The role of adolescent lifestyle habits in biological aging: A prospective twin study
Figures
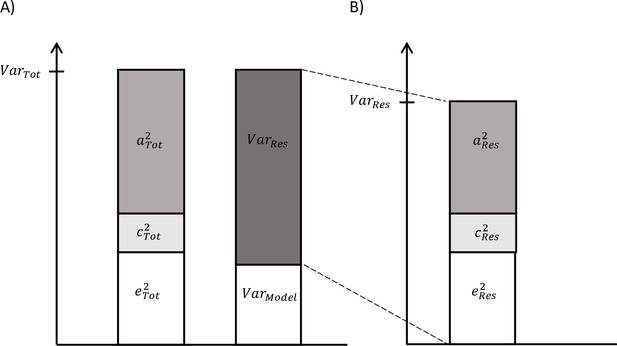
Decomposition of (A) total variation in biological aging and (B) the variation of the residual term.
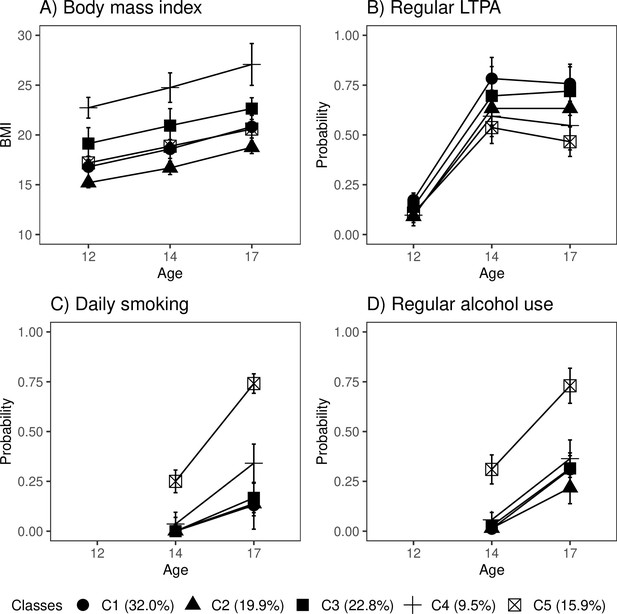
Classes with different lifestyle patterns (n = 5114).
Mean and probability profiles (95% confidence intervals) of the indicator variables utilized in the classification: (A) body mass index, (B) regular leisure-time physical activity (LTPA) (several times a week), (C) daily smoking, and (D) regular alcohol use (once a month or more). For categorical variables, the probabilities of belonging to the highest categories are presented.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
The estimation results of a latent class analysis (LCA) model with five classes.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80729/elife-80729-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
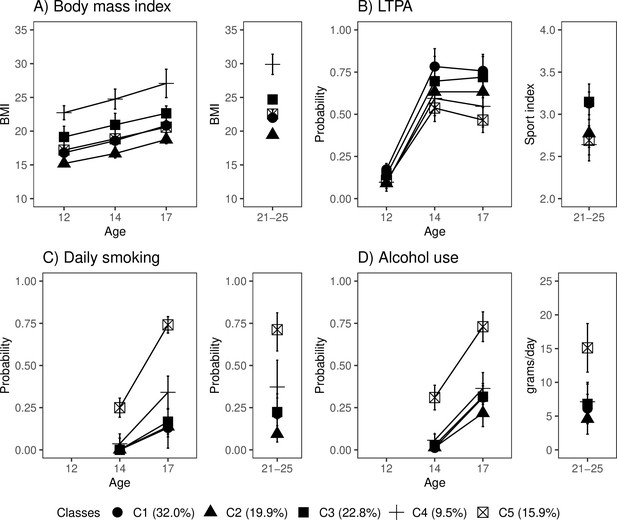
Lifestyle-related factors in adulthood (21–25 years) according to the adolescent lifestyle behavior classes in the subsample of participants with information on biological aging (n = 824).
(A) Body mass index (BMI), (B) leisure-time physical activity (LTPA), (C) prevalence of daily smokers, and (D) alcohol use. Means and 95% confidence intervals are presented. C1, the class with the healthiest lifestyle; C2, the class with low-normal BMI; C3, the class with healthy lifestyle and high-normal BMI; C4, the class with high BMI; C5, the class with the unhealthiest lifestyle pattern. The model was controlled for sex (female), age, and baseline pubertal development.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Means and 95% confidence intervals of the lifestyle-related factors in adulthood according to the adolescent lifestyle behavior classes (BCH approach).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80729/elife-80729-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
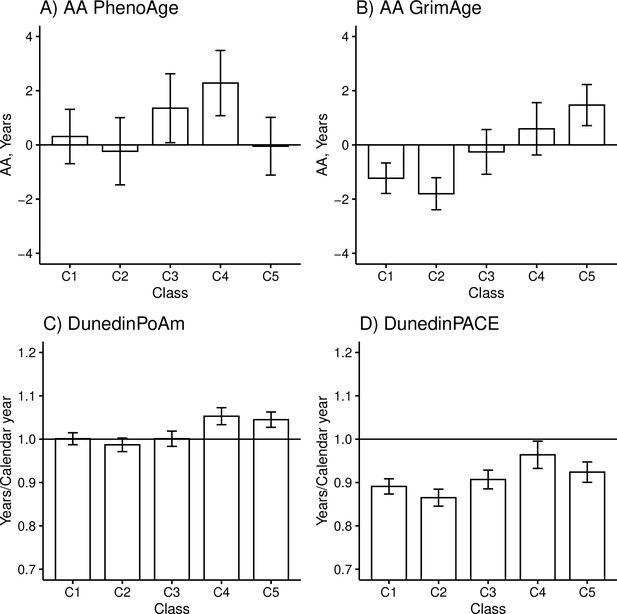
Mean differences between the adolescent lifestyle behavior patterns in biological aging measured with (A) DNAm PhenoAge, (B) DNAm GrimAge, (C) DunedinPoAm, and (D) DunedinPACE estimators (n = 824).
The analysis was adjusted for sex (female), standardized age, and baseline pubertal development. Means and 95% confidence intervals are presented. C1, the class with the healthiest lifestyle pattern; C2, the class with low-normal body mass index (BMI); C3, the class with a healthy lifestyle and high-normal BMI; C4, the class with high BMI; C5, the class with the unhealthiest lifestyle pattern; AA, age acceleration.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Means and 95% confidence intervals of biological aging according to the adolescent lifestyle behavior patterns (BCH approach).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80729/elife-80729-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
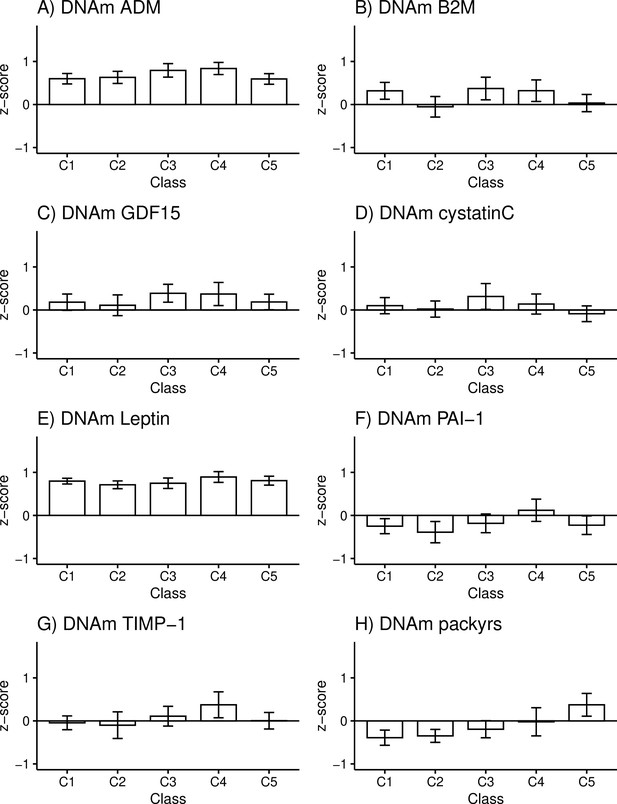
DNA methylation (DNAm)-based plasma proteins and smoking pack-years according to the adolescent lifestyle behavior patterns (n = 824).
(A) DNAm adrenomedullin (ADM), (B) DNAm beta-2 microglobulin (B2M), (C) DNAm growth differentiation factor (GDF15), (D) DNAm cystatin C, (E) DNAm leptin, (F) DNAm plasminogen activation inhibitor 1 (PAI-1), DNAm tissue inhibitor metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1), and (H) DNAm smoking pack-years (packyrs). Means and 95% confidence intervals are presented. C1, the class with the healthiest lifestyle pattern; C2, the class with low-normal body mass index (BMI); C3, the class with healthy lifestyle and high-normal BMI; C4, the class with high BMI; C5, the class with the unhealthiest lifestyle pattern. The model was controlled for sex (female), age, and baseline pubertal development.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Means and 95% confidence intervals of DNA methylation (DNAm)-based plasma proteins and smoking pack-years according to the adolescent lifestyle behavior patterns (BCH approach).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80729/elife-80729-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
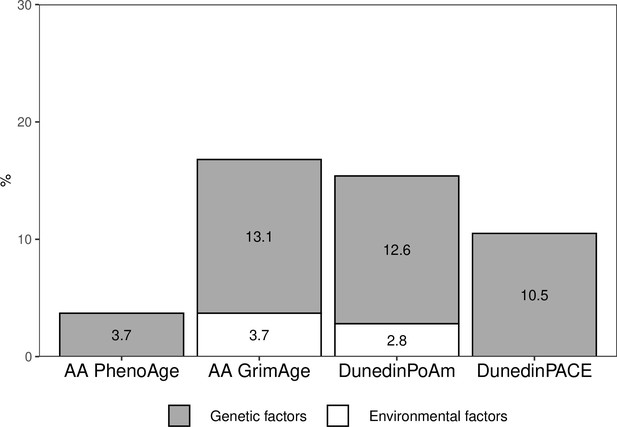
Proportions of the total variation in biological aging explained by genetic and (unshared) environmental factors shared with adolescent lifestyle patterns among young adult twin pairs (MZ n = 154, DZ n = 211).
The results are based on the model including additive genetic and non-shared environmental component (AE model). AA, age acceleration.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Genetic and environmental factors underlying the association between adolescent lifestyle patterns and biological aging.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80729/elife-80729-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx

Correlations between epigenetic age acceleration (AA) measures assessed with different clocks.
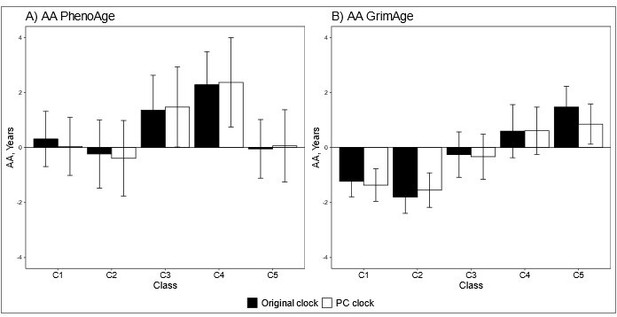
Mean differences between the adolescent lifestyle behavior patterns in biological aging measured with original and PC-based (A) DNAm PhenoAge and (B) DNAm GrimAge.
The analysis was adjusted for sex (female), standardized age and baseline pubertal development. Means and 95% confidence intervals are presented. C1 = the class with the healthiest lifestyle pattern, C2 = the class with low–normal BMI, C3 = the class with a healthy lifestyle and high–normal BMI, C4 = the class with high BMI, C5 = the class with the unhealthiest lifestyle pattern. AA, age acceleration.
Tables
Descriptive statistics of the adolescent lifestyle-related variables in all twins and in the subsample of twins with information on biological aging.
| All twins (n = 5114) | Subsample (n = 824) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean (SD) or % | n | Mean (SD) or % | |
| Zygosity | 4852 | 824 | ||
| MZ | 1650 | 34.0 | 335 | 40.7 |
| Same-sex DZ | 1603 | 33.0 | 262 | 31.8 |
| Opposite-sex DZ | 1599 | 33.0 | 227 | 27.5 |
| Sex | 5114 | 824 | ||
| Female | 2584 | 50.5 | 470 | 57.0 |
| Male | 2530 | 49.5 | 354 | 43.0 |
| At age 12 | ||||
| Pubertal development (1–3) | 5111 | 1.6 (0.5) | 823 | 1.6 (0.5) |
| Body mass index | 4913 | 17.6 (2.6) | 793 | 17.7 (2.6) |
| Leisure-time physical activity | 5038 | 813 | ||
| Less than once a week | 1877 | 37.3 | 295 | 35.3 |
| Once a week | 2499 | 49.6 | 416 | 51.2 |
| Every day | 662 | 13.1 | 102 | 12.5 |
| At age 14 | ||||
| Body mass index | 4473 | 19.3 (2.7) | 787 | 19.5 (2.6) |
| Leisure-time physical activity | 4590 | 799 | ||
| Less than once a week | 688 | 15.0 | 110 | 13.8 |
| Once a week | 796 | 17.3 | 149 | 18.6 |
| 2–5 times a week | 2182 | 47.5 | 370 | 46.3 |
| Every day | 924 | 20.1 | 170 | 21.3 |
| Smoking status | 4570 | 800 | ||
| Never | 3954 | 86.5 | 687 | 85.9 |
| Former | 296 | 6.5 | 57 | 7.1 |
| Occasional | 122 | 2.7 | 24 | 3.0 |
| Daily smoker | 198 | 4.3 | 32 | 4.0 |
| Alcohol use (binge drinking) | 4565 | 796 | ||
| Never | 3501 | 76.7 | 602 | 75.6 |
| Less than once a month | 756 | 16.6 | 135 | 17 |
| Once or twice a month | 275 | 6.0 | 50 | 6.3 |
| Once a week or more | 33 | 0.7 | 9 | 1.1 |
| At age 17 | ||||
| Body mass index | 4158 | 21.4 (3.0) | 760 | 21.4 (2.7) |
| Leisure-time physical activity | 4208 | 766 | ||
| Less than once a week | 748 | 17.8 | 132 | 17.2 |
| Once a week | 686 | 16.3 | 130 | 17.0 |
| 2–5 times a week | 1977 | 47.0 | 363 | 47.4 |
| Every day | 797 | 18.9 | 141 | 18.4 |
| Smoking status | 4190 | 762 | ||
| Never | 2419 | 57.7 | 454 | 59.7 |
| Former | 493 | 11.8 | 83 | 10.9 |
| Occasional | 213 | 5.1 | 48 | 6.3 |
| Daily smoker | 1065 | 25.4 | 176 | 23.1 |
| Alcohol use (binge drinking) | 4217 | 766 | ||
| Never | 881 | 20.9 | 152 | 19.8 |
| Less than once a month | 1807 | 42.9 | 340 | 44.4 |
| Once or twice a month | 1240 | 29.4 | 222 | 29.0 |
| Once a week or more | 289 | 6.9 | 52 | 6.8 |
-
MZ, monozygotic twins; DZ, dizygotic twins; SD, standard deviation.
The intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) of epigenetic aging measures by zygosity and correlation coefficients between the measures (n = 824).
| ICCs (95% CI) | Correlation coefficients (95% CI) off-diagonal and means (standard deviations) on the diagonal | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MZ twin pairs | DZ twin pairs | AAHorvath | AAHannum | AAPheno | AAGrim | DunedinPoAm | DunedinPACE | |
| AAHorvath | 0.71 (0.63, 0.79) | 0.40 (0.24, 0.55) | 0.00 (3.51) | |||||
| AAHannum | 0.66 (0.56, 0.76) | 0.32 (0.16, 0.48) | 0.40 (0.33, 0.48) | 0.00 (3.27) | ||||
| AAPheno | 0.69 (0.60, 0.78) | 0.16 (0.00, 0.33) | 0.36 (0.29, 0.44) | 0.61 (0.56, 0.66) | 0.00 (5.25) | |||
| AAGrim | 0.72 (0.63, 0.80) | 0.35 (0.15, 0.55) | 0.08 (0.01, 0.16) | 0.32 (0.24, 0.40) | 0.39 (0.33, 0.46) | 0.00 (3.24) | ||
| DunedinPoAm | 0.62 (0.52, 0.71) | 0.42 (0.24, 0.60) | –0.05 (-0.12, 0.03) | 0.20 (0.13, 0.27) | 0.41 (0.35, 0.47) | 0.57 (0.52, 0.63) | 1.00 (0.07) | |
| DunedinPACE | 0.71 (0.64, 0.78) | 0.46 (0.31, 0.61) | –0.04 (–0.11, 0.04) | 0.30 (0.22, 0.38) | 0.49 (0.43, 0.55) | 0.55 (0.49, 0.61) | 0.62 (0.57, 0.67) | 0.88 (0.10) |
-
CIs were corrected for nested sampling.
-
CI, confidence interval; AA, age acceleration; MZ, monozygotic; DZ, dizygotic.
Model fit of the latent class models (n = 5114).
| AIC | BIC | ABIC | VLMR | LMR | Class sizes | AvePP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 128842 | 129012 | 128929 | ||||
| 122533 | 122880 | 122711 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 74.0%, 26.0% | 0.95, 0.92 |
| 119937 | 120460 | 120206 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 44.9%, 40.5%, 14.6% | 0.88, 0.89, 0.93 |
| 118030 | 118729 | 118389 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 36.4%, 32.7%, 16.7%, 14.2% | 0.83, 0.86, 0.87, 0.92 |
| 117167 | 118043 | 117617 | 0.529 | 0.530 | 32.0%, 22.8%, 19.9%, 15.9%, 9.5% | 0.78, 0.82, 0.85, 0.88, 0.91 |
| 116526 | 117578 | 117076 | 0.169 | 0.170 | 31.5%, 18.5%, 15.7%, 14.0%, 12.7%, 7.7% | 0.77, 0.84, 0.83, 0.78, 0.78, 0.90 |
| 116099 | 117328 | 116731 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 21.0%, 17.5%, 15.2%, 13.8%, 12.9%, 12.8%, 6.9% | 0.73, 0.82, 0.70, 0.77, 0.83, 0.83, 0.91 |
| 115695 | 117101 | 116418 | 0.407 | 0.408 | 20.3%, 16.2%, 13.6%, 13.5%, 12.3%, 11.3%, 9.3%, 3.4% | 0.72, 0.75, 0.82, 0.71, 0.83, 0.80, 0.82, 0.89 |
-
AIC, Akaike’s information criterion; BIC, Bayesian information criterion; ABIC, sample size-adjusted Bayesian information criterion; VLMR, Vuong–Lo–Mendell–Rubin likelihood ratio test; LMR, Lo–Mendell–Rubin-adjusted likelihood ratio test; AvePP, average posterior probabilities for most likely latent class membership.
The classes with different adolescent lifestyle behavior patterns (n = 5114).
| C1 (32.0%) | C2 (19.9%) | C3 (22.8%) | C4 (9.5%) | C5 (15.9%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Est | 95% CI | Est | 95% CI | Est | 95% CI | Est | 95% CI | Est | 95% CI | |
| Body mass index | ||||||||||
| At age of 12 years | 16.8 | 15.7, 17.9 | 15.2 | 14.7, 15.7 | 19.1 | 17.5, 20.7 | 22.7 | 21.7, 23.8 | 17.2 | 16.9, 17.5 |
| At age of 14 years | 18.6 | 17.6, 19.5 | 16.7 | 16.0, 17.3 | 20.9 | 19.2, 22.6 | 24.8 | 23.3, 26.2 | 18.9 | 18.6, 19.2 |
| At age of 17 years | 20.8 | 19.7, 22.0 | 18.8 | 18.1, 19.4 | 22.6 | 21.6, 23.7 | 27.1 | 25.0, 29.2 | 20.6 | 20.3, 20.9 |
| Leisure-time physical activity | ||||||||||
| At age of 12 years | ||||||||||
| Less than once a week | 0.29 | 0.22, 0.37 | 0.45 | 0.39, 0.51 | 0.35 | 0.26, 0.43 | 0.44 | 0.37, 0.50 | 0.44 | 0.39, 0.48 |
| Once a week | 0.54 | 0.48, 0.59 | 0.46 | 0.41, 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.47, 0.56 | 0.47 | 0.39, 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.41, 0.50 |
| Every day | 0.17 | 0.14, 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.04, 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.07, 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.06, 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.08, 0.14 |
| At age of 14 years | ||||||||||
| Less than once a week | 0.08 | 0.05, 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.12, 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.07, 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.13, 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.22, 0.31 |
| Once a week | 0.14 | 0.07, 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.17, 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.10, 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.17, 0.28 | 0.20 | 0.16, 0.23 |
| 2‒5 times a week | 0.52 | 0.45, 0.59 | 0.45 | 0.41, 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.43, 0.59 | 0.43 | 0.37, 0.49 | 0.40 | 0.35, 0.45 |
| Every day | 0.27 | 0.23, 0.30 | 0.18 | 0.13, 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.12, 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.12, 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.10, 0.17 |
| At age of 17 years | ||||||||||
| Less than once a week | 0.10 | 0.05, 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.14, 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.06, 0.20 | 0.27 | 0.19, 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.29, 0.40 |
| Once a week | 0.15 | 0.11, 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.15, 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.11, 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.14, 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.15, 0.23 |
| 2‒5 times a week | 0.50 | 0.44, 0.56 | 0.45 | 0.41, 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.48, 0.57 | 0.44 | 0.36, 0.52 | 0.36 | 0.32, 0.41 |
| Every day | 0.26 | 0.22, 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.13, 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.12, 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.07, 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.07, 0.13 |
| Smoking status | ||||||||||
| At age of 14 years | ||||||||||
| Never | 0.99 | 0.98, 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.95, 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.95, 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.74, 0.93 | 0.33 | 0.24, 0.43 |
| Former | 0.01 | 0.00, 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00, 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.00, 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.04, 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.24, 0.34 |
| Occasional | 0.00 | 0.01 | –0.01, 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00, 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01, 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.10, 0.16 | |
| Daily smoker | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00, 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.00, 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.19, 0.31 | ||
| At age of 17 years | ||||||||||
| Never | 0.69 | 0.61, 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.65, 0.81 | 0.68 | 0.59, 0.78 | 0.50 | 0.41, 0.59 | 0.03 | 0.00, 0.06 |
| Former | 0.12 | 0.09, 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.05, 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.07, 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.06, 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.12, 0.19 |
| Occasional | 0.06 | 0.04, 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.02, 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.01, 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.02, 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.05, 0.10 |
| Daily smoker | 0.13 | 0.08, 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.09, 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.09, 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.24, 0.44 | 0.74 | 0.69, 0.79 |
| Alcohol use (binge drinking) | ||||||||||
| At age of 14 years | ||||||||||
| Never | 0.88 | 0.85, 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.90, 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.79, 0.89 | 0.76 | 0.69, 0.83 | 0.23 | 0.15, 0.31 |
| Less than once a month | 0.11 | 0.08, 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.02, 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.09, 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.12, 0.24 | 0.46 | 0.41, 0.51 |
| Once or twice a month | 0.01 | 0.00, 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00, 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01, 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.02, 0.08 | 0.27 | 0.22, 0.32 |
| Once a week or more | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00, 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02, 0.06 | |||
| At age of 17 years | ||||||||||
| Never | 0.21 | 0.18, 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.26, 0.41 | 0.22 | 0.16, 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.15, 0.30 | 0.01 | 0.00, 0.02 |
| Less than once a month | 0.48 | 0.43, 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.40, 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.41, 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.35, 0.47 | 0.26 | 0.22, 0.31 |
| Once or twice a month | 0.28 | 0.24, 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.12, 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.23, 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.23, 0.35 | 0.51 | 0.46, 0.55 |
| Once a week or more | 0.03 | 0.00, 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.02, 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.00, 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.04, 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.18, 0.26 |
-
Mean and probability profiles of the indicator variables utilized in the classification.
-
BMI, body mass index; Est, estimated mean or probability; CI, confidence interval; C1, the class with the healthiest lifestyle pattern; C2, the class with low-normal BMI; C3, the class with healthy lifestyle and high-normal BMI; C4, the class with high BMI; C5, the class with the unhealthiest lifestyle pattern.
Differences in biological aging between classes with different adolescent lifestyle behavior patterns.
| AAPheno | AAGrim | DunedinPoAm | DunedinPACE | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diff | 95% CI | SMD | Diff | 95% CI | SMD | Diff | 95% CI | SMD | Diff | 95% CI | SMD | |
| C2 vs. C1 | ||||||||||||
| M1 | –0.55 | –2.15, 1.06 | –0.10 | –0.57 | –1.37, 0.23 | –0.18 | –0.01 | –0.03, 0.01 | –0.14 | –0.03 | –0.05, 0.00 | –0.30 |
| M2 | –0.13 | –1.79, 1.54 | –0.02 | –0.54 | –1.38, 0.29 | –0.17 | –0.01 | –0.03, 0.01 | –0.14 | –0.01 | –0.04, 0.02 | –0.10 |
| C3 vs. C1 | ||||||||||||
| M1 | 1.04 | –0.54, 2.63 | 0.20 | 0.97 | –0.01, 1.95 | 0.30 | 0.00 | –0.02, 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.02 | –0.01, 0.04 | 0.20 |
| M2 | 0.60 | –1.01, 2.21 | 0.11 | 0.94 | –0.10, 1.97 | 0.29 | 0.00 | –0.02, 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | –0.03, 0.03 | 0.00 |
| C4 vs. C1 | ||||||||||||
| M1 | 1.97 | 0.44, 3.50 | 0.38 | 1.83 | 0.74, 2.91* | 0.56 | 0.05 | 0.03, 0.07* | 0.71 | 0.07 | 0.04, 0.11* | 0.70 |
| M2 | 0.66 | –1.31, 2.63 | 0.13 | 1.73 | 0.26, 3.21 | 0.53 | 0.04 | 0.01, 0.07* | 0.57 | 0.02 | –0.02, 0.07 | 0.20 |
| C5 vs. C1 | ||||||||||||
| M1 | –0.36 | –1.76, 1.04 | –0.07 | 2.70 | 1.74, 3.66* | 0.83 | 0.04 | 0.02, 0.07* | 0.57 | 0.03 | 0.00, 0.06 | 0.30 |
| M2 | –0.45 | –1.82, 0.93 | –0.09 | 2.69 | 1.73, 3.66* | 0.83 | 0.04 | 0.02, 0.06* | 0.57 | 0.03 | 0.00, 0.06 | 0.30 |
| C3 vs. C2 | ||||||||||||
| M1 | 1.59 | –0.07, 3.25 | 0.30 | 1.54 | 0.58, 2.50* | 0.48 | 0.01 | –0.01, 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.01, 0.07* | 0.50 |
| M2 | 0.73 | –1.10, 2.55 | 0.14 | 1.48 | 0.36, 2.60* | 0.46 | 0.01 | –0.02, 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.01 | –0.03, 0.04 | 0.10 |
| C4 vs. C2 | ||||||||||||
| M1 | 2.52 | 0.85, 4.18* | 0.48 | 2.40 | 1.28, 3.51* | 0.74 | 0.07 | 0.04, 0.09* | 1.00 | 0.10 | 0.06, 0.14* | 1.00 |
| M2 | 0.79 | –1.59, 3.16 | 0.15 | 2.27 | 0.59, 3.95* | 0.70 | 0.05 | 0.02, 0.09* | 0.71 | 0.03 | –0.02, 0.08 | 0.30 |
| C5 vs. C2 | ||||||||||||
| M1 | 0.19 | –1.40, 1.77 | 0.04 | 3.27 | 2.32, 4.23* | 1.01 | 0.06 | 0.03, 0.08* | 0.86 | 0.06 | 0.03, 0.09* | 0.60 |
| M2 | –0.32 | –1.97, 1.33 | –0.06 | 3.24 | 2.21, 4.27* | 1.00 | 0.05 | 0.03, 0.08* | 0.71 | 0.04 | 0.01, 0.07 | 0.40 |
| C4 vs. C3 | ||||||||||||
| M1 | 0.93 | –0.82, 2.67 | 0.18 | 0.85 | –0.45, 2.16 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.03, 0.08* | 0.71 | 0.06 | 0.02, 0.10* | 0.60 |
| M2 | 0.06 | –1.91, 2.03 | 0.01 | 0.79 | –0.68, 2.26 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0.02, 0.08* | 0.71 | 0.02 | –0.02, 0.07 | 0.20 |
| C5 vs. C3 | ||||||||||||
| M1 | –1.40 | –2.99, 0.18 | –0.27 | 1.73 | 0.62, 2.84* | 0.53 | 0.04 | 0.02, 0.07* | 0.57 | 0.02 | –0.02, 0.05 | 0.20 |
| M2 | –1.05 | –2.63, 0.54 | –0.20 | 1.76 | 0.63, 2.88* | 0.54 | 0.05 | 0.02, 0.07* | 0.71 | 0.03 | 0.00, 0.06 | 0.30 |
| C5 vs. C4 | ||||||||||||
| M1 | –2.33 | −3.84, –0.82* | –0.44 | 0.88 | –0.32, 2.07 | 0.27 | –0.01 | –0.03, 0.02 | –0.14 | –0.04 | –0.08, 0.00 | –0.40 |
| M2 | –1.10 | –3.01, 0.80 | –0.21 | 0.96 | –0.51, 2.44 | 0.30 | 0.00 | –0.03, 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.01 | –0.04, 0.05 | 0.10 |
-
AA, age acceleration; BMI, body mass index; Diff, difference; CI, confidence interval; SMD, standardized mean difference; C1, the class with the healthiest lifestyle pattern; C2, the class with low-normal BMI; C3, the class with healthy lifestyle and high-normal BMI; C4, the class with high BMI; C5, the class with the unhealthiest lifestyle pattern; M1, model was adjusted for sex, age, and pubertal status at age 12; M2, model was additionally adjusted for BMI in adulthood.
-
*
The corresponding 99% confidence interval did not overlap zero.
The estimation results of the univariate model for biological aging among young adult twin pairs (MZ n = 154, DZ n = 211).
| Model fit | Parameter estimates and their 95% confidence intervals | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Χ2 | df | SC | p | CFI | TLI | RMSEA | SRMR | BIC | a2/total | c2 or d2/total | e2/total | Total | |||||
| AAPheno | |||||||||||||||||
| ACE | 5.2 | 3 | 1.27 | 0.155 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 2009 | 0.65 | 0.56, 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.35 | 0.26, 0.45 | 1.00 | 0.89, 1.12 | |
| ADE | 0.6 | 3 | 0.99 | 0.904 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 2003 | 0.03 | –0.46, 0.51 | 0.65 | 0.15, 1.15 | 0.33 | 0.25, 0.41 | 0.99 | 0.88, 1.09 |
| AE | 7.0 | 4 | 0.96 | 0.136 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 2003 | 0.65 | 0.56, 0.74 | - | 0.35 | 0.26, 0.45 | 1.00 | 0.89, 1.12 | |
| CE | 43.5 | 4 | 0.96 | <0.001 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 0.23 | 0.11 | 2038 | - | 0.39 | 0.30, 0.48 | 0.61 | 0.52, 0.70 | 0.99 | 0.88, 1.10 | |
| E | 107 | 5 | 0.96 | <0.001 | 0.00 | 0.59 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 2093 | - | - | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.88, 1.10 | |||
| AAGrim | |||||||||||||||||
| ACE | 4.3 | 3 | 2.05 | 0.231 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 1989 | 0.73 | 0.66, 0.80 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.20, 0.34 | 1.03 | 0.87, 1.20 | |
| ADE | 5.6 | 3 | 1.55 | 0.133 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 1989 | 0.64 | 0.09, 1.19 | 0.09 | –0.48, 0.66 | 0.27 | 0.20, 0.34 | 1.03 | 0.87, 1.19 |
| AE | 5.7 | 4 | 1.54 | 0.220 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 1983 | 0.73 | 0.66, 0.80 | - | 0.27 | 0.20, 0.34 | 1.03 | 0.87, 1.19 | |
| CE | 33.0 | 4 | 0.87 | <0.001 | 0.72 | 0.86 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 2018 | - | 0.50 | 0.40, 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.41, 0.60 | 1.02 | 0.87, 1.17 | |
| E | 104 | 5 | 1.41 | <0.001 | 0.06 | 0.62 | 0.33 | 0.26 | 2115 | - | - | 1.00 | 1.02 | 0.87, 1.17 | |||
| DunedinPoAm | |||||||||||||||||
| ACE | 1.3 | 3 | 1.12 | 0.722 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 2003 | 0.52 | 0.20, 0.85 | 0.09 | –0.20, 0.37 | 0.39 | 0.30, 0.48 | 0.98 | 0.86, 1.11 |
| ADE | 1.2 | 3 | 1.60 | 0.746 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 2003 | 0.62 | 0.53, 0.70 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 0.30, 0.47 | 0.98 | 0.86, 1.10 | |
| AE | 1.6 | 4 | 1.20 | 0.802 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 1997 | 0.62 | 0.53, 0.70 | - | 0.38 | 0.30, 0.47 | 0.98 | 0.86, 1.10 | |
| CE | 12.7 | 4 | 1.10 | 0.013 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 2009 | - | 0.45 | 0.36, 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.45, 0.64 | 0.98 | 0.86, 1.10 | |
| E | 85.1 | 5 | 1.15 | <0.001 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 2087 | - | - | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.86, 1.10 | |||
| DunedinPACE | |||||||||||||||||
| ACE | 2.0 | 3 | 1.08 | 0.582 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 1998 | 0.54 | 0.20, 0.87 | 0.08 | –0.21, 0.37 | 0.39 | 0.30, 0.48 | 0.99 | 0.87, 1.11 |
| ADE | 1.3 | 3 | 1.68 | 0.740 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 1981 | 0.42 | –0.13, 0.97 | 0.27 | –0.31, 0.84 | 0.32 | 0.24, 0.39 | 0.98 | 0.84, 1.13 |
| AE | 2.1 | 4 | 1.58 | 0.724 | 1.00 | 1.10 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 1976 | 0.68 | 0.52, 0.82 | - | 0.32 | 0.24, 0.40 | 0.99 | 0.84, 1.15 | |
| CE | 23.7 | 4 | 1.45 | <0.001 | 0.76 | 0.88 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 2007 | - | 0.45 | 0.35, 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.46, 0.65 | 0.98 | 0.84, 1.13 | |
| E | 78.5 | 5 | 1.47 | <0.001 | 0.09 | 0.64 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 2118 | - | - | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.84, 1.13 | |||
-
The epigenetic aging measures were adjusted for sex, age, and baseline pubertal development prior to analysis.
-
SC, scaling correction; CFI, comparative fit index; RMSEA, root mean square error of approximation; SRMR, standardized root-mean-square residual; BIC, Bayesian information criterion; MZ, monozygotic; DZ, dizygotic.
Means (standard deviations) of the epigenetic age estimates obtained using original and PC-based clocks.
| Original clock | PC clock | PC clock, outliers excluded | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horvath's clock | 28.9 (3.6) | 30.8 (3.8) | - |
| Hannum's clock | 18.2 (3.3) | 34.4 (4.0) | 34.4 (3.8) |
| DNAm PhenoAge | 13.0 (5.3) | 16.8 (6.4) | 16.6 (5.8) |
| DNAm GrimAge | 25.2 (3.3) | 38.8 (3.2) | 38.8 (3.2) |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
The codes used to analyse the data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80729/elife-80729-supp1-v1.txt
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/80729/elife-80729-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx





