Cannabidiol activates neuronal Kv7 channels
Figures
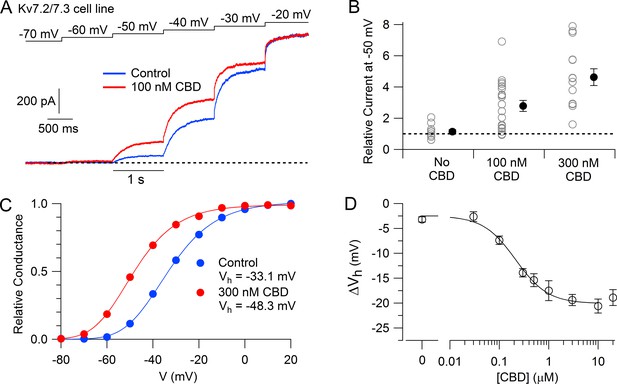
Cannabidiol (CBD) enhancement of cloned human Kv7.2/7.3 channel current in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells.
(A) hKv7.2/7.3 current evoked by staircase depolarizations before and after application of 100 nM CBD. (B) Collected results (mean ± SEM) for current at –50 mV after application of 100 nM (n = 20) or 300 nM CBD (n = 14) for 4–6 min, normalized to current before CBD application, using the protocol in (A). ‘No CBD’ values (n = 11) are for 6 min dummy applications of solution containing only vehicle (DMSO). (C) Voltage-dependent activation of hKv7.2/7.3 channels measured in a cell before and after application of 300 nM CBD. Relative conductance at each voltage was measured from the initial tail current at a step to –50 mV following 1 s depolarizations to voltages between –100 mV and +20 mV from a holding potential of –80 mV. Solid lines: fits to data points of fourth power Boltzmann function, [1/ (1 + exp(-(V – Vhn)/k))]4, where V is test pulse voltage, Vhn is voltage of half-maximal activation for single ‘n’ particle, and k is slope factor for activation of n particles. Control: Vhn = –54.4 mV, k = 12.8 mV (midpoint of function = –33.1); 300 nM CBD: Vhn = –67.9 mV, k = 11.8 mV (midpoint of function –48.3 mV). (D) Concentration-dependent shift of activation midpoint by CBD. Measurements of the midpoint were made before and 10 min after exposure to CBD at various concentrations. mean ± SEM, n = 9 for 30 nM CBD, n = 21 for 100 nM CBD, n = 17 for 300 nM CBD, n = 12 for 500 nM CBD, n = 7 for 1 µM CBD, n = 16 for 3 µM CBD, n = 19 for 10 µM CBD, n = 10 for 20 µM CBD. Value for 0 CBD represents the measurement of a small shift that occurred with dummy applications of DMSO-containing control solution for 10 min (n = 11). Solid line: fit to the Hill equation, ΔVh = −2.5 mV − 17.5 mV/(1 + (EC50/[CBD])^nH), where EC50 = 214 nM and the Hill coefficient nH = 1.3.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Screen data and source data for Figure 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73246/elife-73246-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
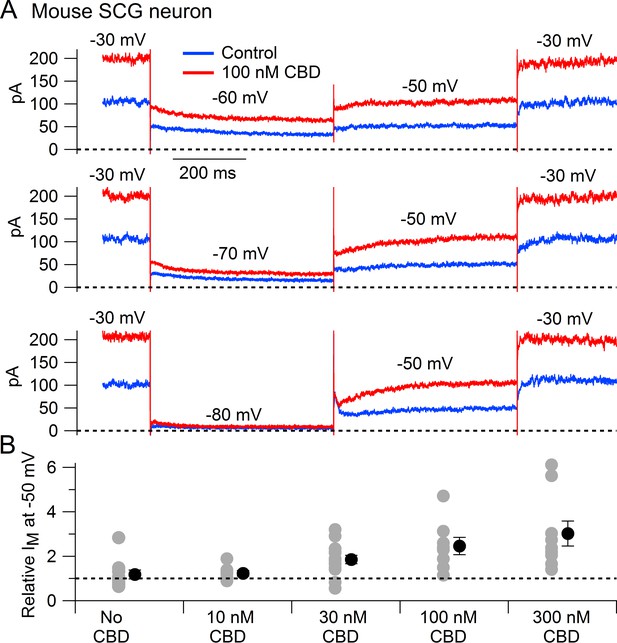
Cannabidiol (CBD) enhancement of M-current in mouse sympathetic neurons.
(A) Currents evoked by hyperpolarizations to –60 mV, –70 mV, and –80 mV from a holding potential of –30 mV before (blue) and after (red) application of 100 nM CBD. (B) Collected results (mean ± SEM) for effect of CBD on steady-state M-current at –50 mV. Current was read at the end of a 1 s step from –30 mV to –50 mV, normalized to current before CBD application, following exposure to 10 nM CBD (n = 7), 30 nM CBD (n = 14), 100 nM CBD (n = 8), or 300 nM CBD (n = 9). The maximum effect of CBD was reached in 6–9 min for 10 nM and 30 nM CBD and 2–6 min for 100 nM and 300 nM CBD. ‘No CBD’ values (n = 10) are for 7–9 min dummy applications. Gray circles: individual cells. Black circles: mean ± SEM. Non-paired two-tailed t-tests: 10 nM CBD vs. No CBD, p=0.85; 30 nM CBD vs. No CBD, p=0.024; 100 nM CBD vs. No CBD, p=0.015; 300 nM CBD vs. No CBD, p=0.012.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73246/elife-73246-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
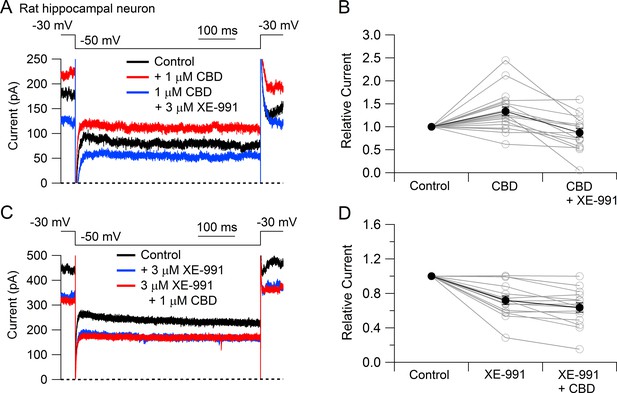
Cannabidiol (CBD) enhancement of Kv7 current in rat hippocampal neurons.
(A) Currents at a holding voltage of –30 mV and during a 500 ms hyperpolarization to –50 mV in control, after application of 1 μM CBD, and after addition of 3 μM XE-991 in the continuing presence of CBD. (B) Collected data with this protocol. Current was measured at the end of the step to –50 mV, normalized to current before application of CBD. Connected open circles indicate data for individual cells (n = 20 for application of CBD, n = 15 for application of CBD followed by XE-991) and closed circles represent mean ± SEM. Paired t-test for currents after CBD compared to control currents, p=0.00017 (n = 20, two-tailed), paired t-test for currents in CBD + XE-991 compared to CBD, p=0.00038 (n = 15, two-tailed). (C) Currents in control, after application of 3 μM XE-991, and after addition of 1 μM CBD in the continuing presence of XE-991. (D) Collected data with symbols as in (B); n = 15 cells for application of XE-991 followed by CBD. Paired t-test for currents after XE-991 compared to control, p=0.00071 (n = 15, two-tailed), paired t-test for currents in XE-991 + CBD compared to XE-991, p=0.0105 (n = 15, two-tailed).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73246/elife-73246-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | Swiss Webster | Charles River | Cat# 024 | |
| Strain, strain background (Rattus norvegicus) | Sprague–Dawley | Charles River | Cat# 400 | |
| Cell line (Cricetulus griseus) | Kv7.2/7.3 CHO cell line | Mayflower Bioscience | BSYS-KV7.2/3-CHO-C | CHO (Chinese hamster [C. griseus ] ovary) cell line stably transfected with recombinant human Kv7.2/7.3 ion channels |
| Commercial assay or kit | MycoAlert PLUS Mycoplasma Detection Kit | Lonza | LT07-703 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | FluxOR II Green Potassium Ion Channel Assay | Invitrogen | LT07-703 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Cannabidiol | Cayman Chemical | Cat# 90080, CAS 13956-29-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ham’s F12-Glutamax-l medium | Gibco | Cat# 31765-035 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Penicillin-streptomycin | Gibco | Cat# 15140-122 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Puromycin | InvivoGen | Cat# ant-pr-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Papain | Worthington Biochemical | Cat# LS003126 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | L-15 | Gibco | Cat# 11415-064 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Neurobasal A Medium | Gibco | Cat# 10888-022 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | B-27 | Gibco | Cat# 17504-010 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Penicillin-streptomycin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# P4333 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Minimal Essential Medium | American Tissue Type Collection | Cat# DMEM 30-2002 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution | Gibco | Cat# 14170-112 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMEM/F12 | Gibco | Cat# 11330-032 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tetrodotoxin w/citrate | Abcam | Ab120055 | |
| Software, algorithm | Clampex | Molecular Devices | Version 10.3.1.5 | https://www.moleculardevices.com |
| Software, algorithm | Igor Pro | WaveMetrics | Version 6.12A | https://www.wavemetrics.com |
| Software, algorithm | DataAccess | Bruxton Corporation | http://www.bruxton.com/DataAccess/index.html |





