Pupil diameter is not an accurate real-time readout of locus coeruleus activity
Figures
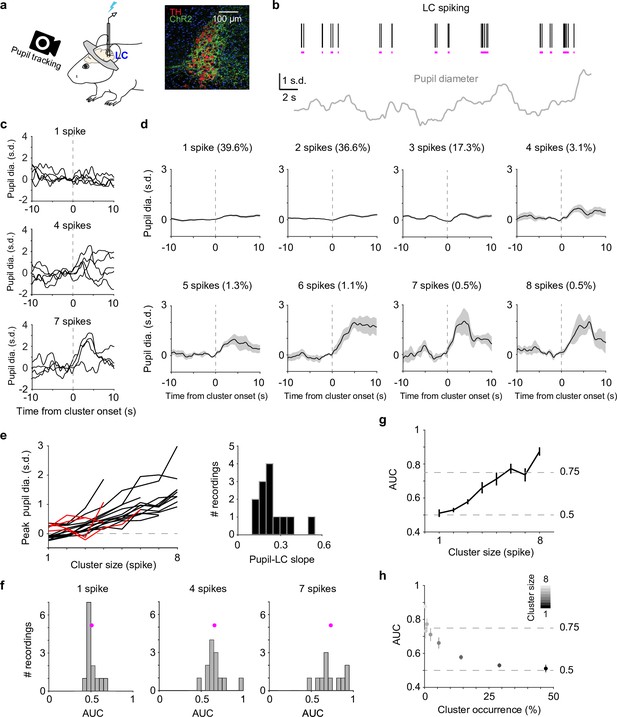
Correlating locus coeruleus (LC) activity to pupil responses.
(a) Left: schematic of experimental setup for simultaneous pupil and LC recording/optical stimulation in head-fixed mice. Lightning bolt: light pulse. Right: expression of ChR2 in a DBH;Ai32 mouse (dopamine beta hydroxylase, DBH; ChR2-EYFP: green; tyrosine hydroxylase, TH: red). (b) Example simultaneously recorded LC spike raster and z-scored pupil diameter. Vertical black lines represent individual spikes. Horizontal magenta lines indicate spike clusters. (c) Example LC spike cluster-triggered pupil responses for cluster sizes 1, 4, and 7. (d) Mean LC cluster-triggered pupil responses (± standard error of the mean [SEM]) for cluster sizes 1 through 8 with occurrence (%) indicated in an example recording. (e) Left: the relationship between peak pupil diameter and LC cluster size for each paired recording. Curves with linear regression R2 > 0.6 are in black (n = 13), <0.6 in red (n = 4). Two recordings with limited cluster sizes (<3) were not suitable for linear regression and not included here. Right: histogram of the linear slopes for curves with R2 > 0.6. For f–h, the 13 recordings with R2 > 0.6 were included. (f) Histograms of area under the curve (AUC) values when using peak pupil diameter to predict the associated cluster sizes 1, 4, and 7. Magenta dot: mean. (g) Group mean AUC values when using peak pupil diameter to predict the associated cluster sizes 1 through 8. (h) Replot of (g) by showing the occurrence (abscissa) associated with each cluster size (gray scale).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70510/elife-70510-fig1-data1-v1.zip

Locus coeruleus (LC) and pupil recordings in mice.
(a) Distribution of interspike interval, spike waveform (top) and spike sorting diagram (bottom) of three example recordings with median interspike interval (ISI, left to right: 0.20, 0.29, and 0.36 s) and spike duration (left to right: 0.23, 0.84, and 1.25 ms). Spike duration was quantified from trough to peak afterhyperpolarization (AHP). (b) Distribution of median interspike interval for 19 recordings. (c) Distribution of R2 values from linear regressing pupil–LC relationship in Figure 1e (n = 17, two recordings with limited cluster sizes [<3] were not suitable for linear regression and not included).
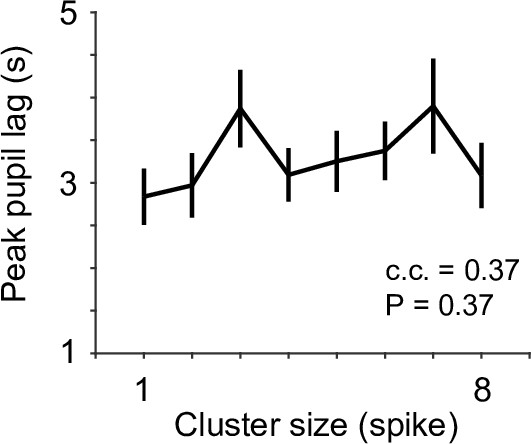
The relationship between the latency of peak pupil diameter and locus coeruleus (LC) spike cluster size.
c.c., Pearson correlation coefficient.

The relationship between pupil size changes and locus coeruleus (LC) spike cluster.
The relationship between pupil size changes and LC spike cluster when pupil responses were quantified as % changes from baseline (a), time derivative (b), or using a shorter time window (3 s, c). Curves with linear regression R2 > 0.6 are in black, <0.6 are in red. Specifically, 13 recordings were identified with R2 > 0.6 in (a), and all were the same as the 13 recordings with R2 > 0.6 in Figure 1e; 9 recordings were identified with R2 > 0.6 in (b), and 8 out of 9 were from the 13 recordings in Figure 1e; 12 recordings were identified with R2 > 0.6 in (c), and all were from the 13 recordings in Figure 1e. In addition, only in 1 out of the 13 recordings (with R2 > 0.6 in Figure 1e) did the number of spikes occurring after a given cluster (in-between spikes) significantly correlate with LC cluster size or peak pupil diameter, and overall in-between spikes did not strongly correlate with LC cluster size (correlation coefficient = 0.35, p = 0.39) or peak pupil diameter (correlation coefficient = 0.29, p = 0.48). Together, these results strongly suggest that in-between spikes did not significantly contribute to the variability of the pupil–LC relationship.
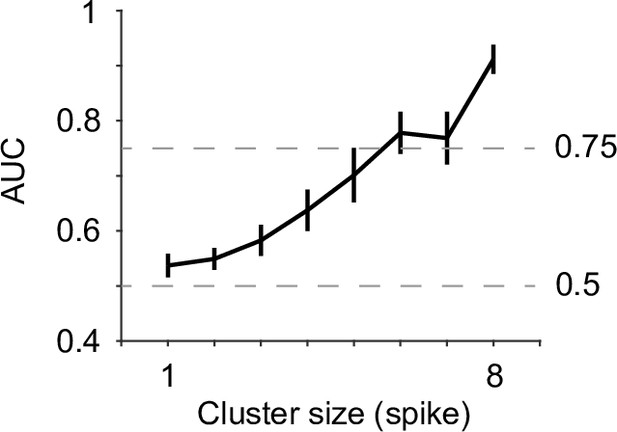
Group mean area under the curve (AUC) values when using peak pupil diameter to predict the associated cluster sizes 1 through 8 from all recordings (n = 19).

Group mean probability distribution of locus coeruleus (LC) spike clusters (n = 19).
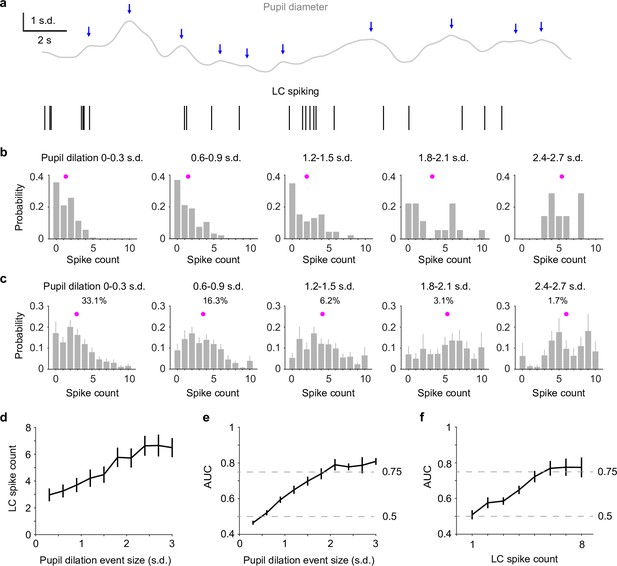
Reverse correlating pupil responses to locus coeruleus (LC) activity.
(a) Example pupil–LC traces showing the detected pupil dilation events (blue arrows) based on zero-crossing of pupil derivatives. (b) Probability distributions of LC spike counts associated with pupil dilation events of similar sizes in an example recording. Magenta dot: mean. Pupil dilation events were binned every 0.3 standard deviation (SD). (c) Group mean probability distributions of LC spikes associated with pupil dilation events of similar sizes. Mean occurrences (%) of pupil dilation events were indicated. (d) Group mean relationship between LC spike counts and pupil dilation events binned every 0.3 SD from 0 to 3 SD. (e) Group mean area under the curve (AUC) values when using LC spike counts to predict the associated pupil dilation events binned every 0.3 SD from 0 to 3 SD. (f) Group mean AUC values when using the detected pupil dilation events to predict the associated LC spike counts 1 through 8, similar to Figure 1g.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70510/elife-70510-fig2-data1-v1.zip
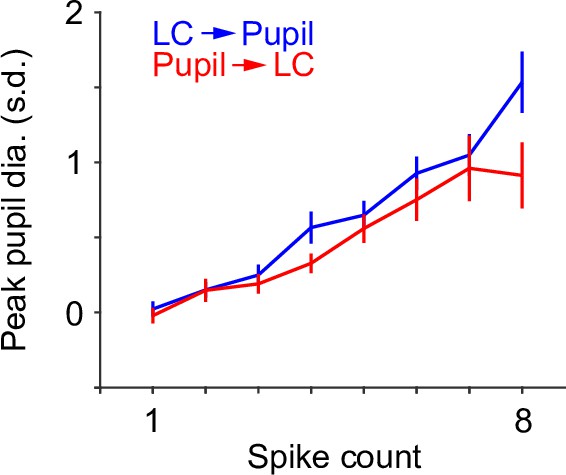
Group mean relationship between peak pupil diameter and locus coeruleus (LC) spike counts using two different methods.
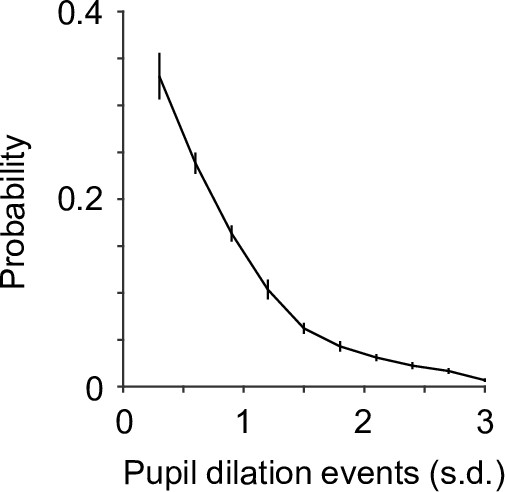
Group mean probability distribution of the detected pupil dilation events (n = 19).
Pupil dilation events were binned every 0.3 standard deviation (SD).
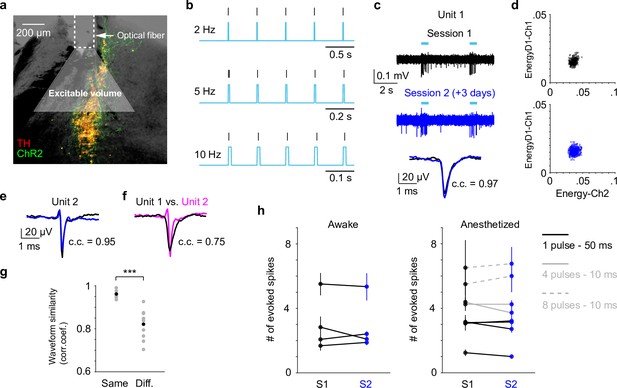
Locus coeruleus (LC) responses to optogenetic stimulation.
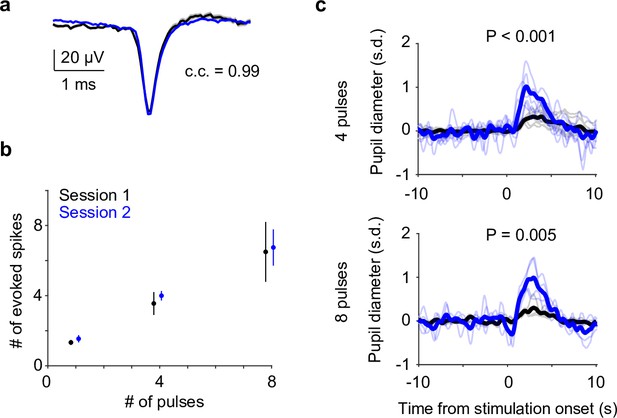
(a) Example LC histological section illustrating optical fiber implant and the estimated excitable volume (light gray cone). Estimates were based on 10-mW laser power, 2.5 mW/mm2 excitation threshold, 1.4 refractive index, and a 30° cylindrical cone. (b) Example spiking activity (vertical lines) from an opto-tagged LC unit in response to 10-ms blue pulse trains at different frequencies. (c) Example traces (top, middle) and waveforms (bottom) from a putatively same LC unit in response to optical stimulation (cyan bars) in two different sessions (3 days apart). Black and blue indicate an earlier and a later session (sessions 1 and 2), respectively. Waveforms from the two sessions were highly similar with Pearson correlation coefficient (c.c.) = 0.97. (d) Spike sorting diagrams corresponding to the two sessions shown in (c). The unit was identified in Ch1. (e) Waveforms from another putatively same unit in two sessions (1 day apart, waveform c.c. = 0.95). (f) Waveforms from the 2 units shown in (c) and (e) were less similar (session 1 unit 1 vs. session 1 unit 2, c.c. = 0.75). (g) Among the tracked 5 units, waveforms from the putatively same units in sessions 1 and 2 (Same) were more similar than waveforms from the putatively different units in session 1 (Different. Same vs. Different, Pearson correlation coefficient (c.c.), 0.96 ± 0.02 vs. 0.82 ± 0.07, mean ± standard deviation (SD), p = 6.6e−4, two-tailed rank sum test). Gray dots: individual pair. Black dots: group mean. (h) Responses from the putatively same units to optical stimulation (S1 vs. S2) during awake, nontask performing (4 units, left) and anesthetized (5 units, right) conditions. p > 0.05 for each S1 vs. S2 comparison, permutation test. Evoked spike counts were quantified in response to (1) single 50 ms pulse (solid black line, 4 units); or (2) four 10 ms pulses at 10 Hz (solid gray line, 2 units); or (3) eight 10 ms pulses at 5 Hz (dashed gray line, 2 units).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70510/elife-70510-fig3-data1-v1.zip

Locus coeruleus (LC) response to optogenetic stimulation.
The number of evoked spikes from an opto-tagged LC unit in response to optical stimulation using different laser power (single 10 ms pulse; left), or different pulse width (single pulse; right). Error bars may be too small to be visible.
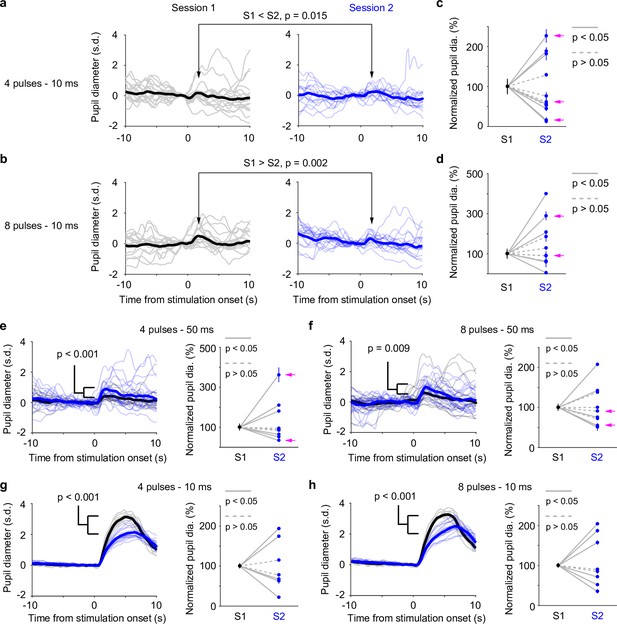
Pupil responses to locus coeruleus (LC) optogenetic stimulation.
(a) Example responses from the same pupil to LC stimulation in two awake, baseline pupil-matched sessions (left and right) aligned to the onset of optical stimulation of four 10 ms pulses at 10 Hz. Thin curves: individual responses; thick curves: mean. Baseline pupil diameter S1 vs. S2, 0.71 vs. 0.75 mm. p values were based on permutation test. (b) Same as in (a), except that optical stimulation was eight 10 ms pulses at 10 Hz. (a, b) were from the same recording. (c) Group data showing pupil responses to optical stimulation of four 10 ms pulses at 10 Hz in awake, baseline pupil-matched sessions (12 paired sessions from 6 mice). To aid visualization, pupil responses in session 2 were normalized to session 1. Unnormalized data in Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Dots: mean peak pupil responses. Vertical lines: 95% confidence interval. Solid lines indicate significant difference (p < 0.05, permutation test). Session 1 always preceded session 2. Magenta arrows indicate same-day comparison. (d) Group data showing pupil responses to optical stimulation of eight 10 ms pulses at 10 Hz in awake, baseline pupil-matched sessions (11 paired sessions from 7 mice). Unnormalized data in Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Conventions are as in (c). (e, f) Left: example pupil responses from one recording. Conventions are as in (a, b), except that optical stimulations consisted of 50 ms pulses instead of 10 ms, and that pupil responses from the two sessions were overlaid. Baseline pupil diameter S1 vs. S2, 0.83 vs. 0.80 mm. Right: group pupil responses as in (c, d), except that optical stimulations consisted of 50 ms pulses instead of 10 ms. 9 paired sessions from 7 mice in (e), and 9 paired sessions from 7 mice in (f). Magenta arrows indicate same-day comparison. (g, h) Left: example pupil responses from one recording. Conventions are as in (a, b), except that the mouse was under anesthesia (2% isoflurane), and that pupil responses from the two sessions were overlaid. Baseline pupil diameter S1 vs. S2, 0.31 vs. 0.35 mm. Right: group pupil responses as in (c, d), except that mice were under anesthesia. 7 paired sessions from 3 mice in (g), and 8 paired sessions from 3 mice in (f).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Source data for Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70510/elife-70510-fig4-data1-v1.zip

Raw pupil traces for the two sessions used in Figure 4a, b.
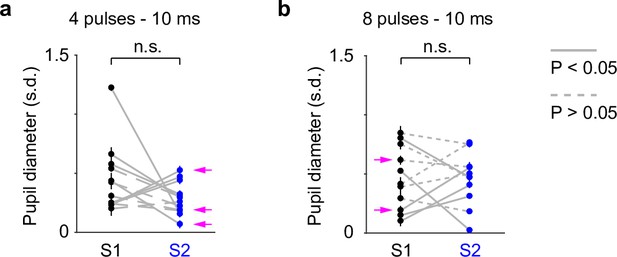
Unnormalized group pupil responses as shown in Figure 4c, d.
Session-to-session fluctuations were not observable from group comparisons. p = 0.38, n = 12 for (a) and p = 0.63, n = 11 for (b). Magenta arrows indicate same-day comparison.
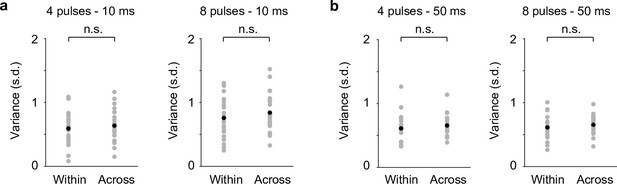
The variability of pupil responses to locus coeruleus (LC) optical stimulation within individual sessions (Within) was comparable to that of across sessions (Across) in awake mice.
(a) p = 0.53, p = 0.58. (b) p = 0.22, p = 0.15. Two-tailed rank sum test. Across-session variability was estimated by resampling pooled trials from all sessions in each condition. The iteration of resampling matched the number of sessions in that condition.

Spontaneous pupil fluctuation was reduced during anesthesia.
(a) The amplitude of spontaneous pupil dilation events in awake, nontask performing condition was larger than in anesthetized condition (five sessions from three mice in each condition, p = 0.0079, two-tailed rank sum test). Gray dots: individual sessions. Red and black dots: group mean. (b) The frequency of significant spontaneous pupil dilation events (>0.3 standard deviation [SD]) was higher in awake, nontask performing condition than in anesthetized condition (5 sessions from 3 mice in each condition, p = 0.0079, two-tailed rank sum test). Gray dots: individual sessions. Red and black dots: group mean.
Simultaneous locus coeruleus (LC) and pupil responses to optical stimulation.
Simultaneous recording of an LC unit waveform (a), spike responses (b), and pupil diameter (c) during optogenetic stimulation (10 ms pulse train: four pulses at 10 Hz [top] and eight pulses at 5 Hz [bottom] under anesthesia). Baseline pupil diameter S1 vs. S2, 0.34 vs. 0.32 mm.

List of all locus coeruleus (LC) recordings.
(a, b) ISI distribution and spike waveform from all recordings, ranked by increasing median ISI. Pupil–LC relationship with R2 > 0.6 (as in Figure 1e) in (a, n = 13), and the remaining in (b, n = 6). All waveforms were plotted on the same scales as shown in the first panel. Each trial lasted 5–6 s, which likely contributed to the peak on the right side of some ISI distributions (e.g., magenta arrow in the last panel of (b)). (c) Average firing rate vs. spike duration (trough to peak AHP). Black dots represent the group in (a), gray dots represent (b). We note that both narrow and wide waveforms were present, supporting recent work (Totah et al., 2018). We did not quantify the width of four waveforms in (a, indicated by *) as their reversed polarity with prominent initial positive deflection indicated that the recording sites were in the more distal axonal or dendritic regions of neurons where mixed-ion capacitive current became more profound (Barry, 2015; Gold et al., 2006; Rall and Shepherd, 1968; Sun et al., 2021). Their firing rates were between 1 and 3 spikes/s.
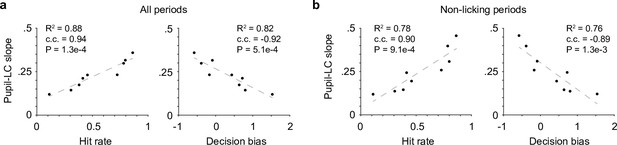
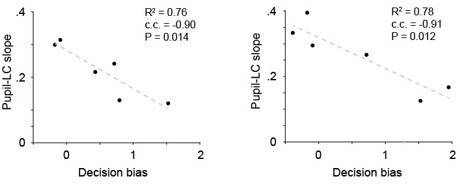
Pupil–locus coeruleus (LC) coupling correlated with decision-bias-related variables.
(a) The variations in the relationship between peak pupil diameter and LC cluster size (linear slopes in Figure 1e) were strongly correlated with Hit rate (left) and decision bias (right, n = 9). c.c., Pearson correlation coefficient. (b) The relationships in (a) held when pupil–LC slopes were quantified in nonlicking periods only.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Source data for Figure 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70510/elife-70510-fig5-data1-v1.zip
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | DBH-Cre | MMRRC | RRID:MMRRC_036778-UCD | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | Ai32 | JAX | RRID:IMSR_JAX:012569 | |
| Software, algorithm | BControl | Princeton University | https://brodylabwiki.princeton.edu/bcontrol | |
| Software, algorithm | WaveSurfer | HHMI Janelia | http://wavesurfer.janelia.org/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Matlab | MathWorks | RRID:SCR_001622 | |
| Software, algorithm | Janelia eye tracker | HHMI Janelia | N/A | |
| Software, algorithm | StreamPix | Norpix | RRID:SCR_015773 | |
| Software, algorithm | Illustrator | Adobe | RRID:SCR_010279 | |
| Other | Camera | PhotonFocus | DR1-D1312-200-G2-8 | |
| Other | Telecentric lens | Edmund Optics | 55–349 | |
| Other | Tetrode drive | Cohen et al., 2012 | N/A | |
| Antibody | Anti-TH primary antibody | Thermo Fisher | OPA104050 RRID:AB_325653 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Secondary antibody | Thermo Fisher | A11008 RRID:AB_2534079 | 1:500 |