Histone H3 clipping is a novel signature of human neutrophil extracellular traps
Figures
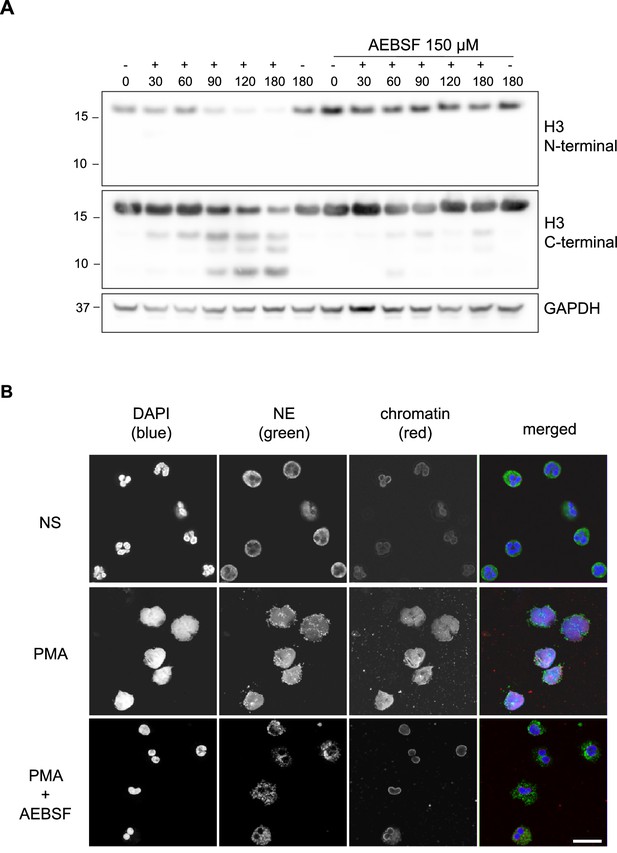
PMA-induced Histone H3 cleavage occurs in the N-terminal domain and is prevented by serine protease inhibition.
(A) Neutrophils were preincubated with the serine protease inhibitor AEBSF for 30 min in microcentrifuge tubes and then stimulated with PMA as indicated in the figure. Lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with N- and C-terminal antibodies to H3. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Blots representative of three independent experiments. (B) Immunofluorescent confocal microscopy of NET formation. Neutrophils were seeded on coverslips and preincubated with AEBSF before stimulation with PMA (50 nM) as indicated in the figure. At 150 min the cells were fixed and stained for neutrophil elastase (NE), chromatin (using a H2A-H2B-DNA antibody PL2.3) and DNA (DAPI [4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole]). NS: non-stimulated. Images were taken using at 63 x (Plan Apochromat, glycerol, numerical aperture 1.30) and the scale bar is 20 µm. Images are representative of three independent experiments. Source data is found in Figure 1—source data 1.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Time course of H3 cleavage and inhibition by AEBSF.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig1-data1-v2.zip
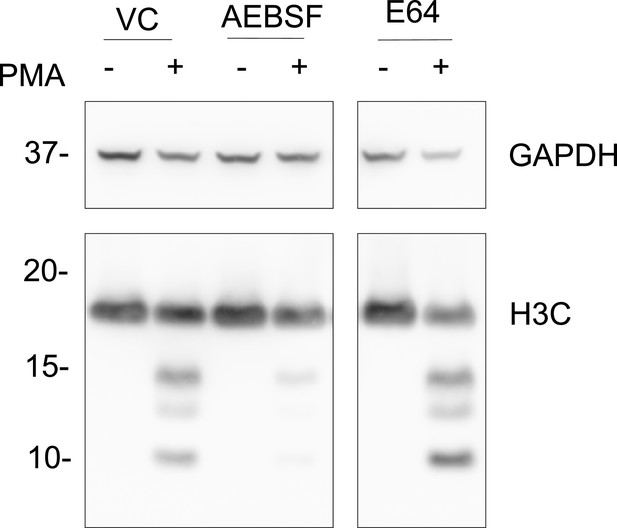
Cysteine protease inhibition by E64 does not inhibit histone H3 cleavage.
Neutrophils were preincubated with the cysteine protease inhibitor E64 (10 µM) or serine protease inhibitor AEBSF (150 µm) for 30 min and then stimulated with or without PMA 50 nM for 120 min. Lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-H3 C-terminal. GAPDH was used as a loading control. VC - vehicle control. Blot is representative of three independent experiments. Source data is found in Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Cysteine protease inhibition does not inhibit Histone H3 cleavage.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
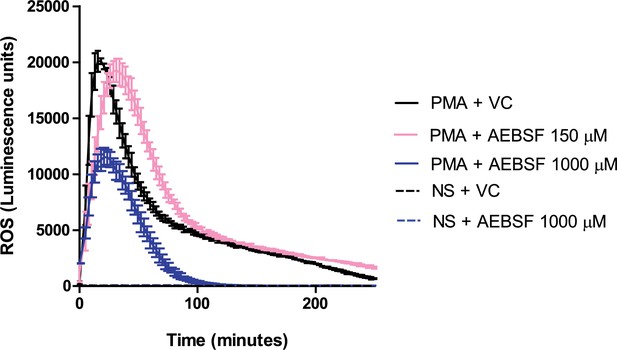
AEBSF does not inhibit ROS production.
Neutrophils were preincubated with AEBSF at the specified concentrations for 30 min before stimulation as indicated. ROS production was assessed using a luminol-HRP assay. Representative trace of three independent experiments. VC – vehicle control; NS – non stimulated (PBS only). Source data can be found in Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1
AEBSF does not inhibit the ROS burst.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig1-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
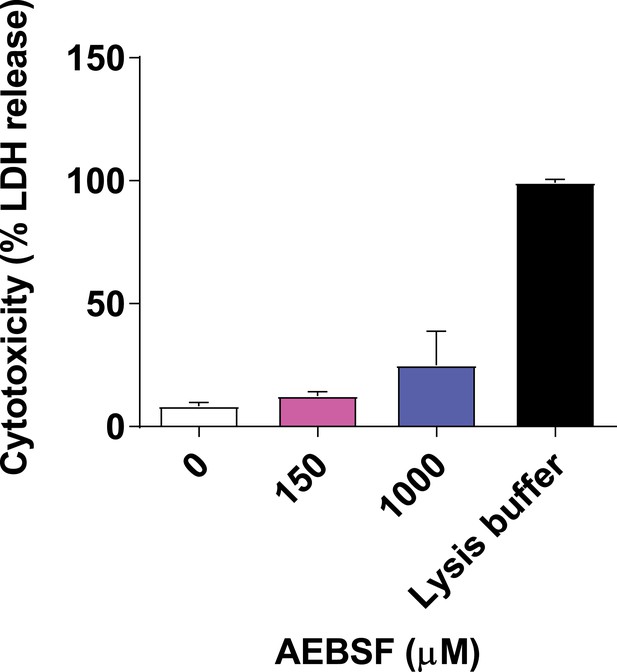
AEBSF is not cytotoxic.
Neutrophils were incubated with AEBSF at the indicated concentration and cytotoxicity was measured by LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) release where 100% lysis was achieved by adding 0.1% (w/v) Triton X-100. Samples were measured at 490 nm and normalised to 100% lysis. Graph represents the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Source data can be found in Figure 1—figure supplement 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 3—source data 1
AEBSF is not cytotoxic.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig1-figsupp3-data1-v2.xlsx
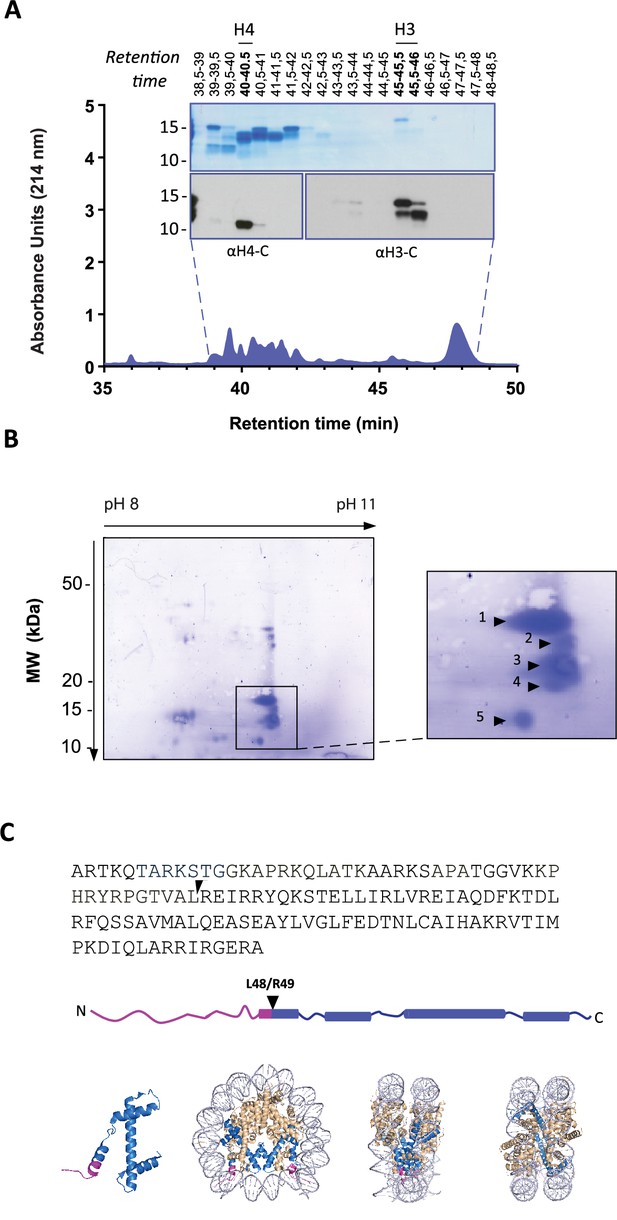
Identification of histone H3 cleavage sites in NET formation.
(A) Representative RP-HPLC chromatogram of acid extracted histones from NETs and corresponding 1D-SDS-PAGE and immunoblots to identify H3 and H4 containing fractions. Histone enriched supernatants were prepared from neutrophils stimulated with PMA for 90 min. Purification and subsequent 2D-electrophoresis (2D-E) was repeated three times with independent donors. Source data is found in Figure 2—source data 1 and Figure 2—source data 2. (B) Representative Coomassie stained blot of pooled H3 fractions separated by 2D-E. Inset is a zoom of all spots (1-5) identified as histone H3 by mass spectrometry. Other proteins identified are listed in Figure 2—figure supplement 2 and Table 1. Source data is found in Figure 2—source data 3. (C) Schematic representation of the cleavage site of the truncated H3 product in both the linear sequence of H3 and in the nucleosomal context. H3 is represented in blue and the pink tail region and partial alpha helix represent the part of H3 that is removed. The nucleosome structure is adapted from PDB 2F8N (Chakravarthy and Luger, 2005).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Western blots and gels for histones H3 and H4 in RP-HPLC fractions.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig2-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 2
RP-HPLC absorbance curve.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig2-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 3
2D-E blots for Edman degradation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig2-data3-v2.zip
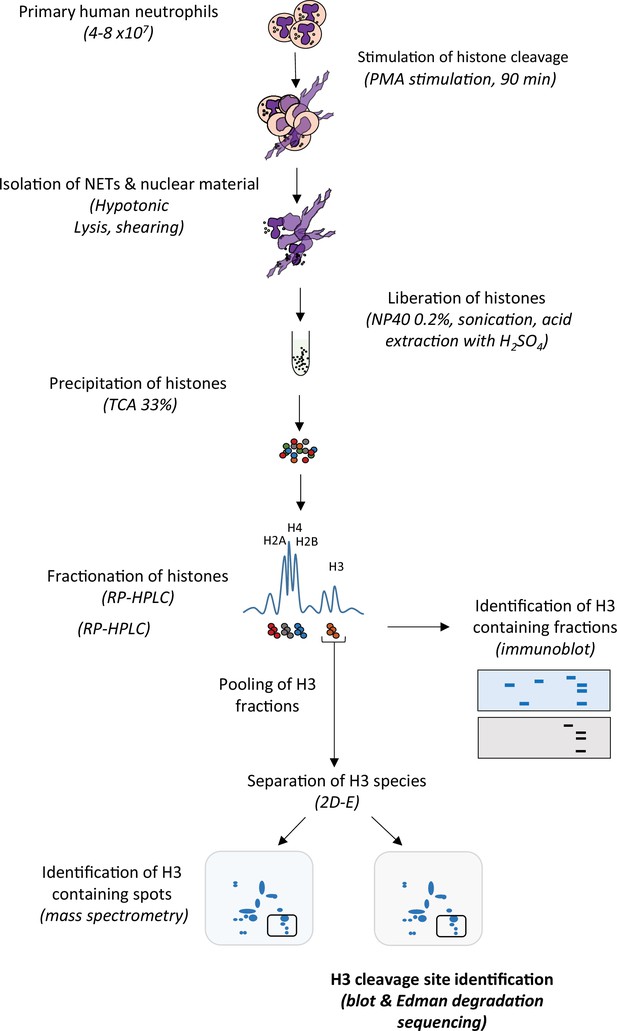
Schematic summary of extraction and identification of histone H3 cleavage sites in NETs.
Neutrophils were stimulated with PMA (50 nM) to induce histone cleavage and the samples were collected in the presence of proteases inhibitors. The nuclear material was isolated by hypotonic lysis and mild shearing. Nuclear material, including intact nuclei, was resuspended in dH2O plus protease inhibitors and NP40, and followed by gentle sonication to disrupt NETs. Histones were liberated from DNA by the addition of H2SO4 (0.4 M) and then precipitated with trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and solubilised in dH2O before separation by RP-HPLC on an acetonitrile gradient. Histone H3 containing fractions were identified by 1D-SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting for H3. H3 containing fractions were pooled, then divided in two, and both separated by 2D-electrophoresis (2D-E). Subsequent gels were either stained with Coomassie Blue and the spots prepared for identification by mass spectrometry, or transferred to PVDF membranes, stained with Coomassie Blue and subjected to N-terminal Edman degradation sequencing.
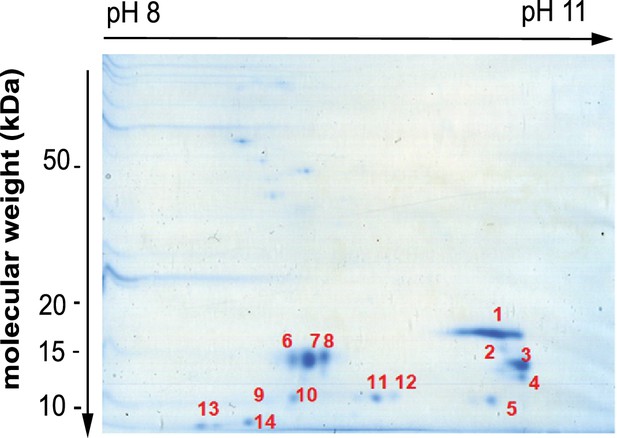
Separation of histone H3 by two dimensional electrophoresis.
Coomassie stained gel of pooled histone H3 containing fractions resolved by two dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE). All labelled spots were subsequently analysed by mass spectrometry to identify the proteins in Table 1. Source data is found in Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1
2DE-gel showing spots for identification by mass spectrometry.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig2-figsupp2-data1-v2.zip
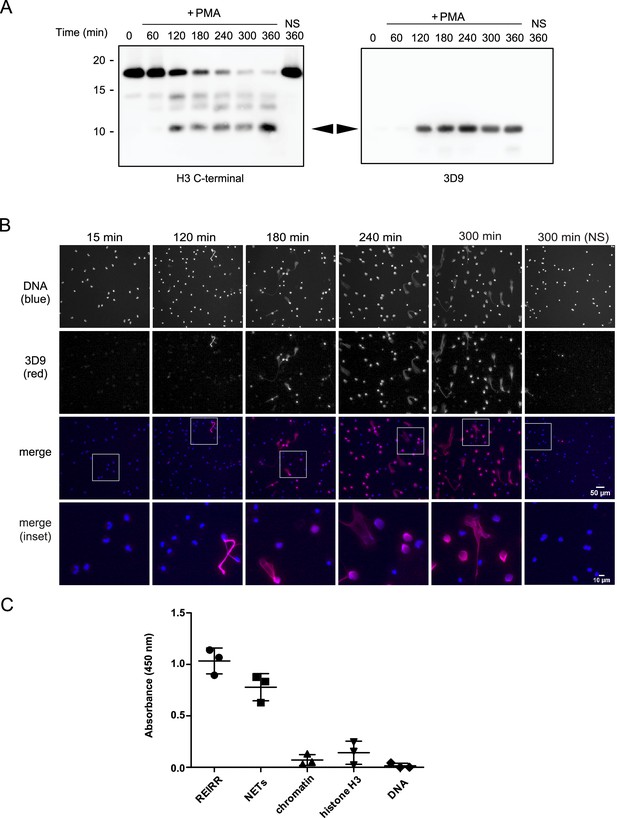
Screening and detection of cleaved H3 and NETs by 3D9.
(A) Immunoblots of lysates prepared from neutrophils stimulated with PMA (50 nM) for the times indicated in the figure. H3 C-terminal antibody was used as a control to detect all H3 forms while a single band (cleaved H3) was detected by the newly generated monoclonal antibody, 3D9. Source data can be found in Figure 3—source data 1. (B) Immunofluorescent microscopy of neutrophils stimulated with PMA and fixed at the indicated times. Samples were stained with Hoechst (DNA - blue) and 3D9 (with Alexafluor-568 conjugated secondary antibody - red). NS: non-stimulated. Images were taken on an upright fluorescent microscope at 20 x (Fluotar, numerical aperture 0.5). Scale bars – 50 µm (full field) and 10 µm (inset) (C) Direct ELISA for cleaved H3 in NETs, chromatin (A549 lung epithelial cells), recombinant histone H3 and DNA. Samples were serially diluted and immobilized on a high-affinity ELISA plate according to DNA content (for NETs, chromatin and DNA) or protein content (for recombinant histone H3) as determined by PicoGreen and bicinchoninic acid assays respectively. Starting concentration was 1 µg/ml DNA or protein. Cleaved H3 was detected using 3D9 (2 µg/ml) and HRP conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibody and reactions were developed using TMB (3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine) as a substrate. Data is presented for dilution 200 ng/ml. REIRR peptide control was coated at 20 ng/ml. Data represents mean ± SD of 3 experiments using independent NET donors. Source data can be found in Figure 3—source data 2.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Western blots with H3-terminal antibody and hybridoma clone 3D9.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig3-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Direct ELISA for cleaved H3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig3-data2-v2.xlsx
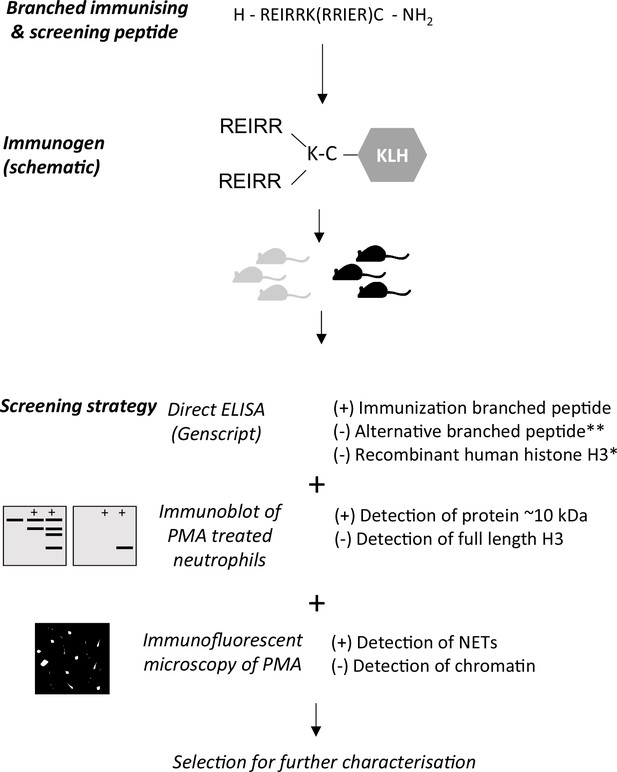
Outline of immunisation and screening strategy for antibody production.
After selection of animals for hybridoma production, clone supernatants were screened similarly. Positive selection (+), negative selection (-). *Performed in the hybridoma screen only. ** Alternative branched peptide used for screening.
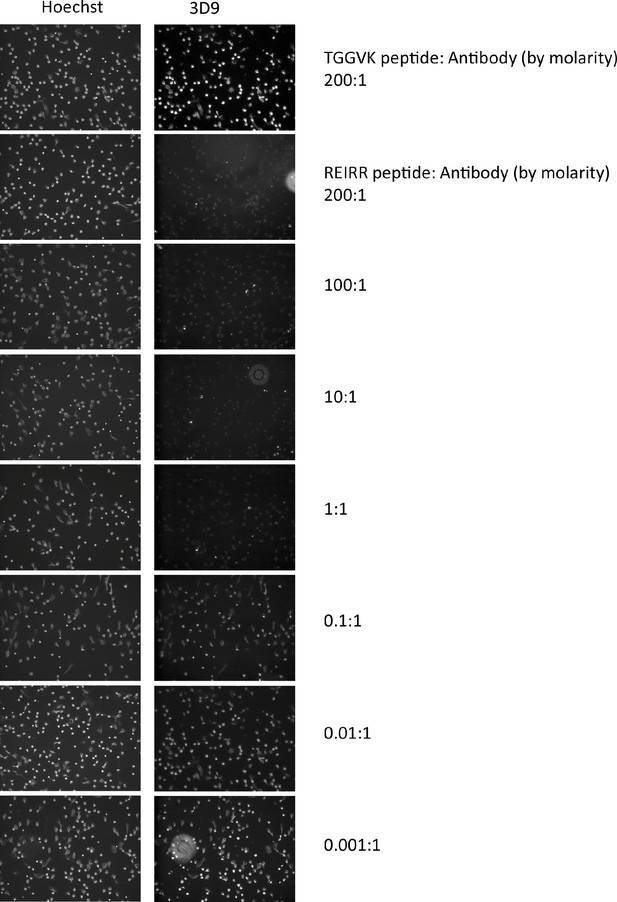
Peptide inhibition of 3D9 binding to NETs.
Immunofluorescent microscopy of neutrophils stimulated with PMA for 3 hr and stained with 3D9 (1 µg/ml) in the presence of competition and control peptides. Prior to staining, 3D9 was preincubated overnight at 4 °C with competition peptide (branched REIRR peptide) and negative control peptide (branched TGGVK peptide) at the indicated ratio of molar concentration. This experiment was performed twice with independent donors.
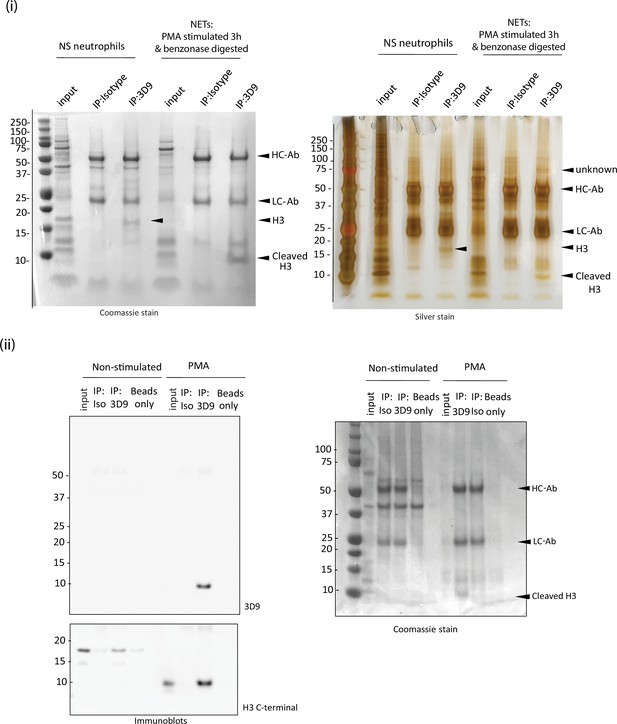
3D9 immunoprecipitation.
Neutrophils were seeded in 10 ml petri dishes and stimulated for 3 hr as indicated. Before total cell lysis and immunoprecipitation, NETs were digested with benzonase to liberate histones and octamers for antibody binding. (i) Coomassie stained gel of proteins immunoprecipitated by 3D9 or isotype control and the corresponding silver stained gel. The predicted cleaved H3 and intact H3 bands are indicated. HC-Ab: heavy chain of antibody, LC-Ab: light chain of antibody. (ii) Immunoblot for total H3 (C-terminal antibody) and cleaved H3 of the proteins immunoprecipitated by 3D9 or isotype control antibodies and Coomassie stained gel of samples run in parallel. Gels and blots are representative of three independent experiments. Source data can be found in Figure 3—figure supplement 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 3—source data 1
3D9 immunoprecipitation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig3-figsupp3-data1-v2.zip
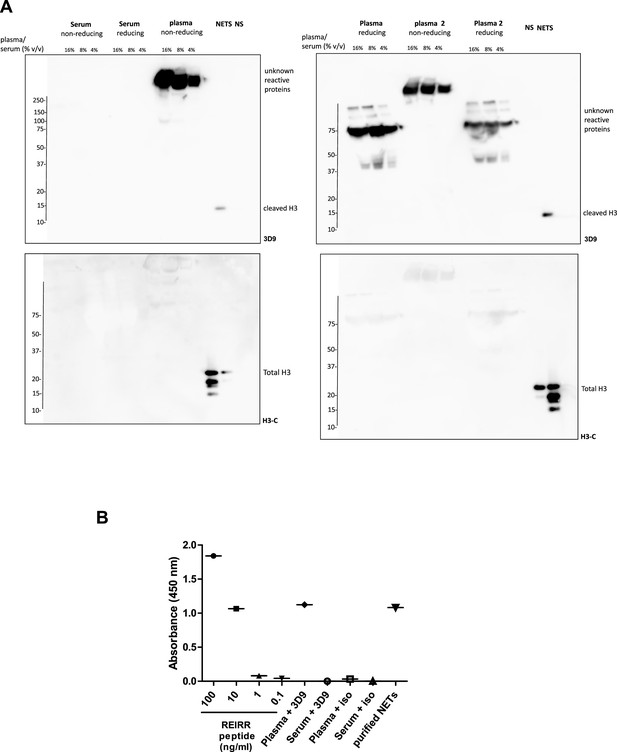
Detection of 3D9 cross reacting proteins from plasma and serum.
(A) Diluted serum (1 donor) and plasma (2 donors) were separated by SDS-PAGE in reducing and non reducing conditions (sample plus/minus 2 mM DTT). NETs and Non-stimulated neutrophils (NS) were used as positive and negative controls for immunoblotting with 3D9 and H3-C terminal antibodies (Ab). Source data can be found in Figure 3—figure supplement 4—source data 1 (B) 3D9 direct ELISA of plasma and serum. Plasma and serum were diluted 1 in 1000 and coated on an ELISA plate. Purified REIRR peptide (ng/ml) and purified NETs were used as positive controls. Samples were probed with 3D9 and or an isotype (iso) control antibody where indicated (n=1). Source data can be found in Figure 3—figure supplement 4—source data 2.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 4—source data 1
Detection of 3D9 cross-reacting proteins from plasma and serum by western blot.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig3-figsupp4-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 4—source data 2
Detection of 3D9 cross-reacting proteins from plasma and serum by ELISA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig3-figsupp4-data2-v2.xlsx
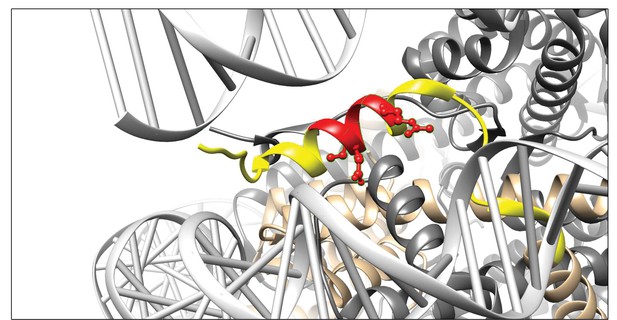
Visualisation of the 3D9 epitope in the nucleosome core complex.
Visualization of the putative core epitope for 3D9 mapped on to histone H3 ribbon structure. The observed core binding site of 3D9 to the peptide arrays was depicted on histone H3 (light brown) in the nucleosome complex structure (file 3AZG.pdb). Part of the peptide sequences used in the peptide arrays is coloured in yellow. The core epitope (R)EIRR is displayed in red, with the atoms of the critical residues (Glu51, Ile52, and Arg54) shown. Binding profiles of antibody to linear and helical arrays, in addition to amino acid replacement analysis are presented in Figure 4—figure supplements 1–3 and Table 3.
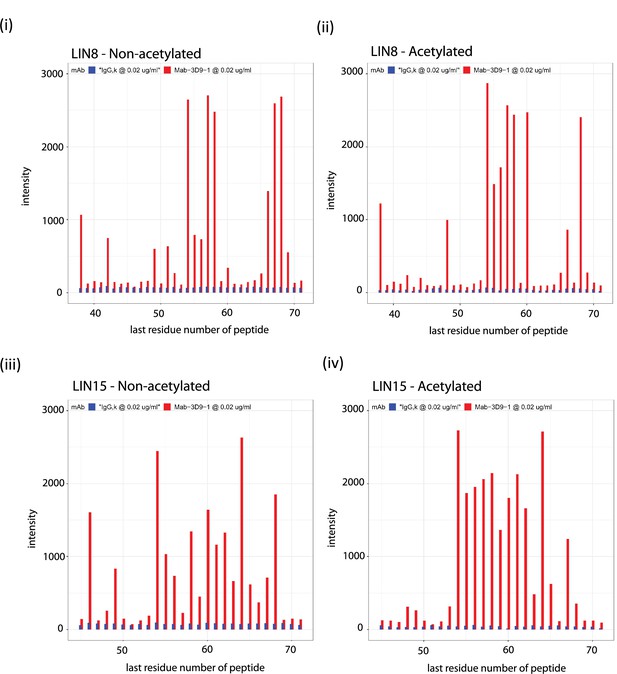
Binding profiles recorded for 3D9 on the linear peptide array.
Antibodies 3D9 (red) and isotype control IgG,k (blue) were incubated on arrays with overlapping linear 8-mer (LIN8 – [i, ii]) and 15-mer (LIN15 – [iii, iv]) peptides and binding measured by ELISA. Separate arrays were used with peptides that were acetylated (ii, iv) or non-acetylated (i, iii) at the N-terminus. Signal intensities are plotted on the y axis and positions of the last residues of a peptide with respect to the target sequence is on the x axis. The antibodies were tested with the arrays 3 or more times. Peptides are listed in the source data file. Source data can be found in Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Linear and helical peptide epitope mapping.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
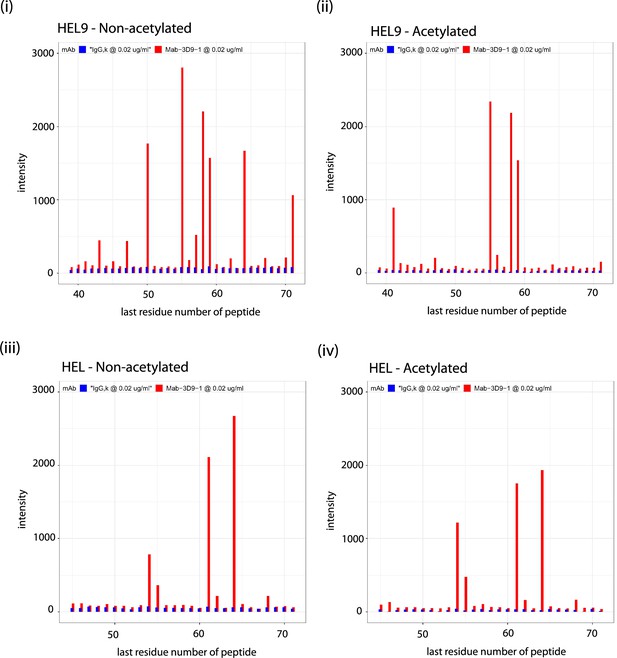
Binding profiles recorded for 3D9 on helical peptide mimics arrays.
Antibodies 3D9 (red) and isotype control IgG,k (blue) were incubated on arrays with overlapping helical 9-mer (HEL9; [i, ii]) and 15-mer (HEL; [iii, iv]) peptides. Separate arrays were used with peptides that were acetylated (ii, iv) or non-acetylated (i, iii) at the N-terminus. Signal intensities are plotted on the y axis and positions of the last residues of a peptide with respect to the target sequence is on the x axis. The antibodies were tested with the arrays 3 times or more times. Peptides are listed in the source data file. Source data can be found in Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Linear and helical peptide epitope mapping.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig4-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
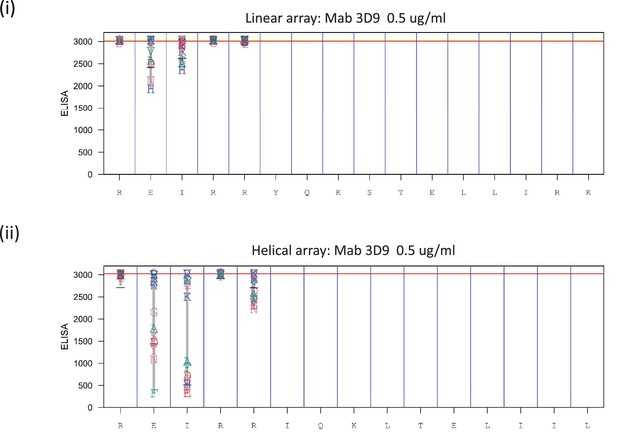
Fine epitope mapping by replacement analysis.
Linear (i) peptides were generated bearing single amino acid substitutions at each position of the native peptide sequence REIRRYQKSTELLIRK of histone H3. In addition, helical peptide mimics were made for the replacement analysis (ii). The peptides were left unacetylated to mimic the cleaved free N-terminus of the peptide. Antibody binding was analyzed at 0.5 μg/ml in PBST + 10% SQ (proprietary buffer). Values obtained for replacements are indicated by the letter code for each replacement residue plotted at the height of the recorded value at a given position. At the bottom of the plot the native sequence is indicated. The antibodies were tested with the arrays 3 times or more times. Red line indicates median value of the native peptide sequence data. Source data can be found in Figure 4—figure supplement 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Fine epitope mapping by replacement analysis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig4-figsupp3-data1-v2.xlsx
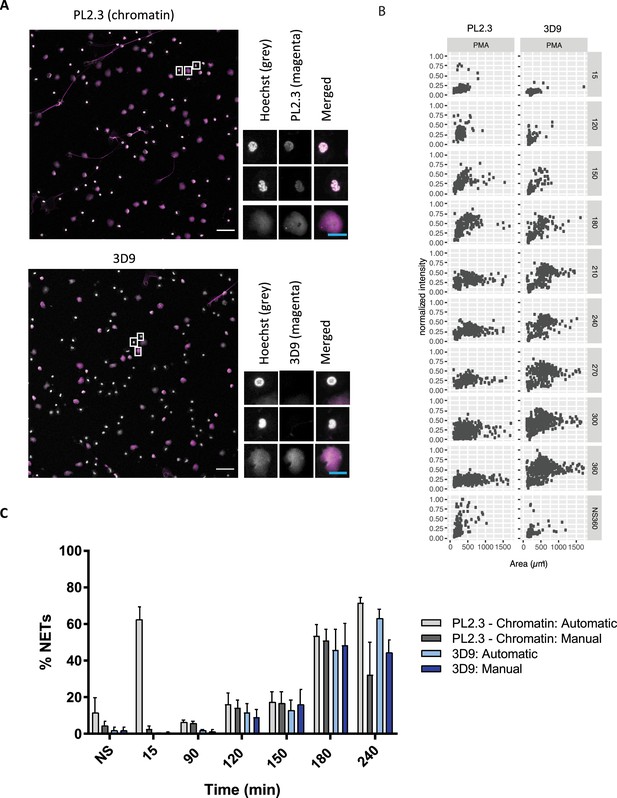
Comparison of NET quantification using an anti-chromatin antibody versus 3D9.
(A) Confocal immunofluorescent microscopy of neutrophils stimulated with PMA (180 min) and stained with Hoechst and anti-chromatin antibody (PL2.3) or 3D9. Insets represent selected cells examined at higher magnification (63 x, Plan Apochromat, glycerol, numerical aperture 1.30) and presented as split channels in grayscale or merged as per the total field of view (20 x, Plan Apochromat, glycerol, numerical aperture 0.75). White scale bar - 50 µm, cyan scale bar - 10 µm. Images are representative of 3 experiments (B) Comparison of the fluorescent distribution of PL2.3 versus 3D9 staining of PMA stimulated cells over time (6 h). Staining intensities were normalized over all images of the respective time course. NS:360: non-stimulated at 360 min. Analysis is performed on one data set that is representative of 3–4 independent time course experiments. Source data can be found in Figure 5—source data 1 and Figure 5—source data 2. (C) Comparison of NET quantification using manual or automatic thresholding and segmentation procedures for chromatin antibody (PL2.3) and cleaved H3 antibody (or 3D9). Manual thresholding excludes cells/NETs with a weak signal whereas automatic thresholding includes all objects irrespective of signal. Images for analysis were taken using a upright fluorescent microscope. Graph represents the mean ± standard deviation, where n=3–5. Source data can be found in Figure 5—source data 3.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Characterisation of PL2.3 NET staining.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig5-data1-v2.csv
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Characterisation of 3D9 NET staining.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig5-data2-v2.csv
-
Figure 5—source data 3
Comparison of NET quantification using manual or automatic thresholding and segmentation procedures for chromatin antibody and 3D9.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68283/elife-68283-fig5-data3-v2.xlsx
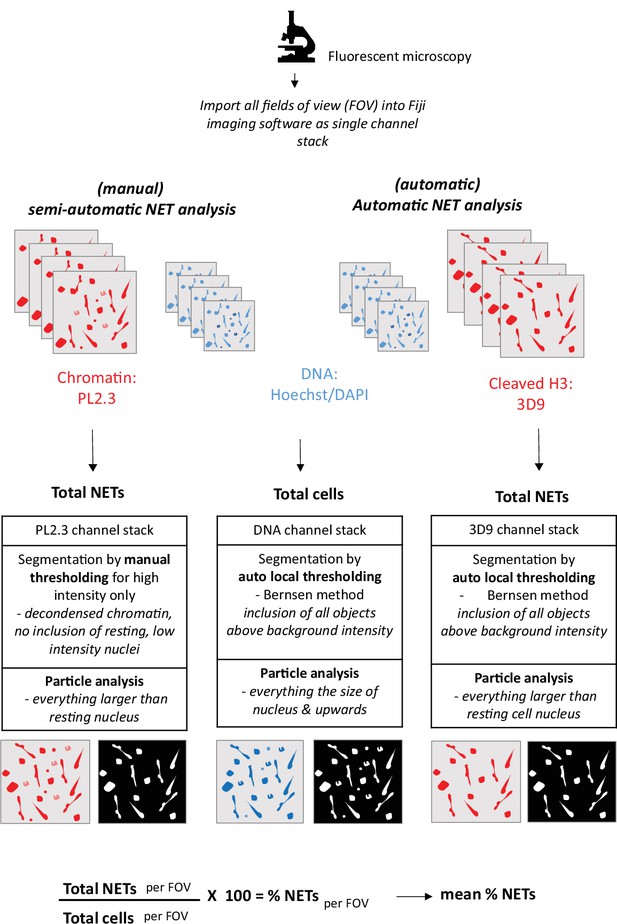
Workflow of NET analysis methods.
Schematic of imaging, segmentation, thresholding and particle analysis for both automatic and semi-automatic NET quantification.
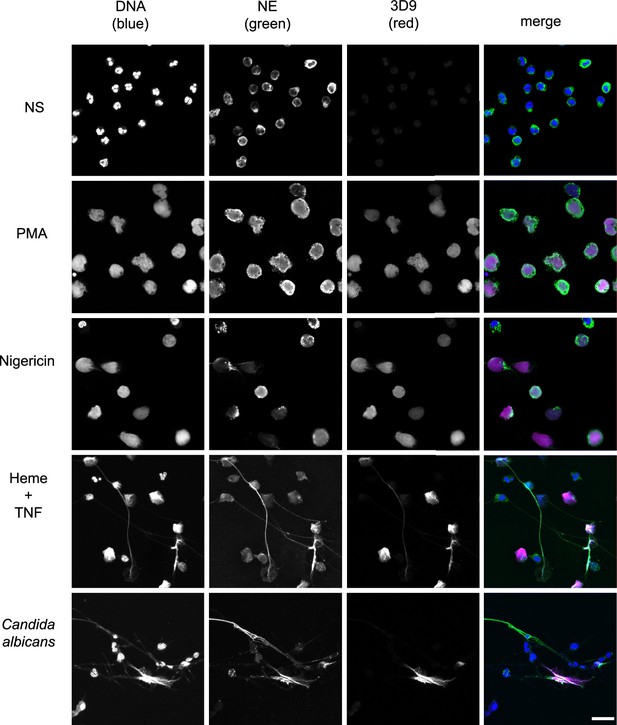
Detection by 3D9 of NETs from diverse stimuli.
Immunofluorescence microscopy of neutrophils left unstimulated (NS), stimulated with PMA (50 nM, 2.5 hr), nigericin (15 µM, 2.5 hr), TNF primed and then stimulated with heme (20 µM, 6 hr), and neutrophils co-cultured with Candida albicans hyphae (MOI 5) for 4 hr. Samples were stained with Hoechst, anti-neutrophil elastase (NE) and 3D9. Scale bar – 50 µm. Images were taken on a confocal microscope at 20 x (Plan Apochromat, glycerol, numerical aperture 0.75) and are representative of three experiments with independent donors. Scale bar - 20 µm.
Detection of NETs in mixed cell fractions.
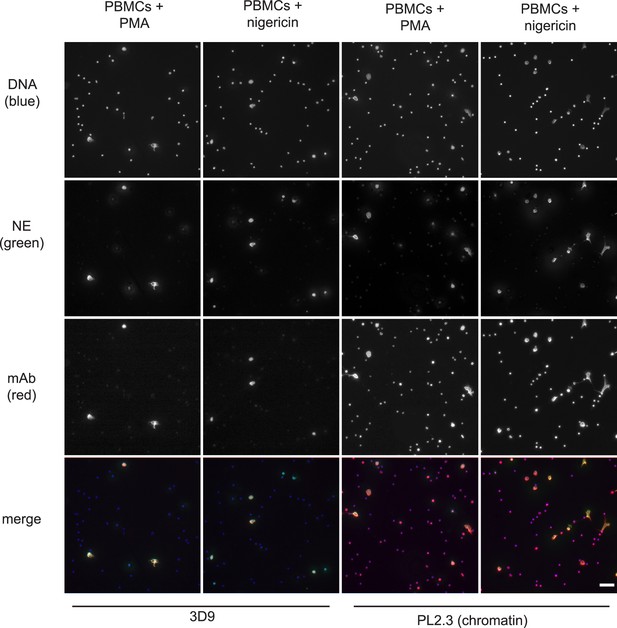
Immunofluorescence microscopy of non-purified peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) fractions treated with the NET stimuli, PMA (50 nM, 2.5 hr) or nigericin (15 µM, 2.5 hr), and then stained with Hoechst, anti-neutrophil elastase (NE) and 3D9 or PL2.3. Images were taken on an upright fluorescent microscope at ×20 magnification (Fluotar, numerical aperture 0.50). The selected images are representative of three independent experiments. Scale bar – 50 µm.
Comparison of 3D9 detection in response to apoptotic, necroptotic, and necrotic cell death stimuli.
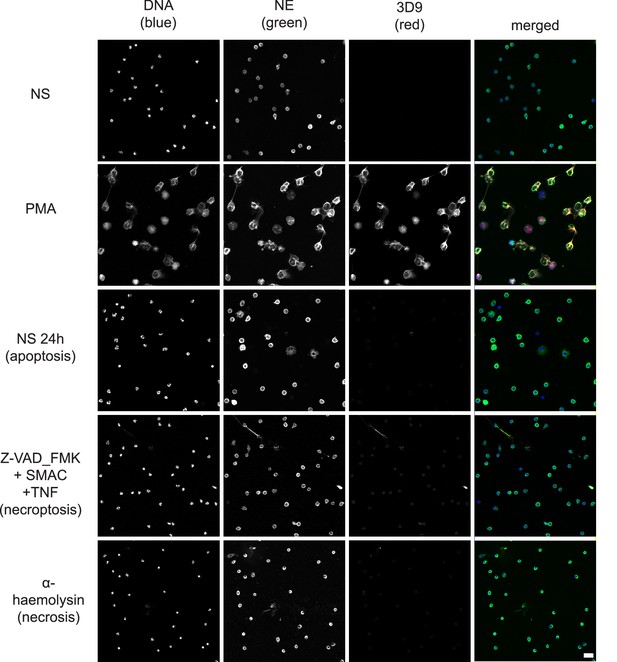
Confocal immunofluorescent microscopy of neutrophils stimulated with different cell death stimuli and subsequently stained with Hoechst, anti-neutrophil elastase (NE) and 3D9. NETs were induced with PMA (100 nM, 3 hr). Apoptosis was induced in resting neutrophils by incubation for 24 hr without stimulation overnight. Neutrophils were stimulated with Z-VAD-FMK (50 µM) plus SMAC mimetic (100 nM) plus TNF (50 ng/ml) for 6 hr to induce necroptosis. Necrosis was induced with the pore forming toxin α-haemolysin (25 µg/ml). Images were taken at 20 x (Plan Apochromat 20 x, numerical aperture 0.75) and are representative of three experiments. Scalebar 20 µm. A comparison was made with parallel samples stained with the chromatin antibody PL2.3 and are presented in Figure 8—figure supplement 1. Apoptotic samples were also stained for apoptotic markers and cleaved H3 (Figure 8—figure supplement 2).
Comparison of PL2.3 detection in response to apoptotic, necroptotic, and necrotic cell death stimuli.
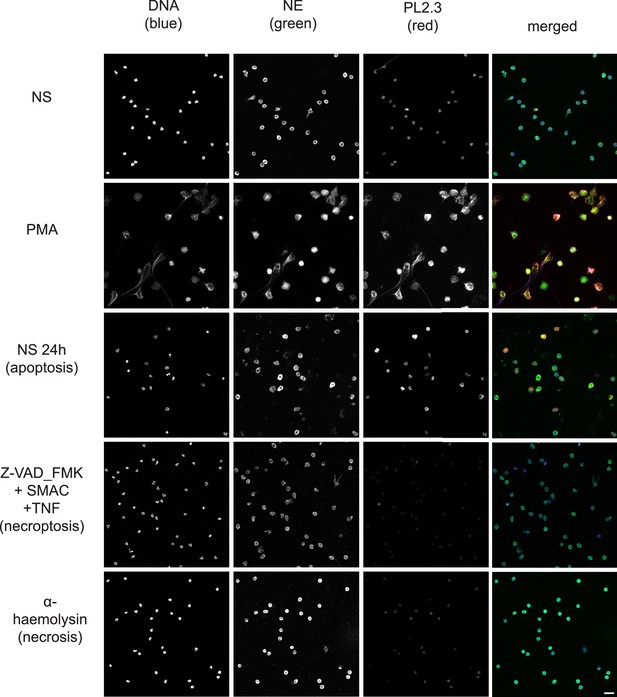
Confocal immunofluorescent microscopy of neutrophils stimulated with different cell death stimuli and subsequently stained with Hoechst, anti-neutrophil elastase (NE) and PL2.3. NETs were induced with PMA (100 nM, 3 hr). Apoptosis was induced in resting neutrophils by incubation for 24 hr without stimulation. Neutrophils were stimulated with Z-VAD-FMK (50 µM) plus SMAC mimetic (100 nM) plus TNF (50 ng/ml) for 6 hr to induce necroptosis. Necrosis was induced with the pore forming toxin α-haemolysin (25 µg/ml). Images were taken at 20 x (Plan Apochromat, numerical aperture 0.75) and are representative of 3 independent experiments. Scalebar 20 µm. A comparison was made with parallel samples stained with the cleaved histone antibody 3D9 and are presented in Figure 8.
Staining of primary human neutrophils for markers of apoptosis and NETs.
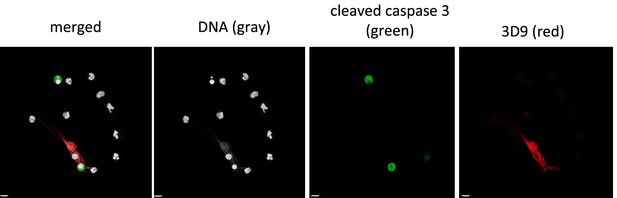
Primary neutrophils were purified from whole blood and left unstimulated to allow spontaneous apoptosis. Samples were fixed and stained for DNA (Hoechst), cleaved caspase 3 (green) and cleaved histone 3 (3D9 – red). Samples were imaged by confocal microscopy at 63 x (Plan Apochromat, numerical aperture 1.30). Scale bar 9 µm.
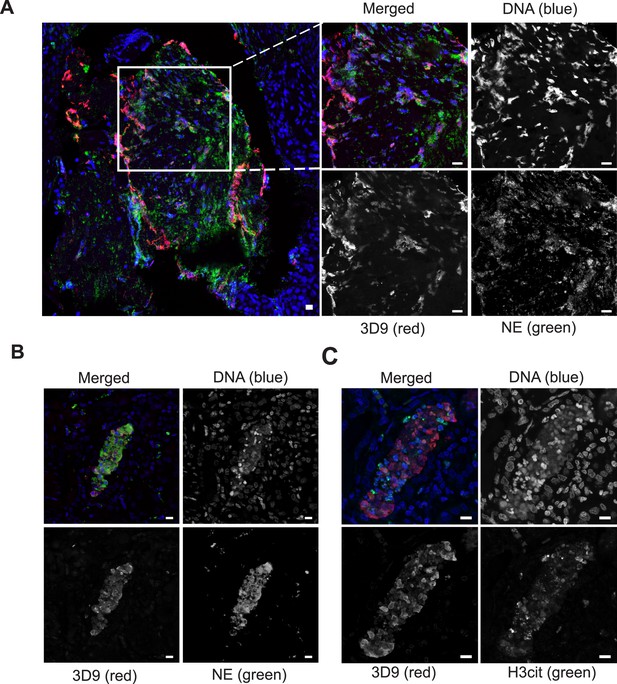
Detection of clipped histone 3 and NETs in human tissues.
Paraffin embedded sections were stained with Hoechst, anti-NE and 3D9 or H3cit antibodies and examined by confocal microscopy at ×63 magnification (Plan Apochromat, glycerol, numerical aperture 1.30). Scale bar - 10 µm (A) human tonsil, denoted ‘normal’ by commercial provider but showing infiltration of neutrophils demonstrating an inflammatory event. (B) & (C) human kidney, denoted ‘inflammed’ by commercial provider.
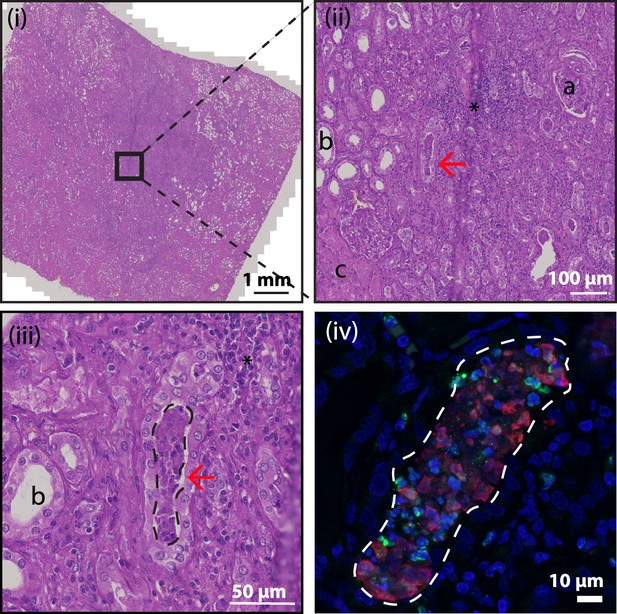
Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain of kidney section.
HE stained tissue overview of NETs represented in Figure 9B, C. Black box indicates area for further magnification in images (ii) and (iii). The red arrow indicates the location of the NET in the collecting duct. ‘a’ - glomerulus, ‘b’- tubule, ‘c’ - area of necrotic tubules and ‘*’ – area of infiltrating lymphocytes (inflammation). Dashed line in (iii) and (iv) indicates area of 3D9 (red) and H3cit (green) staining from Figure 9C.
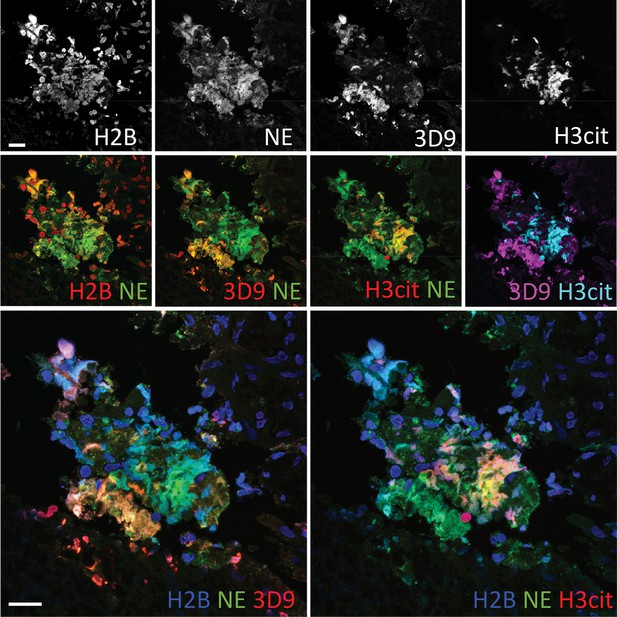
Comparison of Clipped H3, H3cit & H2B staining in the gallbladder from an appendicitis patient.
Paraffin embedded sections were stained with Hoechst, anti-NE and histone antibodies 3D9, H3cit and H2B and examined by confocal microscopy at ×63 magnification (Plan Apochromat, glycerol, numerical aperture 1.30). Scale bar – 20 µm.
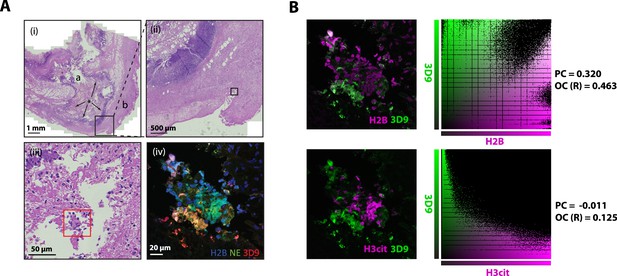
Hematoxylin & eosin (HE) stain of gallbladder and colocalization analysis.
(A) HE stained overview of gallbladder stained for NETs in Figure 10. Magnification increases from (i)-(iii) and boxes represent the field of view of the next image. Red box indicates the area imaged by fluorescent confocal microscopy in Figure 9 (iv). ’a’ – lumen; ‘b’ – serosa (exterior); ‘*’ - area of infiltrating lymphocytes (inflammation). (B) Colocalisation analysis of 3D9 staining versus H2B staining and 3D9 versus H3cit. Analysis was performed using Volocity software and both the image analysed and associated scatter plot of pixel intensities are presented. PC = Pearsons Coefficient and OC (R)=overlap coefficient (R).
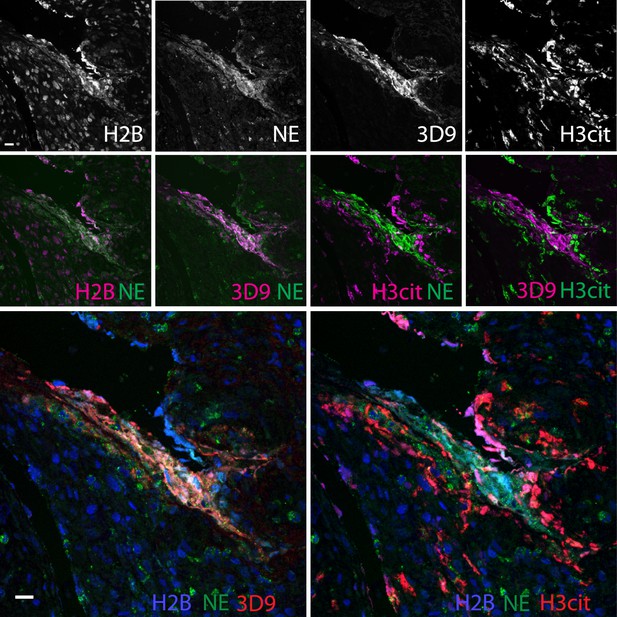
Comparison of Clipped H3, H3cit, and H2B staining in the appendix of an appendicitis patient.
Paraffin embedded sections were stained with Hoechst, anti-NE and 3D9 or H3cit antibodies and examined by confocal microscopy at ×63 magnification (Plan Apochromat, glycerol, numerical aperture 1.30). Scale bar - 20 µm.
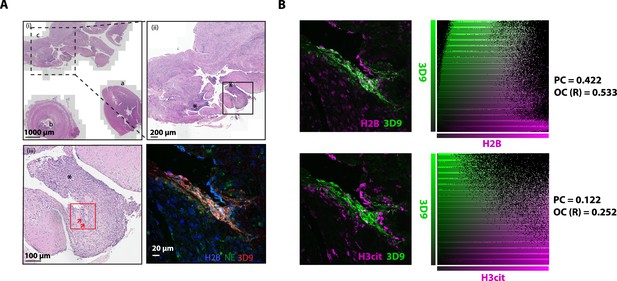
Hematoxylin and eosin stain of inflamed appendix and colocalization analysis.
(A) HE stained overview of appendix with appendicitis and peri-appendicitis stained for NETs in Figure 11. Magnification increases from (i)-(iii) and boxes represent the field of view of the next image. Red box indicates the area imaged by fluorescent confocal microscopy in Figure 11. NETs are indicated by arrows. a- appendix tip; b – lumen; c - associated inflamed tissue with peri-appendicitis. (B) Colocalisation analysis of 3D9 staining versus H2B staining and 3D9 versus H3cit. Analysis was performed using Volocity software and both the image analysed and associated scatter plot of pixel intensities are presented. PC = Pearsons Coefficient and OC (R)=overlap coefficient (R).
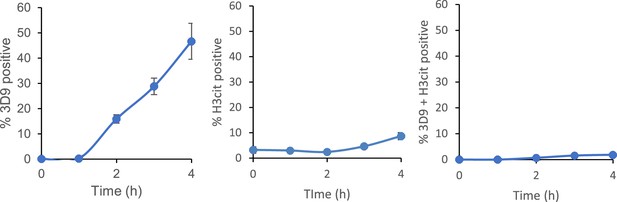
Time course of 3D9 and H3cit co-staining of primary human neutrophils stimulated with PMA.
Neutrophils were stimulated for 4 hr with PMA, fixed with paraformaldehyde and stained for cleaved H3R49 (3D9) and histone citrullination at R2, R8, and R17 (H3cit). Images were taken on an upright fluorescent microscope and quantified using Image J.
Tables
Mass spectrometry identification of proteins co-separating with histone H3 following RP-HPLC and 2-DE.
| Spot | score | accession no. | protein name | MW | pI | sequence coverage | Number of peptides |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 99 | P84243 | Histone H3.3* | 15318 | 11.27 | 25.7 | 8 |
| 2 | 133 | P84243 | Histone H3.3 | 15318 | 11.27 | 25 | 7 |
| 2 | 78 | P0C0S5 | Histone H2A.Z | 13545 | 10.58 | 14.1 | 4 |
| 3 | 140 | P84243 | Histone H3.3 | 15318 | 11.27 | 22.1 | 7 |
| 4 | 193 | P84243 | Histone H3.3 | 15318 | 11.27 | 27.2 | 8 |
| 5 | 198 | P84243 | Histone H3.3 | 15318 | 11.27 | 27.2 | 9 |
| 6 | 317 | P06702 | Protein S100-A9 | 13234 | 5.71 | 70.2 | 10 |
| 7 | 486 | P06702 | Protein S100-A9 | 13234 | 5.71 | 81.6 | 15 |
| 8 | 483 | P06702 | Protein S100-A9 | 13234 | 5.71 | 82.5 | 14 |
| 9 | 57 | P31949 | Protein S100-A11 | 11733 | 6.56 | 9.5 | 2 |
| 10 | 344 | P31949 | Protein S100-A11 | 11733 | 6.56 | 45.7 | 8 |
| 11 | 343 | P05109 | Protein S100-A8 | 10828 | 6.51 | 37.6 | 9 |
| 12 | 140 | P05109 | Protein S100-A8 | 10828 | 6.51 | 25.8 | 5 |
| 13 | 136 | P25815 | Protein S100-P | 10393 | 4.75 | 35.8 | 6 |
| 14 | 48 | P06703 | Protein S100-A6 | 10173 | 5.33 | 16.7 | 3 |
List of immunisation, screening, and competition peptides.
| Immunisation | H - REIRRK(RRIER)C - NH2 KLH conjugated |
| Screening | (+) H - REIRRK(RRIER)C - NH2 (-) H - AARKSK(SKRAA)C - NH2* |
| Validation | H - REIRRK(RRIER) - NH2 competition peptide H - TGGVKK(KVGGT) - NH2 negative control |
-
*
Alternative branched peptide used for screening.The N-terminal is represented by H (H2N) and the C-terminal is represented by NH2 (CONH2).
Summary of identified 3D9 binding regions in the peptide array.
| Sample | Type | Peak | Epitope candidate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D9-1 | LIN8 | 47–58 | REIRRYQK |
| VALREIRR | |||
| EIRRYQKS | |||
| 60–68 | LLIRKLP | ||
| ELLIRKLP | |||
| LIN8 - Ac | 47–60 | VALREIRR | |
| REIRRYQK | |||
| RRYQKSTE | |||
| EIRRYQKS | |||
| LREIRRYQ | |||
| 61–68 | LLIRKLPF | ||
| LIN15 | 40–64 | HRYRPGTVALREIRR | |
| REIRRYQKSTELLIR | |||
| TVALREIRRYQKSTE | |||
| 1–33 | RYQKSTELLIRKLPF | ||
| LIN15 - Ac | 12–44 | HRYRPGTVALREIRR | |
| REIRRYQKSTELLIR | |||
| PGTVALREIRRYQKS | |||
| VALREIRRYQKSTEL | |||
| RPGTVALREIRRYQK | |||
| YRPGTVALREIRRYQ | |||
| RYRPGTVALREIRRY | |||
| TVALREIRRYQKSTE | |||
| ALREIRRYQKSTELL |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line (human) | A549 human lung epithelial cells; A549 | American Type Cell Collection | ATCC:CCL-185 | |
| Genetic reagent (bovine) | Calf thymus DNA; purified DNA | Invitrogen | ||
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-histone H3 C-terminal; anti-H3-C; αH3-C | Active Motif | Active Motif:61277 | Western blot (1:15000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal Histone H4 C-terminal; αH4-C | Abcam | Abcam:ab10158 | Western blot (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-histone H4 N terminal | Upstate Millipore, Sigma Aldrich | SigmaAldrich:05–858 | Western blot (1:30000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-GAPDH; GAPDH | Cell Signalling Technology | CST:2118 | Western blot (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal 3D9; 3D9: mouse anti-cleaved histone 3 3D9 | This paper | Custom synthesis by Genscript. Western blot (1 µg/ml), immunofluorescence (1–2 µg/ml) | |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-histone H3 N-terminal; anti H3-N; αH3N | Active Motif | Active motif:61647 | Western blot (1:15000) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-H2A-H2B-DNA; PL2.3; anti-chromatin | PMID:1371530 | Immunofluorescence (1 µg/ml) | |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti neutrophil elastase; anti-NE; αNE | Calbiochem | Calbiochem 481001 | Immunofluorescence (1:500) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-histone H3 (citrullinine R2+R8+R17); anti- H3cit | Abcam | Abcam:ab5103 | Immunofluorescence (1 µg/ml) |
| Antibody | Chicken polyclonal anti-histone H2B | abcam | Abcam:ab134211 | Immunofluorescence (1:400) |
| Antibody | Polyclonal Sheep anti-ELANE: anti-NE | LSBio | LSBio:LS-B4244-50 | Immunofluorescence (5 µg/ml) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal Anti-mouse Bridging antibody | Active Motif | Active motif:53017 | (50 µg) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal (1H7A8) IgG1, k, isotype control | Genscript | Provided by Genscript as an isotype control (1 µg/ml) | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Recombinant human histone H3.1 | New England Biolabs | NEB:M2503S | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Peptide H-REIRRK(RREIR)C-NH2; immunising peptide REIRR | This paper | Custom synthesis by Eurogentec | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Peptide H-AARKSK(SKRAA)C-NH2; negative screening peptide | This paper | Custom synthesis by Eurogentec | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Peptide H-REIRRK (RRIER_NH2; competition peptide) | This paper | Custom synthesis by Eurogentec | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Peptide H-TGGVKK(KVGGT)-NH2; negative control peptide | This paper | Custom synthesis by Eurogentec | |
| Commercial assay or kit | BD OptEIA TMB substrate reagent set | BD Biosciences | RRID:AB_2869044 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Picogreen Assay kit; Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kits and dsDNA Reagents | Thermofisher Scientific | Thermofisher:P7589 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Cytoxicity assay; CytoTox 96 Non-Radioactive Cytotoxicity assay | Promega | Promega:G1780 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hoechst DNA stain (33342) | Invitrogen Molecular Probes | Invitrogen:H1399 | Immunofluorescence 1 µg/ml |
| Chemical compound, drug | Neutrophil elastase inhibitor GW311616A; NEi | Biomol | Biomol:Cay27957-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | AEBSF hydrochloride; peflabloc | Millipore, Sigma Aldrich | Sigma Aldrich:124839 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Cathepsin G inhibitor I; CGi | Calbiochem, Sigma Aldrich | Sigma Aldrich:219372 | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji; Image J | https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2019 | ||
| Software, algorithm | NETalyser | This paper | (Scripts deposited at https://github.com/tulduro/NETalyser) | |
| Software, algorithm | Volocity | Perkin Elmer |