Structural variability and concerted motions of the T cell receptor – CD3 complex
Figures
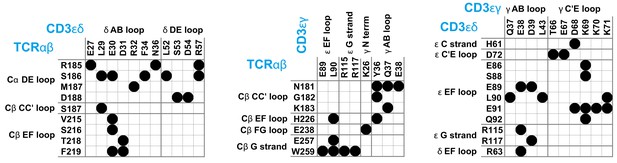
Maps of residue-residue contacts (black disks) between the EC domains of the protein dimers TCRαβ, CD3εδ, and CD3εγ in the cryo-EM structure of the T cell receptor – CD3 complex (Dong et al., 2019).
Here, two residues are taken to be in contact if the minimum distance between non-hydrogen atoms of the residues is smaller than 0.45 nm. The loops and strands of the membrane-proximal constant domains Cα and Cβ of the proteins TCRα and TCRβ and of the EC domains of CD3ε, CD3γ, and CD3δ are labeled according to the standard convention for immunoglobulin-like domains (Garcia et al., 1996; Wang et al., 1998; Sun et al., 2004).
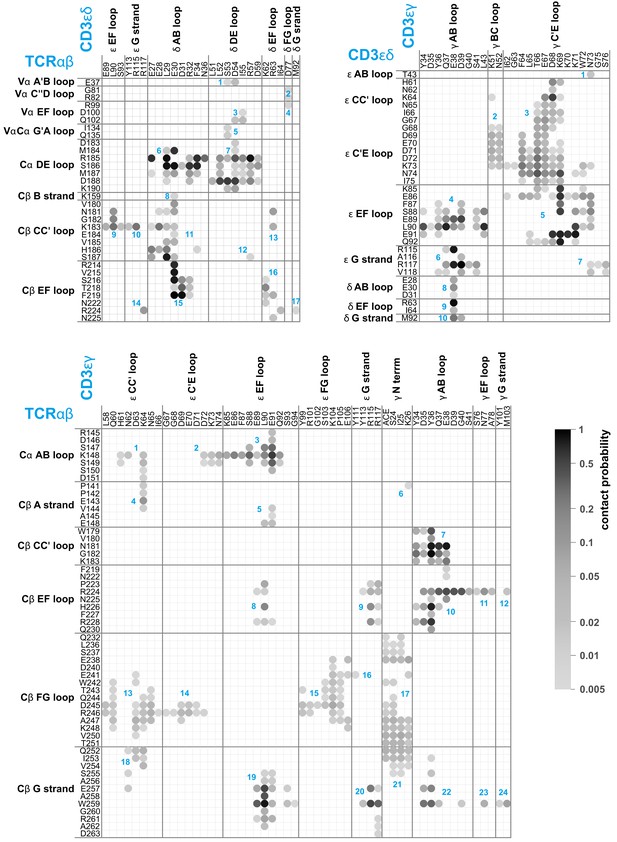
Averaged maps of contacts between the EC domains of TCRαβ, CD3εδ, and CD3εγ in the MD simulation trajectories.
The shading of the contact disks indicates the contact probability, that is the fraction of simulation structures in which the contact is present. The contact analysis is based on 120 × 50 = 6000 structures extracted at intervals of 10 ns from the second halves of the 120 μs-long trajectories, which reflect an equilibrated ensemble of simulation conformations (see Materials and methods) and are available at the Edmond Open Research Data Repository (Pandey and Weikl, 2021). For clarity, only contacts with a contact probability larger than 0.5% are represented. As in Figure 1, two residues are taken to be in contact in a simulation structure if the minimum distance between non-hydrogen atoms of the residues is smaller than 0.45 nm. The contacts occur in clusters with numbers labeled in blue.

Spearman correlation cofficients of the contact clusters in the contact maps of Figure 2.
The Spearman correlation coefficient assesses monotonic relations that can be linear or nonlinear and is calculated here for the numbers of contacts between non-hydrogen atoms of each cluster in the 6000 simulation frames of the contact analysis.
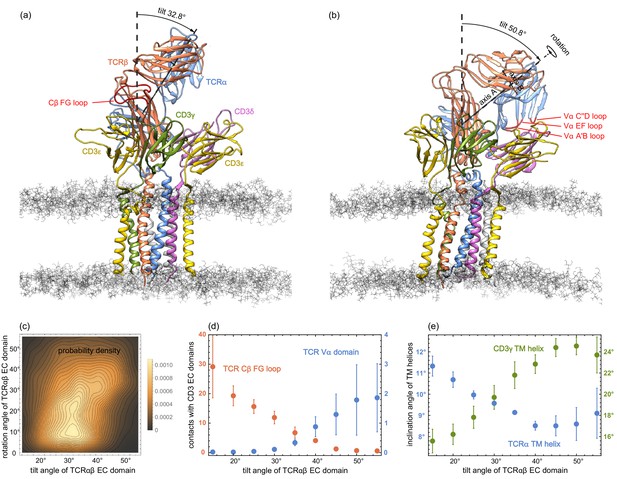
(a) and (b) MD conformations of the TCR – CD3 complex with different tilt angles of the TCRαβ ECdomain relative to the membrane normal.
The rotation angles of the TCRαβ ECdomain are 12.8° and 42.9° in the conformations (a) and (b), respectively. (c) Two-dimensional probability density function for the tilt angle and rotation angle of the 6000 equilibrated MD conformations from the 120 trajectories. (d) Numbers of residue-residue contacts with CD3 EC domains for the Cβ FG loop and the Vα domain versus tilt angle. (e) Inclination angle of the TM helices in the TCRα and CD3γ chain relative to the membrane normal as a function of the tilt angle of the TCRαβ ECdomain. The errors in (d) and (e) have been estimated as error of the mean of averages obtained for five independent subsets of the MD conformations.

Numbers of residue-residue contacts of TCR Cα and Cβ loops and strands in interaction with CD3s versus tilt angle of the TCRαβ EC domain.

Inclination angles of TM helices relative to the membrane normal as a function of the tilt angle of the TCRαβ ECdomain.

(a) Force-free tilt-angle distribution of the TCRαβ EC domain obtained from our simulations (blue data points) and tilt-angle distributions under transversal forces pN and 5 pN acting on the TCR-MHC complex, estimated from the force-free distribution; (b) local membrane thickness around the TM domain of the TCR – CD3 complex as a function of the tilt angle of the TCRαβ ECdomain.
The errors of the force-free tilt-angle distribution in (a) have been estimated as error of the mean of distributions obtained for 10 independent subsets of the MD conformations. The errors for the distributions under transversal force result from error propagation. The errors in (b) have been estimated as error of the mean of averages obtained for five independent subsets of the MD conformations.

Tilt and rotation angle of the TCRαβ EC domain along the three exemplary trajectory segments shown in Figure 3—videos 1, 2 and 3.
Tilt and rotation angle of the TCRαβ EC domain along the three trajectory segments shown in Figure 3—videos 1, 2 and 3. Along these trajectory segments, the tilt angle increases from around 20° to values above 50°. In Figure 3—video 1, 2, the rotation angle increases with the title angle, which allows contacts of the three loops A’B, C”D, and EF in the variable region Vα of TCRα (shown in red in the videos) and the chain of CD3εδ. In Figure 3—video 3, in contrast, the rotation angle does not increase with increasing tilt of the TCRαβ EC domain. Figure 3—video 1 shows MD trajectory 36 from 0.05 to 0.4 μs, Figure 3—video 2 shows MD trajectory 95 from 0.1 to 0.5 μs, and Figure 3—video 3 shows MD trajectory 12 from 0.05 to 0.75 μs.
Movie of trajectory segment 1.
Movie of trajectory segment 2.
Movie of trajectory segment 3.
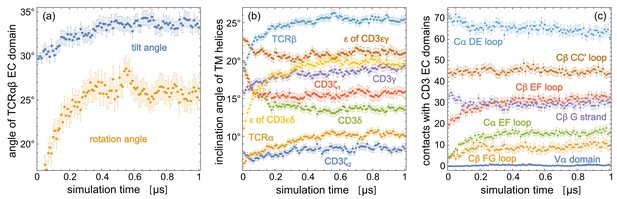
Time-dependent trajectory averages for (a) the tilt angle and rotation angle of the TCRαβ EC domain, (b) the inclination angles of the TM helices of the eight protein chains relative to the membrane normal, (c) the number of contacts of structural elements in the TCR constant domains Cα and Cβ and of the variable domain Vα with the two CD3 EC domains.
Each data point is an average over the simulation structures of the 120 trajectories at the indicated time point, with error bars representing the error of the mean for these 120 structures. The structural elements of Cα and Cβ are defined in Figure 2.

Time-dependent trajectory averages for (a) the angle between the axes A and B of the TCRαβ EC domain and (b) minimal Cα-atom root-mean-square deviations (RSMDs) of the TCRαβ, CD3εγ, and CD3εδ EC domains as well as the transmembrane (TM) domain relative to the cryo-EM structure of the T cell receptor – CD3 complex (Dong et al., 2019).
Time-dependent trajectory averages for (a) the angle between the axes A and B of the TCRαβ EC domain and (b) minimal Cα-atom root-mean-square deviations (RSMDs) of the TCRαβ, CD3εγ, and CD3εδ EC domains as well as the transmembrane (TM) domain relative to the cryo-EM structure of the T cell receptor – CD3 complex (Dong et al., 2019). Each data point is an average over the simulation structures of the 120 trajectories at the indicated time point, with error bars representing the error of the mean for these 120 structures. Axis A of the TCRαβ EC domain connects the centres of mass of Cαβ and Vαβ, where Cαβ is the dimer of the constant domains Cα and Cβ, and Vαβ is the dimer of the variable domains Vα and Vβ. Axis B connects the centres of mass of the variable domains Vα and Vβ (see 3(b) for illustration). The EC domains here are taken to span the residues V26 to C227 of TCRα, residues G22 to C264 of TCRβ, residues Q33 to V118 of CD3ε, residues F22 to M92 of CD3δ, and residues S24 to M103 of CD3γ.





