Cortex-wide response mode of VIP-expressing inhibitory neurons by reward and punishment
Figures
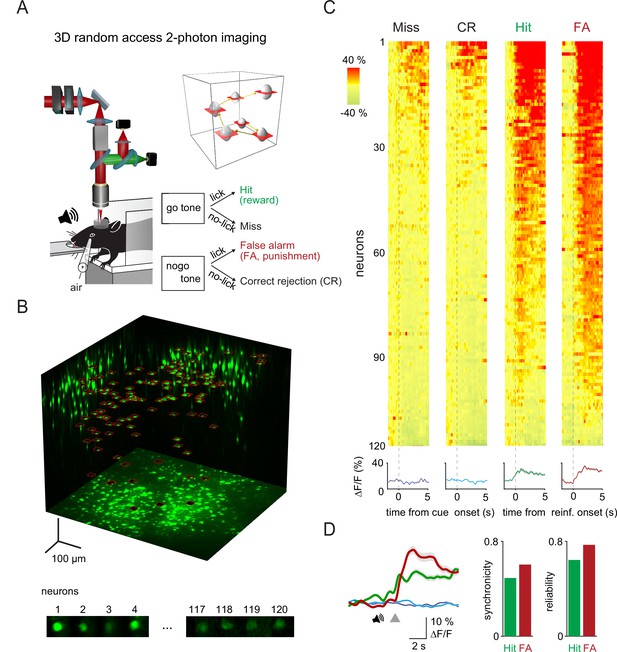
Three-dimensional (3D) random access two-photon imaging of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) neurons in an auditory discrimination task.
(A) Schematic of the combined fast 3D acousto-optical (AO) imaging and behavior experiments. Head-restrained mice were trained to perform a sensory discrimination, an auditory go-no-go task during 3D AO imaging using the chessboard scanning method (inset). (B) Maximal intensity 3D projection of the GCaMP6f-labeled VIP interneuron population imaged by fast 3D AO scanning in the medial parietal association area. All 120 neurons within the cubature were simultaneously imaged using tiled chessboard scanning (red squares). Bottom shows tile examples containing single-neuron somata obtained using chessboard scanning. Note that some background was included to allow for motion correction. (C) Top, example somatic Ca2+ responses recorded of neurons recorded as in (B) during Miss, correct rejection (CR), Hit, and false alarm (FA) trials. Responses were ordered according to their maximum amplitude for each trial types. Traces were aligned to cue onset for Miss and CR trials and to reward or punishment delivery for Hit and FA. Bottom, neuron average response for each trial type (mean ± SEM). (D) Left, average transients of a measurement session (128 trials) for Hit (green), FA (red), Miss (dark blue), and CR (light blue) responses recorded from the 120 VIP interneurons. Gray triangle marks the reinforcement onset in case of Hit and FA. Averages of Miss and CR trials were aligned according to the expected reinforcement delivery calculated based on the average reaction time. Right, average synchronicity (mean ± SEM) and trial-to-trial repeatability (reliability) of individual neuronal responses.
Three-dimensional random access two-photon imaging and fiber photometry of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) neurons in an auditory discrimination task.
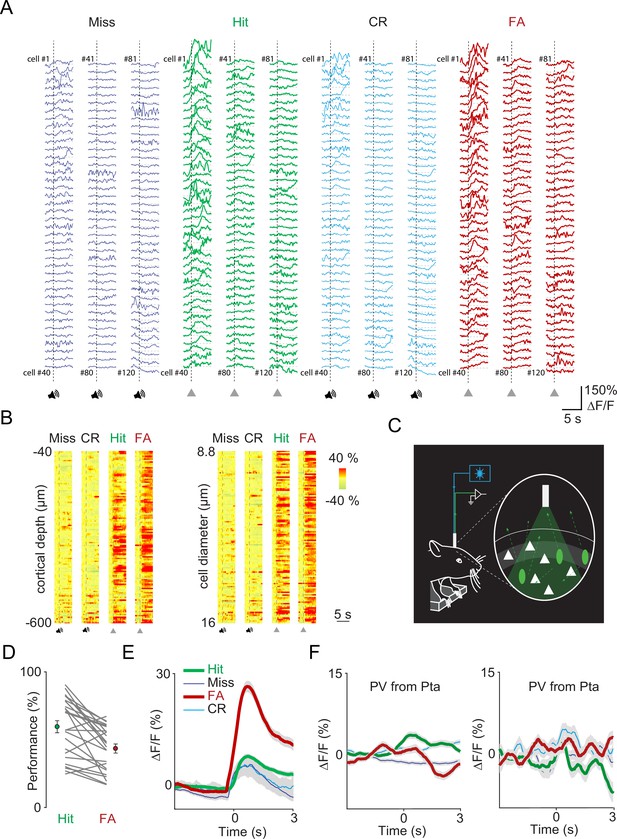
(A) The somatic Ca2+ responses in Figure 1C shown in transient form. (B) The same somatic Ca2+ responses as in Figure 1C but ordered according to their cortical depth (left) and cell diameter (right) for each trial types. Traces were aligned to cue onset for Miss and correct rejection (CR) trials and to reward or punishment delivery for Hit and false alarm (FA). (C) Schematics of fiber photometry experiments. (D) Hit and FA rate of the mice during the imaging and fiber photometry sessions (n=24 sessions, n=22 mice). (E) Average transients of VIP interneurons (mean ± SEM) for Hit (thick green), FA (thick red), Miss (dark blue), and CR (light blue) recorded from the auditory cortex using fiber photometry. The transients of the Hit and FA were aligned to reinforcer onset (time = 0). Note that the auditory discrimination task in case of fiber photometry measurements was designed such that if a mouse licks during the tone, the tone stops immediately, and reinforcers are delivered. The reaction time of mice in Hit and FA trials was 0.35 ± 0.147 s and 0.84 ± 0.108 s, respectively. Because they were aligned to reinforcer onset, the transient of FA slightly advances that of Hit. Miss and CR trials don’t have reinforcer onset, and the onset of transients was aligned to the mean reaction time to make all transients comparable. (F) Average transients of parvalbumin (PV) interneurons (mean ± SEM of n=17 and n=37 cells) for Hit (thick green), FA (thick red), Miss (dark blue), and CR (light blue) recorded from the parietal cortex.
Recording sparse interneuronal population in large volume.
Z-stack from half mm3 neocortical volume was obtained in the parietal cortex. Then small squares containing the vasoactive intestinal polypeptide interneurons’ somata were selected as regions of interest (ROIs). The squares were rearranged to form a three-dimensional matrix to track the cell activity.
Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) population activity during an auditory discrimination task.
Example, false alarm trial of an imaging session with pupillometry, velocity recording, and motion-corrected calcium imaging of 52 VIP interneurons. Flashing white speaker and red air cloud icons mark the tone and air puff onsets.
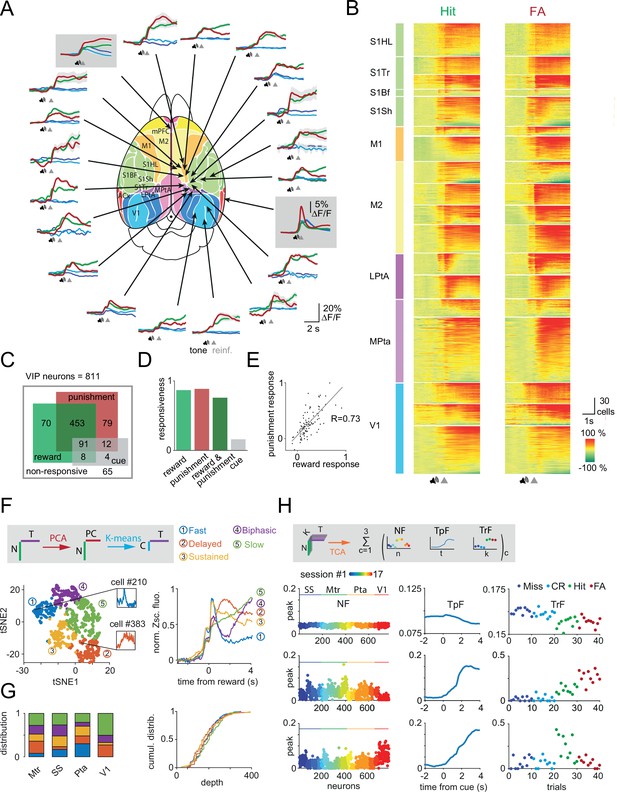
Reward and punishment recruit vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) neuronal activity across the dorsal cortex (A) Ca2+ responses of individual VIP interneurons recorded separately from 18 different cortical regions from 16 mice using fast three-dimensional acousto-optical imaging were averaged for Hit (thick green), false alarm (FA; thick red), Miss (dark blue), and correct rejection (CR; light blue).
Fiber photometry data were recorded simultaneously from medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and auditory cortex (ACx) regions and are shown in gray boxes. Functional map (Pankhurst et al., 2012) used with the permission of the author. Speaker symbols represent the average time of tone onset, and gray triangles mark the reinforcement onset for Hit and FA. Averages of Miss and CR trials were aligned according to the expected reinforcement delivery calculated on the basis of the average reaction time. The auditory discrimination task in case of fiber photometry measurements was designed such that if a mouse licks during the tone, the tone stops immediately, and reinforcers are delivered. Note the different scalebar for photometry measurements. mPFC (n=6 mice), ACx (n=6), S1Hl/S1Tr/S1Bf/S1Sh: primary somatosensory cortex, hindlimb/trunk/barrel field/shoulder region (n=4), M1/M2: primary/secondary motor cortex (n=6), Mpta/Lpta: medial/lateral parietal cortex (n=4), V1: primary visual cortex (n=3). (B) Each line of the raster plots shows average neuronal response for Hit and FA. Responses were aligned to reinforcement onset before averaging. Abbreviations indicate color-coded cortical recording positions shown in panel A. Speaker symbol represents the approximate time of tone onset, as reaction times of the animals could be different. Responses were normalized in each region and ordered according to their maximum amplitude. (C) Responsiveness of 811 VIP interneurons for Hit and FA. (D) Bar chart of data from C. (E) Average response of individual VIP interneurons for FA as a function of the response for Hit. Note the high correlation (R=0.73). (F) Left, T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (tSNE) plot of the reward-mediated activity of VIP interneurons after principal component analysis (PCA). Individual neurons are color coded according to their cluster type obtained using a k-means clustering algorithm. Inserts show the average response of single rapidly (blue) or delayed (orange) activated VIP interneurons. Right, average GCaMP6f responses from different clusters of VIP interneurons after reward delivery. N: number of neurons, T: time, PC: principal components, C: clusters. (G) Left, distribution of the clusters shown in panel F across different cortical areas (Mtr: motor cortex, SS: somatosensory cortex, Pta: parietal cortex, V1: primary visual cortex). Right, cumulative distribution of the clusters shown as a function of cortical depth. (H) Top, schematics of temporal component analysis: single trial neuronal data were decomposed in a sum of latent components. N: number of neurons coming from different sessions, K: trial numbers, and T: time. Below, rank 3 tensor component analysis (TCA) neuron (NF), temporal (TpF), and trial (TrF) factors. Miss and CR trial factors were indicated here with dark and light blue dots. The second component clearly distinguishes between trials with and without reinforcement.
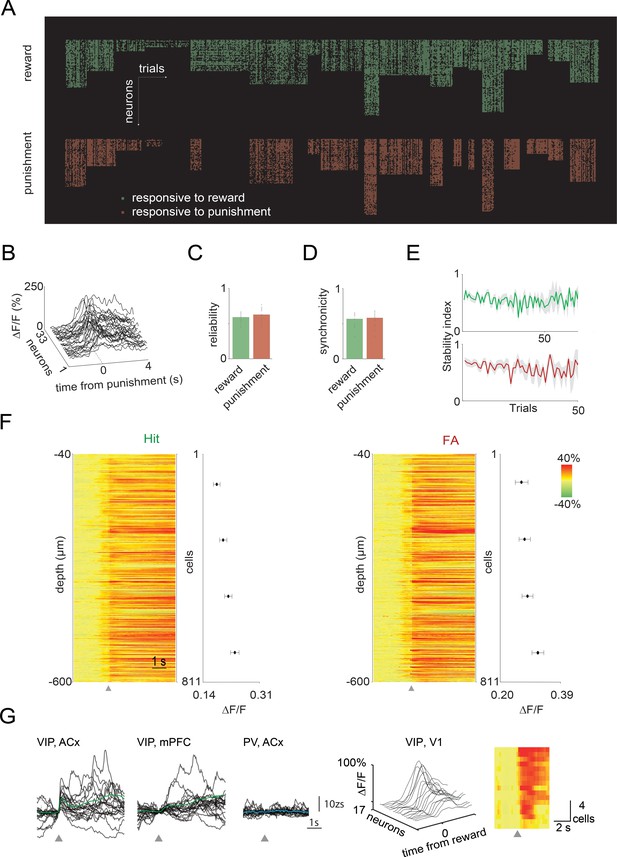
Quantification of the activity of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) neurons across the dorsal cortex.
(A) Raster plot of the trial-to-trial activation of the responsive VIP neurons in Hit and false alarm (FA) trials during the two-photon imaging sessions (n=18 sessions, n=16 mice, n=746 cells). (B) An example of the synchronous activation of the VIP neurons in an FA trial. (C) Reliability of the VIP neurons in Hit and FA trials. (D) Synchronicity of the VIP neurons in Hit and FA trials. (E) Stability of active VIP neuronal responses across trials. A portion of active VIP neurons were maintained across trials. (F) Left, raster plot of the average responses of the VIP neurons in Hit trials ordered according to their cortical depth. Graph shows the binned maximums of the averaged responses (bin size = 223 cells). Right, raster plot and graph for FA trials. Gray triangles mark reinforcement onset. (G) Single trial (black) and average (green or blue) VIP or PV interneuron z-scored activity recorded using fiber photometry during uncued reward delivery. Gray triangle shows the onset of the uncued reward. Right, single trial and average activity of VIP interneurons from V1 recorded with two-photon microscope during uncued reward delivery.
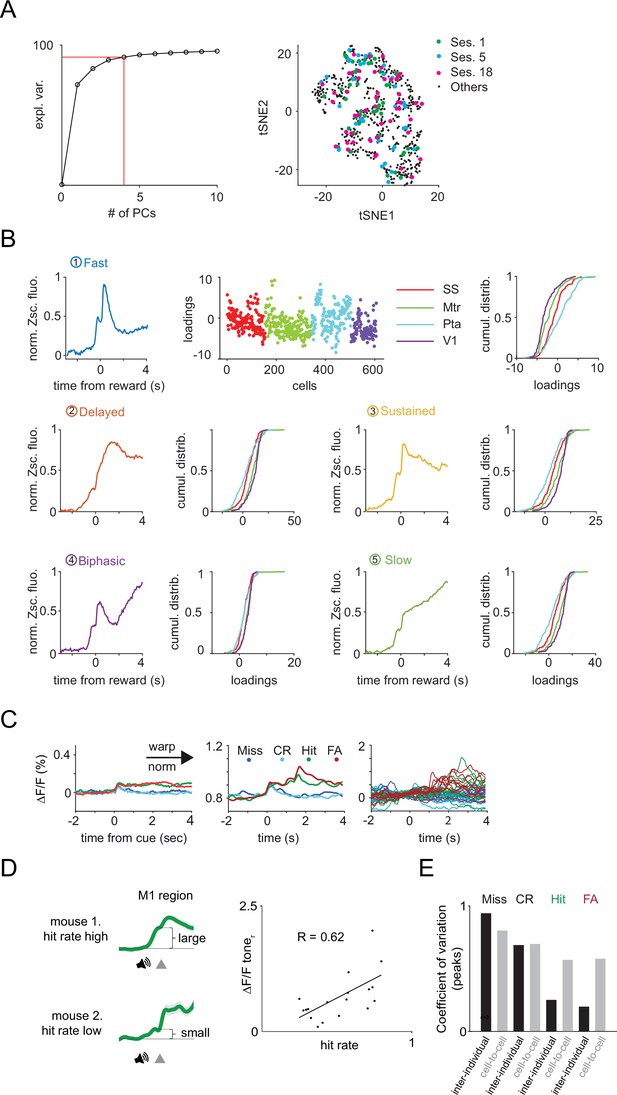
Heterogeneity in vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) neuronal responses across the dorsal cortex.
(A) Left, explained variance. We used five principal components (PCs), explaining >90% of the variance of our data for the k-means clustering. Right, neurons from individual recording sessions are scattered in the T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (tSNE) space. (B) Top, the first PC, corresponding loadings, and regional cumulative distributions of the loadings. Middle and bottom, remaining PCs and the regional cumulative distributions of the corresponding loadings. (C) Average activity of 17 VIP interneurons for different trial types before (left) and after (middle) tensor component analysis (TCA) preprocessing. After smoothing, single-trial neural activities corresponding to reaction time periods for Hit and false alarm (FA) trials were time-wrapped to a fixed 1.5 s in length. All recordings were rendered non-negative by subtracting the minimal ΔF/F value for each cell. Data were finally normalized. Right, only the first 10 trials of each type were selected for the TCA. (D) Heterogeneity of the cue responses. Left, higher hit rate was associated with larger tone-related response components in the population average traces of Hit trials. Right, scatter plot of the size of the average tone response and the hit rate. (E) Comparison of inter-individual and cell-to-cell variability in the four trial types.
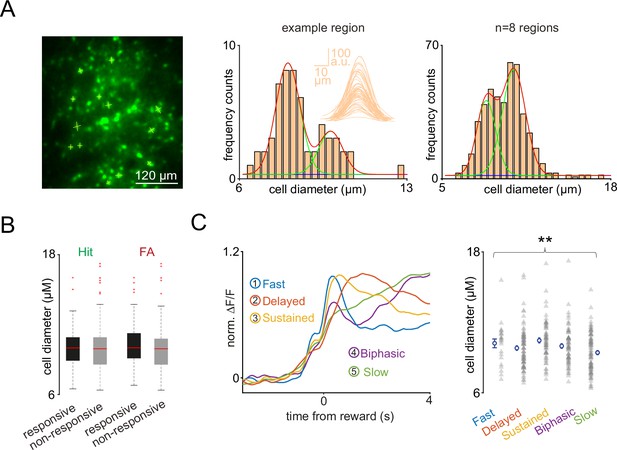
Cell diameter distribution of the recorded vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) interneuron population and its relation to the activity.
(A) Left, maximal intensity projection of the GCaMP6f-labeled VIP interneuron population imaged by fast three-dimensional acousto-optical scanning in one of the sessions. Thin yellow lines symbolize the lines used to determine the fluorescence profile of the somata. Middle, cell diameter distribution of an example region. Inset: Averaged cross-section fluorescence profiles of the somata for full width at half maximum calculation. Right, cell diameter distribution of the n=8 mice that were used for this analysis. (B) Box-and-whisker plots of the cell diameter of Hit and false alarm (FA) responsive and non-responsive cells. Median, 25th and 75th percentiles, and range of nonoutliers and outliers are depicted. (C) Left, average GCaMP6f responses of the VIP interneurons after reward delivery separated into clusters by principal component analysis. Right, variability in the cell diameter of the clusters. Asterisks mark significant differences between the means of the groups. (B) Population averages for Miss and correct rejection (top) and Hit and FA (bottom) by high and low baseline arousal levels in the somatosensory cortex and motor cortex regions (left), and auditory cortex and medial prefrontal cortex regions (right). Bars indicate average peak amplitudes (mean ± SEM).
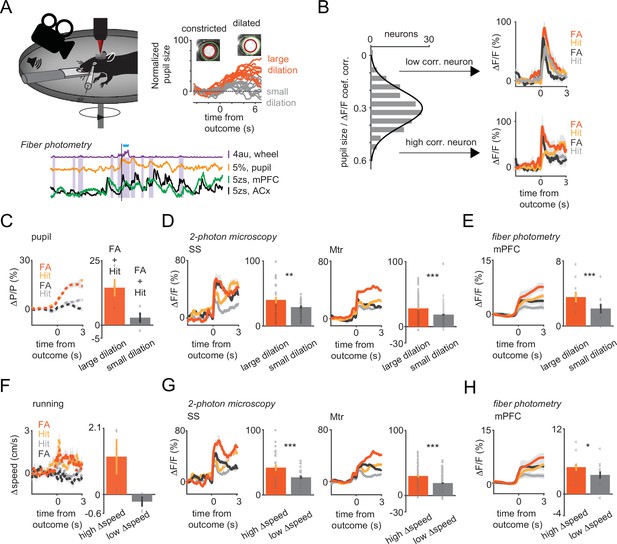
Arousal states modulate vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) neural responses to sensory cues and reinforcers.
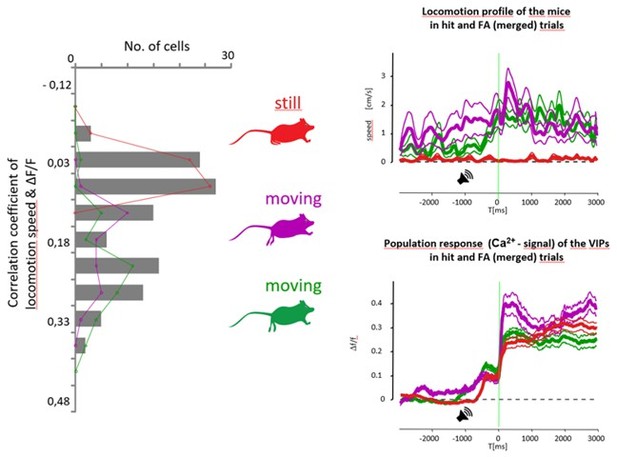
(A) Upper left, schematic of measurements. Pupil and movement were simultaneously monitored during three-dimensional (3D) imaging in the auditory go-no-go task. Upper right, high (orange) and low (gray) arousal states were separated by changes in pupil diameter. Below, 60 s continuous monitoring of different behavioral variables together with VIP interneuron population activity in auditory cortex (ACx) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). The black bar indicates the timing of an uncued reward delivery. Blue triangles indicate licking events. Purple-shaded boxes represent running bouts. (B) Left, distribution of correlation coefficients of relative change in pupil diameter (ΔP/P) and VIP neuronal response. Right, reinforcement-associated responses were significantly larger when relative change in pupil diameter (ΔP/P) was higher during the task. Red and orange indicate false alarm (FA) and Hit responses associated with higher ΔP/P. FA and Hit responses associated with low ΔP/P are in black and gray, respectively. (C) Average pupil dilation traces during high (red and orange) and low (black and gray) pupil changes for FA and Hit trials for somatosensory (SS) and motor (Mtr) recordings in panel D. Bars indicate average amplitudes (mean ± SEM, Hit and FA combined). (D) Population averages for Hit and FA during high and low pupil change in the SS and Mtr regions. Bars indicate average amplitudes (mean ± SEM, Hit and FA combined). Even in the late period, when the outcome responses were dissipated, larger changes in pupil diameter at the time of reinforcement were associated with higher VIP responses. (E) Same as D but for fiber photometry in the mPFC. Corresponding pupil dilation traces can be found in Figure 3—figure supplement 1. (F) Same as C but for running speed. (G) Same as D but for running speed. (H) Same as E but for running speed. Higher relative change in the running speed was associated with larger neuronal responses recorded with 3D imaging or fiber photometry.
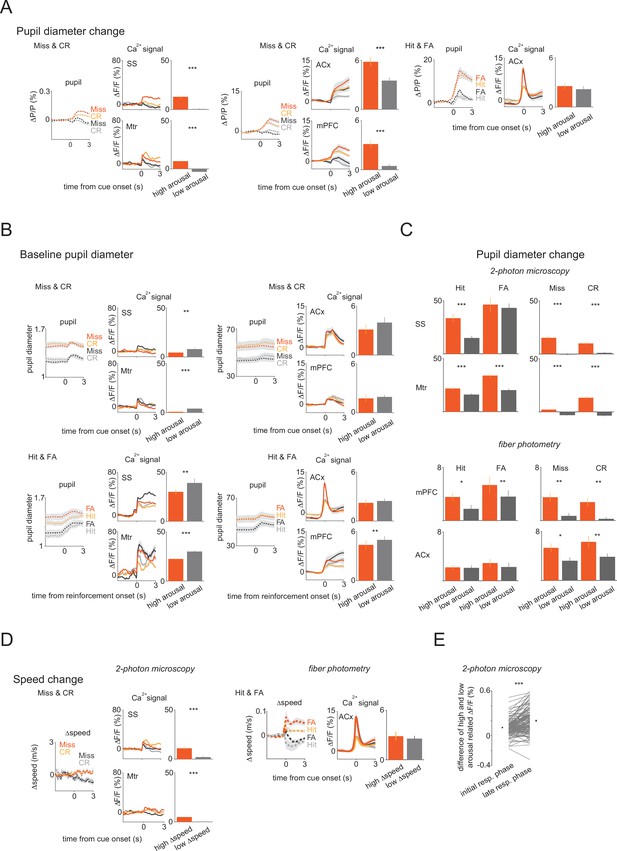
The baseline and the change in pupil diameter, and the change of speed additionally modulate vasoactive intestinal polypeptide neuronal activity on top of activation by cues and outcomes.
(A) Population averages for Miss and correct rejection (CR; left and middle) during high and low arousal change in the somatosensory (SS) and motor (Mtr) regions (left), and auditory cortex (ACx) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) regions (middle). Right, population averages for Hit and false alarm (FA) in ACx. Bars indicate average peak amplitudes (mean ± SEM). (C) Average peak amplitude bars for Hit, FA, Miss, and correct rejection (CR) separately during high and low pupil change in the SS, Mtr, mPFC, and ACx regions. (mean ± SEM). (D) Population averages for Miss and CR (left) during high and low speed change in the SS and Mtr regions (left) and for Hit and FA in ACx (right). Bars indicate average peak amplitudes (mean ± SEM). (E) Difference between high and low arousal change-related reinforcement signals in the initial and in the late response phase in Hit and FA.
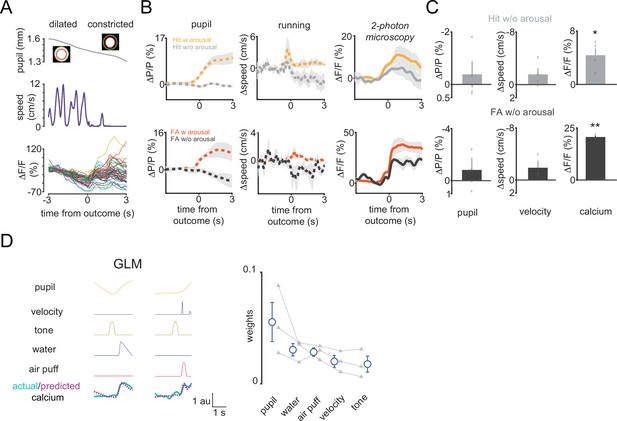
Arousal and reinforcement can make distinct contributions to vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) interneuronal activity.
(A) Pupil diameter, locomotion speed, and activity of multiple VIP interneurons in an example trial where reinforcement did not trigger any increase in arousal. (B) Top, relative change in pupil diameter, locomotion speed, and VIP interneuronal population activity in Hit trials with and without increase in arousal. Bottom, the same but for false alarm (FA). (C) Reinforcement-associated changes of pupil, velocity, and VIP interneuronal population activity in Hit and FA trials with no increase in arousal. (D) Left, actual calcium signal, explanatory variables, and predicted calcium from a generalized linear model that was built to assess distinct contributions of arousal, reinforcement, cue, and motor events. Right, weights of the explanatory variables in the model.
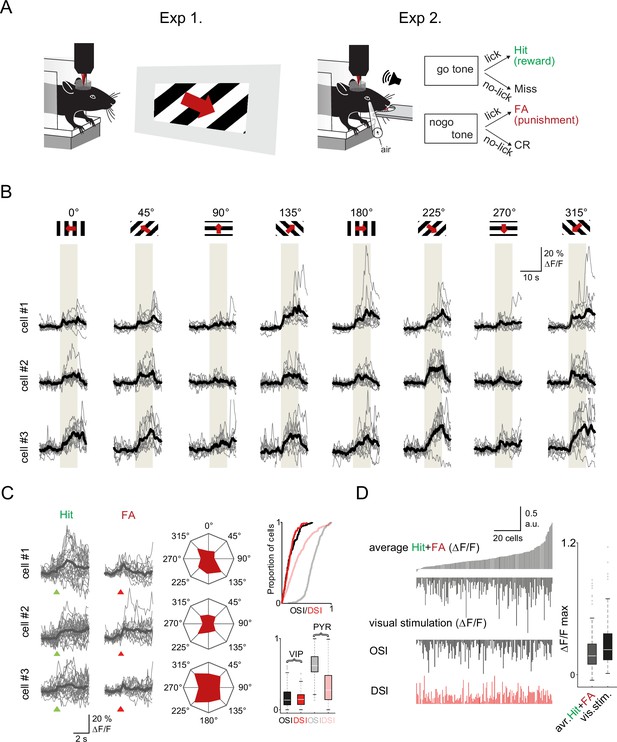
Visual cortex vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) neurons respond to both visual stimuli and reinforcers (A) Schematic of the measurement.
Orientation tuning was mapped in a first set of experiments (Exp. 1) which was followed by recordings of the same neurons during the auditory go-no-go task (Exp. 2). Both set of recordings were performed using fast three-dimensional acousto-optical imaging. (B) Individual Ca2+ responses from three different VIP interneurons to visual stimulation with moving grating in eight different directions. The gray boxes indicate the duration of the visual stimulation. (C) Left, responses of the same three cells to reinforcement. Middle, polar plots of neuronal responses to visual stimulation from the same neurons. Right top, cumulative distribution plot of orientation selectivity index (OSI) and direction selectivity index (DSI) parameters of VIP (black and red) and pyramidal cells (gray and pastel red), (VIP: n=157 cells, n=3 mice, pyramidal cells: n=383 cells, n=3 mice). Right bottom, OSI and DSI values of the same cells. Box-and-whisker plots show the median, 25th and 75th percentiles, and range of nonoutliers and outliers. (D) Correlation between reinforcement and visual responses in the same VIP interneurons (n=157). Each column refers to a single cell. From top to bottom: mean of the average Hit and false alarm (FA) responses, average visual responses, mean OSI, and mean DSI. The cells were ordered according to the amplitude of the averaged reinforcement signal. Right, maximums of reinforcement-related and visual stimulation responses. Box-and-whisker plots show the median, 25th and 75th percentiles, and range of nonoutliers and outliers.
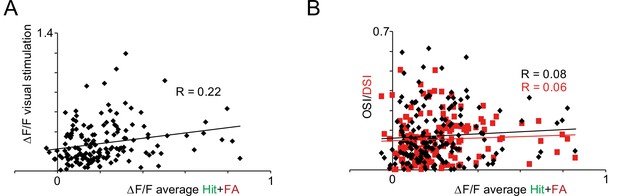
Quantification of the connection of visual tuning parameters and reinforcement-related responses.
(A) Scatter plot of reinforcement- vs visual stimulation-induced responses of the same vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) cells. (B) Scatter plot of reinforcement-induced responses vs orientation selectivity index (OSI) or direction selectivity index (DSI) parameters of the same VIP cells.
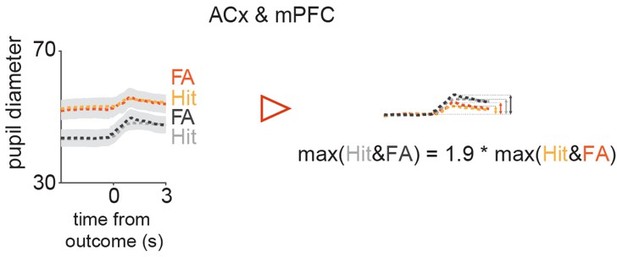
Comparison of peak amplitudes of pupil trace averages split according to their baseline amplitudes in Hit & FA.
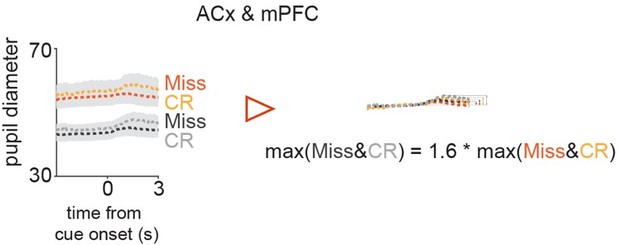
Comparison of peak amplitudes of pupil trace averages split according to their baseline amplitudes in Miss & CR.
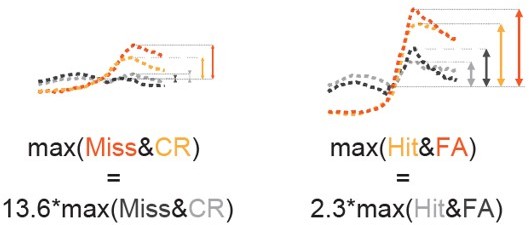
Comparison of peak amplitudes of pupil trace averages split according to the pupil change in Miss & CR and Hit & FA (see Figure 3—figure supplement 1A).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant DNA reagent | AAV9.Syn.Flex. GCaMP6f.WPRE.SV40 | Penn Vector Core | Cat# AV-1-PV2819 | |
| Biological sample (Mus musculus) | Viptm.1(cre)Zjh/J, B6.129P2-Pvalbtm1(cre)Arbr/J, FVB/N-Tg(Thy1-cre)1Vln/J, | The Jackson Laboratory | RRID: IMSR_JAX:010908 RRID: IMSR_JAX:017320 RRID: IMSR_JAX:006143 | |
| Software, algorithm | MATLAB | MathWorks | ||
| Software, algorithm | MES | Femtonics |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Comparison of different scanning methods.
Scanning speed was calculated according to the equations in the column ‘calculation of scanning speed’. Ratio of collected photons was calculated from relative pixel dwell times. All parameters used for calculations are listed in the bottom field. Note, that chessboard scanning provides 170-fold faster measurement speed and 244-fold higher photon collection compared to volume scanning with resonant mirrors.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78815/elife-78815-supp1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Calculation of ratio of responsive neurons following reward.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78815/elife-78815-supp2-v1.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78815/elife-78815-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf