A single-cell atlas of the cycling murine ovary
Figures
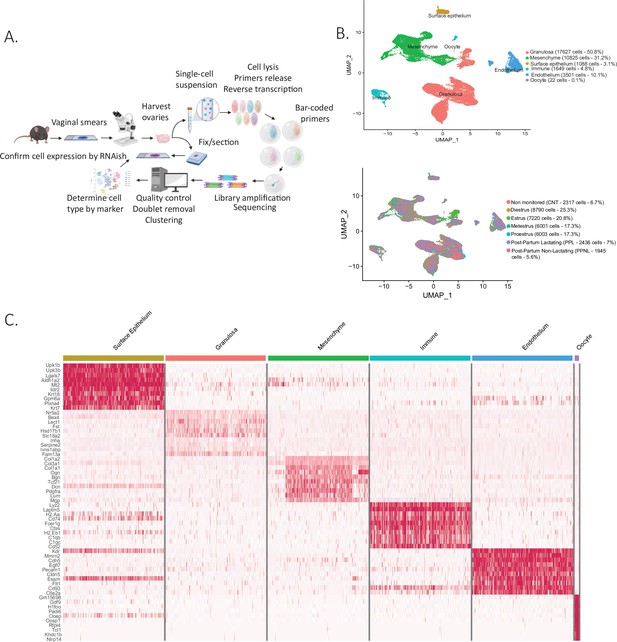
Single-cell RNA sequencing of cycling mouse ovaries.
(A) Schematic of the single-cell sequencing pipeline. (B) Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) plot featuring the different clusters of the ovary and their composition by stage of the estrous cycle, lactating status, or unmonitored. (C) Heatmap of the top 10 markers of each cluster by fold change.
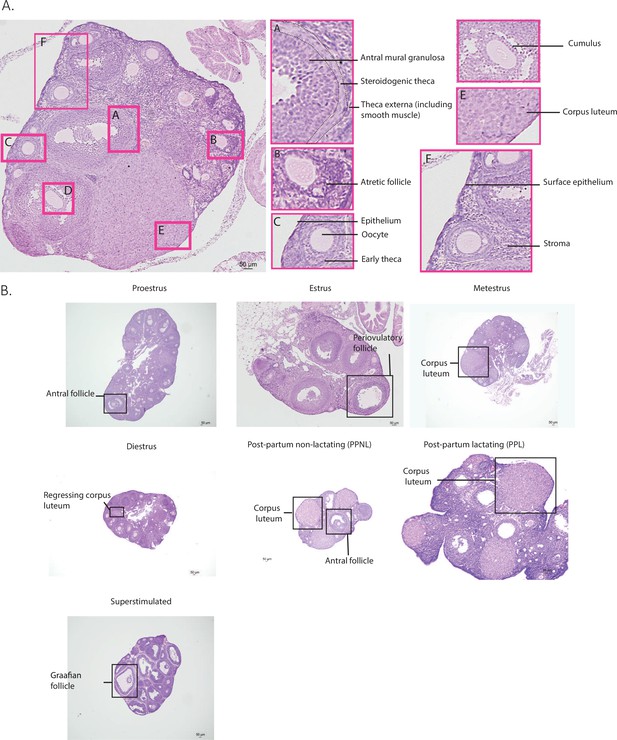
Ovarian morphology by reproductive state.
(A) Representative micrograph illustrating the different cell types of the ovary. (B) Representative micrographs of sections of ovaries at each stage of the estrous cycle, post-partum lactating, and post-partum non-lactating reproductive states with typical features annotated.
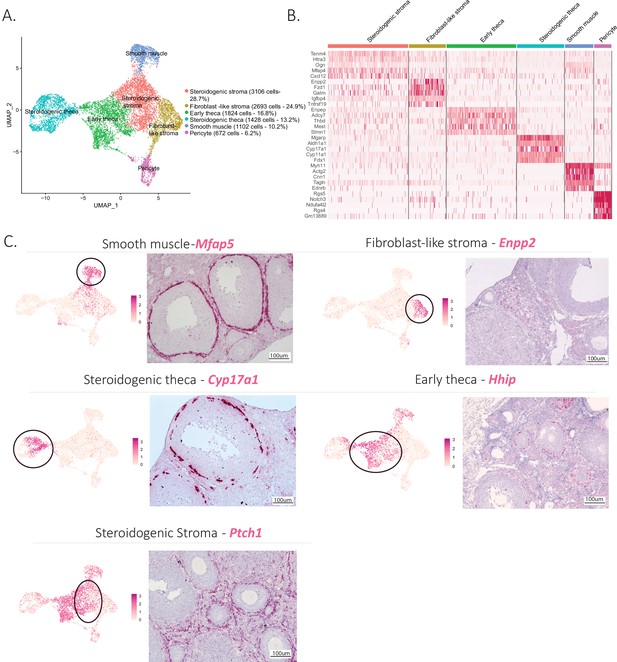
Identification of the different cell types of the mesenchyme cluster.
(A) UMAP plot featuring the different cell subclusters belonging to the mesenchyme cluster. (B) Heatmap of the top five markers of each subcluster by fold change. (C) Validation of the identity of mesenchyme subcluster by UMAP-plots (cluster of interest circled) and RNA in situ hybridization.
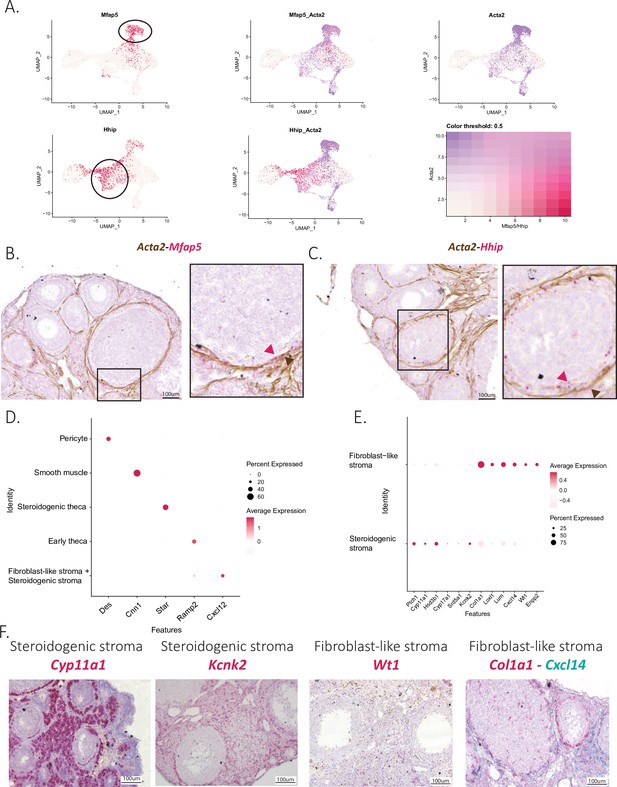
Characterization of mesenchymal cell clusters.
(A) Co-expression of Acta2 and Mfap5 or Acta2 and Hhip in UMAP plots (enriched subcluster circled). Colocalization of (B) Acta2 and Mfap5 or (C) Acta2 and Hhip in ovarian tissue sections stained by Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and RNA in situ hybridization. (D) Expression of mesenchymal markers by cluster in DotPlot. (E) Expression of steroidogenesic and fibroblast markers in DotPlot that differ between the two interstitial stromal cell clusters. (F) RNA in situ hybridization of different markers representative of the steroidogenic stroma (Cyp11a1 and Ptch1) and the fibroblast-like stroma cell clusters (Kcnk2, Cxcl14, and Col1a1).
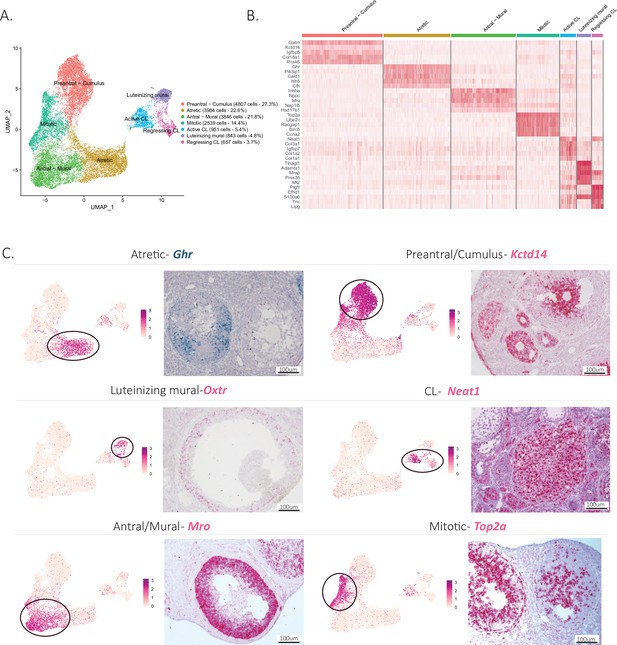
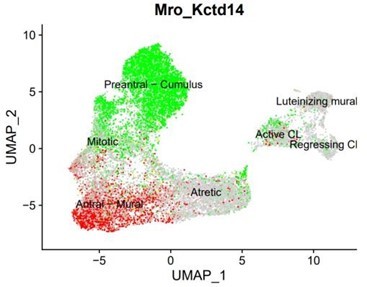
Identification of the different cell types in the granulosa cluster.
(A) UMAP plot featuring the different cell subclusters belonging to the granulosa cluster (specific subcluster circled in each UMAP). (B) Heatmap of the top five markers of each cluster by fold change. (C) Validation of the identity of granulosa subclusters by UMAP-plots and RNA in situ hybridization.
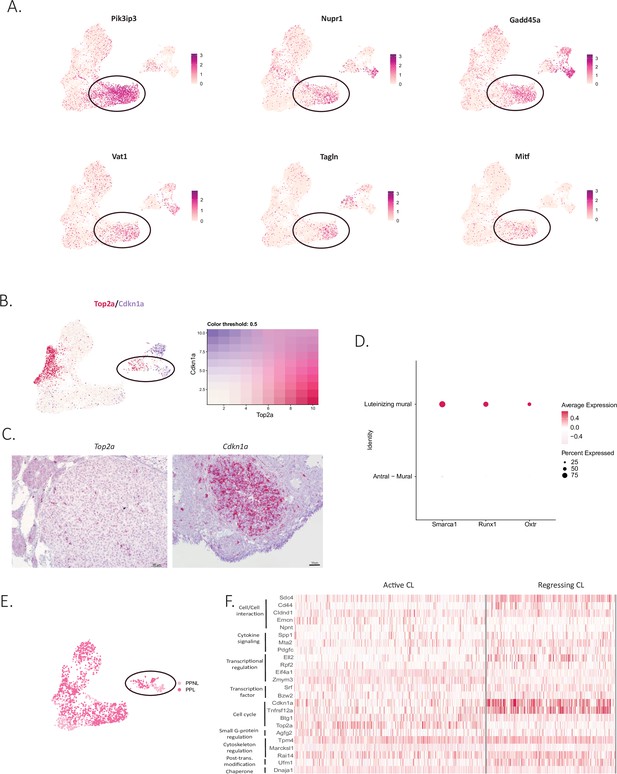
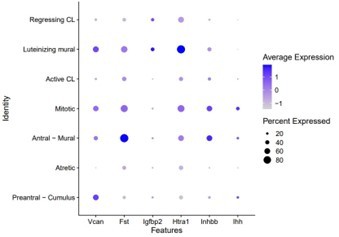
Characterization of active and regressing corpus luteum clusters.
(A) UUMAP plots of different apoptotic markers that colocalize with Ghr in the apoptotic cluster (circled in black). (B) Colocalization of Top2a and Cdkn1a in UMAP plots of corpus luteum clusters (circled in black). (C) RNA in situ hybridization of Top2a and Cdkn1a in ovarian sections. Representative active (Top2a+) and regressing (Cdkn1a+) corpora lutea. (D) Examples of luteinizing mural markers in DotPlot that differ from antral mural. (E) UMAP plot of cellular distribution of post-partum lactating (PPL) cells across the active corpus luteum cluster and post-partum non-lactating (PPNL) cells across the regressing corpus luteum cluster (circled in black). (F) Heatmap of representative markers of active and regressing corpora lutea.
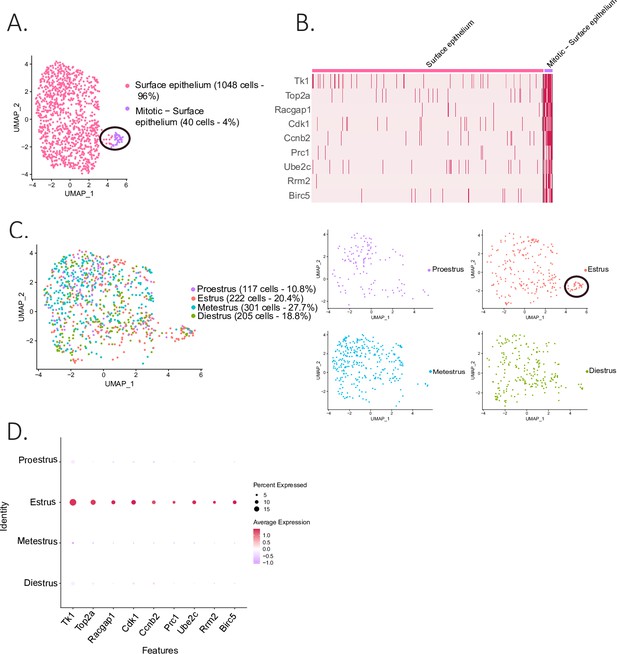
Identification of epithelial subclusters.
(A) UMAP plot of the surface epithelium cluster showing two subclusters: epithelium and mitotic epithelium (circled in black). (B) Heatmap of proliferation markers expressed in the proliferating epithelium cluster. (C) UMAP plot of the cellular composition of the epithelium subclusters by reproductive state (mitotic subcluster circled in the estrous state). (D) Expression of proliferation markers depending on the phase of the estrous cycle.
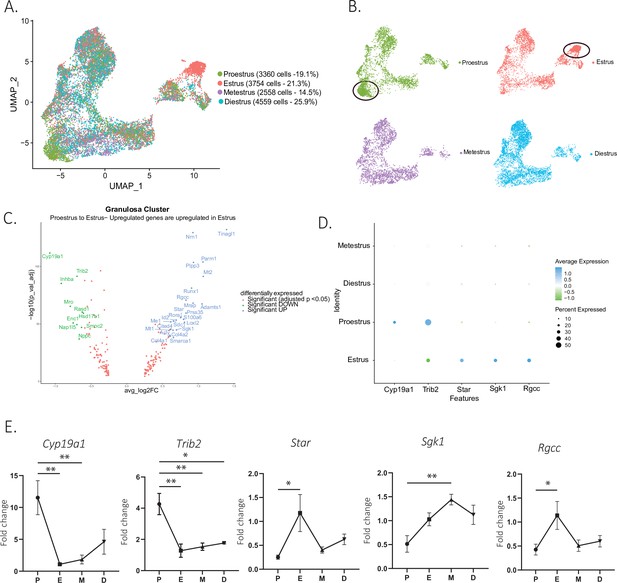
Gene expression in granulosa cells by estrous stage.
(A) UMAP plot featuring estrous cycle stages in the granulosa cell cluster. (B) UMAP plots featuring each of the estrous cycle phases individually (proestrus and estrus enriched subclusters circled in black). (C) Volcano plot of genes differentially expressed between proestrus and estrous stages. (D) DotPlot of differentially expressed markers between proestrus and estrus. (E) Quantitative PCR (qPCR) validation of differentially expressed genes involved in extracellular matrix remodeling and steroidogenesis markers (n=5 per group, mean ± SEM, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005, and ****p<0.001).
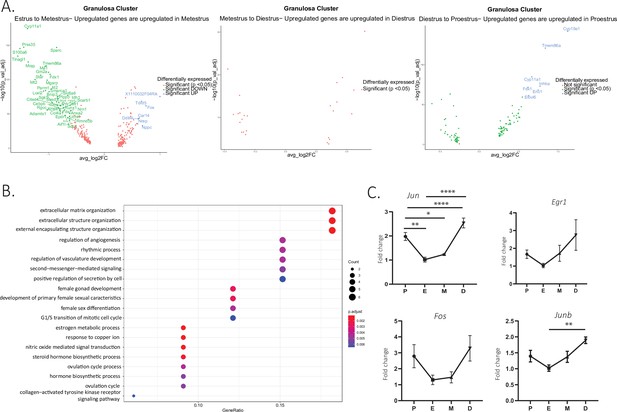
Characterization of the granulosa cell transcriptome across the estrous cycle.
(A) Volcano plot of genes differentially expressed between the estrous/metestrous, metestrous/diestrous, and diestrous/proestrous stages. (B) Pathway analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEG) between the different stages of the estrous cycle. The x-axis shows the gene ratio (the percentage of total DEGs in the given gene ontology [GO] terms). ‘Count,’ reflected by the dot size, represents the number of genes enriched in a GO term, and dot color represents the adjusted p values. (C) Quantitative PCR validation of ovarian surface epithelium-expressed markers (n=5 per group, mean ± SEM, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ****p<0.001).

Identification and validation of new secreted estrous staging markers.
(A) Expression of granulosa cell transcripts varying by estrous cycle stage. (B) Validation of significantly up- and downregulated transcripts of secreted estrous staging markers by qPCR (n=5 per group, mean ± SEM, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.005). (C) Localization of estrous staging markers by in situ hybridization (RNAscope) in ovarian sections. (D) Quantification of circulating estrous staging markers proteins in the blood by enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (n=5 per group, mean ± SEM, *p<0.05, and ***p<0.005). (E) Summary of the timing of expression of estrous staging markers in the blood.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | C57BL/6-Tg(UBC-GFP)30Scha/J | Jackson Laboratory | stock #004353 | |
| Antibody | Smooth muscle alpha action (SMA) (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | #5694 | Dilution: 1:300 |
| Commercial assay or kit | ACTIVIN A commercial ELISA | RnD systems | #DAC00B | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NPPC commercial ELISA | Novus Bio | #NBP2-75790 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Tinagl1 commercial ELISA | LS-Bio | #LS-F49684 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | PRSS35 commercial ELISA | Mybiosource | #MBS9717242 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNA scope 2.5 HD Duplex detection kit | ACD bio | #322500 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNA scope 2.5 HD red detection kit | ACD bio | #322360 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | The target retrieval and protease plus reagents | ACD bio | #322330 | |
| Other | Cdkn1a (M. musculus) NM_007669.4 | ACD bio | # 408551 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Cxcl14 (M. musculus) NM_019568.2 | ACD bio | #459741 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Cyp11a1 (M. musculus) NM_019779.4 | ACD bio | #809181 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Cyp17a1 (M. musculus) NM_007809.3 | ACD bio | #522611 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Ghr (M. musculus) NM_010284.3 | ACD bio | #464951 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Hhip (M. musculus) NM_020259.4 | ACD bio | #448441 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Inhba (M. musculus) NM_008380.1 | ACD bio | # 455871 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Kcnk2 (M. musculus) NM_001159850.1 | ACD bio | #440421 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Kctd14 (M. musculus) NM_001136235.1 | ACD bio | #517811 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Mfap5 (M. musculus) NM_015776.2 | ACD bio | #490211 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Mro (M. musculus) NM_001305882.1 | ACD bio | #491181 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Neat1 (M. musculus) NR_003513.2 | ACD bio | #440351 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Nppc (M. musculus) NM_010933.5 | ACD bio | # 493291 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Onecut2 (M. musculus) NM_194268.2 | ACD bio | #520541 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Oxtr (M. musculus) NM_001081147.1 | ACD bio | #412171 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Prss35 (M. musculus) NM_178738.3 | ACD bio | #492611 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Runx1 (M. musculus) NM_001111021.1 | ACD bio | #406671 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Tinagl1 (M. musculus) NM_001168333 | ACD bio | #312621 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Top2a (M. musculus) NM_011623.2 | ACD bio | # 491221 | RNAscope probe |
| Other | Wt1 (M. musculus) NM_144783.2 | ACD bio | #432711 | RNAscope probe |
| Software and algorithm | R version 4.1.3 | R Project for Statistical Computing | https://scicrunch.org/resolver/SCR_001905 | |
| Software and algorithm | Seurat package 4.1.0 | R toolkit for single-cell genomics | https://satijalab.org/seurat/articles/install.html | |
| Software and algorithm | BZ-X800 analysis software | Keyence | https://www.keyence.com/landing/microscope/lp_fluorescence.jsp | |
| Software and algorithm | GraphPad Prism, version 9.2.0 | Graphpad |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of primers used for quantitative PCR (qPCR) experiments.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77239/elife-77239-supp1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Top 10 markers expressed in each ovary cluster.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77239/elife-77239-supp2-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Top 10 markers from each mesenchyme subclusters.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77239/elife-77239-supp3-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
Top 10 markers from each granulosa subclusters.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77239/elife-77239-supp4-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 5
Secreted markers expressed in granulosa cells varying with the estrous cycle.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77239/elife-77239-supp5-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77239/elife-77239-transrepform1-v1.docx
-
Source data 1
qPCR experiments individual p values.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77239/elife-77239-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Source data 2
ELISA experiments individual p values.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77239/elife-77239-data2-v1.xlsx