Adaptation in cone photoreceptors contributes to an unexpected insensitivity of primate On parasol retinal ganglion cells to spatial structure in natural images
Figures
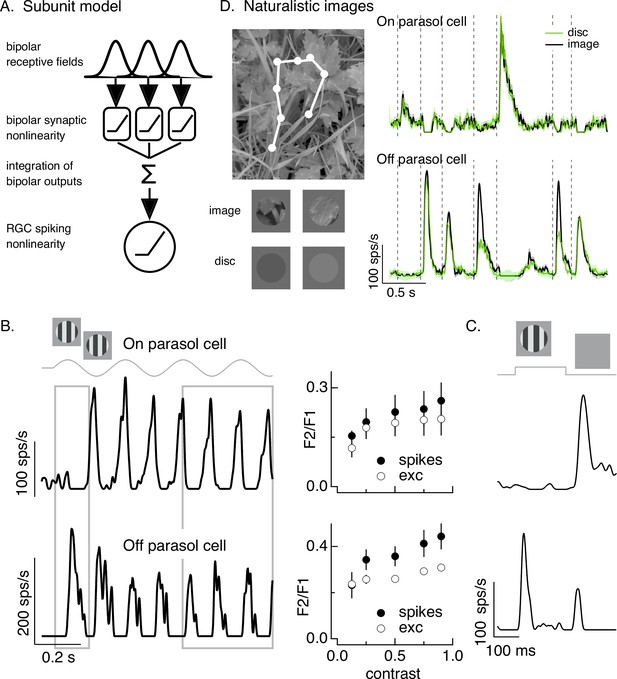
Differences in spatial integration for gratings and naturalistic stimuli.
(A) Standard subunit model often used to account for nonlinear spatial integration by retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). (B) (Left) On and Off parasol RGC spike responses to contrast-reversing gratings. Both RGC types exhibit strong responses well after grating onset (right gray box), but responses at grating onset differ (left gray box). (Right) Dependence of frequency-doubled (F2) response on contrast for both excitatory inputs and spike output. The strength of nonlinear spatial integration was summarized as the ratio of the frequency doubled or F2 response measured for a split-field grating to the F1 response measured for a modulated spot. (C) On and Off parasol cell responses to flashed gratings differ. (D) On but not Off parasol cells show near-linear responses to natural movies. Top left shows image with eye movement trajectory in white. Bottom left shows two natural image movie frames and corresponding linear-equivalent discs. (Right) Black trace shows responses to a natural movie generated using the DOVES database (Van Der Linde et al., 2009). Movies were restricted to the receptive field center with a circular aperture. Green shows responses to a linear-equivalent movie, in which spatial structure within the receptive field center was replaced with a uniform disc with an intensity equal to the weighted average intensity within the receptive field center. The weighting was determined by a gaussian fit to the dependence of the response on the size of a test spot (see Turner and Rieke, 2016 for details).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70611/elife-70611-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
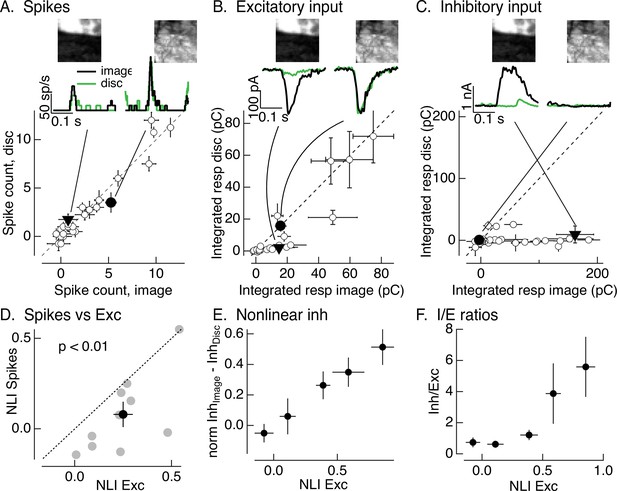
Synaptic integration leads to unexpected linearity of On parasol responses to natural images.
(A) Spike count for responses of one On parasol retinal ganglion cell (RGC) to image patches and corresponding linear-equivalent stimuli. Each stimulus was flashed for 250 ms and spikes counted during that time. Peristimulus time histograms for the two highlighted points are at the top along with the corresponding images; the black trace is the response to the image patch and the green trace is the response to the linear-equivalent stimulus. (B) Excitatory synaptic inputs for the same cell and image patches as in A. Responses are the integrated current during the stimulus presentation. The same two image patches are highlighted. (C) Inhibitory synaptic input for the same cell and image patches. (D) Excitatory inputs are more nonlinear than spike output. Comparison of nonlinearity index (NLI; see Equation 1) for spike response with that for excitatory input for 10 On parasol cells (gray) and mean across cells (black, mean ± standard error of the mean [SEM]). For each cell, NLIs were averaged across all image patches probed. (E) Patches that recruit nonlinear excitatory input also recruit nonlinear inhibitory input. Nonlinear inhibitory input (image response − disc response) plotted against excitatory NLI. Excitatory NLIs were separated into five bins, and the nonlinear inhibitory input for the image patches in each bin was averaged across patches and cells (n = 8). For each cell, inhibitory input was normalized by the largest input produced across patches. (F) Ratio of inhibitory input to excitatory input increases for patches that elicit strong nonlinear excitatory input. Excitatory NLIs were binned as in E, and the average I/E ratio (for 8 cells) was computed for all patches in each bin.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2A–F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70611/elife-70611-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
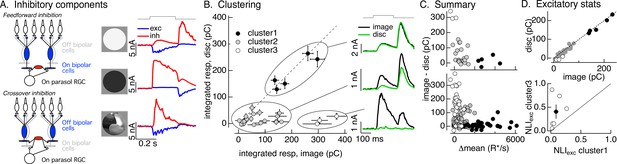
Identifying the components of inhibitory input to On parasol cells elicited by natural image patches.
(A) (Left) Circuits responsible for two components of inhibitory synaptic input to On parasol retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). (Right) The onset of a light increment (top) produces an increase in excitatory input (blue) and a small, delayed increase in feedforward inhibitory input (red). The onset of a light decrement (middle) produces a decrease in excitatory input and a large increase in crossover inhibitory input. Different regions of spatially structured inputs (bottom) can produce large crossover inhibitory input that coincide with increases in excitatory input. (B) Clustering of inhibitory synaptic inputs elicited by image patches. Clustering was based on response time course. Panels at right show average responses to the image (black) and corresponding linear-equivalent disc (green) for each cluster. Cluster 1 is dominated by feedforward inhibitory input and shows linear spatial integration (i.e., image and disc responses are near identical). Cluster 3 is dominated by crossover inhibitory input and shows strongly nonlinear spatial integration. Cluster 2 is intermediate between the two others. (C) Summary of relation between nonlinear inhibitory input (image–disc) and mean luminance for each of the clusters from B (top), and summary across cells (bottom). (D) (top) Excitatory responses to image patches and corresponding linear-equivalent discs for each cluster from B. (bottom) Comparison of nonlinearity indices (see Equation 1) for excitatory inputs corresponding to clusters 1 and 3 for six cells (open circles) and mean across cells (closed circle).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3B–D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70611/elife-70611-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
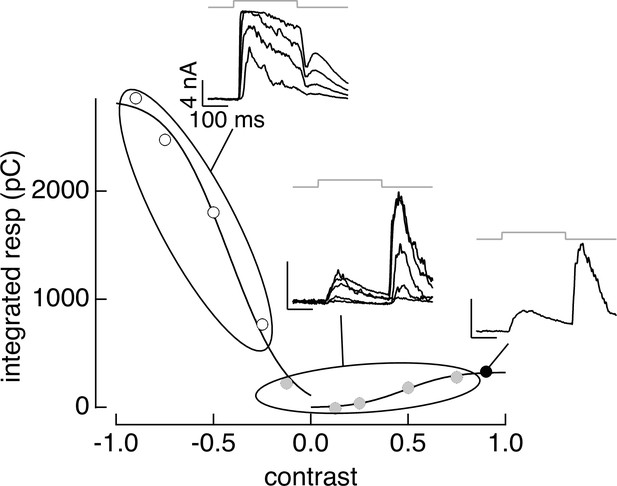
PCA-based clustering applied to contrast–response data.
The cluster definitions from responses to natural image patches were applied to responses to contrast increments and decrements. Same cell as Figure 3.
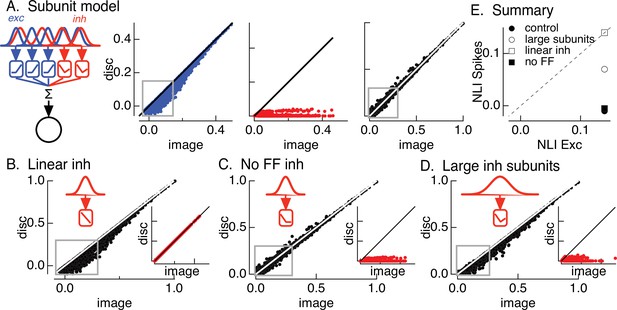
Crossover inhibitory synaptic input is necessary and sufficient for linear spatial integration.
(A) Model construction. (left) Architecture of subunit models. Parallel pathways generated excitatory (blue) and inhibitory (red) synaptic input to a retinal ganglion cell (RGC). Each pathway was composed of multiple subunits, each with a separate spatial filter and output nonlinearity. Excitatory and inhibitory subunits covered the same region of space but were positioned independently. (right) Excitatory inputs (blue), inhibitory inputs (red), and spike outputs (black) for ‘default’ model parameters (see Materials and methods). Gray boxes highlight patches that exhibit the strongest nonlinear spatial integration in excitatory inputs. (B) Spike output for model in which inhibitory synaptic input integrates linearly over space. (C) Spike output for model lacking feedforward inhibitory synaptic input. Feedforward inhibitory input was eliminated by changing the shape of the nonlinearity in the inhibitory pathway (inset). (D) Spike output for model in which the spatial filters for inhibitory subunits were doubled in size and the density of inhibitory subunits was correspondingly decreased. (E) Summary of difference in nonlinearity index (NLI) for spikes and excitatory input for several models for inhibitory input (see also Figure 2D).
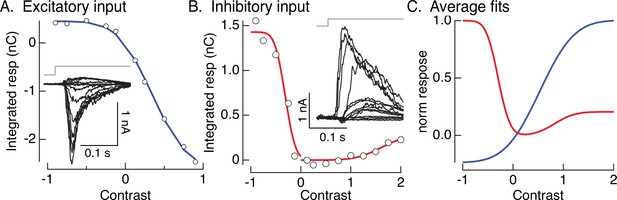
Contrast–response functions and fits.
(A, B) Examples of contrast–response functions for excitatory and inhibitory synaptic input to an On parasol cell. Insets show measured responses. Open circles are the integrals of the measured responses. Colored smooth curves are fits (cumulative Gaussians). (C) Average fits across cells. These are the nonlinearities used in the models of Figures 4A, 6,, 8.
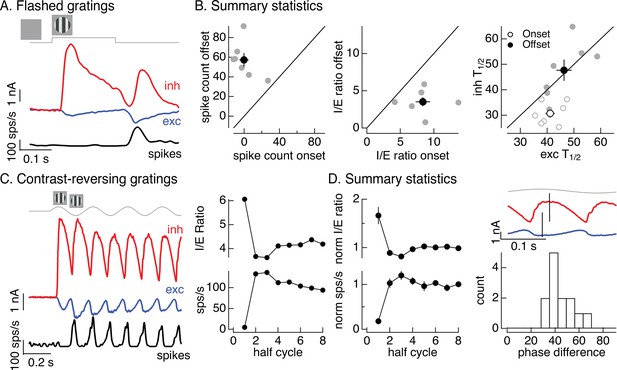
Time dependence of On parasol responses to flashed and contrast-reversing gratings.
(A) Excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs and spike response to a flashed grating. (B) Summary of responses to flashed gratings from seven On parasol retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). (left) Spike count at grating offset vs that at grating onset. Individual cells are in gray, mean (± standard error of the mean, SEM) is in black. (middle) Ratio of inhibitory input to excitatory input at grating offset vs that at grating onset. (right) Relative timing of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs, measured as the time to reach half-maximal amplitude. (C) (left) Excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs and spike output in response to a contrast-reversing grating modulated at 4 Hz. (right) I/E ratio and peak spike rate for each grating half-cycle. (D) Summary of statistics of grating responses across 13 On parasol RGCs. (left) I/E ratio (mean ± SEM) and spike rate (mean ± SEM) have been normalized by the mean value for a half-cycle number of 6 or more. (right) Histogram of time of peak excitatory input relative to inhibitory input. Response timing estimated by fitting each response with a sinusoid. For 4 Hz stimuli, a phase difference of 40° corresponds to 14 ms.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Source data for Figure 5B–D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70611/elife-70611-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
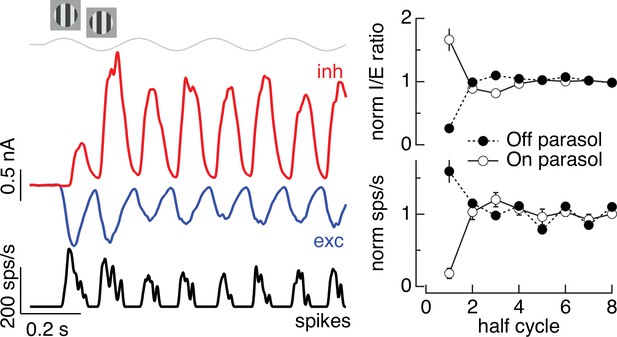
Time dependence of Off parasol responses to contrast-reversing gratings.
The left panel shows the spike response and excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs from an example Off parasol cell for conditions identical to the On parasol recordings in Figure 5. The right panel compares the I/E ratio (top) and spike count (bottom) for 13 On and 6 Off parasol cells (mean ± standard error of the mean [SEM]).
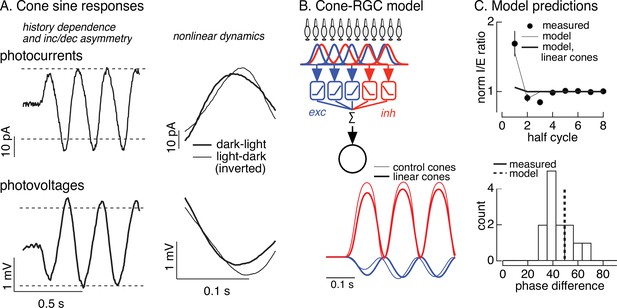
Nonlinearities in cone responses to contrast-reversing gratings and implications for On parasol synaptic inputs.
(A) Cone phototransduction currents elicited by contrast-reversing gratings exhibit three properties that could shape the time course of retinal ganglion cell (RGC) responses: (1) a dependence on stimulus history, (2) an asymmetry between light increments and decrements, and (3) a difference in kinetics of cones responding to light-to-dark vs dark-to-light transitions. Photocurrents are average responses to 5 Hz, 75% contrast sinusoidal stimuli from six cones. Photovoltages are average responses to 4 Hz, 50% contrast sinusoidal stimuli from 16 cones. Dashed horizontal lines are displaced equally above and below the mean response to highlight the asymmetry between increment and decrement responses. (B) Circuit model to explore how properties of cone responses from A could alter RGC responses. The model from Figure 4 was adapted to incorporate a first stage based on models for the cone responses (Figure 6—figure supplement 1). Subunit nonlinearities were set by measured contrast–response functions. Shown are examples of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs predicted by models with adapting and linear cone models. (C) Comparison of model predictions with experiment. (top) Histogram of I/E ratio from On parasol recordings (from Figure 5D) and predictions from models with adapting (thin line) and nonadapting (thick line) cones. (bottom) Histogram of phase difference between excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs elicited by contrast-reversing gratings (from Figure 5D) and prediction from model (dashed vertical line).
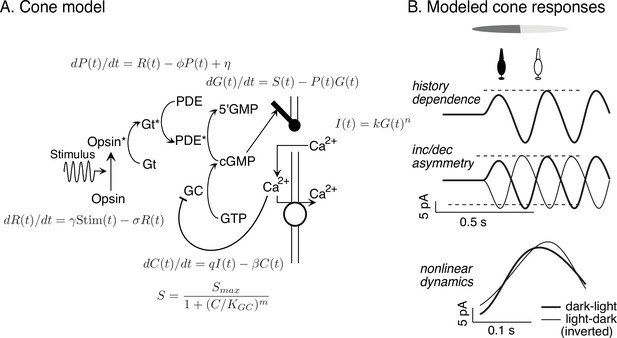
Cone model and responses to sinusoidal stimuli.
(A) Schematic of phototransduction cascade and differential equations that comprise the full (i.e., adapting) cone phototransduction model (see for details). R: receptor activity; PDE and P: phoshodiesterase; cGMP and G: cyclic GMP; GC: guanylate cyclase; S: cGMP synthesis rate; C: calcium concentration. γ, φ, σ, η, β, KGC: free model parameters. Predicted cone responses to sinusoidal grating stimulus. Compare to measured responses in Figure 6A. Dashed horizontal lines are displaced equally above and below the mean response to highlight the asymmetry between increment and decrement responses. (B) The full cone model reproduces the three experimentally-observed properties that could shape RGC dynamics: history dependence, an increment/decrement asymmetry, and nonlinear dynamics that result in differences between dark-to-light compared to light-to-dark responses.

Measured and predicted excitatory synaptic inputs in responses to contrast-reversing gratings across a range of frequencies.
Predictions are from the cone/subunit model in Figure 6B.
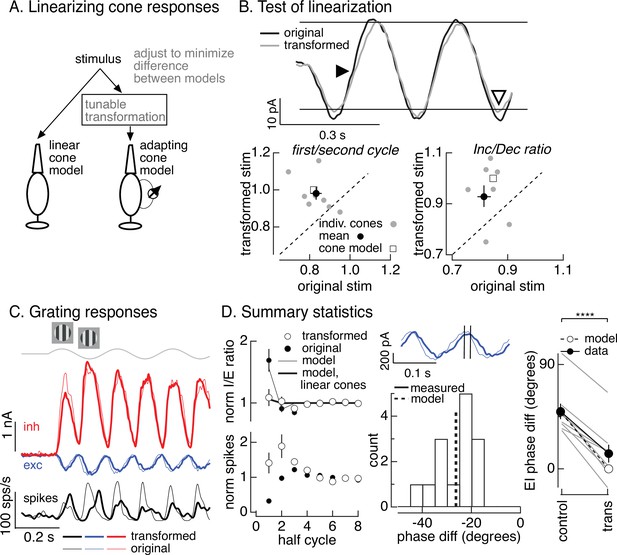
Minimizing cone adaptation minimizes time dependence of On parasol responses to contrast-reversing gratings.
(A) Approach to minimize nonlinearities in cone responses. Standard grating stimuli were transformed to minimize the difference between the modeled responses of an adapting cone responding to the transformed grating and a linear (nonadapting) cone responding to the original grating. (B) Test of procedure from A. (top) Measured cone responses to original (black) and transformed (gray) grating stimuli. (bottom) Summary across recorded cones. Responses to the transformed stimulus showed less history dependence (left; ratio of the amplitude of the measured response on the first cycle of the grating to that on the second cycle) and less of an increment/decrement asymmetry (right). Open squares show predictions from adapting cone model. (C) On parasol responses to original (thin traces) and transformed (thick traces) grating stimuli. (D) Summary of responses to original and transformed gratings from nine On parasol cells. (left) I/E ratios and spike counts have been normalized in each cell by the responses for grating half-cycles >6. (middle) Histogram of difference in timing of excitatory input in response to original and transformed gratings. A phase shift of 30° corresponds to a 21-ms difference in timing. (right) Difference in timing of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs for original and transformed gratings and prediction from model of Figure 6B (open circles and dashed line, **** denotes p < 0.0001 for difference in phase).
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Source data for Figure 7B–D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70611/elife-70611-fig7-data1-v2.xlsx
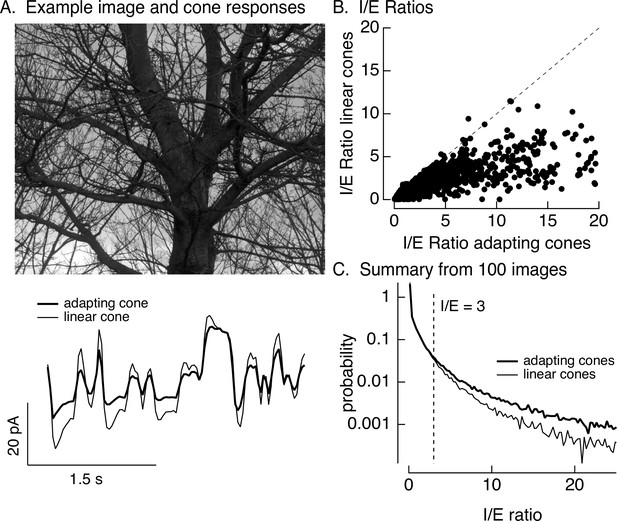
Cone adaptation substantially increases I/E ratio for natural images.
(A) The model from Figure 6B with either adapting or nonadapting cones was used to predict excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs during eye movements about a scene. Predicted cone photocurrents from the adapting and linear cone models are shown below the image. (B) I/E ratios were computed for every 30 ms time window for models incorporating adapting and linear cones. Ratios for linear cones were systematically smaller than those for adapting cones (i.e., most points fall below the unity line). (C) Histogram of I/E ratios, calculated as in B, for many images.
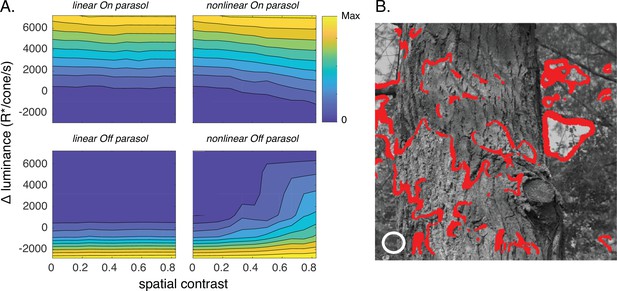
Joint activity of On and Off parasol retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) encodes patches with positive luminance and high spatial structure.
(A) Responses of On and Off parasol models as a function of the spatial contrast (x-axis) and change in mean luminance (y-axis) for a collection of image patches. Panels show predicted constant–response contours for both On and Off parasol RGC models for linear and nonlinear spatial integration. Mean luminance and spatial contrast were computed for a simulated receptive field center with a size shown by the white circle in B. Spatial contrast was defined as the standard deviation divided by the mean of the pixel values in the receptive field center. (B) Image patches eliciting activity of both On and Off parasol cells for the linear On parasol and nonlinear Off parasol RGC models. These are in the upper right corner of the contour plots in A.
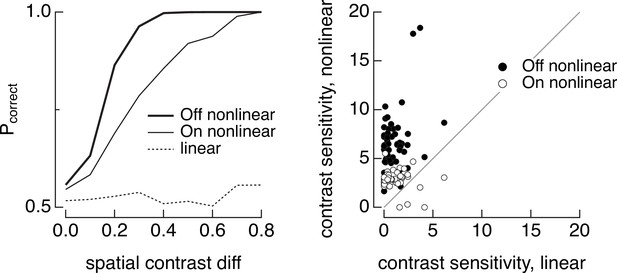
Discrimination of image patches with similar mean luminance (5000 R*/cone/s) but different spatial contrast for joint responses of On and Off parasol cells.
(left) The dashed line shows discrimination when both On and Off parasol retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) integrate linearly over space, the thin line shows discrimination when the the On parasol RGC integrates nonlinearly over space and the Off parasol integrates linearly, and the thick line shows discrimination when the Off parasol integrates nonlinearly and the On parasol linearly. (right) Summary of discrimination as in left panel across 50 images. Contrast sensitivity was defined as the inverse of the spatial contrast required for a probability of correct discrimination of 0.75.
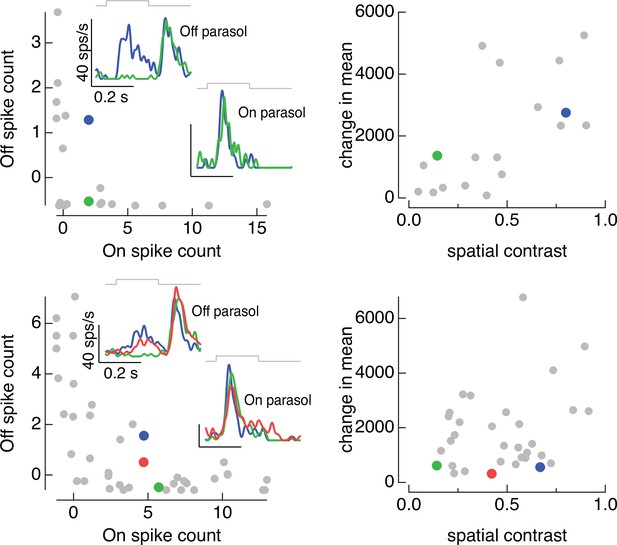
On and Off parasol cell responses to the same collection of image patches for two On/Off pairs.
(left) Spike count of responses of Off parasol cell plotted against that of On parasol for a collection of image patches. Insets show highlighted patches. (right) Mean and spatial contrast of each of the patches sampled on the left, with example patches highlighted. Spatial contrast was defined by dividing the standard deviation of the pixel values in the receptive field center by the mean pixel value.





