Switch-like and persistent memory formation in individual Drosophila larvae
Figures
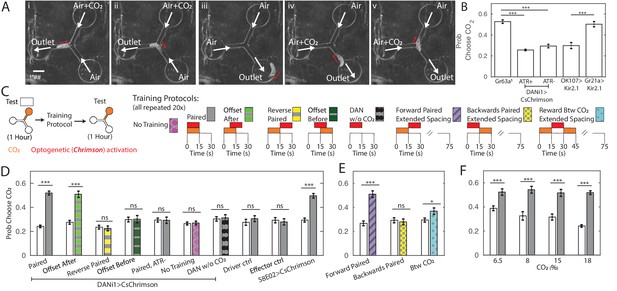
Y-maze assay to quantify innate and learned preference.
(A) Image sequence of a larva making two consecutive decisions in the Y-maze assay. White arrows indicate direction of air flow; red arrow shows direction of larva’s head. (B) Probability of choosing channel containing CO2 without any training. (C) Schematic representation of experiments in (D,E,F). All larvae were tested in the Y-maze for 1 hr to determine initial preference and again following manipulation to determine a final preference. The manipulations were: Paired Training - reward in concert with CO2 presentation, 15 s intervals, 20 repetitions; Offset After - reward presentation 7.5 s after CO2 onset, 15 s intervals, 20 repetitions; Reverse-Paired Training - reward opposite CO2 presentation, 15 s intervals, 20 repetitions; Offset Before - reward presentation 7.5 s before CO2 onset, 15 s intervals, 20 repetitions; DAN Activation Without CO2 - CO2 is never presented, while reward is presented at 15 s intervals, 20 repetitions; no training - no manipulation between two testing periods; Forward Paired (extended spacing) - 15 s reward follows 15 s CO2 presentation, followed by 60 s of air, 20 repetitions; Backwards Paired (extended spacing) - 15 s reward prior to 15 s CO2 presentation, followed by 60 s of air, 20 repetitions; Reward Between CO2 (extended spacing) - 15 s reward presentation between two 15 s CO2 presentations, followed by 45 s of air, 20 repetitions. (D) Probability of choosing CO2 containing channel before and after manipulation. All animals were fed ATR supplemented food, except those marked ATR-. (E) Probability of choosing CO2 containing channel before and after training as a function of reward timing, in training protocols with extended air spacings. All animals were DANi1>CsChrimson and fed ATR. (F) Probability of choosing CO2 containing channel before and after 20 cycles of paired training, as a function of CO2 concentration, used both during training and testing. All animals were DANi1>CsChrimson and fed ATR. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Spreadsheet containing each individual animal’s decisions in temporal sequence.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70317/elife-70317-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
Recording of a larva making 2 decisions within the Y-maze.
The direction of airflow and the larva’s decisions are noted. Video was recorded at 20 frames per second; the playback speed of 25 fps represents 1.25x real time.
Recording of a larva before training, showing a sequence of decisions made at the Y-maze juncture.
Recordings show 12.5 s before and 12.5 s after each decision. Video was recorded at 20 frames per second; the playback speed of 100 fps represents 5x real time.
Recording of a larva after training, showing a sequence of decisions made at the Y-maze juncture.
Recordings show 12.5 s before and 12.5 s after each decision. Video was recorded at 20 frames per second; the playback speed of 100 fps represents 5x real time.
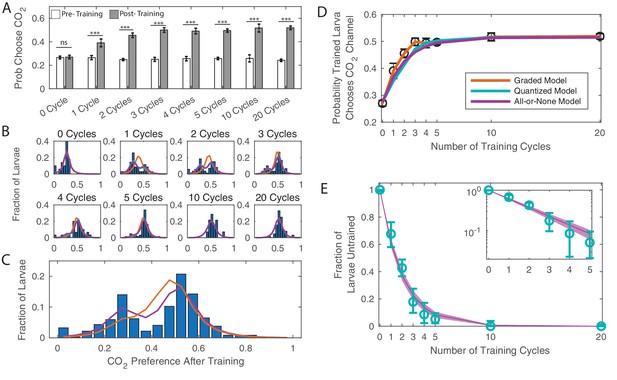
Dose dependence of learning DANi1>CsChrimson were given varying cycles of paired training (as in Figure 1C).
(A) Probability of choosing CO2 containing channel before and after training, as a function of amount of training. *** p<0.001. (B) Histograms of individual larva preferences after training, grouped by number of training cycles. (C) Histogram of individual larva preference after training for all larvae. (D) Population average probability of choosing CO2 following training vs. dose. (E) Fraction of larvae untrained vs. number of training cycles. Teal: fit parameters and error ranges from quantized model, purple lines, prediction and error ranges from memoryless model. Note logarithmic y-axis on insert. (C–E) Orange: graded model prediction - post-training preference is represented by a single Gaussian distribution whose mean and variance depend on amount of training; Teal: quantized model prediction - post-training preference is represented by two fixed Gaussian distributions and the fraction of larvae in each population depends on the amount of training; Purple: all-or-none model prediction - post-training preference is represented by two fixed Gaussian distributions and the effect of a single training cycle is to train a fixed fraction of the remaining untrained larvae.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Spreadsheet containing each individual animal’s decisions in temporal sequence.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70317/elife-70317-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
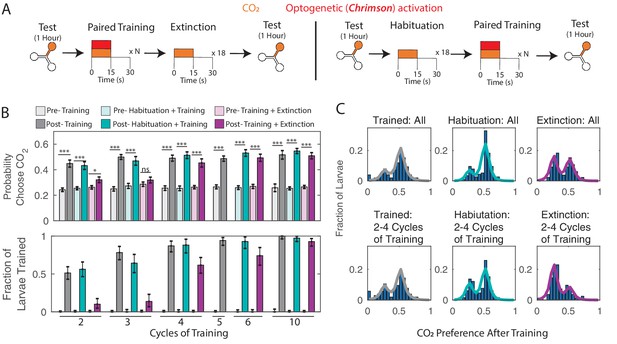
Memory extinction (A) Testing and training protocols for B,C.
Training + Extinction: larvae were exposed to 18 cycles of alternating CO2 and air following training. Habituation + Training: larvae were exposed to 18 cycles of alternating CO2 and air prior to training. (B) Probability of choosing CO2 containing channel (top) and fraction of larvae in trained group according to double Gaussian model fit (bottom) before and after training scheme. (C) Histograms of individual larva preference after training, for all larva and for larva trained with 2–4 training cycles. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Spreadsheet containing each individual animal’s decisions in temporal sequence.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70317/elife-70317-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
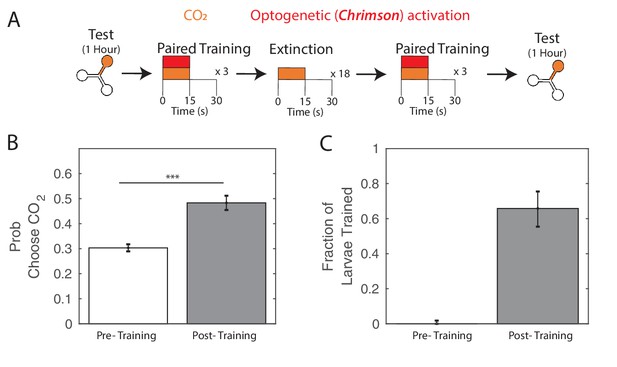
After extinction, larvae can be trained again.
(A) Testing and training protocol for B,C. Larvae were trained with three cycles of paired training, followed by 18 extinction cycles of alternating CO2 and air with no reward presented. After extinction, larvae were presented with three additional paired training cycles before testing. (B) Probability of choosing CO2 containing channel before and after training scheme. (C) Fraction of larvae in trained group according to double Gaussian model fit before and after training scheme. All larvae were DAN-i1>CsChrimson and raised on ATR+ food. *** p<0.001.
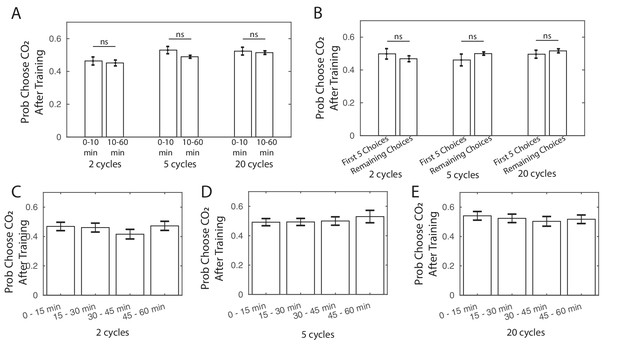
Larvae population average response following training.
(A) Larvae population average response in the first ten minutes following training (0–10 min), compared to the latter fifty minutes of testing (10–60 min), for larvae that had been given 2, 5, or 20 cycles of paired training. (B) Larvae population average response for the first five choices made by the larvae following training, compared to the remaining choices, for larvae that had been given 2, 5, or 20 cycles of paired training and made at least 10 decisions following training. (C,D,E) Larvae population average response over 15-min segments following training, for larvae trained with (C) 2 cycles, (D) 5 cycles, or (E) 20 cycles of training. All larvae were DAN-i1>CsChrimson and raised on ATR+ food.
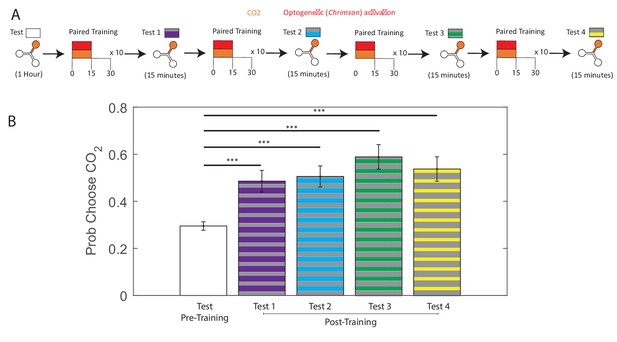
Larvae given additional training between testing periods.
(A) Testing and training protocols for experiments in B. All larvae are tested in the Y-maze for one hour to determine initial preference. Larvae were then trained with 10 cycles of paired training, followed by a 15-min test period. The 10 cycle train/15 min test was repeated four times. (B) Probability of choosing CO2-containing channel before training, and during each of the four test periods. All larvae were DAN-i1>CsChrimson and raised on ATR+ food. *** p <0.001.
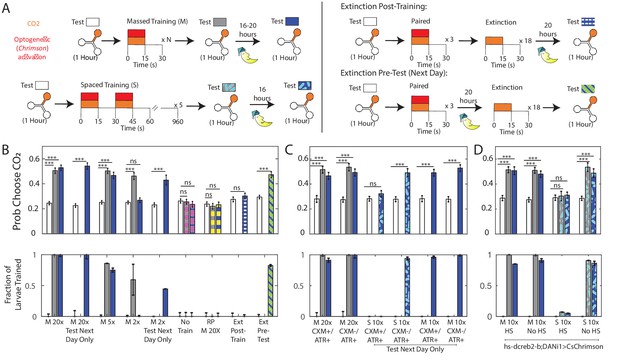
Memory retention overnight.
(A) Testing and training protocols. Except where indicated, larvae were tested, trained immediately after testing, tested again, then placed on food overnight and tested the following day. For extinction experiments, larvae were trained three times, and then exposed to 18 cycles of alternating CO2 and air either immediately following training or prior to testing the next day. (B,C,D) Probability of choosing CO2 containing channel (top) and fraction of larvae in trained group according to double Gaussian model fit (bottom) prior to training, immediately following training, and the next day. When the center bar is missing, larvae were not tested immediately following training but instead removed immediately to food. M Nx = massed training, N repetitions, S 10x = spaced training 10 total pairings, RP = reverse paired (see Figure 1C), No Train = no training. Larvae in (B,C) were DANi1>CsChrimson. Larvae in (D) were DANi1>hs-dCREB2-b;CsChrimson. Larvae were raised on food containing ATR, except for ATR+/CXM-, ATR+/CXM+ larvae who were fed ATR supplemented yeast paste (without/with cycloheximide) for 4 hr prior to initial testing. For reverse-paired (RP) and no training schemes, see Figure 1B. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Spreadsheet containing each individual animal’s decisions in temporal sequence.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70317/elife-70317-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | w[1118]; P{y[+t7.7]w[+mC]=20XUAS-IVS-CsChrimson.mVenus}attP2 (w;;UAS-CsChrimson) | Bloomington Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_55136 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | SS00864 split-Gal4 (DAN-i1-Gal4) | Saumweber et al., 2018 | Gift of Marta Zlatic, Janelia Research Campus | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | w[*]; Gr63a[1] | Bloomington Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_9941 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | w[1118]; P{y[+t7.7] w[+mC]=GMR58E02-GAL4}attP2 (GMR58E02-Gal4) | Bloomington Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41347 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | w;hs-dCREB2-b 17–2 | Yin et al., 1995 | FlyBase_ FBti0038019 | Gift of Jerry Chi-Ping Yin, University of Wisconsin, Madison |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | w[*]; P{w[+mW.hs]=GawB}ey[OK107]/In(4)ci[D], ci[D] pan[ciD] sv[spa-pol] (OK107-Gal4) | Bloomington Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_854 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | w[*]; P{w[+mC]=UAS-Hsap\KCNJ2.EGFP}7 (UAS-kir2.1) | Bloomington Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_6595 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | w[*]; P{w[+mC]=Gr21a-GAL4.C}133t52.1 (Gr21a-Gal4) | Bloomington Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_23890 | |
| Software, algorithm | livetracker | github.com/GershowLab/TrainingChamber (copy archived at URL swh:1:rev:e2a7ccc4e8d845e6cac59d3b2f344cca826c4727, Lesar, 2021) | This work |
Crosses used to generate larvae for experiments throughout this work.
For strain information, see key resource table.
| Figure | Designation | Female parent | Male parent |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gr63a1 | w;Gr63a1 | |
| 1 | OK107>Kir2.1 | UAS-Kir2.1-GFP | OK107-Gal4 |
| 1 | Gr21a>Kir2.1 | UAS-Kir2.1-GFP | Gr21a-Gal4 |
| 1-4 | DANi1>CsChrimson | w;;UAS-CsChrimson | SS00864 |
| 1 | Driver ctrl | SS00864 | |
| 1 | Effector ctrl | w;;UAS-CsChrimson | |
| 1 | 58E02>CsChrimson | w;;UAS-CsChrimson | 58E02-Gal4 |
| 4 | hs-dcreb2-b;DANi1>CsChrimson | w;hs-dcreb2-b;UAS-CsChrimson | SS00864 |
Data for experiments in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, and Figure 4.
# Larva: number of individual larvae tested for experiment type; # Approach Pre-Train: total number of times all larvae chose the channel containing air with CO2 prior to training; # Avoid Pre-Train: total number of times all larvae chose the channel containing pure air prior to training; # Approach Post-Train: total number of times all larvae chose the channel containing air with CO2 after the indicated training scheme; # Avoid Post-Train: total number of times all larvae chose the channel containing pure air after the indicated training scheme; # Approach Next Day: total number of times all larvae chose the channel containing air with CO2 during testing approximately 20 hr after training; # Avoid Next: total number of times all larvae chose the channel containing pure air during testing approximately 20 hr after training. All tests were 1 hr (for each larva).
| Experiment | Genotype | # Larva | # Approach Pre-Train | # Avoid Pre-Train | # Approach Post-Train | # Avoid Post-Train | # Approach Next Day | # Avoid Next Day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 1B | ||||||||
| Gr63a1 | Gr63a1 | 44 | 831 | 745 | - | - | - | - |
| DANi1> CsChrimson, ATR+ | DANi1> CsChrimson | 159 | 1714 | 4978 | - | - | - | - |
| DANi1> CsChrimson, ATR- | DANi1> CsChrimson | 16 | 256 | 614 | - | - | - | - |
| Figure 1D | ||||||||
| Paired | DANi1> CsChrimson | 64 | 561 | 1760 | 936 | 868 | - | - |
| Offset After | DANi1> CsChrimson | 20 | 288 | 757 | 316 | 305 | - | - |
| Reverse Paired | DANi1> CsChrimson | 29 | 315 | 1022 | 154 | 530 | - | - |
| Offset Before | DANi1> CsChrimson | 19 | 218 | 512 | 136 | 315 | - | - |
| Paired, ATR- | DANi1> CsChrimson | 16 | 256 | 614 | 127 | 307 | - | - |
| No Training | DANi1> CsChrimson | 50 | 578 | 1599 | 479 | 1295 | - | - |
| DAN w/o CO2 | DANi1> CsChrimson | 16 | 260 | 597 | 161 | 354 | - | - |
| Driver ctrl | SS00864 | 17 | 110 | 289 | 158 | 358 | - | - |
| Effector ctrl | UAS-CsChrimson | 18 | 214 | 516 | 114 | 294 | - | - |
| 58E02> CsChrimson | 58E02> CsChrimson | 21 | 380 | 912 | 493 | 501 | - | - |
| Figure 1E | DANi1> CsChrimson | |||||||
| Forward Paired | 22 | 181 | 496 | 350 | 337 | - | - | |
| Backwards Paired | 18 | 181 | 438 | 124 | 320 | - | - | |
| Btw CO2 | 23 | 272 | 652 | 165 | 283 | - | - | |
| Figure 1F | DANi1> CsChrimson | |||||||
| 6.5% | 19 | 361 | 568 | 319 | 290 | - | - | |
| 8% | 27 | 256 | 567 | 295 | 255 | - | - | |
| 15% | 19 | 170 | 368 | 249 | 233 | - | - | |
| 18% | 64 | 561 | 1760 | 936 | 868 | - | - | |
| Figure 2A | DANi1> CsChrimson | |||||||
| 0 Cycles | 50 | 578 | 1599 | 479 | 1295 | - | - | |
| 1 Cycles | 35 | 218 | 606 | 317 | 495 | - | - | |
| 2 Cycles | 87 | 840 | 2552 | 1081 | 1292 | - | - | |
| 3 Cycles | 31 | 310 | 930 | 686 | 686 | - | - | |
| 4 Cycles | 32 | 245 | 712 | 493 | 511 | - | - | |
| 5 Cycles | 63 | 863 | 2491 | 975 | 993 | - | - | |
| 10 Cycles | 14 | 100 | 287 | 154 | 144 | - | - | |
| 20 Cycles | 64 | 561 | 1760 | 936 | 868 | - | - | |
| Figure 3B | DANi1> CsChrimson | |||||||
| 2 Cycles, Training | 87 | 840 | 2552 | 1081 | 1292 | - | - | |
| 2 Cycles, Habituation + Training | 30 | 385 | 1127 | 422 | 554 | - | - | |
| 2 Cycles, Training + Extinction | 30 | 336 | 946 | 375 | 793 | - | - | |
| 3 Cycles, Training | 30 | 308 | 924 | 675 | 679 | - | - | |
| 3 Cycles, Habituation + Training | 18 | 222 | 591 | 260 | 294 | - | - | |
| 3 Cycles, Training + Extinction | 26 | 279 | 695 | 195 | 416 | - | - | |
| 4 Cycles, Training | 30 | 225 | 659 | 490 | 502 | - | - | |
| 4 Cycles, Habituation + Training | 18 | 239 | 701 | 372 | 352 | - | - | |
| 4 Cycles, Training + Extinction | 27 | 384 | 1074 | 394 | 475 | - | - | |
| 5 Cycles, Training | 63 | 863 | 2491 | 975 | 993 | - | - | |
| 6 Cycles, Habituation + Training | 19 | 266 | 758 | 367 | 324 | - | - | |
| 6 Cycles, Training + Extinction | 18 | 253 | 687 | 309 | 317 | - | - | |
| 10 Cycles, Training | 14 | 100 | 287 | 154 | 144 | - | - | |
| 10 Cycles, Habituation + Training | 30 | 406 | 1193 | 607 | 503 | - | - | |
| 10 Cycles, Training + Extinction | 30 | 426 | 1180 | 401 | 386 | - | - | |
| Figure 4B | DANi1> CsChrimson | |||||||
| 20x | 28 | 380 | 1172 | 509 | 499 | 459 | 409 | |
| 20x (Only Test Next Day) | 14 | 224 | 768 | - | - | 296 | 250 | |
| 5x | 29 | 472 | 1427 | 488 | 480 | 404 | 461 | |
| 2x | 42 | 514 | 1537 | 594 | 693 | 201 | 548 | |
| 2x (Only Test Next Day) | 22 | 209 | 696 | - | - | 213 | 283 | |
| No Train | 20 | 316 | 889 | 187 | 544 | 104 | 337 | |
| RP 20x | 21 | 282 | 905 | 121 | 430 | 109 | 361 | |
| Ext Post-Train | 23 | 181 | 477 | - | - | 158 | 365 | |
| Ext Pre-Test | 31 | 417 | 1002 | - | - | 385 | 429 | |
| Figure 4C | DANi1> CsChrimson | |||||||
| M 20x (CXM+/ATR+) | 20 | 110 | 282 | 252 | 237 | 237 | 272 | |
| M 20x (CXM-/ATR+) | 17 | 159 | 419 | 271 | 236 | 228 | 235 | |
| S 20x (CXM+/ATR+) | 23 | 191 | 486 | - | - | 150 | 316 | |
| S 20x (CXM-/ATR+) | 20 | 197 | 511 | - | - | 254 | 264 | |
| M 10x (CXM+/ATR+) | 23 | 136 | 345 | - | - | 331 | 344 | |
| M 10x (CXM-/ATR+) | 20 | 175 | 454 | - | - | 419 | 375 | |
| Figure 4D | DANi1> hs-dCREB2-b;CsChrimson | |||||||
| M 10x HS | 21 | 175 | 434 | 392 | 370 | 253 | 246 | |
| M 10x No HS | 22 | 248 | 656 | 367 | 353 | 451 | 490 | |
| S 10x HS | 24 | 172 | 420 | 68 | 156 | 153 | 339 | |
| S 10x No HS | 22 | 294 | 736 | 212 | 184 | 335 | 352 |
p-Values for experiments in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, and Figure 4.
P-values for experiments were calculated: Bootstrap - p-values calculated as explained in Materials and methods; Fisher - p-values calculated using Fisher’s exact test; U-test - p-values calculated using two-sided Mann–Whitney U test. Unless otherwise noted, p-values are calculated between pre-train and post-train data. A shaded row indicates not all tests reach the same significance level (out of ns, p <0.05, p <0.01, p <0.001).
| Experiment | Genotype | Hierarchical Bootstrap | Bootstrap Animal Only | Fisher | U-test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 1B | |||||
| Gr63a1/DANi1> CsChrimson, ATR+ | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| Gr63a1/DANi1> CsChrimson, ATR- | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| Figure 1D | |||||
| Paired | DANi1> CsChrimson | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 |
| Offset After | DANi1> CsChrimson | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 |
| Reverse Paired | DANi1> CsChrimson | 0.3429 | 0.2689 | 0.6166 | 0.9379 |
| Offset Before | DANi1> CsChrimson | 0.4479 | 0.4373 | 0.9479 | 0.9770 |
| Paired, ATR- | DANi1> CsChrimson | 0.4762 | 0.4315 | 1.000 | 0.2658 |
| No Training | DANi1> CsChrimson | 0.4066 | 0.3664 | 0.7726 | 0.9835 |
| DAN w/o CO2 | DANi1> CsChrimson | 0.3935 | 0.3102 | 0.7173 | 0.4852 |
| Driver ctrl | SS00864 | 0.3106 | 0.0313 | 0.3411 | 0.3977 |
| Effector ctrl | UAS-CsChrimson | 0.3383 | 0.2361 | 0.6336 | 0.8366 |
| 58E02> CsChrimson | 58E02> CsChrimson | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 |
| Figure 1C | DANi1> CsChrimson | ||||
| Forward Paired | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| Backwards Paired | 0,3368 | 0.163 | 0.6801 | 0.1939 | |
| Btw CO2 | 0.0107 | 0.0001 | 0.006543 | 0.0003257 | |
| Figure 1D | DANi1> CsChrimson | ||||
| 6.5% | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 8% | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 15% | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 18% | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| Figure 2A | DANi1> CsChrimson | ||||
| 0 Cycles | 0.4132 | 0.3647 | 0.7726 | 0.9835 | |
| 1 Cycles | 0.0003 | <10−4 | <10−4 | 0.0591 | |
| 2 Cycles | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 3 Cycles | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 4 Cycles | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 5 Cycles | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 10 Cycles | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 20 Cycles | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| Figure 3B | DANi1> CsChrimson | ||||
| 2 Cycles, Training | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 2 Cycles, Habituation + Training | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 2 Cycles, Training + Extinction | 0.0117 | 0.0020 | 0.001339 | 0.04743 | |
| 3 Cycles, Training | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 3 Cycles, Habituation + Training | <10−4 | <10−4 | 0.0007459 | <10−4 | |
| 3 Cycles, Training + Extinction | 0.1133 | 0.0176 | 0.1763 | 0.03069 | |
| 4 Cycles, Training | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 4 Cycles, Habituation + Training | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 4 Cycles, Training + Extinction | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 5 Cycles, Training | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 6 Cycles, Habituation + Training | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 6 Cycles, Training + Extinction | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 10 Cycles, Training | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 10 Cycles, Habituation + Training | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 10 Cycles, Training + Extinction | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| Figure 4B | DANi1> CsChrimson | ||||
| 20x Pre-Test/Post-Test | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 20x Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 20x (Only Test Next Day) Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 5x Pre-Test/Post-Test | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 5x Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 2x Pre-Test/Post-Test | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| 2x Pre-Test/Next Day | 0.2086 | 0.0501 | 0.3524 | 0.07216 | |
| 2x (Only Test Next Day) Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| No Train Pre-Test/Post-Test | 0.4035 | 0.3319 | 0.7893 | 0.2003 | |
| No Train Pre-Test/Next Day | 0.1583 | 0.0530 | 0.3071 | 0.8884 | |
| RP 20x Pre-Test/Post-Test | 0.2677 | 0.1507 | 0.4276 | 0.7396 | |
| RP 20x Pre-Test/Next Day | 0.4205 | 0.3481 | 0.8474 | 0.3765 | |
| Ext Post-Train Pre-Test/Next Day | 0.1801 | 0.0146 | 0.3315 | 0.01336 | |
| Ext Pre-Test Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| Figure 4C | DANi1> CsChrimson | ||||
| M 20x (CXM+/ATR+) Pre-Test/Post-Test | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| M 20x (CXM+/ATR+) Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| M 20x (CXM-/ATR+) Pre-Test/Post-Test | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| M 20x (CXM-/ATR+) Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| S 10x (CXM+/ATR+) Pre-Test/Next Day | 0.1099 | 0.014 | 0.1671 | 0.02985 | |
| S 10x (CXM-/ATR+) Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| M 10x (CXM+/ATR+) Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| M 10x (CXM-/ATR+) Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| Figure 4D | DANi1> hs-dCREB2-b;CsChrimson | ||||
| M 10x, HS Pre-Test/Post-Test | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| M 10x, HS Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| M 10x, No HS Pre-Test/Post-Test | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| M 10x, No HS Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| S 10x, HS Pre-Test/Post-Test | 0.3804 | 0.2830 | 0.7310 | 0.2750 | |
| S 10x, HS Pre-Test/Next Day | 0.2645 | 0.08860 | 0.4650 | 0.3802 | |
| S 10x, No HS Pre-Test/Post-Test | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | |
| S 10x, No HS Pre-Test/Next Day | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 | <10−4 |
Model fits to data in Figure 2.
Shifting Mean and , shifting fraction, and exponential fraction models are presented in Figure 2. Model name: name of the model. Formula: expression for the probability of the data given the model and its parameters. # params: number of free parameters in the model. logarithm of the probability of the data given best fit to this model minus logarithm of the probability of the data given the best fit model overall. A higher (less negative) value means the model better fits the data without regard to the number of parameters. , - Aikake and Bayes Information Criterion minus the lowest values over the models tested. Lower numbers indicate model is favored. According to both criterion, the exponential fraction model is strongly favored over the shifting fraction model, and the shifting fraction model is strongly favored over all models except the exponential fractional model.
| Model name | Formula | # params | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shifting Mean (fixed ) | 9 | −42.7 | 84.86 | 104.45 | |
| Shifting Mean and (Graded learning) | 16 | −12.9 | 39.3 | 86.3 | |
| Shifting Fraction (Quantized learning) | … | 11 | −3.93 | 11.3 | 38.7 |
| Shifting Fraction (3 clusters) | … … | 20 | 0 | 21.4 | 84.1 |
| Exponential Fraction (All-or-none) | … | 4 | −5.3 | 0 | 0 |
| Symbol | Definition | Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| number of training cycles | fraction of times larva chose CO2 after cycles | ||
| mean probability of choosing CO2 after training cycles | # choices made by larva after training cycles | ||
| global adjustment to binomial standard deviation | training dependent standard deviation | ||
| probability of larva in untrained group choosing CO2 | probability of larva in trained group choosing CO2 | ||
| fraction of larvae in untrained group after cycles | probability of larva in group 1,2,3 choosing CO2 | ||
| fraction of larvae in groups 1,2 after cycles | fraction of larvae not trained after one cycle | ||
| normal cdf: | relative log probability of data given model | ||
| AIC | Aikake Information Criterion: , k = # params | AIC - lowest AIC | |
| BIC | Bayes Information Criterion: , k = # params, = # animals | BIC - lowest BIC |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Schematics and production files for y-maze components.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70317/elife-70317-supp1-v1.zip
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70317/elife-70317-transrepform-v1.docx





