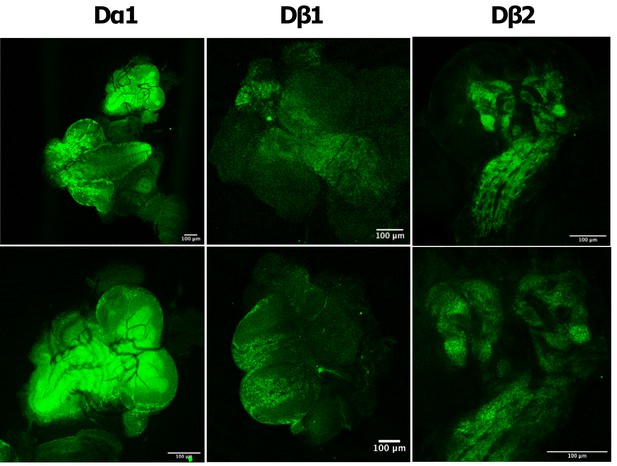
Drosophila nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits and their native interactions with insecticidal peptide toxins
Figures
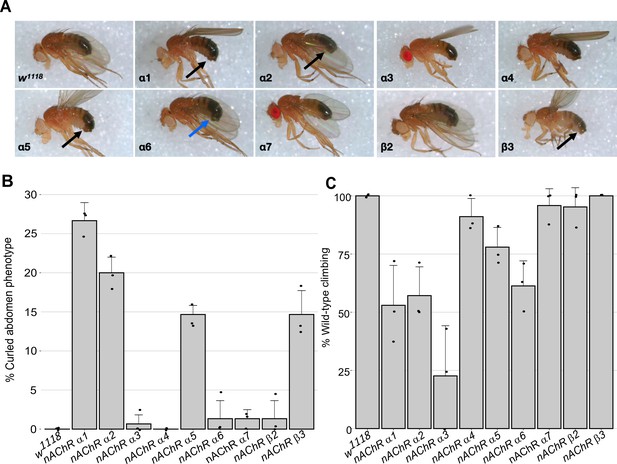
Morphological and locomotor phenotypes in nAChR subunit mutants.
(A) Adult males from indicated nAChR subunit null mutants, black arrows indicate curled abdomens but even in lines with a low frequency the phenotype is prominent (blue arrow). (B) Frequency of curled abdomen phenotype (%), n=3. (C) Graph of locomotor activity determined in climbing assays as a percentage of wild-type, n=3.
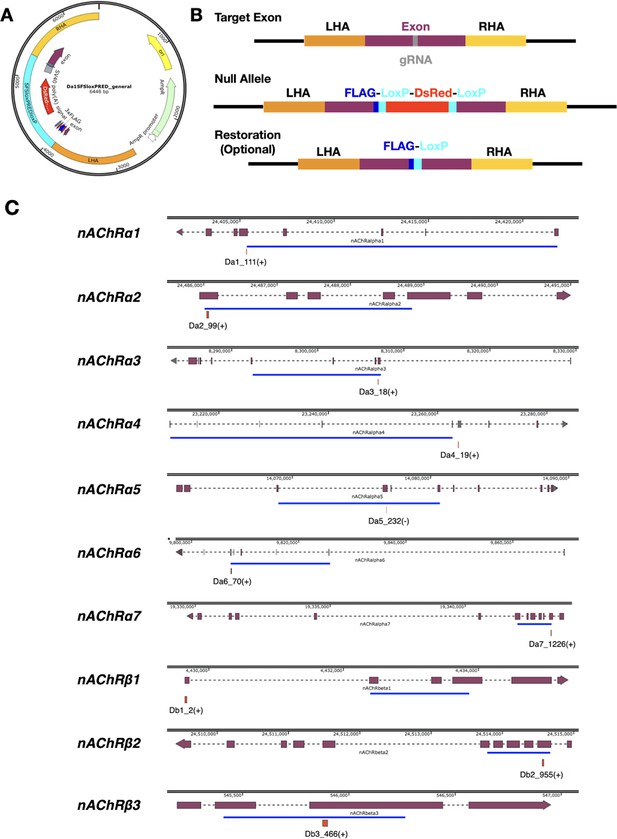
Construction of new D. melanogaster nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit gene mutations.
(A) Diagram of the construct used to generate DsRED insertions into each of the nAChR subunit genes. LHA and RHA = Left and Right homology arms. (B) A guide RNA target site is identified in the exon of interest. Insertion by homology directed repair after Cas9 cleavage disrupts the exon by insertion of a 3XFLAG-DsRED cassette. If required, the DsRED may be removed by Cre-LoxP recombination, restoring the reading frame with the addition of a 3XFLAG tag. (C) Diagramatic representation of DsRED insertion sites in each of the subunit genes with the gRNA specified in Supplementary file 6. Purple blocks represent coding exons on longest transcript, dotted lines represent introns. Genomic coordinates are above each gene model. The blue line represents the approximate extend of the ligand-binding domains.
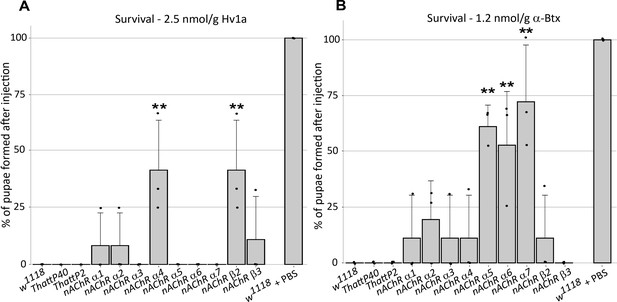
ω-Hexatoxin-Hv1a and α-Bungarotoxin target different nAChR subunits.
(A) Bar graph of the survival rate, measured as the percentage of pupae formed, following larval injection of 2.5 nmol/g Hv1a in the indicated homozygous lines. **p=0.0035 (one-way ANOVA F(11,24) = 4.99, p=0.0005 with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test). Mean ± SD of three independent replicates in each group (10 injected larvae in total). Individual replicate data points are shown (B) Survival rate following larval injection of 1.25 nmol/g α-Btx. **p<0.001, ***p=0.0001, one-way ANOVA (F(11,24) = 7.921, p<0.0001, followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test). Mean ± SD of three independent replicates in each group (10 injected larvae in total). w1118 is the wild-type base stock, THattp40 and THattP2 are the Cas9 lines used to establish the mutants, w1118 + PBS represents the injection control.
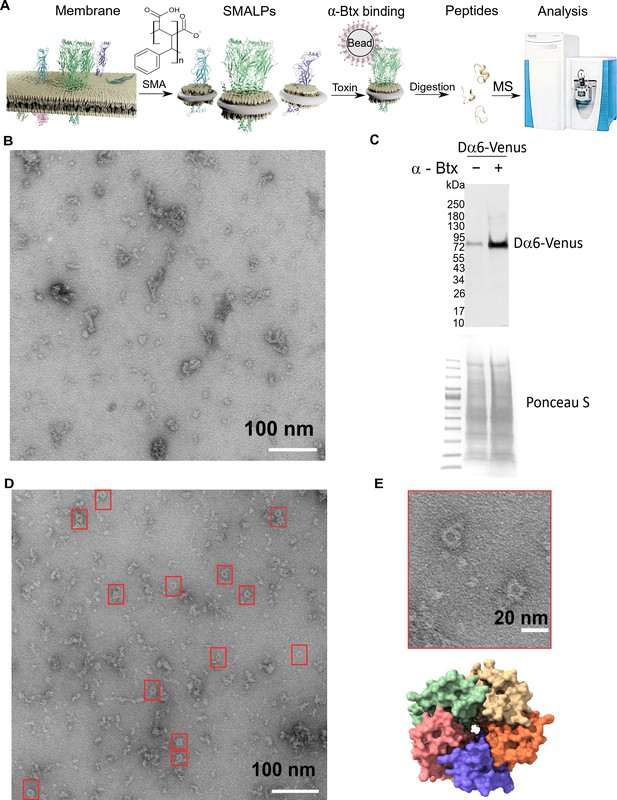
Forming styrene maleic acid lipid particles (SMALPs).
(A) Schematic representation of the SMALPs extraction and nAChRs pull-down for mass spectrometric analysis. (B) Negative staining of extracted SMALPs by transmission electron microscopy, n=3. Scale bar 100 nm. (C) Western blot for Dα6-mVenus nAChR with and without enrichment using α-Btx, n=2. Detected with anti-GFP antibody. The fusion protein was detected at approximately 83 kDa. Ponceau S staining was used as sample equal loading control. (D, E) Negative staining of extracted SMALPs after α-Btx pull-downs, n=3, ring-like protein structures are boxed (scale bar = 100 nm) with an example in the magnified image (scale bar = 20 nm). A top view of the nAChR structure from PDB entry 4HQP is shown for reference.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Transmission electron microscopy micrographs.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-fig3-data1-v1.zip
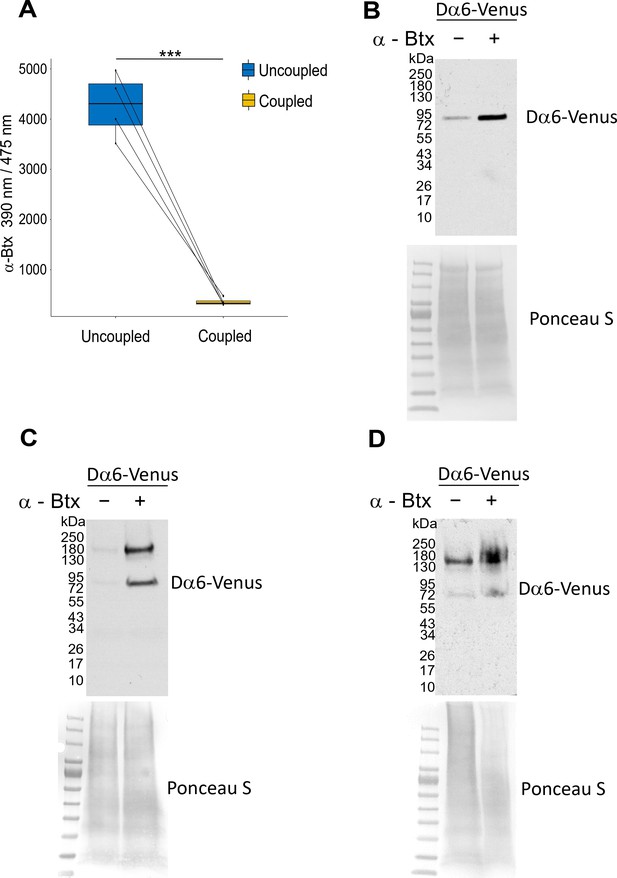
Coupling α-Btx and testing pull-down efficiency with affinity beads.
(A) Fluorescence signal of uncoupled α-Btx in solution before and after coupling to affinity beads (two-tailed t-test, ***p<0.001, n=4). (B) Biological replicate: same condition as in Figure 3C, samples were reduced with 1% DTT. To allow the detection of the fusion protein Dα6-mVenus an anti-GFP (Ab252881) antibody was used. The fusion protein was detected at approximatly 83 kDa. (C) Pull-down samples were not reduced with 1% DTT. A signal at about 180 kDa was also detected and mostly indicative of a dimer. (D) Biological replicate: same condition as in (C), samples were not reduced with 1% DTT. Ponceau S staining was used as sample an equal loading control.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Coupling efficiency of α-Btx to affinity beads.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
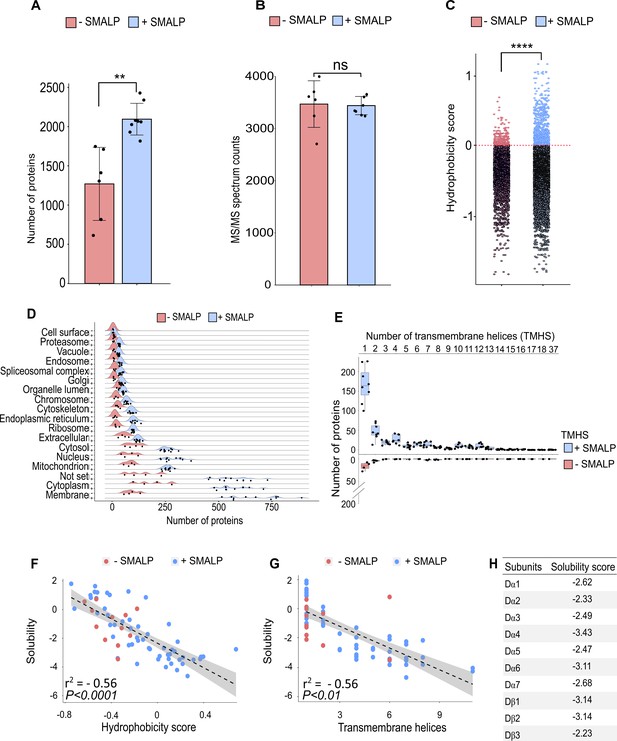
Identification of proteins enriched by SMALP extraction.
(A) Number of identified proteins in affinity pull-down samples solubilised with or without SMA, two-tailed t-test, **p<0.01, n=6 or 8 replicates per condition. (B) MS/MS spectrum counts from samples solubilised with or without SMA, ns = not significant after two-tailed t-test with n=6 or 8. (C) Calculated hydrophobicity score of amino acid residues found in protein sequences obtained with and without SMA solubilisation, ****p<0.0001, two-tailed t-test, n=3 per condition. (D) GO term (cellular compartment) enrichment of proteins identified with and without SMA solubilisation, n=4 or 11. (E) Predicted numbers of proteins containing transmembrane helices obtained with or without SMA solubilisation, n=4 or 8. (F, G) Analysis of solubility and hydrophobicity of receptors identified with and without SMA solubilisation (r2 = –0.56, p<0.0001, n=4) and of transmembrane receptor helices (r2=0.56, p < 0.01, n = 4). (H) Solubility score of individual nAChR subunits.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
SMALP extraction raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
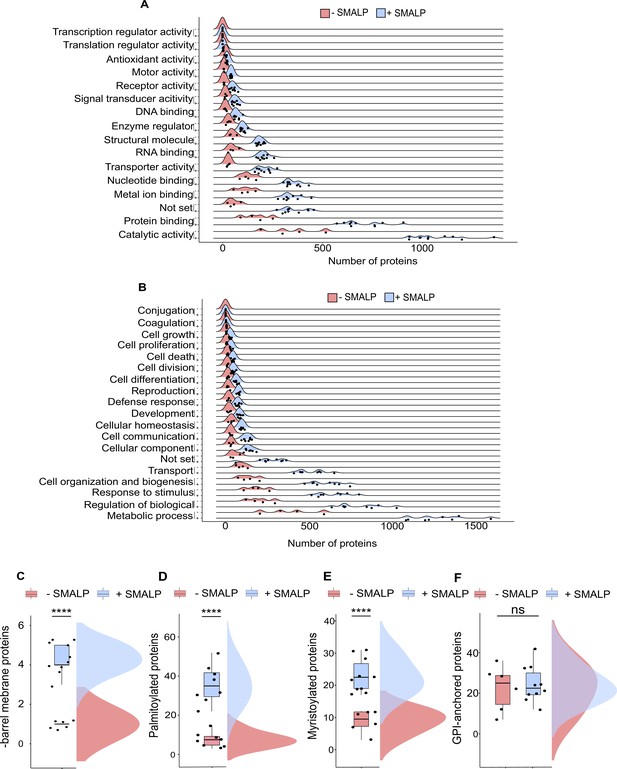
GO terms and predicted membrane proteins.
(A) GO slim term for biological process and (B) for molecular function analysed within samples solubilised without or with SMA, n=4 or 11 per conditions. Predicted β-barrel membrane- (C), two-tailed t-test ****p<0.0001, n=6 or 10; palmitoylated- (D), ****p<0.0001, each n=8; myristoylated- (E), ****p<0.0001, n=6 or 10; and GPI-anchored proteins (F), non-significant ns, n=6 or 10.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Further SMALP extraction raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
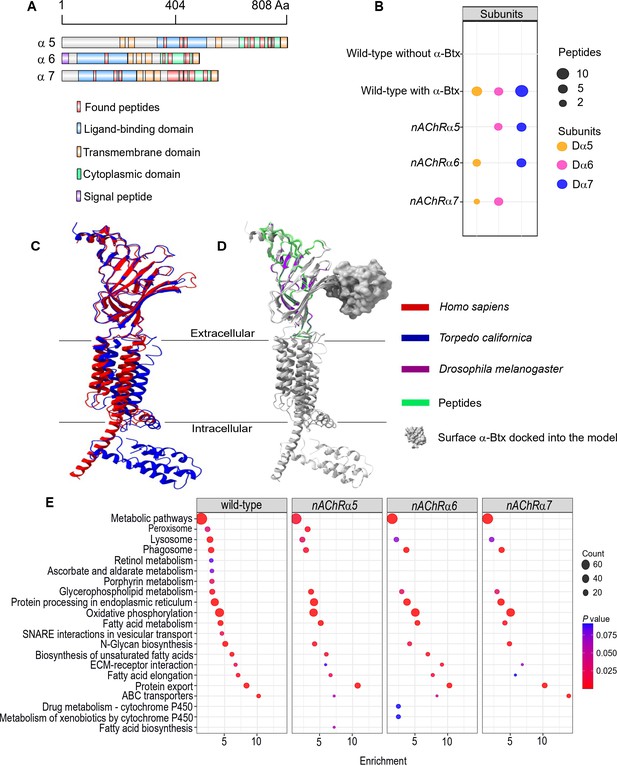
Three nAChR α-subunits bind to α-Bungarotoxin (α-Btx).
(A) Identified Dα5, Dα6, and Dα7 subunit peptides in pull-downs using α-Btx affinity beads. Peptides from the ligand-binding and cytoplasmic domain are highlighted in red. (B) Numbers of identified unique peptides in wild-type pull-downs using affinity beads in absence and presence of α-Btx, n=3. Deleting nAChRα5, nAChRα6, nAChRα7 and performing pull-downs identified unique peptides for nAChR subunits suggesting that functional complexes can be formed in each of the mutants, n=3. (C) Superimposed nAChR α-subunit structures from Homo sapiens (blue, PDB 6USF) and Torpedo californica (red, 6UWZ). The extracellular ligand-binding domains (LBD) exhibit a structure similarity. (D) Same superimposed structures docked to α-bungarotoxin (α-Btx, surface structure). Peptides found in LBD are highlighted in green. The homology regions of the Dα6 LBD are shown in violet.(E) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of pull-downs in wild-type and nAChRα5, nAChRα6, nAChRα7 mutants, Fisher’s exact test, n=3. Protein counts with p values of enriched pathways are shown. p values of ≤ 0.05 are to be considered as strongly enriched with default threshold of 0.1.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Null pull-down raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
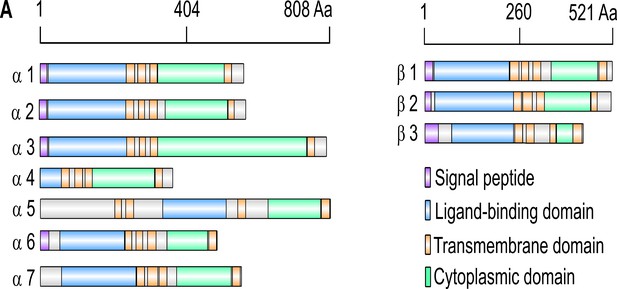
Illustration of nAChR subunits.
(A) Graphical representation of ten nAChR subunits. The position of protein domains and signal peptides are shown.
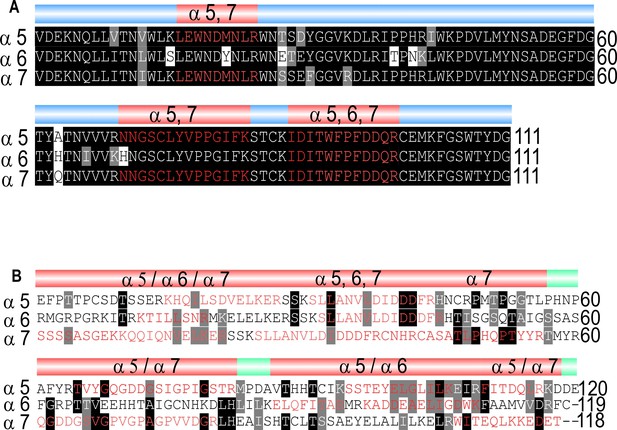
Identified peptides in ligand-binding and cytoplasmic domain.
(A) Shared peptides found in the ligand-binding domains are shown in red. (B) Identified unique (/) and shared (,) peptides in cytoplasmic domain.
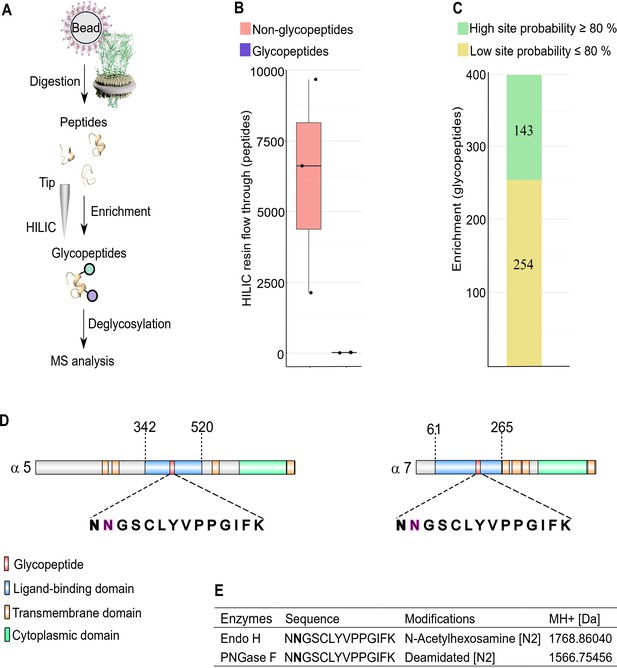
N-glycosylation sites in nAChR subunits.
(A) Diagrammatic representation of nAChR subunit glycopeptide enrichment. Pull-downs with α-Btx affinity beads enrich for nAChRs and after tryptic digestion glycopeptides were enriched. Glycopeptides were deglycosylated with Endo H or PNGase F and analyzed by mass spectrometry. (B) Low numbers of glycopeptides (average 20) are detected in HILIC resin flow through fractions. (C) Numbers of identified glycopeptides according to site probabilities are shown (n=3). (D) Shared glycopeptide identified in the ligand-binding domain of Dα5 and Dα7, an N-linked glycosylated asparagine (N) residue is highlighted. (E) Deglycosylated peptide with either Endo H or PNGase F and contains either an N-acetylhexosamine or is deamidated on asparagine (N2). The two different modifications on the same peptide lead to a different monoisotopic mass (MH+ [Da]). Peptide contains an additional carbamidomethyl on cysteine (C5).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Glycopeptide raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
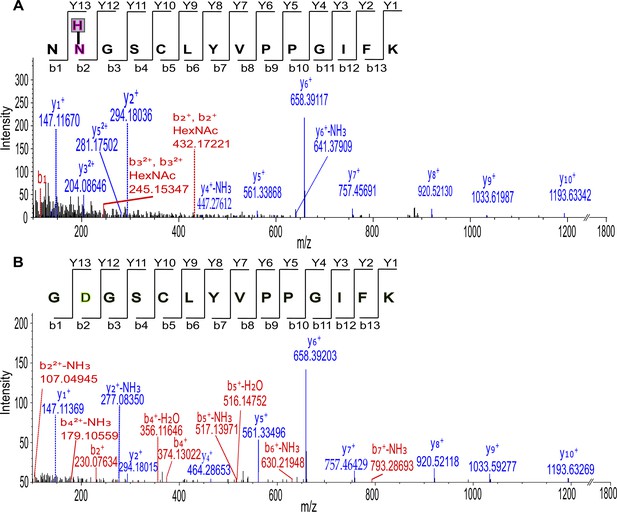
MS/MS spectra of Da5 and Da7 subunit peptides.
(A) MS/MS spectra of fragmented shared Dα5 and Dα7 subunit peptides. Glycopeptides were deglycosylated with Endo H and the second asparagine (N) residue is modified with an N-acetylhexosamine, HexNAc (H). (B) Same deglycosylated peptide with PNGase F and deamination (D) of asparagine residue is shown.
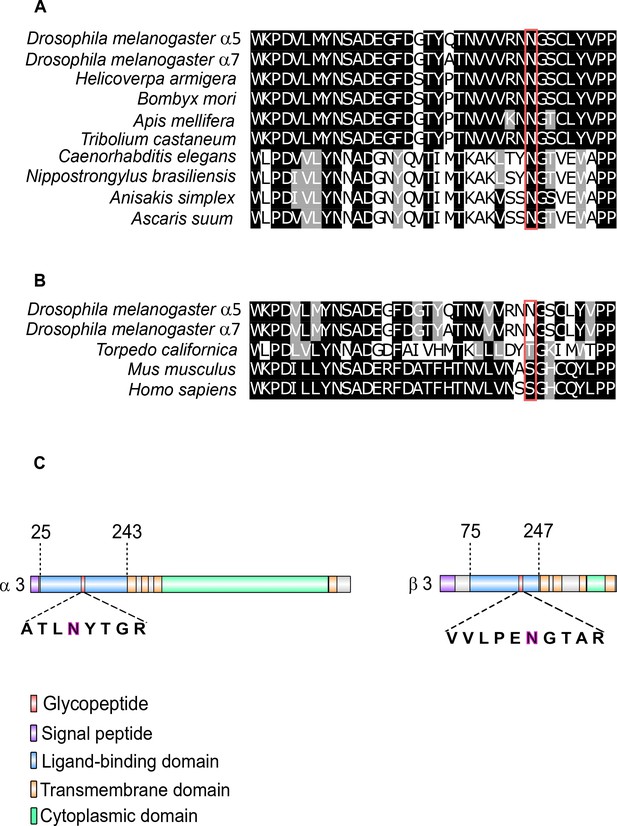
Glycosylation sites of nAChR subunits.
(A) Multiple sequence alignment of insect α7 nAChR subunits compared to sequences of nematodes. The glycosylated ligand-binding domain (LBD) sequence of Dα5 and Dα7 nAChR subunits are shown. Glycosylated asparagine residues highlighted in red are conserved within insects and nematodes (Dα5 422 and Dα7 170 amino acids). (B) Same Dα5 and Dα7 nAChR subunit sequences compared to T.californica, D.rerio, M. musculus, and H. sapiens. (C) Graphical representation of Dα3 and Dβ3 nAChR subunits. N-acetylhexosamine (H) modification on asparagine residues are highlighted and are of low site probability ≤ 80%.
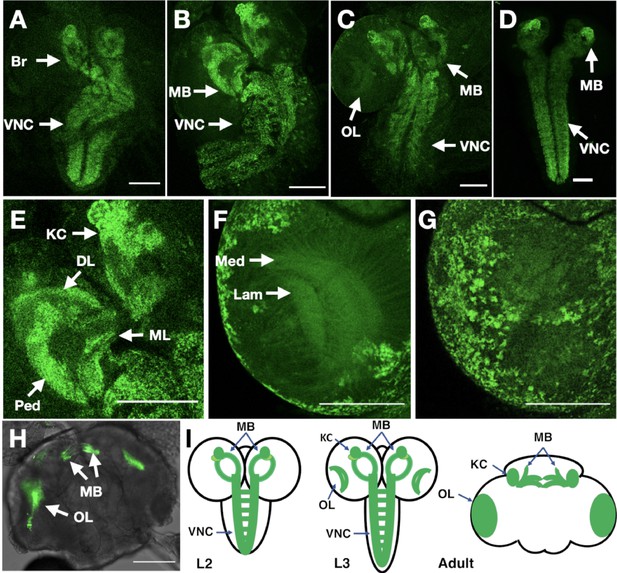
In vivo imaging of endogenously tagged Dα6 nAChR subunit.
(A–C) Dα6-YFP localisation from live confocal imaging in 2nd A, early B and late C 3rd instar larval brains. Visible localisation in brain (Br), ventral nerve cord (VNC), mushroom bodies (MB), and optic lobes (OL). Scale bar = 100 µm. (D) Imaging Dα6-YFP localisation in fixed late 3rd instar larval brain. (E) Dα6-YFP in mushroom bodies of 3rd instar larvae with detectable fluorescence signal in Kenyon cells (KC), calyx (CX), peduncle (Ped), dorsal lobes (DL), and medial lobes (ML). Scale bar = 100 µm. (F) Dα6-YFP was observed in developing optic lobes, lamina (Lam) and medulla (Med) of later 3rd instar larvae. Scale bar = 100 µm. (G) Dα6-YFP on external structures of developing lobes in later 3rd instar larvae. Scale bar = 100 µm. (H) Dα6-YFP in the adult fly brain, strong signal is detected in mushroom bodies (MB) and optic lobe (OL). Scale bar = 100 µm. (I) Schematic summary of Dα6 subunit expression during different developmental stages, (L2, L3 and Adult) in which the green shading indicate the localisation of the Dα6 subunit.
Videos
Late 3rd instar larvae, with defined expression of Dα6-YFP in the Kenyon cells, calyx, peduncle, dorsal and medial lobes.
Scale bar = 100 µm.
Third instar larvae, with detectable fluorescence signal in Kenyon cells, calyx, peduncle, dorsal lobes and medial lobes.
Scale bar = 100 µm.
Later 3rd instar larvae, with signal of Dα6-YFP in developing optic lobes, lamina (Lam) and medulla (Med).
Scale bar = 100 µm.
Adult brain, expression of Da6-YFP is largely restricted to the mushroom bodies.
Scale bar = 100 µm.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent | pCDF3 | Port et al., 2014 | N/A | |
| Genetic reagent | FSVS | Korona et al., 2020 | N/A | |
| Genetic reagent | 3 × P3-DsRED | Gratz et al., 2014 | N/A | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | {nos-Cas9}attP40 | Ren et al., 2013 | BDSC:78,781 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | {nos-Cas9}attP2 | Ren et al., 2013 | BDSC:78,782 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | w1118 | FlyBase | FBal0018186 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRα1 KO | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRα2 KO | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRα3 KO | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRα4 KO | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRα5 KO | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRα6 KO | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRα7 KO | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRβ2 KO | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRβ3 KO | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRα1FSVS | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRα6FSVS | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRβ1FSVS | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nAChRβ2FSVS | This study | N/A | Steven Russell/ https://www.flyfacility.gen.cam.ac.uk |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | E. coli competent cells | New England Biolabs | Catalogue number: C2987H | |
| Commercial assay or kit | BbsI | New England Biolabs | Catalogue number: R0539 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Gibson Assembly Master Mix | New England Biolabs | Catalogue number: E2611L | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Q5 High-Fidelity 2 X Master Mix | New England Biolabs | Catalogue number: M0492L | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Pierce fluorometric peptide kit | Thermo Scientific | Catalogue number: 23,290 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Trypsin/Lys-C mix | Promega | Catalogue number: V5073 | |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (goat monoclonal) | Abcam | Catalogue number: Ab252881 | 1:1,000 |
| Antibody | Anti-rat IgG (goat polyclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Catalogue number: A9037 | 1:10.000 |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | ω‐hexatoxin‐Hv1a | Syngenta | CH-4332 Stein, Switzerland | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | α-Bungarotoxin | Abcam | Catalogue number: ab120542 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Carbachol | Insight Biotechnology Ltd | Catalogue number: CAS 51-83-2 | |
| Other | CNBr-activated sepharose | Sigma-Aldrich | Catalogue number: C9 142–5 G | |
| Other | Styrene maleic acid copolymer (3:1) | Dafforn, p.c. | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | Mini-Protean TGX precast gels | Bio-Rad Laboratories | Catalogue number: 456–1,084 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | ECL-Chemiluminescent detection solution | GE Healthcare | Catalogue number: 45-000-999 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | CL-XPosure films | Thermo Scientific | Catalogue number: 10465145 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Software | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| Software, algorithm | Proteome Discoverer 2.3 | Thermo Scientific | RRID:SCR_014477 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Abdomen phenotype.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-supp1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Climbing ability.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-supp2-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Drosophila larval injection of ω-Hexatoxin-Hv1a & α-Bungarotoxin.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-supp3-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
Identified nAChR peptides in pull-downs with α-Bungarotoxin.
Peptides from Dα3, Dα5, Dα6, Dα7 and Dβ3 nAChR subunits are listed and found [N] times within individual replicates. Protein domains are marked with: Ed extracellular-, Id Intracellular-, LBD ligand-binding-, and Non-domain localization. The mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of the precursor ions, the protonated monoisotopic masses, the theoretical MH+ masses in Dalton [Da] and peptide modifications are listed. Peptide modifications are listed with: (C) Carbamidomethylation; (N,Q) Deamidation; (H) N-acetylhexosamine (HexNAc); (M) Oxidation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-supp4-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 5
Identified nAChR peptides in pull-downs without α-Bungarotoxin.
Identified peptides of nAChR subunits which are found in control pull-down samples without α-Bungarotoxin (α-Btx).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-supp5-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 6
List of gRNAs and oligonucleotides used for cloning.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-supp6-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 7
List of oligonucleotides used for amplification from genomic DNA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-supp7-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 8
C-terminal tagging of nAChRa6 with FSVS.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-supp8-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 9
Wet pellet weight of membrane fractions.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-supp9-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74322/elife-74322-transrepform1-v1.pdf