Activation of the EGFR/MAPK pathway drives transdifferentiation of quiescent niche cells to stem cells in the Drosophila testis niche
Figures
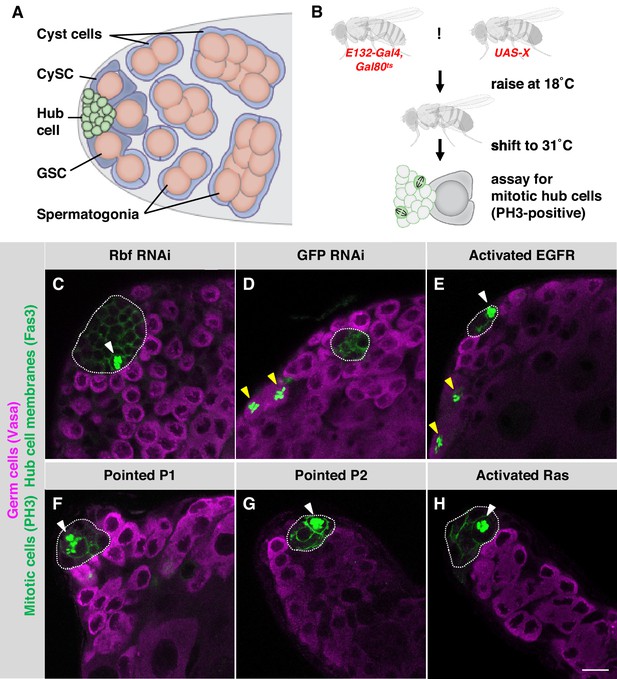
Activation of EGFR signaling in adult hub cells causes them to re-enter the cell cycle.
(A) Schematic of the Drosophila testis stem cell niche. Somatic hub cells (green) secrete signals to adjacent germline stem cells (GSCs, orange) and somatic cyst stem cells (CySCs, dark blue). Both types of stem cells divide asymmetrically to produce differentiating daughter cells. Somatic cyst cells (light blue) envelop clusters of spermatogonia (orange), and together they move away from the testis apex as they differentiate. (B) Schematic of the screen for signals that can trigger hub cells to re-enter the cell cycle. Candidate signaling pathway genes were conditionally mis-expressed in adult hub cells using the hub specific driver E132-Gal4, and mitotic hub cells were identified by immunostaining for phospho-histone H3 (PH3) (see main text for details). (C–H) Single confocal sections through the apex of testes immunostained for Fas3 (hub cell membranes, green), PH3 (mitotic chromosomes, nuclear green), and Vasa (germ cells, magenta). Hubs are outlined in white. Mitotic hub cells (white arrowheads) are found in positive control testes (with Rbf knockdown in the hub, C) and in testes over-expressing components of the canonical EGFR/MAPK pathway in the hub (E–H) but not in negative control testes (D). Mitotic cells are also found outside the hub in both control and experimental testes, as expected (yellow arrowheads). Scale bar (in H, for all panels) is 10 μm.
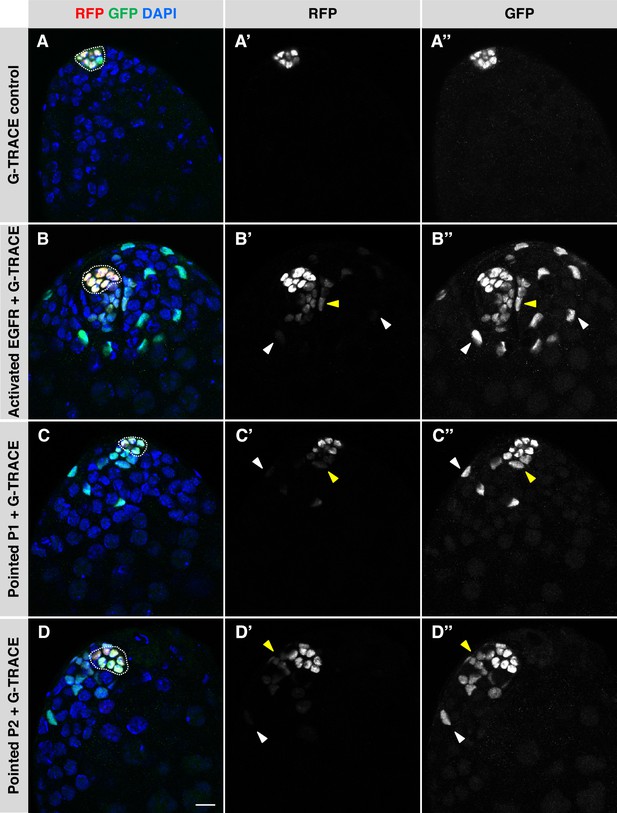
Activation of EGFR signaling in adult hub cells causes them to convert to CySCs.
(A–D) Single confocal sections through the apex of testes after 8 days of G-TRACE lineage tracing system expression in adult hub cells. Testes were immunostained for RFP (red fluorescent protein, marking current expression of the hub-specific driver E132-Gal4) and GFP (green fluorescent protein, marking both current and past expression of E132-Gal4) and counterstained with DAPI (blue; marks all nuclei). Hubs are outlined in white. (A'-D') Red channel alone, in white; (A"-D") green channel alone, in white. In control testes (A), hub cells expressing the G-TRACE system alone are marked with RFP and GFP, but no cells outside the hub are marked. In testes over-expressing components of the EGFR signaling pathway in the hub together with G-TRACE (B–D), hub cells are marked with RFP and GFP, and cells outside the hub are also marked, either with GFP and low levels of RFP (yellow arrowheads) or with GFP only (white arrowheads). The marked cells outside the hub appear to be cyst lineage cells that arose by conversion of hub cells to CySCs, which no longer express RFP once they lose their hub cell fate. Scale bar in D, for all panels, is 10 μm.
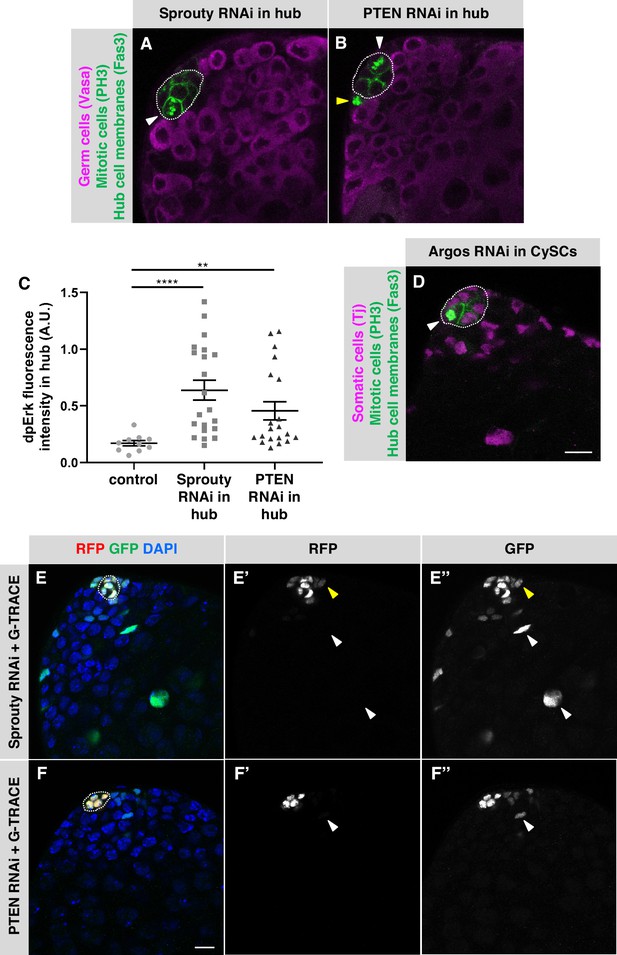
Negative regulators of EGFR signaling maintain hub cell quiescence and identity.
(A–B, D) Single confocal sections through the apex of testes immunostained for Fas3 (hub cell membranes, green), PH3 (mitotic chromosomes, nuclear green), and either (A–B) Vasa (germ cells, magenta) or (D) Traffic jam (Tj; somatic cell nuclei, magenta). Hubs are outlined in white. Mitotic hub cells (white arrowheads) are found after knockdown of Sprouty (A) or PTEN (B) in the hub or after knockdown of Argos (D) in cyst lineage cells. Mitotic cells outside the hub are also found (yellow arrowhead). (C) Quantification of dpERK levels in the hub in control, Sprouty knockdown, or Pten knockdown in the hub. dpErk levels in the hub are significantly higher when either Sprouty or Pten are knocked down in the hub than in control testes suggesting these proteins normally inhibit MAPK signaling in the hub. A.U., arbitrary units. Black bars indicate the mean and standard error. Unpaired t test, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001. (E–F) Single confocal sections through the apex of testes after 8 days of G-TRACE lineage tracing system expression in adult hub cells. Testes were immunostained for RFP (red, current expression of the hub-specific driver E132-Gal4) and GFP (green, current and past expression of the driver) and counterstained with DAPI (blue; marks all nuclei). Hubs are outlined in white. (E'-F') Red channel alone, in white; (E"-F") green channel alone, in white. After knockdown of Sprouty (E) or PTEN (F) in the hub together with expression of G-TRACE, hub cells are marked with RFP and GFP, and cells outside the hub are also marked, either with GFP and low levels of RFP (yellow arrowheads) or with GFP only (white arrowheads), suggesting that marked cyst lineage cells arose by conversion of hub cells to CySCs. Scale bars in D (for A-B, D) and in F (for E-F) are 10 μm.
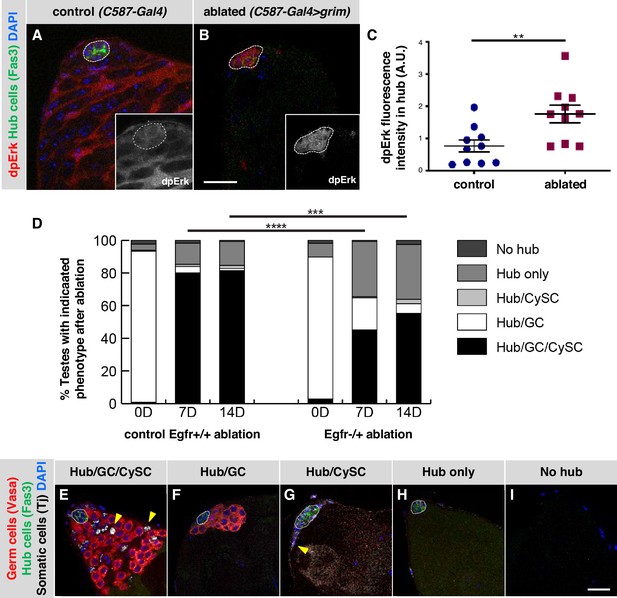
EGFR signaling is important for testis recovery from CySC ablation.
(A–B) Single confocal sections through the apex of testes immunostained for Fas3 (hub cell membranes, green), dpERK (EGFR pathway activation, red), and counterstained with DAPI (nuclei, blue). Hubs are outlined in white. Insets show the red channel alone, in white and enlarged. In control C587-Gal4, Gal80ts testes (A), dpERK levels are high in cyst lineage cells (indicating high levels of EGFR pathway activation) but low in hub cells. In C587-Gal4, Gal80ts > UAS grim testes (B), 2 days after genetic ablation of all CySCs and early cyst cells, dpERK levels are high in hub cells. Scale bar in B (for A-B) is 20 μm. (C) Quantification of dpERK levels in the hub in control (A) and ablated (B) testes. dpErk levels in the hub are significantly higher in ablated testes than in control testes. A.U., arbitrary units. Black bars indicate the mean and standard error. Unpaired t test, **p < 0.01. (D) Bar graph showing the distribution of testis phenotypes in control C587-Gal4, Gal80ts > UAS grim, Egfr+/+ flies ("control Egfr+/+ ablation") and in C587-Gal4, Gal80ts > UAS grim, Egfr-/+ flies ("EGFR-/+ ablation") at 0, 7, or 14 days after genetic ablation of CySCs and early cyst cells. After ablation (0 days), in both control and Egfr-/+ flies, most testes lack all CySCs and early cyst cells but retain a hub and germ cells (GC) as expected (white bars). At 7 and 14 days after ablation, fewer testes have regained CySCs and early cyst cells (black bars) in Egfr-/+ flies than in control flies and there is a significant difference in phenotype distribution. Chi square test, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. (E–I) Single confocal sections through the apex of testes at 7 days after ablation, immunostained for Vasa (germ cells, red), Fas3 (hub cell membranes, green), and Tj (somatic cell nuclei, white), and counterstained with DAPI (nuclei, blue), to illustrate the phenotypes listed in (D). Testes that recover CySCs and early cyst lineage cells have Tj-positive nuclei outside the hub (yellow arrowheads); most also contain germ cells (E) but a few contain just a hub and cyst cells (G). Testes that fail to recover CySCs and early cyst lineage cells can retain a hub and germ cells (F) or just a hub (H) or no hub or germ cells (I). Hubs are outlined in white. Scale bar in I (for E-I) is 20 μm.
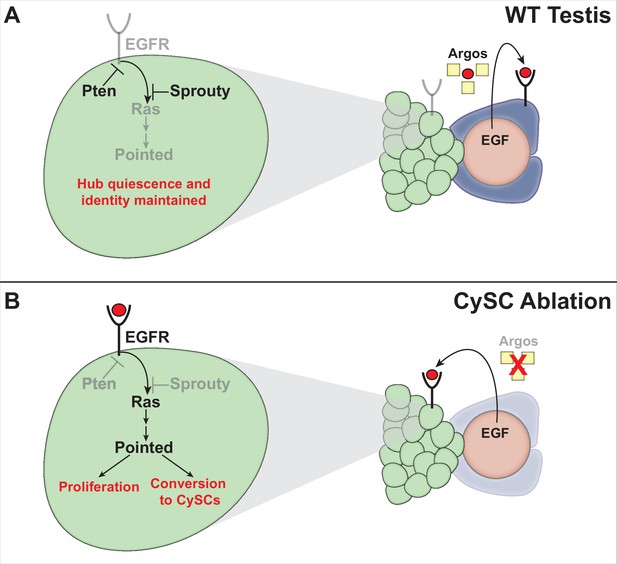
Model for cyst lineage recovery after ablation.
(A) In wild type testes, EGF ligands (red circles) are secreted by germ cells and received by cyst lineage cells. The EGFR pathway is repressed in hub cells by the secreted inhibitor Argos (yellow squares), which sequesters EGF ligands, and by intrinsic pathway inhibitors (Sprouty and PTEN). Hub quiescence and identity are maintained. (B) After genetic ablation of all CySCs and early cyst lineage cells, EGF ligands are no longer sequestered by Argos and are received by the hub. The EGFR pathway is activated in hub cells, driving expression of the downstream transcription factor Pointed and its target genes, resulting in hub cell proliferation and conversion to CySCs. As new CySCs are generated, Argos is once again expressed, down-regulating EGFR signaling in the hub.
Tables
Hub cell proliferation after EGFR pathway activation.
| Gal4 driver | UAS line (BDSC #) | Days at 31 °C | % Testes with PH3-positive hub cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | |||
| E132-Gal4, Gal80ts | UAS-Rbf-RNAi (41863) | 7 | 31% (n = 34/108)**** |
| UAS-Rbf-RNAi (36744) | 7 | 29% (n = 53/183)**** | |
| UAS-GFP-RNAi (9330 or 9331) | 7 | 0% (n = 0/237) | |
| C587-Gal4, Gal80ts | UAS-GFP-RNAi (9331) | 7 | 0% (n = 0/294) |
| Downstream Effectors and Transcription Factors | |||
| E132-Gal4, Gal80ts | UAS-Pointed.P1 (869) | 7 | 7% (n = 4/55)** |
| UAS-Pointed.P2 (399) | 7 | 6% (n = 6/100)*** | |
| UAS-Ras85D.V12 (4847) | 3 | 11% (n = 2/18)** | |
| 5 | 6% (n = 2/36)* | ||
| UAS-Rolled (59006) | 7 | 0% (n = 0/92)ns | |
| Receptors | |||
| E132-Gal4, Gal80ts | UAS-Egfr Type I (9534) | 7 | 1% (n = 1/143)ns |
| UAS-Egfr Type II (9533) | 7 | 4% (n = 5/117)** | |
| UAS-Egfr λ (59843) | 7 | < 1% (n = 1/163)ns | |
| UAS-PvR λ (58496) | 7 | 1% (n = 1/106)ns | |
| UAS-PvR λ (58428) | 7 | 0% (n = 0/156)ns | |
| UAS-InR (8250) | 7 | 0% (n = 0/48)ns | |
| UAS-InR (8263) | 7 | 0% (n = 0/41)ns | |
| UAS-Heartless λ (5367) | 7 | 2% (n = 3/181)ns | |
| UAS-Breathless λ (29045) | 7 | 0% (n = 0/90)ns | |
| Negative Regulators | |||
| E132-Gal4, Gal80ts | UAS-Sprouty-RNAi (36709) | 7 | 3% (n = 4/144)* |
| UAS-Pten-RNAi (33643) | 7 | 3% (n = 4/125)* | |
| UAS-Argos-RNAi (28383) | 7–8 | < 1% (n = 1/170)ns | |
| C587-Gal4, Gal80ts | UAS-Argos-RNAi (28383) | 7–8 | 2% (n = 6/348)* |
-
Percentages in bold are significant compared to the negative control (UAS-GFP-RNAi driven by the same Gal4 driver).
-
Fisher’s Exact Test: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns = not significant.
Hub cell proliferation upon EGFR and Notch signaling changes.
| UAS lines (with E132-Gal4, Gal80ts) | Source | Days at 31 °C | % Testes with PH3-positive hub cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | |||
| UAS-GFP-RNAi | BDSC 9330 or 9331 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/237)* |
| Egfr knockdown | |||
| UAS-Egfr-DN | BDSC 5364 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/103)†,ns |
| UAS-Egfr-RNAi | BDSC 36770 | 0% (n = 0/45)†,ns | |
| UAS-Egfr-RNAi | BDSC 60012 | 0% (n = 0/46)†,ns | |
| UAS-Egfr-RNAi | VDRC 43267 | 0% (n = 0/29)†,ns | |
| UAS-Egfr-RNAi✝✝ | VDRC 107130 | 0% (n = 0/43)†,ns | |
| Notch over-expression or knockdown | |||
| UAS-N-CA | BDSC 52008 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/48)†,,ns |
| UAS-N-DN | BDSC 51667 | 0% (n = 0/54)†,ns | |
| UAS-N-RNAi | BDSC 33611 | 0% (n = 0/119)†,ns | |
| UAS-N-RNAi | BDSC 33616 | 0% (n = 0/63)†,ns | |
| UAS-N-RNAi | BDSC 35213 | 0% (n = 0/29)†,ns | |
| UAS-N-RNAi | BDSC 35640 | 0% (n = 0/26)†,ns | |
| Egfr over-expression and Notch combinations | |||
| UAS-Egfr Type II | BDSC 9533 | 7 | 4% (n = 5/117)* |
| UAS-EGFR Type I; UAS-EGFR Type II | BDSC 9533 + 9534 | 7–8 | 4% (n = 11/301)‡,ns |
| UAS-N-DN; UAS-EGFR Type II | BDSC 9533 + 51667 | 3% (n = 4/138)‡,ns; §,ns | |
| UAS-N-CA; UAS-EGFR Type II | BDSC 9533 + 52008 | 6% (n = 12/205)‡,ns; §,ns | |
| Sprouty knockdown and Notch combinations | |||
| UAS-Sprouty-RNAi | BDSC 36709 | 7 | 3% (n = 4/144)* |
| UAS-EGFR Type I; UAS-Sprouty-RNAi | BDSC 36709 + 9534 | 7–8 | 3% (n = 3/101)¶,ns |
| UAS-N-DN; UAS-Sprouty-RNAi | BDSC 36709 + 51667 | 1% (n = 1/129)¶,ns; **,ns | |
| UAS-N-CA; UAS-Sprouty-RNAi | BDSC 36709 + 52008 | 0% (n = 0/80) ¶,ns; **,ns | |
-
Fisher’s Exact Test: ns = not significant.
-
*
Data from Table 1. ✝✝Another UAS-Egfr-RNAi line, BDSC 36773, did not show a phenotype with the control driver (C587-Gal4) and is not included here.
-
†
Compared with UAS-GFP RNAi.
-
‡
Compared with UAS-EGFR Type II.
-
§
Compared with UAS-EGFR Type I; UAS-EGFR Type II.
-
¶
Compared with UAS-Sprouty RNAi.
-
**
Compared with UAS-EGFR Type I; UAS-Sprouty RNAi.
Hub cell fate conversion after EGFR pathway activation.
| Gal4 driver | UAS lines (BDSC #) | Days at 29 °C | % Testes with GFP-marked cells outside the hub |
|---|---|---|---|
| E132-Gal4, Gal80ts | UAS-G-TRACE (28280) | 8 | 0% (n = 0/39) |
| UAS-G-TRACE (28280); UAS-Egfr Type II (9533) | 61% (n = 19/31)**** | ||
| UAS-G-TRACE (28280); UAS-Pointed.P1 (869) | 38% (n = 19/50)**** | ||
| UAS-G-TRACE (28280); UAS-Pointed.P2 (399) | 22% (n = 4/18)** | ||
| UAS-G-TRACE (28280); UAS-Sprouty-RNAi (36709) | 36% (n = 32/89)**** | ||
| UAS-G-TRACE (28280); UAS- Pten-RNAi (33643) | 18% (n = 6/34)** | ||
| E132-Gal4, Gal80ts | UAS-G-TRACE (28281) | 8 | 0% (n = 0/84) |
| UAS-Egfr Type I (9534); UAS-G-TRACE (28281) | 2% (n = 1/47)ns |
-
Percentages in bold are significant compared to the negative control (corresponding UAS-G-TRACE alone).
-
Fisher’s Exact Test: **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001, ns = not significant.
Overexpression of EGF ligands in the adult testis niche does not cause hub cell proliferation.
| Gal4 driver | UAS line | Source | Days at 31 °C | % Testes with PH3-positive hub cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C587-Gal4, Gal80ts | UAS-GFP-RNAi | BDSC 9330 or 9331 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/294)* |
| UAS-secreted spitz | BDSC 63134 | 7–9 | 0% (n = 0/219)a,ns | |
| UAS-secreted spitz | BDSC 58436 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/75)a,ns | |
| UAS-gurken ΔTC | Queenan et al., 1999 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/82)a,ns | |
| UAS-secreted gurken | BDSC 58417 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/118)a,ns | |
| UAS-secreted keren | Urban et al., 2002 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/113)a,ns | |
| UAS-vein | Schnepp et al., 1996 | 6 | 0% (n = 0/96)a,ns | |
| E132-Gal4, Gal80ts | UAS-GFP-RNAi | BDSC 9330 or 9331 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/237)* |
| UAS-secreted spitz | BDSC 63134 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/208)a,ns | |
| UAS-secreted spitz | BDSC 58436 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/92)a,ns | |
| UAS-gurken ΔTC | Queenan et al., 1999 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/86)a,ns | |
| UAS-secreted gurken | BDSC 58417 | 7 | 1% (n = 1/77)a,ns | |
| UAS-secreted keren | Urban et al., 2002 | 7 | 0% (n = 0/113)a,ns | |
| UAS-vein | Schnepp et al., 1996 | --- | --- | |
| C587-Gal4, Gal80ts | UAS-secreted spitz +UAS-Argos-RNAi | BDSC 63134 +BDSC 28383 | 7–9 | 2% (n = 4/203)b,ns |
Ablation phenotypes with and without reduced EGFR.
| Genotype | Days recovered | Hub/GC/CySC | Hub/GC | Hub/CySC | Hub only | No hub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/+; Tub-Gal80ts | 0 | < 1%(n = 2/213) | 93%(n = 197/213) | < 1%(n = 1/213) | 4%(n = 8/213) | 2%(n = 5/213) |
| C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/ EgfrF24; Tub-Gal80ts | 0*,§,ns | 3%(n = 3/108) | 87%(n = 94/108) | 0%(n = 0/108) | 8%(n = 9/108) | 2%(n = 2/108) |
| C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/+; Tub-Gal80ts | 7 | 80%(n = 180/225) | 4%(n = 9/225) | 1%(n = 3/180) | 13%(n = 29/225) | 2%(n = 4/225) |
| C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/ EgfrF24; Tub-Gal80ts | 7†,§,**** | 45%(n = 64/142) | 20%(n = 28/142) | < 1%(n = 1/142) | 34%(n = 48/142) | < 1%(n = 1/142) |
| C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/+; Tub-Gal80ts | 14 | 81%(n = 123/151) | 1%(n = 2/151) | 2%(n = 3/151) | 15%(n = 22/151) | < 1%(n = 1/151) |
| C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/ EgfrF24; Tub-Gal80ts | 14‡,§,*** | 55%(n = 64/116) | 6%(n = 7/116) | 3%(n = 3/116) | 33%(n = 39/116) | 3%(n = 3/116) |
-
*
Compared with C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/+; Tub Gal80ts at 0 days recovered.
-
†
Compared with C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/+; Tub Gal80ts at 7 days recovered.
-
‡
Compared with C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/+; Tub Gal80ts at 14 days recovered.
-
§
Chi Square Test: ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns = not significant.
Percentage of testes with ectopic hubs after 14 day recovery from CySC ablation.
| Genotype | DaysRecovered | % Recovered Testes with Ectopic Hubs | % Recovered Testes without Ectopic Hubs |
|---|---|---|---|
| C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/+; Tub-Gal80ts | 14 | 29%(n = 139/487) | 71%(n = 348/487) |
| C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/EgfrF24; Tub-Gal80ts | 14**** | 12%(n = 32/270) | 88%(n = 238/270) |
-
Fisher’s Exact Test: ****p < 0.0001 (compared to testes with ectopic hubs in control C587-Gal4; UAS-Grim/+; Tub-Gal80ts flies).
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | E132Gal4: P{w[ + mW.hs] = GawB}E132, w[*] (also called upd-Gal4) | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_26796 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | TubGal80ts: w[*];P{w[ + mC] = tubP-GAL80[ts]}2/TM2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:DSC_7017 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-GFP RNAi: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS GFP.dsRNA.R}142 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_9330 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-GFP RNAi: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS GFP.dsRNA.R}143 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_9331 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Rbf RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS03004}attP2/TM3, Sb1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_36744 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Rbf RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL01293}attP40/CyO | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41863 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | C587Gal4: P{w[ + mW.hs] = GawB}C587, w[*] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_67747 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Pointed.P1: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] pnt[P1.UAS] = UAS pnt.P1}3 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_869 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Pointed.P2: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] pnt[P2.UAS] = UAS pnt.P2}2/TM3, Sb1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_399 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Ras85D.V12: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS-Ras85D.V12}TL1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_4847 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Rolled: y1 w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS-rl[Sem].S}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_59006 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Egfr Type I: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = Egfr.1 .A887T.UAS}12–4/CyO, P{ry[ + t7.2] = sevRas1 .V12}FK1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_9534 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Egfr Type II: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = Egfr.2 .A887T.UAS}8–2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_9533 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Egfrλ: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS Egfr.lambdatop}3/TM6C, Sb1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_59843 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-PVRλ: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UASp Pvr.lambda}mP10 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_58496 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-PVRλ: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UASp Pvr.lambda}mP1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_58428 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-InR: y1 w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS InR.K414P}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_8250 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-InR: y1 w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS InR.A1325D}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_8263 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Heartlessλ: y1 w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS htl.lambda.M}40-22-2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_5367 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Breathlessλ: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS btl.lambda}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_29045 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Sprouty RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS01599}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_36709 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Pten RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00044}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_33643 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Argos RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.JF03020}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_28383 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Egfr DN: y1 w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS Egfr.DN.B}29-77-1; P{w[ + mC] = UAS Egfr.DN.B}29-8-1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_5364 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Egfr RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.JF02283}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_36770 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Egfr RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS05003}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_60012 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Egfr RNAi: w1118; P{GD1654}v43267 | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | Stock #: 43,267 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Egfr RNAi: P{KK100051}VIE-260B | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | Stock #: 107,130 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-N-CA: P{ry[ + t7.2] = hsFLP}1, y1 w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS N.intra.GS}2/CyO; MKRS/TM2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_52008 | No longer available |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-N-DN: y[ + t7.2] = hsFLP}12, y1 w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS N.ECN}2; MKRS/TM2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_51667 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Notch RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00001}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_33611 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Notch RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00009}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_33616 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Notch RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL00092}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_35213 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Notch RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.GLV21004}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_35620 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-G-TRACE: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS-RedStinger}4, P{w[ + mC] = UAS FLP.D}JD1, P{w[ + mC] = Ubi-p63E(FRT.STOP)Stinger}9F6/CyO | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_28280 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-G-TRACE: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS-RedStinger}6, P{w[ + mC] = UAS FLP.Exel}3, P{w[ + mC] = Ubi-p63E(FRT.STOP)Stinger}15F2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_28281 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-secreted spitz: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS-sSpiCS}T28 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_63134 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-secreted spitz: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UASp spi.sec}3/TM3, Ser1() | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_58436 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-secreted gurken: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UASp grk.sec}2/CyO | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_58417 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-gurken ΔTC | PMID: 10559478 | Dr. Trudi Schüpbach (Princeton University) | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS- secreted Keren | PMID:12169630 | Dr. Matthew Freeman (MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology) | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Vein | PMID:8824589 | Dr. Amanda Simcox (The Ohio State University) | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Grim | PMID:9846179 | Dr. John Nambu (University of Massachusetts) | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Egfr(-): Egfr[f24]/T(2;3)TSTL, CyO: TM6B, Tb1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_6500 | |
| Antibody | (Mouse monoclonal) anti–Fasciclin III (Drosophila) | DSHB | Cat#: 7G10; RRID: AB_528238 | IHC (1:50) |
| Antibody | (Mouse monoclonal) anti-phospho-Histone H3 (Ser10) (6G3) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#: 9,706 S; RRID:AB_331748 | IHC (1:400) |
| Antibody | (Guinea Pig polyclonal) anti-Traffic Jam | Laboratory of D. Godt (Li et al., 2003) | N/A | IHC (1:20,000) |
| Antibody | (Rabbit polyclonal) anti-Vasa (d-260) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat#: SC-30210; RRID:AB_793874 | IHC (1:200) |
| Antibody | (Chicken polyclonal) anti-GFP | Abcam | Cat#: ab13970; RRID:AB_300798 | IHC (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | (Rabbit polyclonal) anti-DsRed | Takara Bio | Cat#: 632496; RRID:AB_10013483 | IHC (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | (Rabbit polyclonal) anti-dpErk | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#: 4370; RRID:AB_2315112 | IHC (1:100) |
| Antibody | (Goat polyclonal) anti-Mouse IgG (H + L) secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat#: A11029; RRID:AB_2534088 | IHC (1:400) |
| Antibody | (Goat polyclonal) anti-Rabbit IgG (H + L) secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 568 conjugate | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat#: A11011; RRID:AB_143157 | IHC (1:200) |
| Antibody | (Goat polyclonal) anti-Chicken IgY (H + L) secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat#: A11039; RRID:AB_2534096 | IHC (1:400) |
| Antibody | (Goat polyclonal) anti-Guinea Pig IgG (H + L) secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 568 conjugate | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat#: A11075; RRID:AB_2534119 | IHC (1:200) |
| Antibody | (Goat polyclonal) anti-Guinea Pig IgG (H + L) secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 633 conjugate | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat#: A21105; RRID:AB_2535757 | IHC (1:200) |
| Chemical compound, drug | 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) | Millipore/Sigma (formerly Sigma-Aldrich) | Cat#: 10236276001; CAS: 28718-90-3 | IHC (1 μg/mL) |
| Chemical compound, drug | 16% Paraformaldehyde (formaldehyde) aqueous solution | Electron Microscopy Sciences | Cat#: 15710; CAS: 50-00-0 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Goat Serum | Millipore/Sigma (formerly Sigma-Aldrich) | Cat#: G9023 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Vectashield antifade mounting medium | Vector Laboratories | Cat#: H-1000 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail 2 | Millipore/Sigma (formerly Sigma-Aldrich) | Cat#: P5726 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMSO (Dimethyl Sulfoxide), Sterile | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#: 12,611 P | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | Schindelin et al., 2012 | https://www.fiji.sc/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Zeiss LSM | Carl Zeiss Microscopy | https://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/us/downloads/lsm-5-series.html | |
| Software, algorithm | Zen | Carl Zeiss Microscopy | https://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/int/products/microscope-software/zen.html | |
| Software, algorithm | Prism 6 | GraphPad | http://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ |
Screen Summary.
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Pathway | AdditionalInformation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-EcR-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMC03114}attP2/TM3, Sb1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50712 | Ecdysone | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Ecr RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMJ22371}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_58286 | Ecdysone | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-btl-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS02038}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_ 40871 | FGFR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-btl-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS02656}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_43544 | FGFR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-btl-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMC04140}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_55870 | FGFR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-btl-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS05005}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_ 60013 | FGFR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-htl-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS01437}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_35024 | FGFR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-htl-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS04514}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_57313 | FGFR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-htl-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMJ22375}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_ 58289 | FGFR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Galphaf-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL01545}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_43201 | GPCR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Galphai-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS01273}attP2/TM3, Sb1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_34924 | GPCR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Galphai-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL00328}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_ 35407 | GPCR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Galphai-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS02138}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40890 | GPCR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Galphao-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS01129}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_34653 | GPCR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Galphaq-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.JF02464}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_33765 | GPCR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Galphaq-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS03015}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_36775 | GPCR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Galphaq-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL01048}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_36820 | GPCR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Galphas-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMC03106}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50704 | GPCR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-ci: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS ci.HA.wt}3 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_32570 | Hedgehog | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Ci-activated: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS HA.ci.m1-3*103}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_32571 | Hedgehog | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-ci-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMC05801}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_64928 | Hedgehog | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Hmgcr-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMC03053}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50652 | Hedgehog | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-hpo-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00006}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_33614 | Hippo | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-hpo-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL00046}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_35176 | Hippo | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-yki-activated: w[*]; P{y[ + t7.7] w[ + mC] = UAS yki.S111A.S168A.S250A.V5}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_28817 | Hippo | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-yki-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00041}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_34067 | Hippo | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Akt: y1 w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS Akt.Exel}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_8191 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Akt-activated: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS-myr-Akt1.V}3/TM3, Sb1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_50758 | InR | No longer available |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Akt-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00007}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_33615 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Akt-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.JF02668}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_27518 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Foxo: y1 w[*]†; P{w[ + mC] = UAS foxo.P}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_9575 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Foxo: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UASp foxo.S}3 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_42221 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Foxo: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UASp foxo.GFP}3 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_43633 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Foxo: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UASp foxo.GFP}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_44214 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Foxo RNAi: y[1] sc[*] v[1] sev[21]; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00422}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_32427 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Foxo RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00793}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_32993 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-InR-DN: y1 w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS InR.K1409A}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_8252 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-InR-DN: y1 w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS InR.K1409A}3 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_8253 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-InR-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS03166}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_51518 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Pi3K21B: y1 w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS-Pi3K21B.HA}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_25899 | InR | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-dome-RNAi: w[1118]; P{GD14494}v36356 | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | Stock #: 36356 | Jak-Stat | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-dome-RNAi:P{KK104700}VIE-260B | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | Stock #: 106071 | Jak-Stat | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-hop-activated: w; UAS-hop[TumL]/CyO | PMID:7796812 | Jak-Stat | Dr. Norbert Perrimon(Harvard Medical School) | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Stat92E-RNAi: w[1118]; P{GD4492}v43866 | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | Stock #: 43866 | Jak-Stat | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Stat92E-RNAi:P{KK100519}VIE-260B | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | Stock #: 106980 | Jak-Stat | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-upd1 | PMID: 10346822 | Jak-Stat | Dr. David Strutt (Harvard Medical School) | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-upd1-RNAi: w[1118]; P{GD1158}v3282 | Stock #: 3282 | Jak-Stat | ||
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-upd1-RNAi: y[1] sc[*] v[1] sev[21]; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00545}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_33680 | Jak-Stat | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-upd2-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00901}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_33949 | Jak-Stat | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-upd2-RNAi:1sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00948}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_33988 | Jak-Stat | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-upd3-RNAi: y1 sc[ *]‡ v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00646}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_32859 | Jak-Stat | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-hep-activated: y1 w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS hep.CA}4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_6406 | Jnk | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-hep-activated: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS Hep.Act}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_9306 | Jnk | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-kay: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS-Fra}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_7213 | Jnk | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-kay-DN: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS Fra.Fbz}5 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_7214 | Jnk | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-kay-DN: y1 w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS Fra.Fbz}7 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_7215 | Jnk | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-jra: y1 w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS-Jra}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_7216 | Jnk | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-kay-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00254}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_33379 | Jnk | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-wgn-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMC03962}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_55275 | Jnk | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-egr-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMC03963}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_55276 | Jnk | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Pvr-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS01662}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_37520 | Pvr | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Pvf1-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS01958}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_39038 | Pvr | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Pvr-DN: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UASp Pvr.DN}D1/CyO | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_58430 | Pvr | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Pvr-DN: w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UASp Pvr.DN}D7 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_58431 | Pvr | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-aop: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS aop.WT}Ia/CyO | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_5790 | RTK | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-aop-activated: w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS aop.ACT}IIa | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_5789 | RTK | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-pnt-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS01452}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_35038 | RTK | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-rl-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00173}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_34855 | RTK | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-rl-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL00215}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_36058 | RTK | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-sev-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.JF02393}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_36778 | RTK | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-sev-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMC04136}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_55866 | RTK | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-tor-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00021}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_33627 | RTK | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-tor-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMJ22419}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_58312 | RTK | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Mad:P{ry[ + t7.2] = hsFLP}12, y1 w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS Mad.FLAG}2; P{y[ + t7.7] w[ + mC] = mir-ban-lacZ.brC12}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_44256 | TGFβ | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Mad-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.GLV21013}attP2/TM3, Sb1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_35648 | TGFβ | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Mad-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL01527}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_43183 | TGFβ | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Smox-RNAi:1sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS02203}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_41670 | TGFβ | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Smox-RNAi: y1 v1; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL01476}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_43138 | TGFβ | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-cact-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00084}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_34775 | Toll | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-cact-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL00627}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_37484 | Toll | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-dl: y1 w[*]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS dl.H}2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_9319 | Toll | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-dl-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00727}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_32934 | Toll | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-dl-RNAi:y1sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS00028}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_34938 | Toll | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-dl-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL00610}attP40 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_36650 | Toll | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-dl-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP .GL00676}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_38905 | Toll | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-arm-RNAi: y1 sc[*] v1 sev21; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS01414}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_35004 | Wnt | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-pan: y1 w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS pan.dTCF}24/CyO | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_4837 | Wnt | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-pan: y1 w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS pan.dTCF}4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_4838 | Wnt | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-pan-constitutive repressor: y[1] w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS pan.dTCFDeltaN}4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_4784 | Wnt | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-pan-constitutive repressor: y[1] w[1118]; P{w[ + mC] = UAS pan.dTCFDeltaN}5 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_4785 | Wnt | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-pan-RNAi: y v; P{y[ + t7.7] v[ + t1.8] = TRiP.HMS02015}attP40/CyO | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID:BDSC_40848 | Wnt | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-wg-RNAi: w[1118]; P{GD5007}v13352 | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | Stock #: 13352 | Wnt |
-
*
n = at least 20–199 testes for all lines.
-
†
lines listed in the key resource table are not repeated here.
-
‡
no lines listed here had significant numbers of dividing hub cells compared to UAS-GFP-RNAi controls.





