Robust and Efficient Assessment of Potency (REAP) as a quantitative tool for dose-response curve estimation
Figures
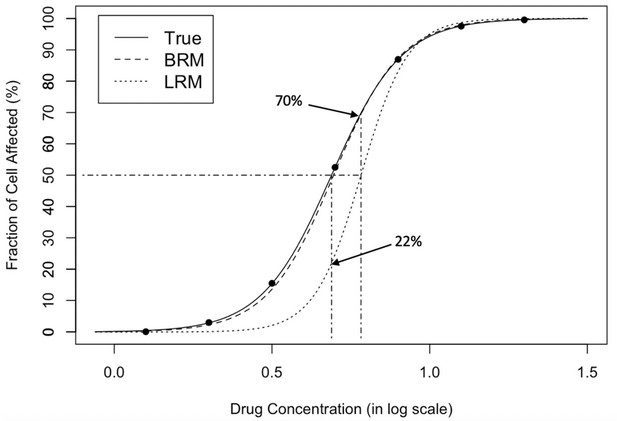
Dose-response curve fitting with extreme observations.
The original data points are on the true curve. The leftmost data point is changed from 0.005 to 1e-6, referring to a small white noise that cannot be visually recognized. The change leads to the obvious departure between the estimated curve by linear regression model (dotted) and the true curve (solid), which demonstrates that standard regression is sensitive to extreme values. The response at the true IC50 (dotdashed, vertical, left) is only 22% from the estimated curve; the estimated IC50 (dotdashed, vertical, right) corresponds to the 70% fraction of cell affected, effecting a substantive 20% inflation (50% ->70%) in estimation error. In contrast, the estimated curve by beta regression model (dashed) is almost overlapped with the true curve (solid), which shows that BRM is much more robust to extreme values. LRM: linear regression model; BRM: robust beta regression model. Detailed model descriptions of LRM and BRM are provided in Materials and methods section.
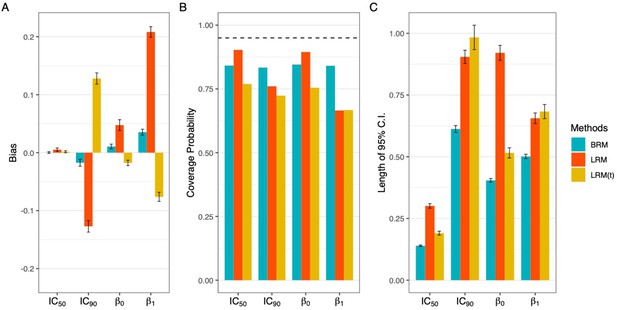
Comparison of estimation efficiency and accuracy using linear regression model and beta regression model.
Deleting the extreme values could not eliminate the bias (panel A), but only harmed the accuracy with worse coverage probabilities (panel B) and impaired the efficiency of interval estimation with wider nominal 95% confidence intervals (panel C). A total of 1000 data sets were generated following the data simulating process described in Appendix 1, using the dose sets and true dose-response curve under 7 dose setting with a precision parameter of 100. Responses ≤5% or ≥95% were considered extreme responses. Dashed line in panel B denotes 95% nominal coverage probability. BRM: beta regression with extreme data points; LRM: linear regression model with extreme data points; LRM(t): linear regression model with truncated dataset after deleting extreme values. Detailed model descriptions of LRM and BRM are provided in Materials and methods section.
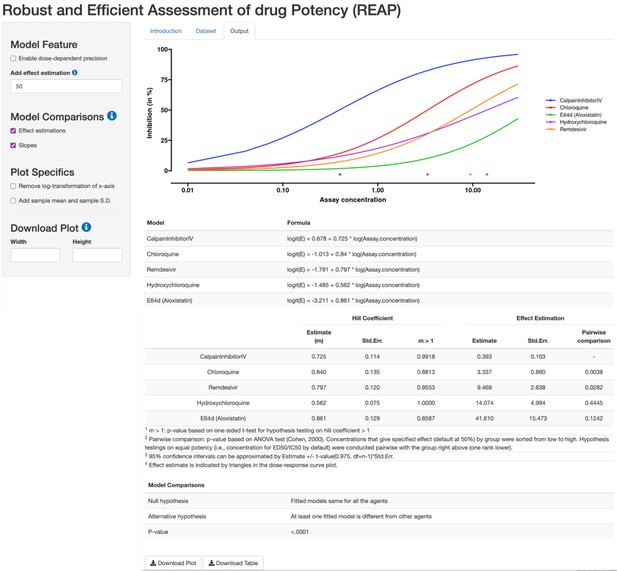
REAP App interface, with a highlight of Output section.
Using the robust beta regression method, REAP produces a dose-response curve plot with effect and model estimations. The left panel allows users to specify model features and design plot specifics. REAP also provides hypothesis testing results to compare effect estimations, slopes and models.
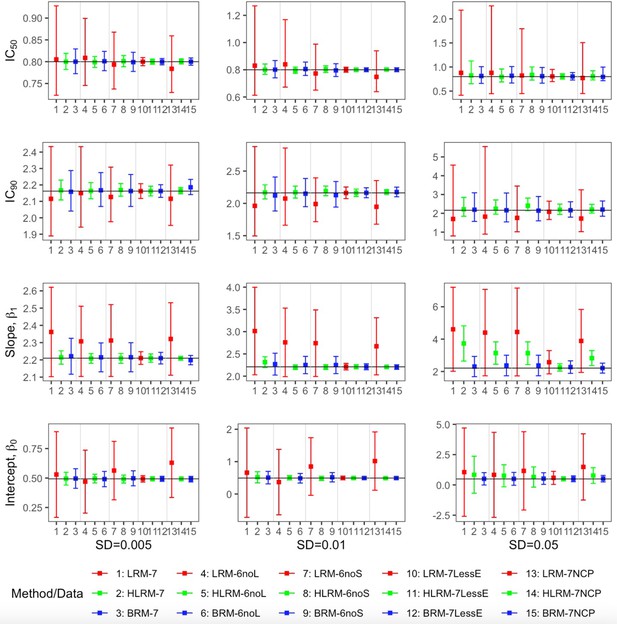
Comparison of the point estimates and 95% confidence intervals using linear regression model, heavy-tailed linear regression model and robust beta regression model, with data simulated from normal error term.
The vertical solid lines indicate the true values. The dots represent the averaged point estimates and the bars represent the averaged lower and upper bound of 95% CIs. The point estimation by robust beta regression is consistently closer to the true value with a narrower 95% CI compared to the linear regression model. The 95% CI of heavy-tailed linear regression underestimates the nominal coverage probability. LRM: linear regression model; LRM-7: LRM under 7-dose dataset with extreme data points; LRM-6noL: LRM under 6 dose dataset after removing the highest dose data point; LRM-6noS: LRM under 6-dose dataset after removing the lowest dose data point; LRM-7lessE: LRM under 7-dose dataset with less extreme data points; LRM-7NCP: LRM under 7-dose dataset with extreme data points and dose-dependent precision; HLRM: heavy-tailed linear regression model; HLRM-7: Heavy-tailed LRM under 7-dose dataset with extreme data points; HLRM-6noL: Heavy-tailed LRM under 6-dose dataset after removing the highest dose data point; HLRM-6noS: Heavy-tailed LRM under 6-dose dataset after removing the lowest dose data point; HLRM-7lessE: Heavy-tailed LRM under 7-dose dataset with less extreme data points; HLRM-7NCP: Heavy-tailed LRM under 7-dose dataset with extreme data points and dose-dependent precision; BRM: robust beta regression model; BRM-7: BRM under 7-dose dataset with extreme data points; BRM-6noL: BRM under 6-dose dataset after removing the highest dose data point; BRM-6noS: BRM under 6-dose dataset after removing the lowest dose data point; BRM-7lessE: BRM under 7-dose dataset with less extreme data points; BRM-7NCP: BRM under 7-dose dataset with extreme data points and dose-dependent precision. Detailed model descriptions of LRM, HLRM, and BRM are provided in Materials and methods section.
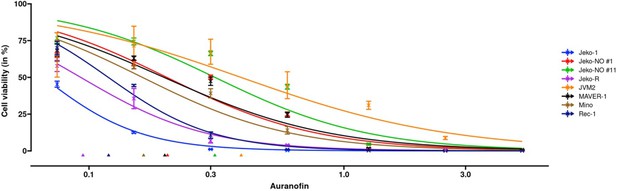
Dose-response curve estimation of auranofin (μM) under different MCL cell lines.
The dose-response curve was fitted with a dose-dependent precision with as an additional regressor for the precision estimator. Observed dose effects are displayed with interval bars, which end with arrows when estimated intervals exceed (0,1). Triangles at the bottom indicate IC50 values for each MCL cell line. MCL: mantle cell lymphoma.
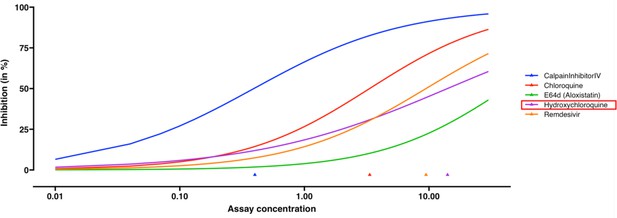
Dose-response curve estimation of anti-viral drugs under the same biological batch with SARS-CoV-2 data.
The robust beta regression gives reasonable estimations to the dose-response curve of hydroxychloroquine, compared to the inconclusive dose-response curve fitted by linear regression in Bobrowski et al. (2020). The plot is generated without selecting the option of mean and confidence interval for observations. Triangles indicate the estimated EC50 values for each drug.
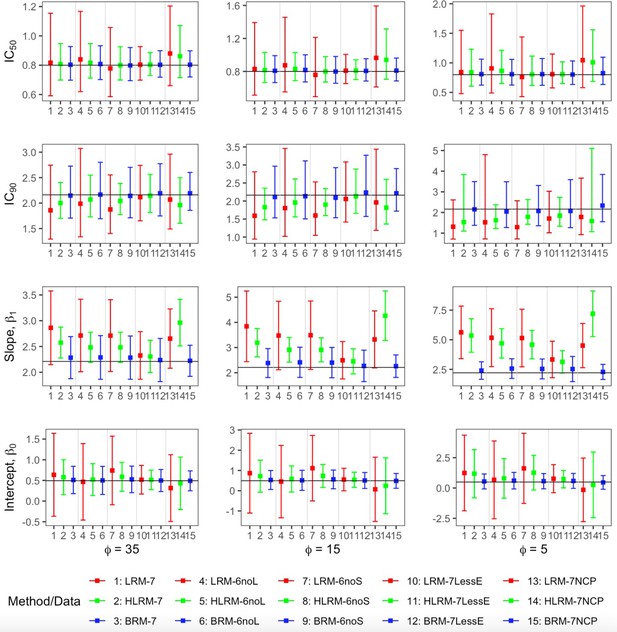
Comparison of the point estimates and 95% confidence intervals using linear regression model, heavy-tailed linear regression model and robust beta regression model, with data simulated from beta error term.
The vertical solid lines indicate the true values. The dots represent the averaged point estimates and the bars represent the averaged lower and upper bound of 95% CIs. The point estimation by robust beta regression is consistently closer to the true value with a narrower 95% CI compared to the linear regression model. The 95% CI of heavy-tailed linear regression underestimates the nominal coverage probability. LRM: linear regression model; LRM-7: LRM under 7 dose dataset with extreme data points; LRM-6noL: LRM under 6 dose dataset after removing the highest dose data point; LRM-6noS: LRM under 6 dose dataset after removing the lowest dose data point; LRM-7lessE: LRM under 7 dose dataset with less extreme data points; LRM-7NCP: LRM under 7 dose dataset with extreme data points and dose-dependent precision; HLRM: heavy-tailed linear regression model; HLRM-7: Heavy-tailed LRM under 7 dose dataset with extreme data points; HLRM-6noL: Heavy-tailed LRM under 6 dose dataset after removing the highest dose data point; HLRM-6noS: Heavy-tailed LRM under 6 dose dataset after removing the lowest dose data point; HLRM-7lessE: Heavy-tailed LRM under 7 dose dataset with less extreme data points; HLRM-7NCP: Heavy-tailed LRM under 7 dose dataset with extreme data points and dose-dependent precision; BRM: robust beta regression model; BRM-7: BRM under 7 dose dataset with extreme data points; BRM-6noL: BRM under 6 dose dataset after removing the highest dose data point; BRM-6noS: BRM under 6 dose dataset after removing the lowest dose data point; BRM-7lessE: BRM under 7 dose dataset with less extreme data points; BRM-7NCP: BRM under 7 dose dataset with extreme data points and dose-dependent precision.
Tables
Simulation result of bias, RMSE and 95% CI coverage probability corresponding to normal error terms.
| Scenario | Method | Bias | RMSE | 95% CI Coverage Probability | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | IC90 | IC50 | IC90 | IC50 | IC90 | ||||||||
| (a)data simulated using normal error term with SD = 0.005 | |||||||||||||
| 7 doses with extreme values | LRM | 0.005 | –0.047 | 0.037 | 0.152 | 0.098 | 0.298 | 0.525 | 0.557 | 0.954 | 0.773 | 0.943 | 0.666 |
| HLRM | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.018 | 0.102 | 0.063 | 0.169 | 0.468 | 0.335 | 0.463 | 0.225 | |
| BRM | 0.000 | –0.004 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.130 | 0.044 | 0.088 | 0.981 | 0.927 | 0.975 | 0.889 | |
| 6 doses after removing largest | LRM | 0.009 | –0.01 | –0.024 | 0.098 | 0.045 | 0.184 | 0.129 | 0.517 | 0.967 | 0.921 | 0.971 | 0.691 |
| HLRM | –0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | –0.001 | 0.014 | 0.063 | 0.037 | 0.065 | 0.453 | 0.408 | 0.467 | 0.250 | |
| BRM | 0.001 | 0.005 | –0.00 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.132 | 0.024 | 0.089 | 0.955 | 0.892 | 0.950 | 0.844 | |
| 6 doses after removing smallest | LRM | –0.007 | –0.036 | 0.070 | 0.102 | 0.037 | 0.306 | 0.362 | 0.533 | 0.969 | 0.623 | 0.933 | 0.695 |
| HLRM | 0.001 | 0.007 | –0.002 | –0.001 | 0.014 | 0.083 | 0.046 | 0.064 | 0.456 | 0.249 | 0.400 | 0.259 | |
| BRM | –0.001 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.151 | 0.039 | 0.089 | 0.956 | 0.872 | 0.940 | 0.853 | |
| 7 doses with less extreme values | LRM | 0.000 | –0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.030 | 0.016 | 0.026 | 0.891 | 0.828 | 0.883 | 0.799 |
| HLRM | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.031 | 0.016 | 0.028 | 0.668 | 0.599 | 0.661 | 0.567 | |
| BRM | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.026 | 0.013 | 0.024 | 0.864 | 0.823 | 0.860 | 0.800 | |
| 7 doses with extreme values and dose-dependent precision | LRM | –0.016 | –0.047 | 0.137 | 0.111 | 0.069 | 0.409 | 0.583 | 0.520 | 0.965 | 0.573 | 0.921 | 0.685 |
| HLRM | 0.000 | 0.003 | –0.001 | –0.001 | 0.008 | 0.049 | 0.027 | 0.036 | 0.325 | 0.188 | 0.290 | 0.151 | |
| BRM | 0.000 | 0.023 | –0.003 | –0.011 | 0.003 | 0.196 | 0.023 | 0.095 | 0.957 | 0.849 | 0.931 | 0.794 | |
| (b)data simulated using normal error term with SD = 0.01 | |||||||||||||
| 7 doses with extreme values | LRM | 0.030 | –0.200 | 0.166 | 0.804 | 0.224 | 0.544 | 1.234 | 1.305 | 0.958 | 0.699 | 0.950 | 0.716 |
| HLRM | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.025 | 0.105 | 0.031 | 0.238 | 0.199 | 0.795 | 0.408 | 0.286 | 0.404 | 0.194 | |
| BRM | 0.001 | –0.039 | 0.013 | 0.060 | 0.030 | 0.172 | 0.094 | 0.155 | 0.981 | 0.931 | 0.976 | 0.892 | |
| 6 doses after removing largest | LRM | 0.040 | –0.088 | –0.125 | 0.549 | 0.101 | 0.280 | 0.314 | 1.245 | 0.966 | 0.924 | 0.972 | 0.734 |
| HLRM | –0.004 | 0.007 | 0.008 | –0.008 | 0.027 | 0.125 | 0.075 | 0.123 | 0.424 | 0.384 | 0.445 | 0.241 | |
| BRM | 0.005 | –0.012 | –0.007 | 0.040 | 0.019 | 0.140 | 0.044 | 0.148 | 0.954 | 0.893 | 0.949 | 0.850 | |
| 6 doses after removing smallest | LRM | –0.027 | –0.172 | 0.357 | 0.531 | 0.080 | 0.534 | 0.836 | 1.220 | 0.966 | 0.561 | 0.937 | 0.734 |
| HLRM | 0.004 | 0.027 | –0.010 | –0.005 | 0.028 | 0.160 | 0.089 | 0.125 | 0.434 | 0.247 | 0.384 | 0.253 | |
| BRM | –0.005 | –0.035 | 0.025 | 0.040 | 0.018 | 0.178 | 0.078 | 0.143 | 0.958 | 0.877 | 0.943 | 0.857 | |
| 7 doses with less extreme values | LRM | 0.000 | –0.001 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.011 | 0.060 | 0.032 | 0.053 | 0.892 | 0.826 | 0.883 | 0.799 |
| HLRM | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 0.061 | 0.032 | 0.056 | 0.665 | 0.597 | 0.657 | 0.564 | |
| BRM | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.009 | 0.052 | 0.026 | 0.048 | 0.865 | 0.822 | 0.860 | 0.801 | |
| 7 doses with extreme values and dose-dependent precision | LRM | –0.052 | –0.215 | 0.524 | 0.462 | 0.130 | 0.622 | 1.123 | 0.984 | 0.965 | 0.521 | 0.921 | 0.726 |
| HLRM | 0.002 | 0.011 | –0.004 | –0.003 | 0.016 | 0.096 | 0.053 | 0.071 | 0.303 | 0.180 | 0.273 | 0.148 | |
| BRM | 0.000 | 0.012 | –0.001 | –0.005 | 0.009 | 0.142 | 0.054 | 0.080 | 0.957 | 0.851 | 0.932 | 0.798 | |
| (c)data simulated using normal error term with SD = 0.05 | |||||||||||||
| 7 doses with extreme values | LRM | 0.079 | –0.463 | 0.560 | 2.399 | 0.393 | 0.924 | 2.128 | 1.853 | 0.948 | 0.612 | 0.942 | 0.591 |
| HLRM | 0.024 | 0.047 | 0.345 | 1.524 | 0.223 | 1.050 | 1.600 | 2.638 | 0.477 | 0.258 | 0.447 | 0.083 | |
| BRM | 0.013 | 0.029 | 0.010 | 0.095 | 0.129 | 0.524 | 0.371 | 0.377 | 0.857 | 0.861 | 0.869 | 0.855 | |
| 6 doses after removing largest | LRM | 0.079 | –0.338 | 0.337 | 2.194 | 0.276 | 0.749 | 2.054 | 2.239 | 0.968 | 0.779 | 0.975 | 0.675 |
| HLRM | –0.005 | 0.080 | 0.260 | 0.926 | 0.170 | 0.820 | 1.392 | 2.547 | 0.407 | 0.293 | 0.417 | 0.146 | |
| BRM | 0.017 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.160 | 0.124 | 0.512 | 0.387 | 0.430 | 0.879 | 0.835 | 0.912 | 0.812 | |
| 6 doses after removing smallest | LRM | 0.022 | –0.403 | 0.666 | 2.232 | 0.335 | 0.965 | 1.936 | 2.220 | 0.972 | 0.610 | 0.898 | 0.681 |
| HLRM | 0.035 | 0.244 | 0.162 | 0.919 | 0.158 | 0.998 | 1.332 | 2.526 | 0.410 | 0.209 | 0.320 | 0.146 | |
| BRM | 0.009 | –0.021 | 0.030 | 0.160 | 0.119 | 0.511 | 0.358 | 0.420 | 0.874 | 0.754 | 0.862 | 0.819 | |
| 7 doses with less extreme values | LRM | 0.005 | –0.077 | 0.086 | 0.362 | 0.084 | 0.383 | 0.693 | 1.215 | 0.905 | 0.795 | 0.895 | 0.813 |
| HLRM | 0.001 | 0.029 | 0.009 | 0.039 | 0.053 | 0.327 | 0.185 | 0.446 | 0.619 | 0.551 | 0.610 | 0.520 | |
| BRM | 0.002 | –0.001 | 0.012 | 0.062 | 0.054 | 0.296 | 0.187 | 0.311 | 0.861 | 0.810 | 0.858 | 0.815 | |
| 7 doses with extreme values and dose-dependent precision | LRM | –0.029 | –0.441 | 0.994 | 1.679 | 0.297 | 0.955 | 1.840 | 1.715 | 0.945 | 0.444 | 0.904 | 0.678 |
| HLRM | 0.006 | 0.037 | 0.278 | 0.617 | 0.106 | 0.710 | 1.152 | 1.781 | 0.335 | 0.145 | 0.295 | 0.105 | |
| BRM | –0.005 | 0.037 | 0.023 | –0.002 | 0.040 | 0.323 | 0.172 | 0.271 | 0.954 | 0.819 | 0.930 | 0.758 | |
Simulation result of bias, RMSE and 95% CI coverage probability corresponding to beta error terms.
| Scenario | Method | Bias | RMSE | 95% CI Coverage Probability | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | IC90 | IC50 | IC90 | IC50 | IC90 | ||||||||
| (a)data simulated using beta error term with ϕ=35 | |||||||||||||
| 7 doses with extreme values | LRM | 0.017 | –0.304 | 0.142 | 0.653 | 0.163 | 0.481 | 0.658 | 0.686 | 0.924 | 0.697 | 0.909 | 0.566 |
| HLRM | 0.008 | –0.161 | 0.085 | 0.366 | 0.117 | 0.478 | 0.402 | 0.576 | 0.581 | 0.429 | 0.571 | 0.313 | |
| BRM | 0.003 | –0.014 | 0.018 | 0.073 | 0.074 | 0.339 | 0.219 | 0.275 | 0.835 | 0.818 | 0.832 | 0.829 | |
| 6 doses after removing largest | LRM | 0.039 | –0.174 | –0.027 | 0.504 | 0.115 | 0.402 | 0.354 | 0.666 | 0.933 | 0.864 | 0.936 | 0.666 |
| HLRM | 0.015 | –0.092 | 0.026 | 0.273 | 0.109 | 0.463 | 0.337 | 0.486 | 0.581 | 0.518 | 0.594 | 0.368 | |
| BRM | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.077 | 0.077 | 0.375 | 0.229 | 0.298 | 0.812 | 0.808 | 0.811 | 0.803 | |
| 6 doses after removing smallest | LRM | –0.022 | –0.288 | 0.248 | 0.502 | 0.108 | 0.501 | 0.499 | 0.670 | 0.930 | 0.620 | 0.901 | 0.664 |
| HLRM | 0.000 | –0.120 | 0.094 | 0.274 | 0.106 | 0.509 | 0.366 | 0.487 | 0.596 | 0.383 | 0.547 | 0.368 | |
| BRM | –0.002 | –0.020 | 0.031 | 0.074 | 0.075 | 0.353 | 0.223 | 0.298 | 0.815 | 0.782 | 0.805 | 0.800 | |
| 7 doses with less extreme values | LRM | 0.004 | –0.045 | 0.023 | 0.117 | 0.063 | 0.332 | 0.195 | 0.300 | 0.900 | 0.828 | 0.891 | 0.821 |
| HLRM | 0.003 | –0.017 | 0.021 | 0.096 | 0.067 | 0.382 | 0.205 | 0.323 | 0.686 | 0.630 | 0.680 | 0.619 | |
| BRM | 0.003 | 0.031 | 0.004 | 0.028 | 0.058 | 0.331 | 0.170 | 0.272 | 0.845 | 0.837 | 0.847 | 0.838 | |
| 7 doses with extreme values and dose-dependent precision | LRM | 0.080 | –0.093 | –0.179 | 0.444 | 0.147 | 0.281 | 0.435 | 0.548 | 0.904 | 0.908 | 0.927 | 0.639 |
| HLRM | 0.061 | –0.200 | –0.063 | 0.753 | 0.199 | 0.553 | 0.676 | 0.967 | 0.484 | 0.447 | 0.520 | 0.231 | |
| BRM | 0.003 | 0.031 | –0.003 | 0.012 | 0.067 | 0.277 | 0.182 | 0.236 | 0.755 | 0.780 | 0.768 | 0.772 | |
| (b)data simulated using beta error term with ϕ=15 | |||||||||||||
| 7 doses with extreme values | LRM | 0.029 | –0.571 | 0.373 | 1.633 | 0.233 | 0.555 | 1.177 | 1.197 | 0.941 | 0.588 | 0.910 | 0.406 |
| HLRM | 0.016 | –0.334 | 0.225 | 0.983 | 0.172 | 0.657 | 0.725 | 1.186 | 0.561 | 0.353 | 0.544 | 0.213 | |
| BRM | 0.008 | –0.050 | 0.036 | 0.174 | 0.109 | 0.464 | 0.324 | 0.403 | 0.817 | 0.790 | 0.820 | 0.805 | |
| 6 doses after removing largest | LRM | 0.074 | –0.360 | –0.043 | 1.269 | 0.164 | 0.516 | 0.635 | 1.192 | 0.942 | 0.823 | 0.939 | 0.556 |
| HLRM | 0.029 | –0.206 | 0.086 | 0.702 | 0.164 | 0.715 | 0.594 | 0.925 | 0.552 | 0.445 | 0.551 | 0.272 | |
| BRM | 0.018 | –0.028 | 0.019 | 0.203 | 0.117 | 0.527 | 0.355 | 0.446 | 0.778 | 0.783 | 0.794 | 0.776 | |
| 6 doses after removing smallest | LRM | –0.042 | –0.564 | 0.620 | 1.280 | 0.157 | 0.596 | 0.890 | 1.180 | 0.939 | 0.503 | 0.905 | 0.555 |
| HLRM | –0.001 | –0.262 | 0.237 | 0.700 | 0.160 | 0.712 | 0.663 | 0.917 | 0.546 | 0.300 | 0.486 | 0.268 | |
| BRM | –0.001 | –0.071 | 0.066 | 0.192 | 0.115 | 0.499 | 0.345 | 0.449 | 0.787 | 0.733 | 0.782 | 0.777 | |
| 7 doses with less extreme values | LRM | 0.008 | –0.104 | 0.059 | 0.286 | 0.096 | 0.513 | 0.320 | 0.489 | 0.906 | 0.795 | 0.884 | 0.807 |
| HLRM | 0.009 | –0.030 | 0.048 | 0.240 | 0.103 | 0.726 | 0.325 | 0.517 | 0.694 | 0.602 | 0.678 | 0.598 | |
| BRM | 0.006 | 0.074 | 0.012 | 0.062 | 0.088 | 0.553 | 0.260 | 0.409 | 0.838 | 0.836 | 0.841 | 0.847 | |
| 7 doses with extreme values and dose-dependent precision | LRM | 0.165 | –0.202 | –0.425 | 1.114 | 0.218 | 0.374 | 0.771 | 0.959 | 0.916 | 0.886 | 0.941 | 0.534 |
| HLRM | 0.141 | –0.347 | –0.250 | 2.055 | 0.291 | 1.027 | 1.270 | 1.798 | 0.515 | 0.440 | 0.576 | 0.136 | |
| BRM | 0.010 | 0.053 | –0.008 | 0.050 | 0.104 | 0.423 | 0.281 | 0.368 | 0.763 | 0.790 | 0.764 | 0.769 | |
| (c)data simulated using beta error term with ϕ=5 | |||||||||||||
| 7 doses with extreme values | LRM | 0.042 | –0.851 | 0.748 | 3.414 | 0.270 | 0.527 | 1.611 | 1.421 | 0.948 | 0.423 | 0.898 | 0.198 |
| HLRM | 0.040 | –0.629 | 0.689 | 3.147 | 0.278 | 1.518 | 1.480 | 2.112 | 0.681 | 0.241 | 0.644 | 0.094 | |
| BRM | 0.008 | –0.011 | 0.047 | 0.191 | 0.161 | 0.606 | 0.589 | 0.767 | 0.811 | 0.800 | 0.815 | 0.811 | |
| 6 doses after removing largest | LRM | 0.106 | –0.636 | 0.181 | 2.962 | 0.234 | 0.865 | 1.401 | 1.604 | 0.949 | 0.684 | 0.938 | 0.356 |
| HRLM | 0.075 | –0.098 | 0.276 | 2.410 | 0.274 | 8.599 | 1.351 | 2.082 | 0.607 | 0.362 | 0.600 | 0.142 | |
| BRM | 0.007 | –0.115 | 0.112 | 0.355 | 0.166 | 0.643 | 0.621 | 0.761 | 0.762 | 0.752 | 0.773 | 0.769 | |
| 6 doses after removing smallest | LRM | –0.039 | –0.871 | 1.126 | 2.935 | 0.231 | 0.649 | 1.428 | 1.620 | 0.953 | 0.380 | 0.883 | 0.362 |
| HLRM | 0.004 | –0.371 | 0.773 | 2.379 | 0.261 | 5.238 | 1.464 | 2.068 | 0.599 | 0.206 | 0.492 | 0.149 | |
| BRM | 0.008 | –0.087 | 0.070 | 0.328 | 0.166 | 0.588 | 0.509 | 0.724 | 0.766 | 0.755 | 0.772 | 0.773 | |
| 7 doses with less extreme values | LRM | 0.008 | –0.456 | 0.275 | 1.126 | 0.152 | 0.515 | 0.679 | 1.041 | 0.915 | 0.639 | 0.874 | 0.707 |
| HLRM | 0.007 | –0.315 | 0.236 | 0.923 | 0.164 | 0.767 | 0.651 | 1.047 | 0.681 | 0.475 | 0.644 | 0.491 | |
| BRM | 0.002 | –0.088 | 0.093 | 0.318 | 0.132 | 0.588 | 0.423 | 0.660 | 0.839 | 0.812 | 0.834 | 0.835 | |
| 7 doses with extreme values and dose-dependent precision | LRM | 0.245 | –0.378 | –0.646 | 2.300 | 0.274 | 0.470 | 1.207 | 1.262 | 0.908 | 0.833 | 0.947 | 0.343 |
| HLRM | 0.209 | –0.578 | –0.233 | 4.982 | 0.332 | 6.852 | 2.016 | 2.017 | 0.683 | 0.381 | 0.728 | 0.050 | |
| BRM | 0.025 | 0.171 | –0.032 | 0.074 | 0.161 | 0.762 | 0.426 | 0.549 | 0.757 | 0.796 | 0.761 | 0.770 | |
The first example of REAP application with B-cell lymphoma data, corresponding with Figure 5.
IC50 estimations are ranked from low to high. Hypothesis testings on equal potency (i.e., concentration for IC50) were conducted pairwise with the group right above (one rank lower). Jeko-1 has the highest potency and the difference of IC50 estimations between Jeko-1 and Jeko-R is significant with a P-value <0.0001. The B-cell lymphoma dataset is available on Github (Fang et al., 2022).
| Model | Intercept | Slope (m) | Std. Err for m | P-value for m>1 | IC50 estimation | Std. Err for IC50 estimation | Pairwise comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jeko-1 | –4.807 | –1.252 | 0.155 | 0.0519 | 0.021 | 0.008 | - |
| Jeko-R | –4.305 | –1.822 | 0.112 | <.0001 | 0.094 | 0.006 | <0.0001 |
| Rec-1 | –5.304 | –2.63 | 0.091 | <.0001 | 0.133 | 0.004 | <0.0001 |
| Mino | –2.684 | –1.474 | 0.141 | 0.0004 | 0.162 | 0.015 | 0.0656 |
| Jeko-NO #1 | –2.012 | –1.192 | 0.135 | 0.0769 | 0.185 | 0.021 | 0.3755 |
| MAVER-1 | –2.21 | –1.37 | 0.125 | 0.0015 | 0.199 | 0.021 | 0.6312 |
| Jeko-NO #11 | –1.459 | –1.267 | 0.152 | 0.0398 | 0.316 | 0.038 | 0.0114 |
| JVM2 | –1.056 | –1.271 | 0.135 | 0.0223 | 0.436 | 0.055 | 0.0818 |
The output for the estimated dose-response curve of anti-viral drugs under the same biological batch with SARS-CoV-2 data.
Calpain inhibitor IV has the highest potency (P-value = 0.0038). The reconstructed SARS-CoV-2 dataset is available on Github (Fang et al., 2022).
| Model | Intercept | Slope (m) | Std. Err for m | P-value for m>1 | EC50 estimation | Std. Err for EC50 estimation | Pairwise comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CalpainInhibitorIV | 0.678 | 0.725 | 0.114 | 0.9918 | 0.393 | 0.103 | - |
| Chloroquine | –1.013 | 0.84 | 0.135 | 0.8813 | 3.337 | 0.88 | 0.0038 |
| Remdesivir | –1.791 | 0.797 | 0.12 | 0.9553 | 9.469 | 2.638 | 0.0282 |
| Hydroxychloroquine | –1.485 | 0.562 | 0.075 | 1 | 14.074 | 4.994 | 0.4445 |
| E64d (Aloxistatin) | –3.211 | 0.861 | 0.129 | 0.8587 | 41.61 | 15.473 | 0.1242 |





