labels.
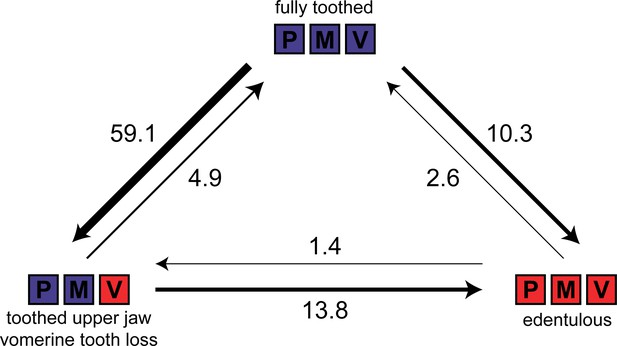
Estimated number of evolutionary transitions among three dental states (fully toothed, toothed upper jaw with vomerine tooth loss, edentulous) inferred from stochastic character mapping using 1000 replicates.
P = premaxilla, M = maxilla, V = vomer. Width of arrows corresponds to estimated number of changes.
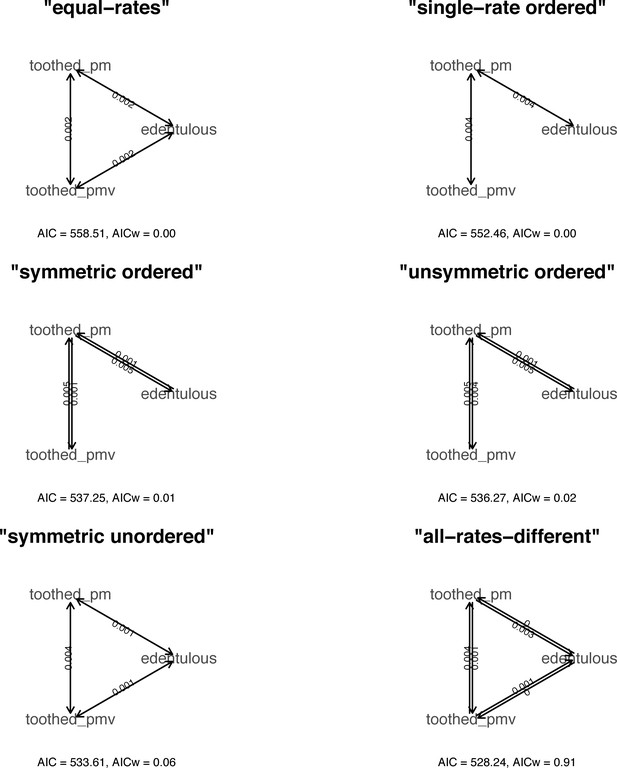
Discrete character evolution model comparisons for three dental states (fully toothed, toothed upper jaw with vomerine tooth loss, edentulous) in 425 species of frogs.
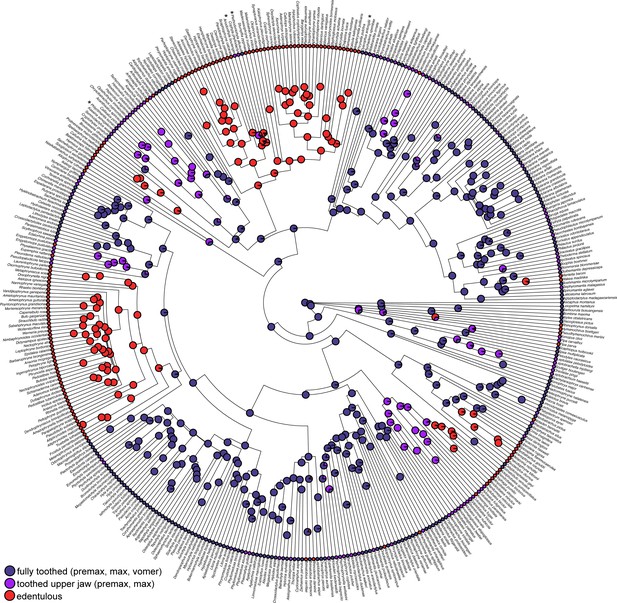
Ancestral reconstruction of three dental character states (fully toothed, toothed upper jaw with vomerine tooth loss, edentulous) using stochastic character mapping in 425 species of frogs.
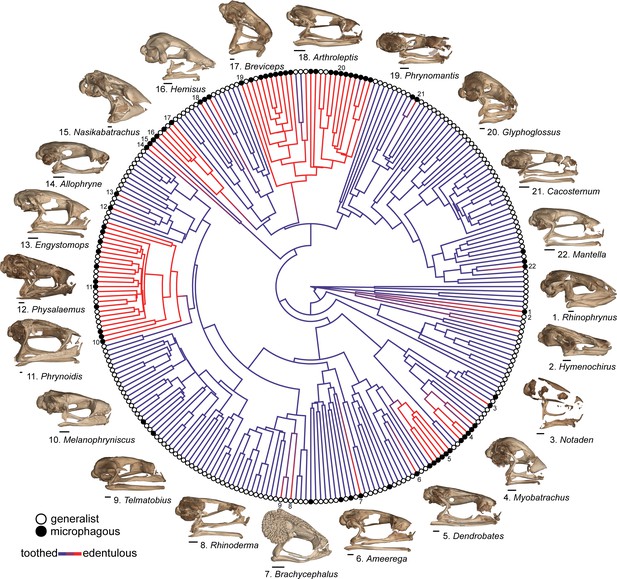
Phylogeny of 268 frog species with a stochastic character map of dentition states and distribution of generalist and microphagous diet states (tip point colors) illustrating the correlated evolution of edentulism and microphagy.
Diversity of edentulous frog skulls: 1. Rhinophrynus dorsalis (CAS:Herp:71766), 2. Hymenochirus boettgeri (CAS:Herp:253587), 3. Notaden bennetti (CAS:Herp:78115), 4. Myobatrachus gouldii (MCZ:Herp:A-139543), 5. Dendrobates tinctorius (YPM:VZ:HERA 016010), 6. Ameerega trivittata (UF:Herp:107200), 7. Brachycephalus ephippium (UF:Herp:72725), 8. Rhinoderma darwinii (UF:Herp:62022), 9. Telmatobius carrillae (UF:Herp:39717), 10. Melanophryniscus stelzneri (UF:Herp:63183), 11. Phrynoidis asper (USNM:Amphibians and Reptiles:586870), 12. Physalaemus nattereri (MCZ:Herp:A30113), 13. Engystomops pustulosus (CAS:SUA:21892), 14. Allophryne ruthveni (KU:Kuh:166716), 15. Nasikabatrachus sahadryensis (CES:F:203), 16. Hemisus guineensis (CAS:Herp:258533), 17. Breviceps gibbosus (AMNH:Herpetology:3053), 18. Arthroleptis schubotzi (CAS:Herp:201762), 19. Phrynomantis annectens (UF:Herp:187273), 20. Glyphoglossus molossus (CAS:Herp:243121), 21. Cacosternum namaquense (CAS:Herp:156975), 22. Mantella baroni (CAS:Herp:250387). Scale bars = 1 mm. For species tip labels display Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Corresponding data are provided in Dataset S2.
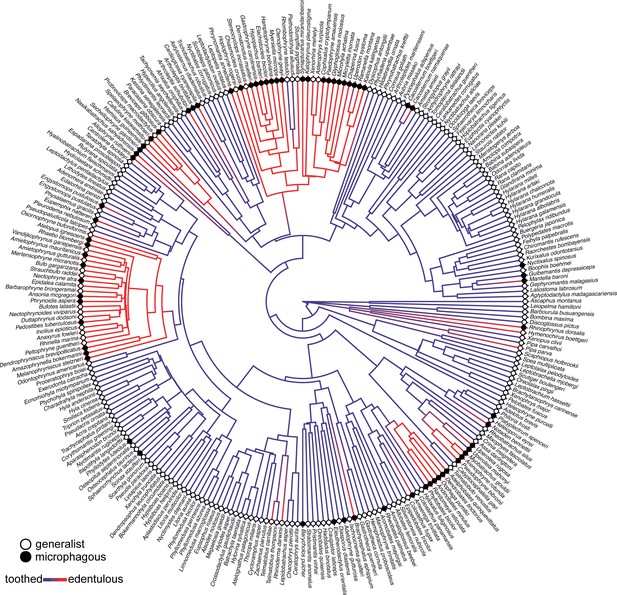
Phylogeny of 268 frog species with a stochastic character map of dentition and the distribution of diet states with species tip labels.
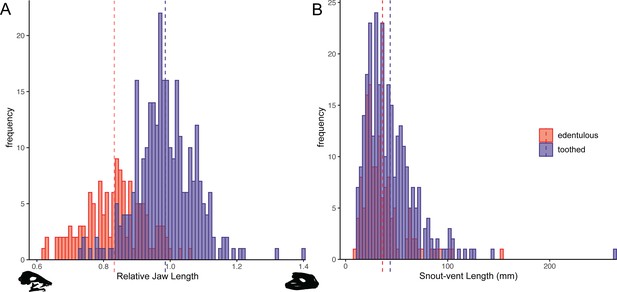
Histograms of relative jaw length (mandible length divided by skull length; A) and body size (snout–vent length [SVL]; B) in 423 frog species plotted by dentition states (blue = toothed; red = edentulous).
A phylogenetic correlation was identified between tooth loss and shortened lower jaws. There is no association between edentulism and body size. Left skull silhouette is Hemisus guineensis (CAS:Herp:258533) and right skull is Lepidobatrachus asper (UF:Herp:12347). Corresponding trait data are provided in Dataset S3.