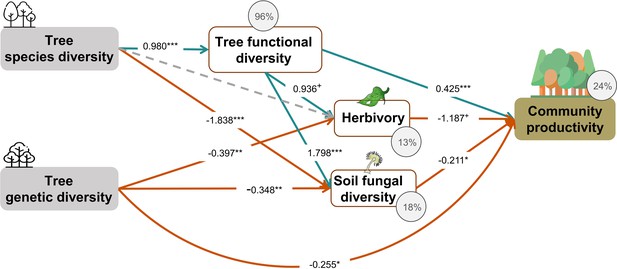
Tree species and genetic diversity increase productivity via functional diversity and trophic feedbacks
Figures
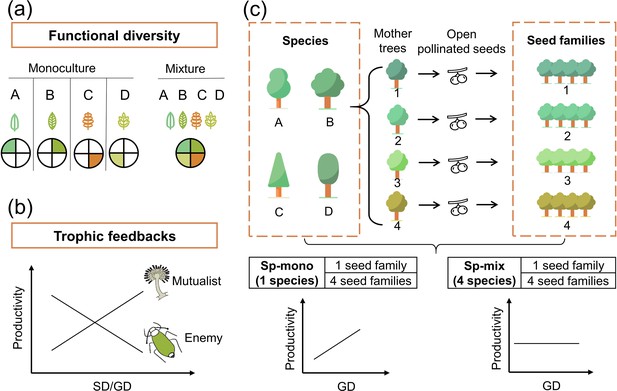
Conceptual illustration of the effects of functional diversity (a) and trophic feedbacks on tree productivity (b) and the species × genetic diversity experimental design (c).
(a) shows resources for plant growth or other trophic groups in complementary ways due to functional diversity: the four hypothetical species/genotypes (A, B, C, D) with different functional traits (indicated by colored leaves) are able to use a heterogeneous resource (indicated by colored segments), thereby resulting in increased plant growth or providing niche opportunities for other trophic groups (Diaz and Cabido, 2001). (b) shows the mechanism of trophic feedbacks: with the increase in species diversity (SD) or genetic diversity (GD), negative feedbacks of enemies (e.g., herbivores) on tree productivity decrease due to diluted densities (Duffy, 2003) and positive feedbacks of mutualists on tree productivity increase due to increased diversity (e.g., mycorrhizal fungi; Semchenko et al., 2018). (c) We represent tree species and genetic diversity by the number of species and seed families (all seeds from the same mother tree are defined as a single seed family), respectively. Species diversity and genetic diversity per plot were both 1 or 4, resulting in a full factorial design of species × genetic diversity. We hypothesize that the positive effects of tree genetic diversity should be stronger in tree species monocultures (Sp-mono) than mixtures (Sp-mix).
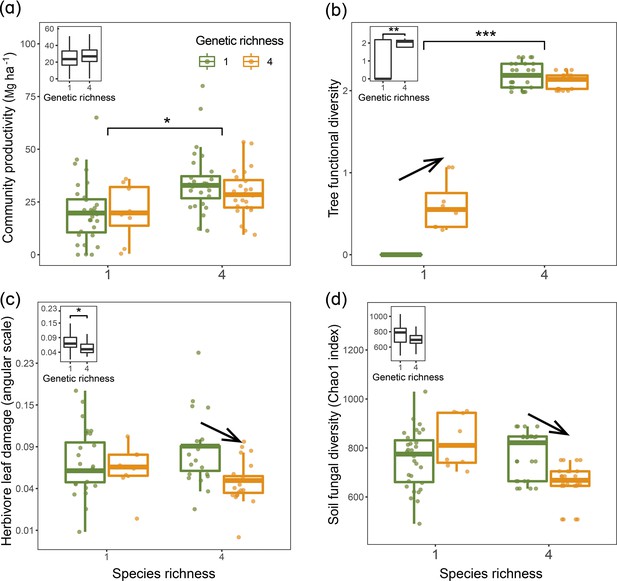
Tree community productivity, tree functional diversity, and trophic interactions in tree communities of low vs. high species and genetic richness.
The following effects were tested in linear mixed-effects models (LMMs) (n=92): species richness main effect (left vs. right pair of bars in each panel), genetic richness main effect (inset on upper left in each panel), genetic richness effect within each species richness level (arrows between bars within pairs). (a) tree community productivity, (b) tree functional diversity, (c) herbivore leaf damage, and (d) soil fungal diversity. The lower and upper hinges of the bars correspond to the first and third quartiles (the 25th and 75th percentiles); the lower and upper whisker extends from the hinge correspond to 1.5 * interquartile range (third quartiles - first quartiles). Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*** p<0.0001, ** p<0.001, * p<0.05); solid arrow indicates (p<0.05, without arrow indicates p>0.1). Details of the fitted models are given in Appendix 2—table 1.
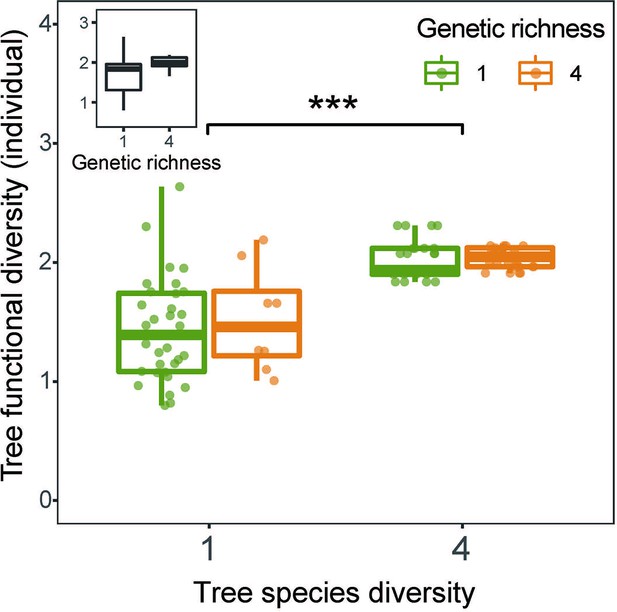
Effects of tree species diversity and genetic diversity on tree functional diversity calculated from traits measured on individual trees.
The lower and upper hinges of the bars correspond to the first and third quartiles (the 25th and 75th percentiles); the lower and upper whisker extends from the hinge correspond to 1.5 * interquartile range (third quartiles - first quartiles), n=92. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*** p<0.0001, ** p<0.001, * p<0.05, + p<0.1, and ns p>0.1). Details of the fitted models are shown in Appendix 2—table 1. .
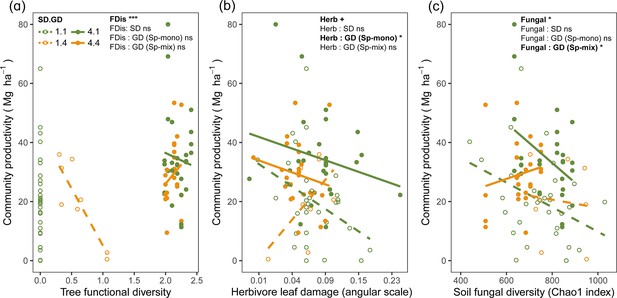
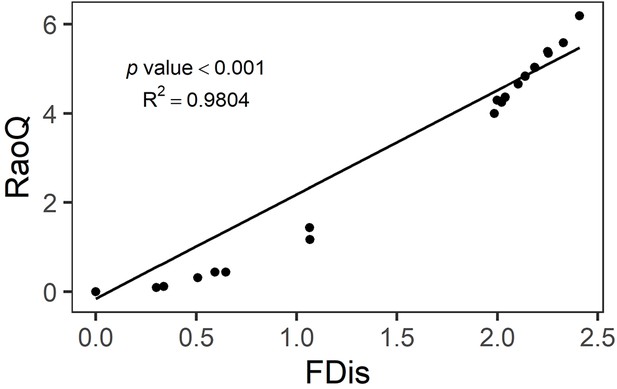
Bivariate relationships between tree community productivity and tree functional diversity (a), herbivory (b), and soil fungal diversity (c).
Green unfilled/dashed symbols represent genetic monocultures in species monocultures, green filled/solid symbols represent genetic monocultures in species mixture, orange unfilled/dashed symbols represent genetic mixtures in species monocultures, orange filled/solid symbols represent genetic mixture in species mixture. FDis, tree functional diversity; Herb, herbivore damage; Fungal, soil fungal diversity; Sp-mono, species monocultures; Sp-mix, species mixtures; SD, species diversity; GD, genetic diversity. ‘:’ indicates the interaction effects. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.001, * p < 0.05, + p < 0.1, and ns p > 0.1).
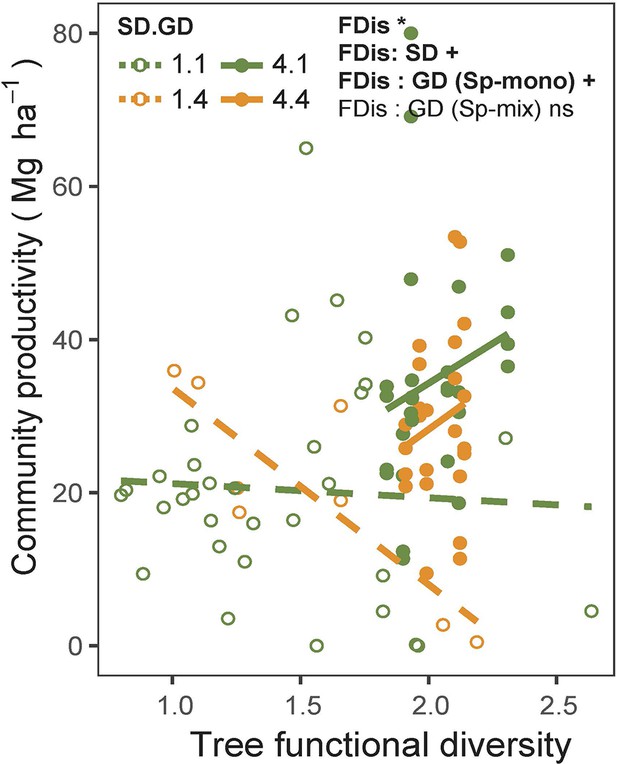
Effects of tree functional diversity calculated from traits measured on individual trees on community productivity.
Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.001, * p < 0.05, + p < 0.1, and ns p > 0.1). Details of the fitted models are shown in Appendix 2—table 1.
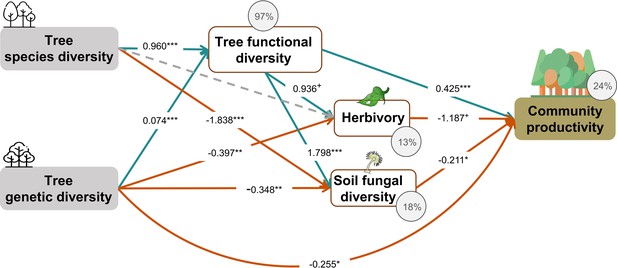
Effects of tree diversity on higher trophic levels and tree community productivity (global Fisher’s C = 1.677, DF = 4, p = 0.795).
Positive and negative paths are indicated in green and orange, respectively. The standardized path coefficients are indicated by the numbers, statistical significance is indicated by asterisks (*** p < 0.0001, ** p< 0.001, * p < 0.05, and + p < 0.1), and the explained variance of dependent variables is indicated by the percentage values. The gray dashed line indicates a nonsignificant (p > 0.1) pathway in the final model. The direct effect of tree species diversity on tree community productivity was removed in the model because it was not significant (p > 0.5) and the removal reduced the AICc by more than 2 (ΔAICc = 3.269).
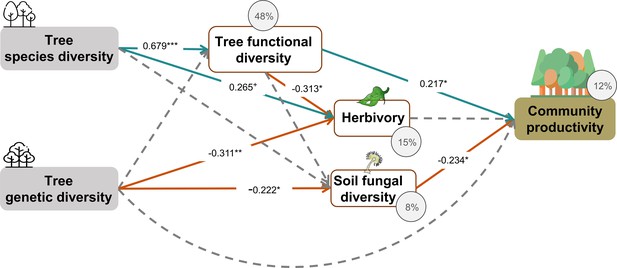
Effects of tree diversity on higher trophic levels and tree community productivity with functional diversity calculated using trait values of individual trees (global Fisher’s C = 119.558 DF = 4, p=0.001).
Positive and negative paths are indicated in green and orange, respectively. The standardized path coefficients are indicated by the numbers, statistical significance is indicated by asterisks (*** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.001, * p < 0.05, and + p < 0.1), and the explained variance of dependent variables is indicated by the percentage values. Gray dashed lines indicate nonsignificant (p > 0.1) pathways in the final model. To allow comparison, the same structural equation model (SEM) as for Figure 4 was used.
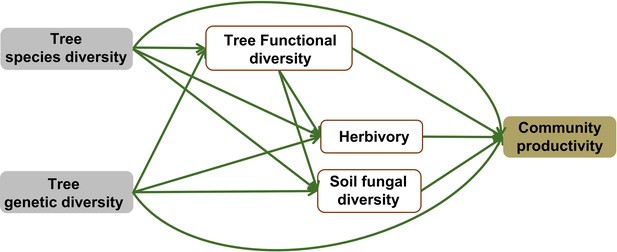
Initial structural equation model (SEM) used in this study.
Tree species diversity represents the number of tree species, genetic diversity represents the number of seed families per tree species, and functional diversity (based on FDis) represents the mean distance of seed-family means to the centroid of all seed families. Herbivory represents the percentage of herbivore leaf damage, soil fungal diversity was quantified by Chao1 diversity index, and community productivity represents tree productivity of subplots (Mg ha–1).
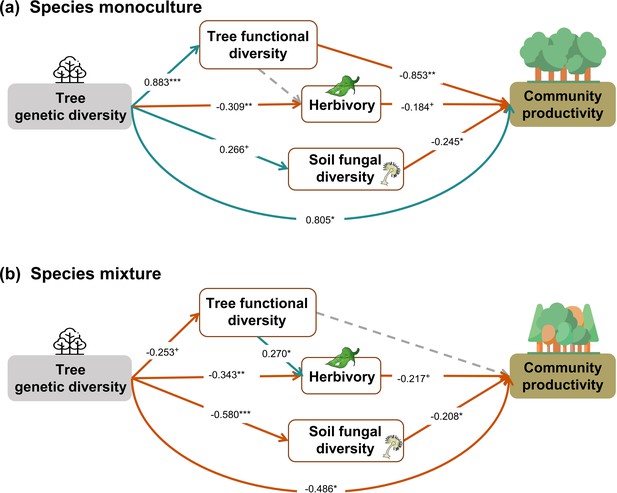
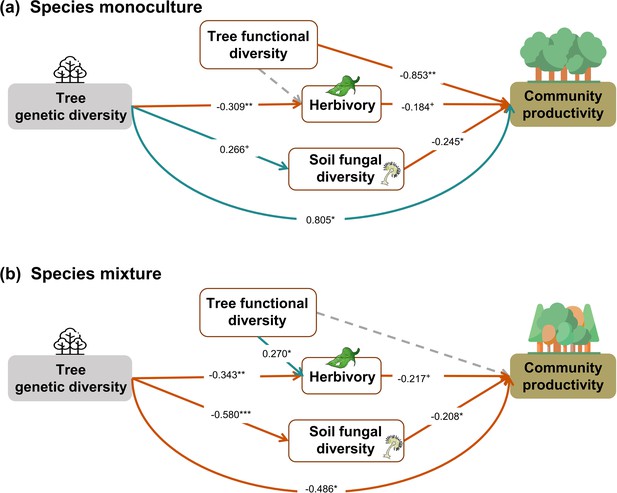
Effects of tree genetic diversity on higher trophic levels and tree community productivity in tree species monocultures (a) and the mixture of the four tree species (b).
The results were obtained by a multigroup structural equation models (SEM) (global Fisher’s C = 3.416, DF = 4, p = 0.491). Positive and negative paths are indicated in green and orange, respectively. The standardized path coefficients are indicated by the numbers, and statistical significance is indicated by asterisks (*** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.001, * p < 0.05, and + p < 0.1). Gray dashed lines indicate nonsignificant (p > 0.1) pathways in the final model. The nonsignificant path from tree functional diversity to soil fungal diversity was removed because the removal decreased the AICc by more than 2 (ΔAICc = 2.176). Multigroup SEM analyses first test the interaction (explanatory variable × groups) in the whole model using the full dataset and then estimate the local coefficient for each path by using different datasets (the full dataset or group sub-datasets [species richness = 1 or 4, respectively]) depending on the significance of explanatory variable × groups interactions. Thus, we could not get the percentage of the explained variance in the local multi-group SEM model. All the paths were allowed to be different between species monocultures and mixtures (none of the paths was constrained manually beforehand); the interaction statistics of the multigroup model, and the explained variance of the whole model for each response is shown in Appendix 2—table 5.
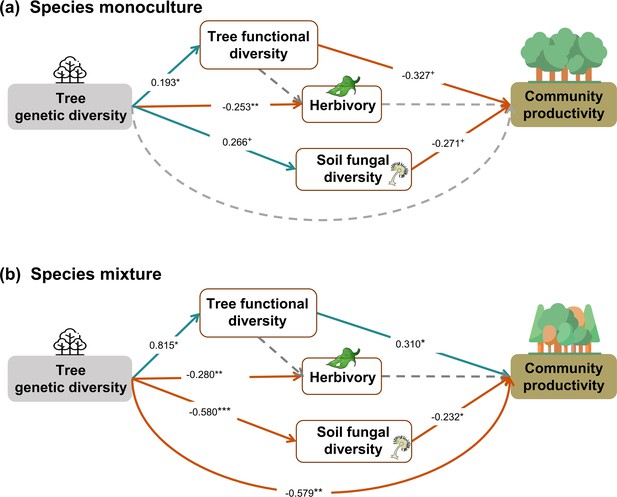
Effects of tree genetic diversity on higher trophic levels and tree community productivity in tree species monocultures (a) and mixtures of four tree species (b) with functional diversity calculated using trait values of individual trees.
The results were obtained by a multigroup structural equation models (SEM) (global Fisher’s C = 2.747, DF = 4, p = 0.601). Positive and negative paths are indicated in green and orange. The standardized path coefficients are indicated by the numbers, and statistical significance is indicated by asterisks (*** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.001, * p < 0.05, and + p < 0.1). Gray dashed lines indicate nonsignificant (p > 0.1) pathways in the final model. Here, tree functional diversity was calculated from traits measured on individual trees. To allow comparison, the same SEM as for Figure 5 was used. Multigroup SEM analyses first test the interaction (explanatory variable × groups) in the whole model using the full dataset and then estimate the local coefficient for each path by using different datasets (the full dataset or group sub-datasets [species richness = 1 or 4, respectively]) depending on the significance of explanatory variable × groups interactions. Thus, we could not get the percentage of the explained variance in the local multigroup SEM model.
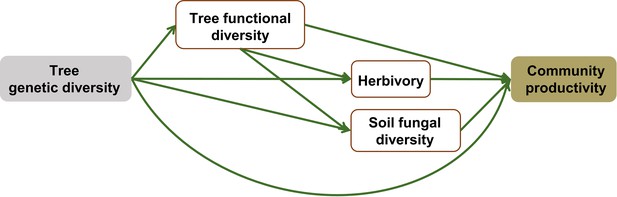
Initial structural equation models (SEM) structure of genetic diversity effects in both species monocultures and mixtures.
Genetic diversity represents the number of seed families per tree species. Functional diversity (based on FDis) represents the mean distance of seed-family means to the centroid of all seed families. Herbivory represents the percentage of herbivore leaf damage, soil fungal diversity was quantified by Chao1 diversity index, community productivity represents tree productivity of subplots (Mg ha–1).
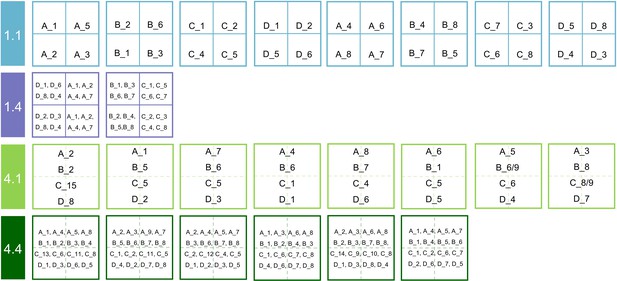
Diagram of the seed families planted in the species × genetic diversity experiment.
1.1: species diversity = 1, genetic diversity = 1; 1.4: species diversity = 1, genetic diversity = 4; 4.1: species diversity = 4, genetic diversity = 1; 4.4: species diversity = 4, genetic diversity = 4. The uppercase letters indicate four tree species (A: Alniphyllum fortunei; B: Cinnamomum camphora; C: Daphniphyllum oldhamii; D: Idesia polycarpa), the number after ‘_’ indicates the seed family tag of a given species, two numbers indicate both of the seed families were used in this plot due to not enough designed seedlings.
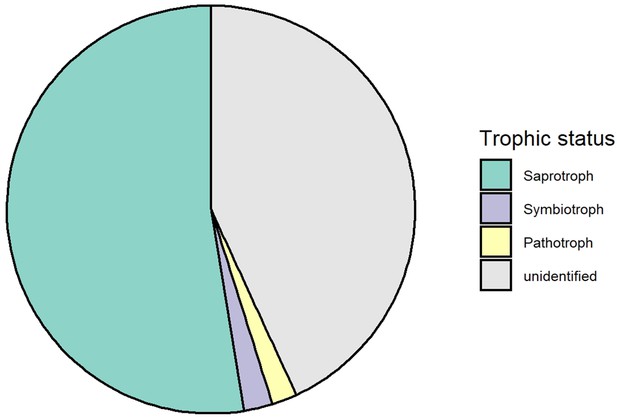
Trophic composition of soil fungi in this study.
All fungi from this study were pooled together to calculate the relative abundance of each trophic group.
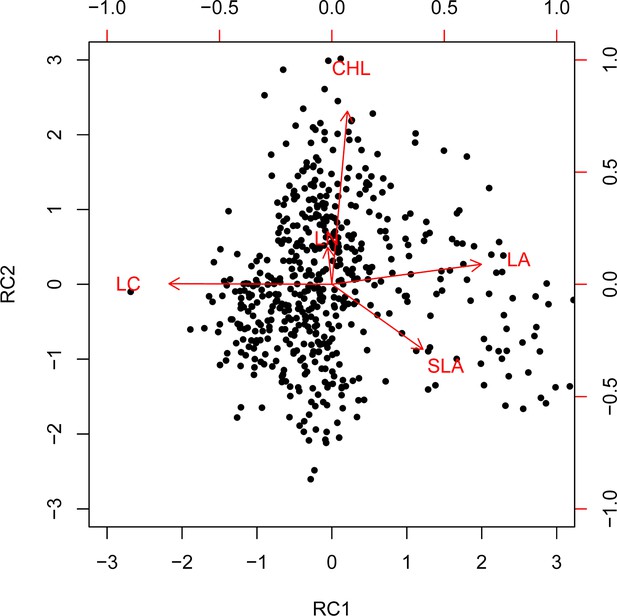
Varimax rotation principal component analysis (PCA) biplot for the five functional traits.
Effects of tree diversity on higher trophic levels and tree community productivity without the path between genetic diversity and functional diversity (global Fisher’s C = 16.766, DF = 6, p = 0.01).
Positive and negative paths are indicated in green and orange, respectively. The standardized path coefficients are indicated by the numbers, statistical significance is indicated by asterisks (*** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.001, * p < 0.05, and + p <0.1), and the explained variance of dependent variables is indicated by the percentage values. The gray dashed line indicates a nonsignificant (p > 0.1) pathway in the final model. To allow comparison, the same structural equation model (SEM) as for Figure 4 was used except excluding the path between genetic diversity and functional diversity.
Effects of tree genetic diversity on higher trophic levels and tree community productivity in tree species monocultures (a) and mixtures of four tree species (b) without the paths between genetic diversity and functional diversity.
The results were obtained by a multigroup structural equation model (SEM) (global Fisher’s C = 3.485, DF = 4, p = 0.480). Positive and negative paths are indicated in green and orange, respectively. The standardized path coefficients are indicated by the numbers, and statistical significance is indicated by asterisks (*** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.001, * p < 0.05, and + p <0.1). Gray dashed lines indicate nonsignificant (p > 0.1) pathways in the final model. Here, tree functional diversity was calculated from traits measured on individual trees. To allow comparison, the same SEM as for Figure 5 was used. Multigroup SEM analyses first test the interaction (explanatory variable × groups) in the whole model using the full dataset and then estimate the local coefficient for each path by using different datasets (the full dataset or group sub-datasets [species richness = 1 or 4, respectively]) depending on the significance of explanatory variable × groups interactions. Thus, we could not get the percentage of the explained variance in the local multigroup SEM model.
Tables
The designed and planted occurrence times of each seed family per species in the four diversity treatment combinations.
1.1: species diversity = 1, genetic diversity = 1; 1.4: species diversity = 1, genetic diversity = 4; 4.1: species diversity = 4, genetic diversity = 1; 4.4: species diversity = 4, genetic diversity = 4. ‘SP’ is the species name and ‘SF’ is the tag of seed family.The experiment was designed to use eight seed families per species, but additional or repeated seed families were used to complement the lack of enough individuals in some seed families. The numbers in brackets indicate the seed family tags that were used to complement. AlFo (A): Alniphyllum fortune’, CiCa (B): Cinnamomum camphora; DaOl (C): Daphniphyllum oldhamii; IdPo (D): Idesia polycarpa. ‘x’ represents the number of individuals per subplot, and the number of the ‘x’ represents the number of subplots.
| Tree diversity | 1.1 (x = 100) | 1.4 (x = 25) | 4.1 (x = 100) | 4.4 (x = 25) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP | SF | Tree individuals | Tree individuals | Tree individuals | Tree individuals |
| AlFo | 1 | x | x | x | x + x + x |
| (A) | 2 | x | x | x | x + x + x |
| 3 | x | x(1) | x | x + x + x | |
| 4 | x | x | x | x + x + x | |
| 5 | x | x(2) | x | x + x + x | |
| 6 | x | x(4) | x | x + x + x(9) | |
| 7 | x | x | x | x + x + x | |
| 8 | x | x(7) | x | x + x + x | |
| CiCa | 1 | x | x | x | x + x + x |
| (B) | 2 | x | x | x | x + x + x |
| 3 | x | x | x(6) | x + x + x | |
| 4 | x | x | x(6/9) | x + x + x | |
| 5 | x | x | x | x + x + x(3) | |
| 6 | x | x | x | x + x + x | |
| 7 | x | x | x | x + x + x | |
| 8 | x | x | x | x + x + x | |
| DaOl | 1 | x | x | x | x + x + x |
| (C) | 2 | x | x | x(7) | x + x + x |
| 3 | x | x | x(7) | x(11) + x(11) + x(9) | |
| 4 | x | x | x | x + x(10) + x(12) | |
| 5 | x | x | x | x + x + x(13) | |
| 6 | x | x | x | x + x + x | |
| 7 | x | x | x | x + x + x(14) | |
| 8 | x | x | x(8/9) | x + x + x | |
| IdPo | 1 | x | x | x | x + x + x |
| (D) | 2 | x | x | x | x + x + x |
| 3 | x | x | x | x + x + x | |
| 4 | x | x | x | x + x + x | |
| 5 | x | x(4) | x | x + x + x | |
| 6 | x | x | x | x + x + x | |
| 7 | x(5) | x(8) | x | x + x + x | |
| 8 | x | x | x | x + x + x | |
Data description of multi-trophic levels.
| Data type | Data description | Subplots | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant trait | LA, SLA, CHL, LN, LC | 77 | 2017 |
| Herbivore damage | Visually estimated | 77 | 2017 |
| Soil fungi | Mainly composed of saprophytes | 53 | 2017 |
| Community productivity | Sum of the biomass per subplot/area of subplot | 92 | 2018 |
-
LA, leaf area; SLA, specific leaf area; CHL, chlorophyll content; LN, leaf nitrogen content; LC, leaf carbon content.
Summary of linear mixed-effects models (LMMs) of species diversity (SD), genetic diversity (GD), and their interactions on tree productivity, tree functional diversity, trophic interactions, and community-weighted mean (CWM) of functional traits.
Expressed values are Df representing degree of freedom and F-values with related significances, *** p < 0.001; * *p < 0.01; * p < 0.05, + p < 0.1. Note that the very small F-values for CWMs are due to the equal representation of seed families across all tree diversity treatments (Appendix 1—table 1).
| Tree productivity | FD(Mean) | FD (Individual) | Herbivory | Soil fungal diversity | CWM (RC1) | CWM (RC2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | Df | Random | F-value | F-value | F-value | F-value | F-value | F-value | F-value |
| SD | 1 | Plot | 6.16* | 44.80*** | 20.60*** | 0.08 | 1.06 | 0.004 | 0.002 |
| GD | 1 | Plot | 0.51 | 3.66+ | 0.11 | 5.86* | 1.57 | 0.000 | 0.033 |
| SD × GD | 1 | Plot | 0.23 | 7.44* | 0.05 | 1.44 | 5.29* | 0.003 | 0.011 |
| SD | 1 | Plot | 6.16* | 44.80*** | 20.60*** | 0.08 | 1.06 | 0.004 | 0.002 |
| GD (Sp-mono) | 1 | Plot | 0.00 | 11.09** | 0.15 | 0.17 | 1.35 | 0.002 | 0.000 |
| GD (Sp-mix) | 1 | Plot | 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 7.13* | 5.51* | 0.001 | 0.044 |
Dimension reduction of community-weighted mean trait values (CWMs) by varimax rotation principal component analysis (PCA).
Loadings and eigenvalues of rotation principal components (RC) selected from a varimax rotation PCA on the CWM of leaf traits (most influential variables in bold).
| RC1 | RC2 | |
|---|---|---|
| LA | 0.49 | 0.11 |
| SLA | 0.17 | –0.34 |
| CHL | 0.05 | 0.86 |
| LN | –0.20 | 0.16 |
| LC | –0.55 | –0.01 |
| Explained | 41% | 23% |
| Cumulative explained | 41% | 64% |
-
LA, leaf area; SLA, specific leaf area; CHL, chlorophyll content; LN, leaf nitrogen content; LC, leaf carbon content.
Results of linear models of leaf damage excluding undamaged leaves (this study) – leaf damage including undamaged leaves (from other plots of the BEF-China experiment) for the four species used in this study.
These models were used to correct the potential bias of herbivory estimates as a result of only collecting damaged leaves.
| Species | Slope | Intercept | R2 | Pearson’s correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alniphyllum fortunei | 0.89970 | 2.83483 | 0.86 | 0.93 |
| Cinnamomum camphora | 0.94465 | 2.07484 | 0.73 | 0.86 |
| Daphniphyllum oldhamii | 0.88387 | 2.54032 | 0.92 | 0.96 |
| Idesia polycarpa | 0.92406 | 1.77523 | 0.86 | 0.93 |
Contrast coding of genetic diversity in species monocultures and species mixtures separately.
Sp-mono presents species monocultures, and Sp-mix presents species mixtures.
| Species diversity | Genetic diversity | Genetic diversity in Sp-mono | Genetic diversity in Sp-mix |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | -1 | 0 |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | -1 |
| 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | 1 |
The interaction of significant results and the explained variance of the whole model of the multigroup structural equation models (SEM) shown in Figure 5.
*** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05.
| Response | Predictor | DF | Test.Stat | Explained variance % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree functional diversity | GD:SD | 1 | 0.5* | 11 |
| Herbivory | GD:SD | 1 | 0.0 | 11 |
| Herbivory | Tree functional diversity:SD | 1 | 0.0* | |
| Soil fungal diversity | GD:SD | 1 | 52982.7*** | 6 |
| Tree community productivity | GD:SD | 1 | 327.6*** | 24 |
| Tree community productivity | Herbivory:SD | 1 | 327.6 | |
| Tree community productivity | Soil fungal diversity:SD | 1 | 327.6 | |
| Tree community productivity | Tree functional diversity:SD | 1 | 327.6* |
-
SD, species diversity; GD, genetic diversity.