Ovipositor and mouthparts in a fossil insect support a novel ecological role for early orthopterans in 300 million years old forests
Figures
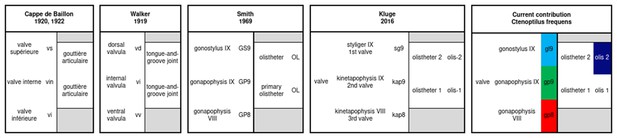
Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov., holotype (CNU-NX1-326).
(A) Habitus drawing and (B) habitus photograph (composite); (C–D) details of head and right foreleg (location as indicated in B), (C) color-coded interpretative drawing and (D) photograph (composite); and (E–F) details of ovipositor (location as indicated in B), (E) drawing and (F) photograph (composite). Color-coding and associated abbreviations: red, lacina (la); dark blue-purple, mandible (md); green, pharynx (pha). Other indications, head: ce, composite eye; f, frons; co, coronal cleavage line; fc, frontal cleavage line. Wing morphology abbreviations: LFW, left forewing; LHW, left hind wing; RFW, right forewing; RHW, right hind wing; ScP, posterior subcosta; RA, anterior radius; RP, posterior radius; M, media; CuA, anterior cubitus; CuPa, anterior branch of posterior cubitus; CuPb, posterior branch of posterior cubitus; AA, anterior analis. Photograph (composite). Color-coding and associated abbreviations: red, lacina (la); dark blue-purple, mandible (md); green, pharynx (pha). Other indications, head: ce, composite eye; f, frons; co, coronal cleavage line; fc, frontal cleavage line. Wing morphology abbreviations: LFW, left forewing; LHW, left hind wing; RFW, right forewing; RHW, right hind wing; ScP, posterior subcosta; RA, anterior radius; RP, posterior radius; M, media; CuA, anterior cubitus; CuPa, anterior branch of posterior cubitus; CuPb, posterior branch of posterior cubitus; AA, anterior analis.
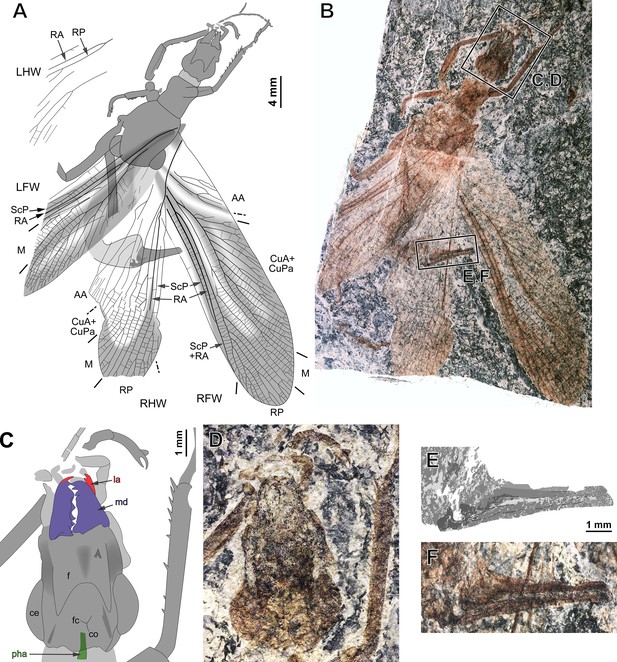
External ovipositor in Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov. in lateral view.
(A–C) Specimen CNU-NX1-749, (A) overview of the ovipositor with overlaid indications of the ovipositor parts (see also) overview of the ovipositor with overlaid indications of the ovipositor parts (see also Appendix 1—figure 7A–C) and (B, C) details of basal part of the same ovipositor as in A. (B) composite photograph and (C) reflectance transforming imaging (RTI) extract in normals visualization; (D–F) specimen CNU-NX1-742, (D) overview of the ovipositor with overlaid indications of the ovipositor parts (see also) overview of the ovipositor with overlaid indications of the ovipositor parts (see also Appendix 1—figure 8B and C) and (E, F) details of basal part of the same ovipositor as in D; (E) composite photograph and (F) RTI extract in normals visualization. Olistheter (‘olis’) configurations at different parts of each respective ovipositor are shown as insets. Abbreviations: Gonostylus IX (gs9); gonapophysis IX (gp9); gonapophysis VIII (gp8).
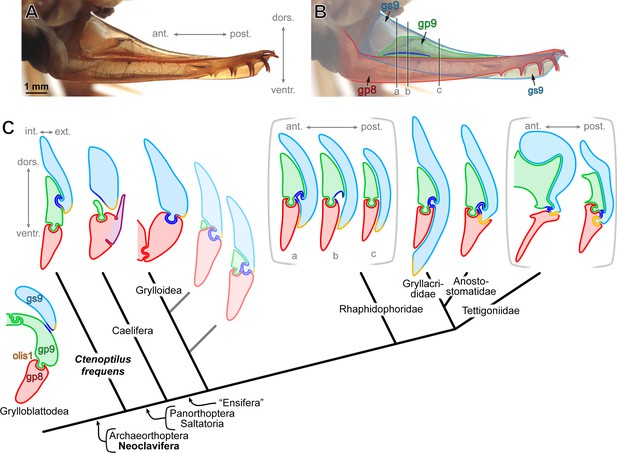
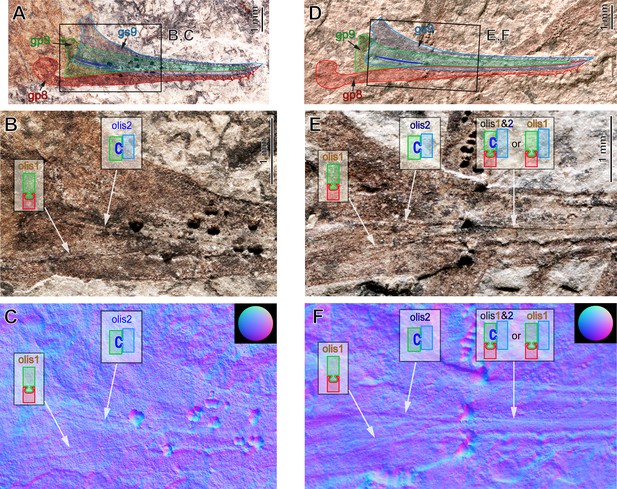
The evolution of major ovipositor configurations across Orthoptera.
(A) External ovipositor of external ovipositor of Ceuthophilus sp. (Orthoptera: Rhaphidophoridae; extant species) in laterial view (left side, flipped horizontally, left gonostylus IX [gs9] removed). (B) Same as above, but annotated. The three black vertical lines labelled ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’ indicate the position of the three schematic sections shown in C. (C) Schematic ovipositor cross-sections in Grylloblattodea, Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov., and several extant Orthoptera possessing well-developed ovipositors (not to scale; (see Appendix 1, Section 2.2). Ovipositor configurations are mapped onto the phylogenomic inference carried out by Song et al., 2020. Pale cross-section along the stem of Grylloidea is hypothetical; sections delineated by brackets represent conditions along the antero-posterior axis. Color-coding and associated abbreviations: light blue, gonostylus IX (gs9; light green, gonapophysis IX (gp9); red, gonapophysis VIII (gp8); royal blue, secondary olistheter (olis2); light orange, tertiary olistheter (olis3); purple, ‘lateral basivalvular sclerite’ (specific to Caelifera). Other indications: olis1, primary olistheter; int./ext., internal/external, respectively; dors./ventr., dorsal/ventral, respectively; and ant./post., anterior/posterior, respectively.
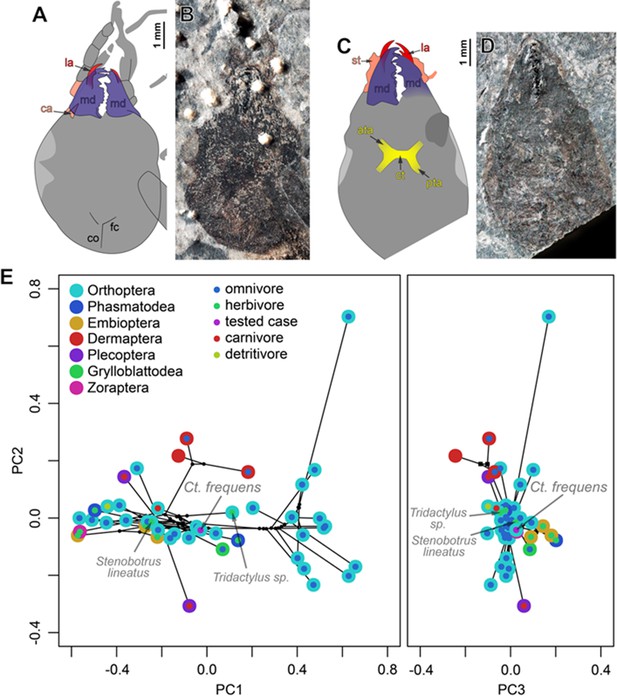
Head morphology (A–D) in Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov. and (E) mandibular mandibular mechanical advantage in Ct. frequens sp. nov. and a selection of polyneopteran species.
(A–B) Specimen CNU-NX1-754, (A) color-coded interpretative drawing, and (B) photograph (composite) (as located on Appendix 1—figure 7I); (C–D) Specimen CNU-NX1-764, (C) color-coded interpretative drawing, and (D) photograph (composite). (E) Principal component analysis of the mandibular mechanical advantage. Color-coding: (A–D) red, lacina (la); salmon, cardinal and stipital sclerites (ca and st, respectively); dark blue-purple, mandible (md); yellow, tentorium, including anterior tentorial arm (ata), posterior tentorial arm (pta), and corpotentorium (ct). Other indications: co, coronal cleavage line; fc, frontal cleavage line.

Reconstruction of a female of Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov. laying eggs.
Courtesy of Xiaoran Zuo.
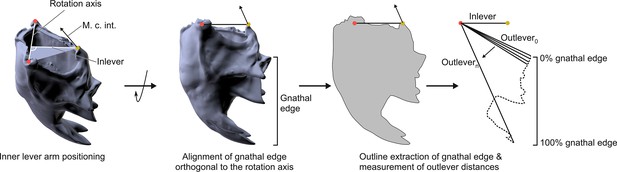
Workflow for the extraction of the mandibular mechanical advantage based on 3D models.
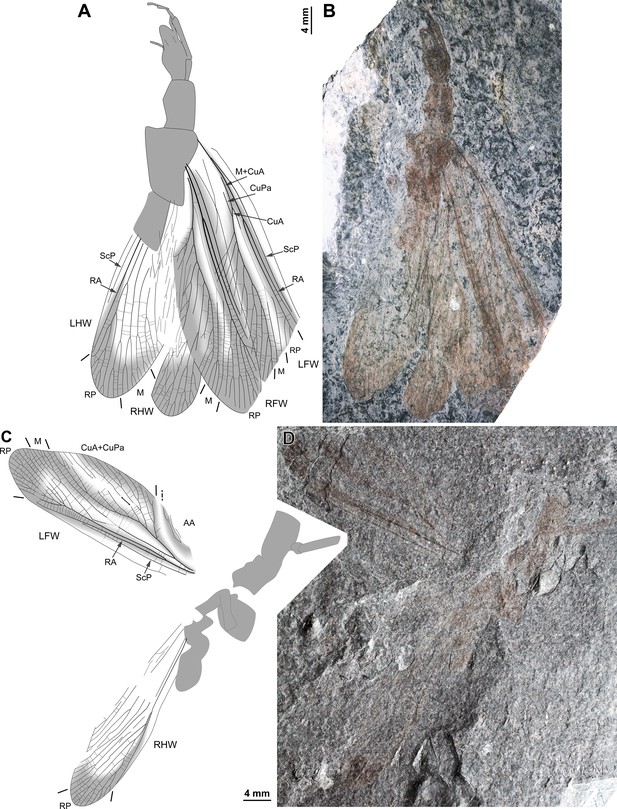

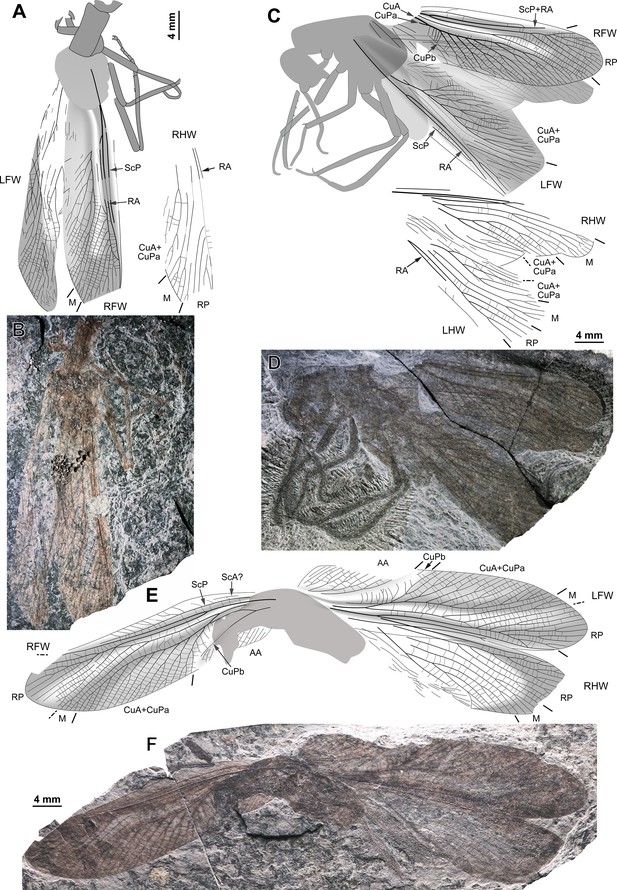
Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov., specimens composed of fore- and hind wings in connection with body remains.
(A–B) Specimen CNU-NX1-752; habitus, left forewing as positive imprint and right forewing and hind wings as negative imprints, (A) drawing and (B) photograph (composite). (C–D) Specimen CNU-NX1-738; habitus, right hind wing as positive imprints and left forewing as negative imprints, (C) drawing and (D) photograph (composite; slightly shifted vertically with respect to drawing).
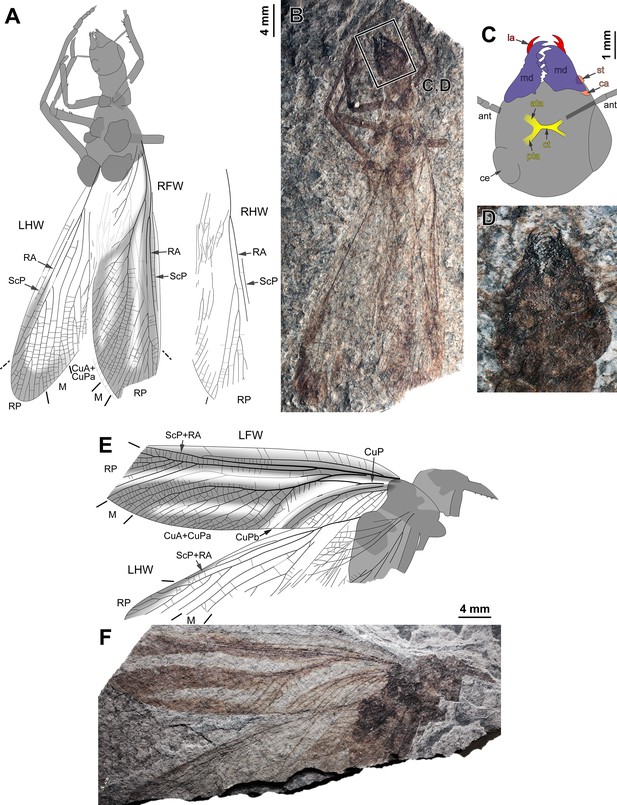
Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov., specimens composed of fore- and hind wings in connection with body remains.
(A–B) Specimen CNU-NX1-759; habitus, left hind wing as positive imprint and right wings as negative imprints, (A) drawing (for clarity, drawing of right hind wing venation duplicated and relocated, original location in light grey on complete drawing) and (B) photograph (composite). (C–D) Specimen CNU-NX1-750; habitus, all wings as negative imprints, (C) drawing (for clarity, drawing of hind wings venation duplicated and relocated, original location in light grey on complete drawing) and (D) photograph (composite). (E–F) Specimen CNU-NX1-731; habitus, left forewing as positive imprint and right forewing and right hind wing as negative imprints, (E) drawing and (F) photograph (composite).
Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov., specimens composed of fore- and hind wings in connection with body remains.
(A–D) Specimen CNU-NX1-747; (A–B) habitus, all wings as negative imprints, (A) drawing (for clarity, drawing of right hind wing venation duplicated and relocated, original location in light grey on complete drawing) and (B) photograph (composite); and (C–D) details of head (location as indicated in B), polarity unclear, (C) color-coded interpretative drawing, and (D) photograph (composite). Color-coding: red, lacina (la); salmon, cardinal and stipital sclerites (ca and st, respectively); dark blue-purple, mandible (md); yellow, tentorium, including anterior tentorial arm (ata), posterior tentorial arm (pta), and corpotentorium (ct). Other indications: ant, antenna; ce, composite eye. (E–F) Specimen CNU-NX1-741; habitus, all wings as positive imprints, (E) drawing and (F) photograph (composite).
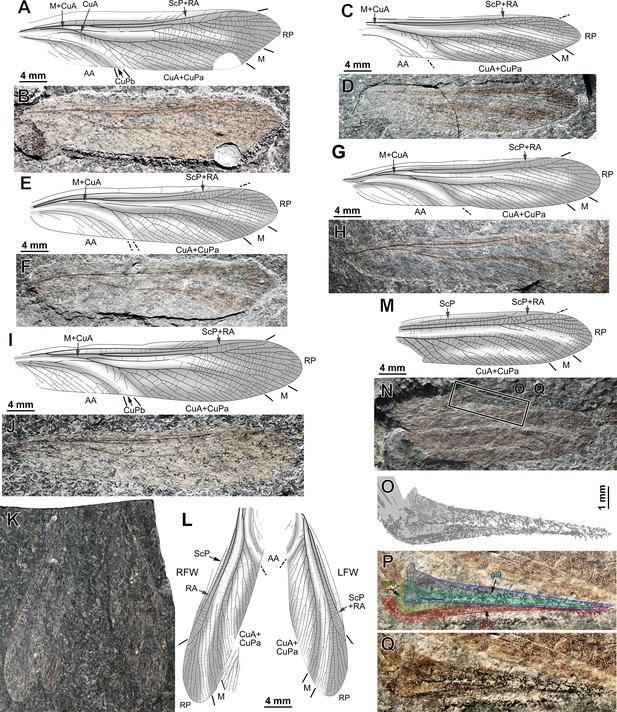
Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov., specimens composed of forewings, isolated or by pair, and forewing and ovipositor.
(A–B) Specimen CNU-NX1-748; right forewing, negative imprint, (A) drawing and (B) photograph (composite, flipped horizontally, light-mirrored). (C–D) Specimen CNU-NX1-732; right forewing, positive imprint, (C) drawing and (D) photograph (composite). (E–F) Specimen CNU-NX1-757; right forewing, negative imprint, (E) drawing and (F) photograph (composite, flipped horizontally, light-mirrored). (G–H) Specimen CNU-NX1-758; left forewing, negative imprint, (G) drawing and (H) photograph (composite). (I–J) Specimen CNU-NX1-744; right forewing, negative imprint, (I) drawing and (J) photograph (composite, flipped horizontally, light-mirrored). (K–L) Specimen CNU-NX1-751; forewing pair, both as negative imprints, and apical fragment of a hind wing, (K) drawing and (L) photograph (composite). (M–Q) Specimen CNU-NX1-743; (M–N) habitus, right forewing, positive imprint, (M) drawing and (N) photograph (composite); and (O–Q) details of ovipositor (location as indicated in N), polarity unknown, (O) drawing and (P–Q) photographs, (P) with color-coded interpretative drawing and (Q) without (composite, flipped horizontally).
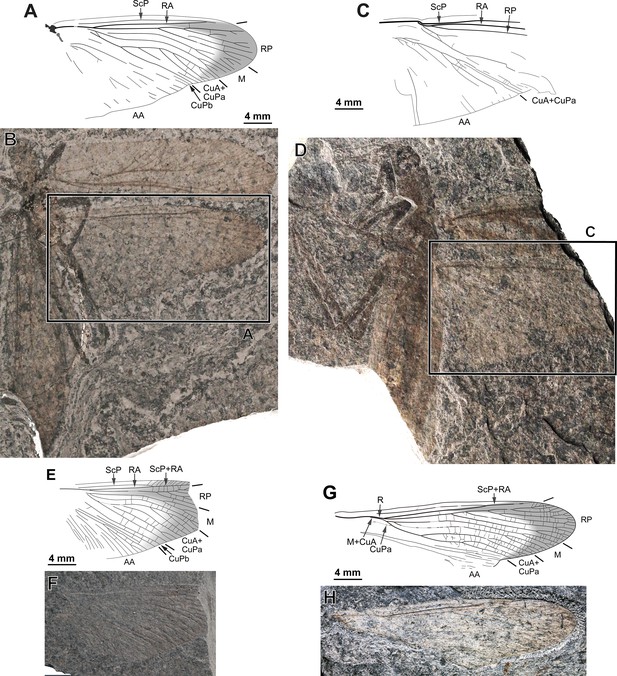
Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov., specimens composed of well-exposed hind wings in connection with body remains or isolated.
(A–B) Specimen CNU-NX1-198; (A) drawing of right hind wing (location as indicated in B) and (B) photograph of habitus (composite, flipped horizontally), left forewing as positive imprints and left hind wing and right wings as negative imprints. (C–D) Specimen CNU-NX1-740; (C) drawing of right hind wing; (D) photograph for habitus (composite, flipped horizontally, light-mirrored), right wings as positive imprints. (E–F) Specimen CNU-NX1-199; right hind wing, positive imprint, (E) drawing and (F) photograph (composite). (G–H) Specimen CNU-NX1-753; left hind wing, negative imprint, (G) drawing and (H) photograph (composite).
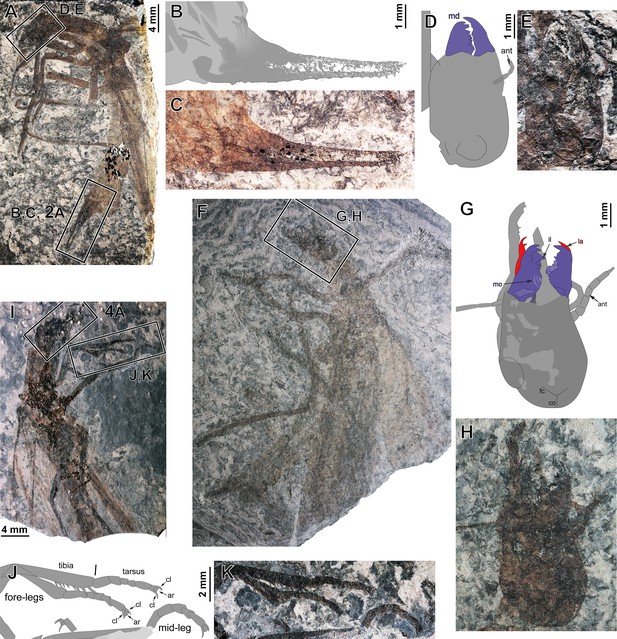
Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov., specimens composed of body remains including well-preserved head, legs, and/or ovipositor.
(A–E) Specimen CNU-NX1-749; (A) photograph of habitus (composite), left forewing as positive imprint; (B–C) details of ovipositor (location as indicated in A; to be compared with main document Figure 2C), polarity unclear, (B) drawing and (C) photograph (composite); and (D–E) details of head (location as indicated in A), (D) color-coded interpretative drawing and (E) photograph (composite). (F–H) Specimen CNU-NX1-756; (F) photograph of habitus (composite); and (F–H) details of head (location as indicated in F), imprint polarity unclear, (G) color-coded interpretative drawing (F) photograph (composite). (I–K) Specimen CNU-NX1-754; (I) photograph of habitus (composite; frame delimiting head indicating the location of main document Figure 3A–B), (J–K) details of distal portions of fore-legs and a mid-leg (location as indicated in I), (J) drawing and (K) photograph (composite).
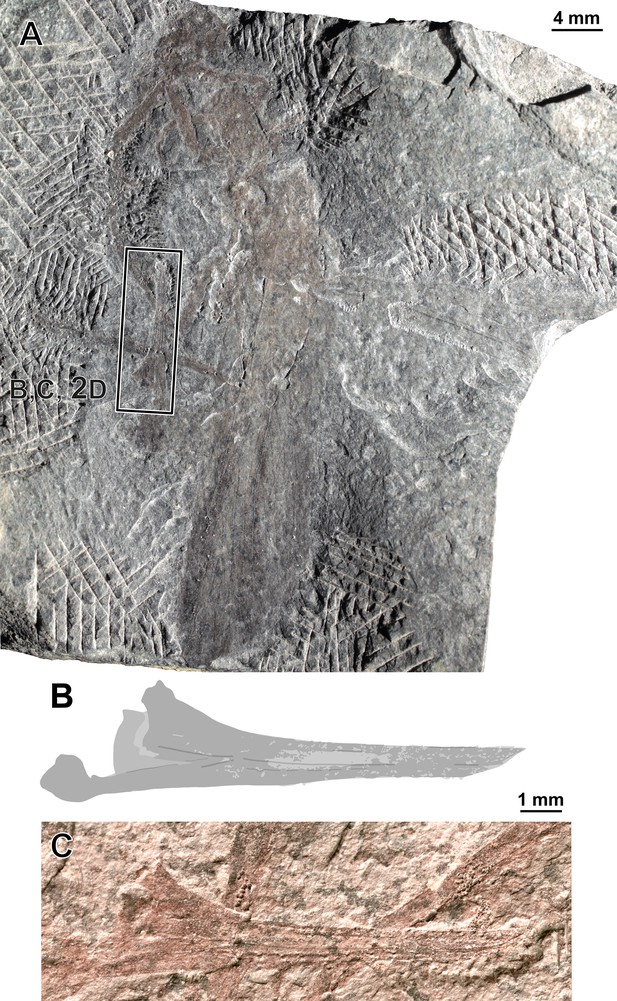
Ctenoptilus frequens sp. nov., specimen CNU-NX1-742.
(A) Photograph of habitus (composite), right forewing as positive imprint, flipped horizontally, and (B–C) details of ovipositor (location indicated in A; to be compared with main document). Photograph of habitus (composite), right forewing as positive imprint, flipped horizontally, and (B–C) details of ovipositor (location indicated in A; to be compared with main document Figure 2D), (B) drawing and (C) photograph (light-mirrored).
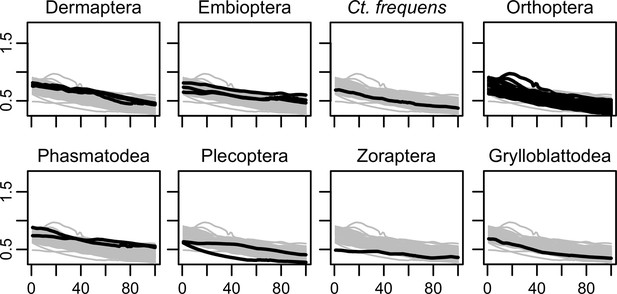
Progression of mechanical advantage curves for the studied taxa.
x-axis = % tooth row; y-axis = MA (mechanical advantage).
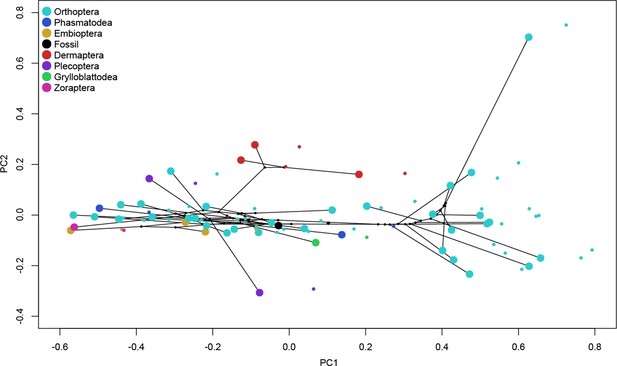
Results of the principal component (PC) analysis of the mandibular mechanical advantage for the first two PCs together with results for the first two PCs after phylogenetic signal correction.
Large dots, distribution of species in PC space uncorrected for phylogenetic signal; small dots, distribution of species in PC space corrected for phylogenetic signal. Although phylogenetic signal was significant, differences do not affect the relative position of the sampled species to each other in PC space.
Tables
Food preference of polyneopteran species included in the mechanical advantage (MA) principal component analyses.
| Order | Species | Food preference |
|---|---|---|
| Dermaptera | Diplatys flavicollis | Omnivore |
| Dermaptera | Forficula auricularia | Omnivore |
| Dermaptera | Hemimerus sp. | Carnivore |
| Embioptera | Aposthonia japonica | Herbivore |
| Embioptera | Embia ramburi | Herbivore |
| Embioptera | Metoligotoma sp. | Herbivore |
| Grylloblattodea | Grylloblatta bifratrilecta | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Acheta domesticus | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Comicus calcaris | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Conocephalus sp. | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Myrmecophilus sp. | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Gryllus bimaculatus | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Cyphoderris sp. | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Hemideina crassidens | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Meconema meridionale | Carnivore |
| Orthoptera | Papuaistus sp. | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Prosopogryllacris sp. | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Stenobothrus lineatus | Herbivore |
| Orthoptera | Stenopelmatus sp. | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Pholidoptera griseoaptera | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Tettigonia viridissima | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Tridactylus sp. | Herbivore |
| Orthoptera | Troglophilus neglectus | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Xya variegata | Fetritivore |
| Phasmatodea | Agathemera sp. | Herbivore |
| Phasmatodea | Peruphasma schultei | Herbivore |
| Plecoptera | Eusthenia lacustris | Carnivore |
| Plecoptera | Perla marginata | Carnivore |
| Zoraptera | Zorotypus caudelli | Herbivore |
| Orthoptera | Ctenoptilus frequens CFMR | Tested |
| Orthoptera | Ametrosomus sp. | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Ametrus tibialis | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Apotrechus illawarra | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Bothriogryllacris brevicauda | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Chauliogryllacris grahami | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Cnemotettix bifascicatus | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Cooraboorama canberrae | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Kinemania ambulans | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Mooracra sp. | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Nullanullia maitlia | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Nunkeria brochis | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Paragryllacris combusta | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Pararemus sp. | Omnivore |
| Orthoptera | Wirritina brevipes | Omnivore |
Importance and factor loadings of the principal component analyses of the polynomial regressions of the mechanical advantages (MAs).
| Principal component analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | |
| Standard deviation | 0.380 | 0.158 | 0.083 | 0.061 | 0.039 | 0.025 |
| Proportion of variance | 0.794 | 0.136 | 0.038 | 0.021 | 0.008 | 0.003 |
| Cumulative proportion | 0.794 | 0.930 | 0.968 | 0.988 | 0.997 | 1.000 |
| Factor loadings: | ||||||
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | |
| Intercept | −0.013 | 0.288 | 0.150 | 0.907 | 0.258 | 0.074 |
| Regression coefficient 1 | −0.948 | −0.250 | 0.173 | 0.046 | −0.048 | 0.065 |
| Regression coefficient 2 | 0.300 | −0.754 | 0.497 | 0.090 | 0.186 | 0.229 |
| Regression coefficient 3 | −−.037 | 0.509 | 0.528 | −0.372 | 0.290 | 0.489 |
| Regression coefficient 4 | −0.057 | −0.164 | −0.650 | −0.015 | 0.436 | 0.597 |
| Regression coefficient 5 | 0.079 | 0.028 | −0.010 | 0.171 | −0.789 | 0.585 |
| Phylogenetic principal component analysis | ||||||
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | |
| Standard deviation | 0.745 | 0.368 | 0.172 | 0.131 | 0.099 | 0.055 |
| Proportion of variance | 0.740 | 0.180 | 0.040 | 0.023 | 0.013 | 0.004 |
| Cumulative proportion | 0.740 | 0.921 | 0.960 | 0.983 | 0.996 | 1.000 |
| Factor loadings: | ||||||
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | |
| Intercept | 1.000 | −0.021 | −0.003 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Regression coefficient 1 | −0.088 | −0.995 | −0.048 | 0.009 | 0.005 | 0.004 |
| Regression coefficient 2 | 0.054 | −0.228 | 0.940 | −0.247 | −0.008 | −0.024 |
| Regression coefficient 3 | 0.076 | 0.026 | −0.412 | −0.905 | 0.067 | −0.006 |
| Regression coefficient 4 | −0.023 | 0.067 | 0.096 | 0.101 | 0.985 | 0.078 |
| Regression coefficient 5 | 0.077 | 0.085 | 0.180 | −0.112 | −0.241 | 0.940 |