TIR-1/SARM1 inhibits axon regeneration and promotes axon degeneration
Figures
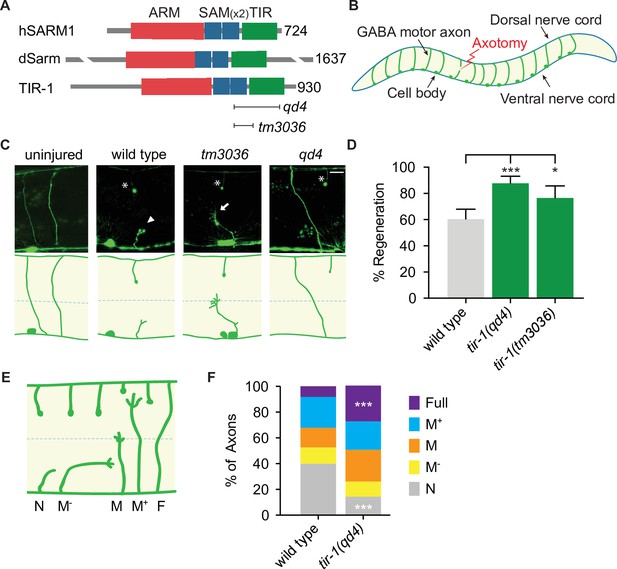
TIR-1 inhibits axon regeneration.
(A) Human SARM1, fly dSarm, and worm TIR-1 contain an N-terminal auto-inhibitory domain, two sterile alpha motif (SAM) domains and a toll-interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain. Null alleles qd4 and tm3036 disrupt the essential TIR domain. (B) C. elegans GABA motor neurons are axotomized to study the injury response in vivo and with single-axon resolution. (C) Representative GABA motor neurons before and 24 hr after single laser injury at the lateral midline of late larval stage (L4) animals (dashed line). Asterisks indicate distal fragments, arrowheads indicate retraction bulbs, and arrows indicate growth cones. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) More axons regenerate in tir-1 mutants compared to wild-type animals, as quantified by the percentage of axons that form a growth cone 24 hr after laser surgery. N = 152, 99, 60. (E) Regeneration phenotypes were categorized according to whether regenerating axons reached landmarks M−, M, M+, F, or failed to form a growth cone, N. (F) More tir-1(-) axons initiate regeneration and reach the dorsal cord compared to wild-type axons, as indicated by a significant reduction in the number of axons that failed to form a growth cone (N) and a significant increase in the number of fully regenerated axons (Full). N = 158, 154. Significance relative to wild type is indicated by *p≤0.05, ***p≤0.001, Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
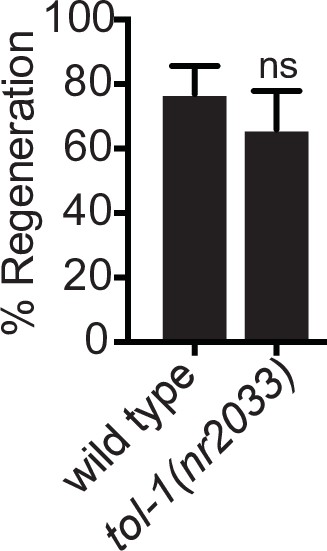
TOL-1 does not regulate axon regeneration.
Axon regeneration is not significantly different in tol-1(nr2033) mutants compared to wild-type controls 24 hr after laser surgery. N = 6 5, 47. Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
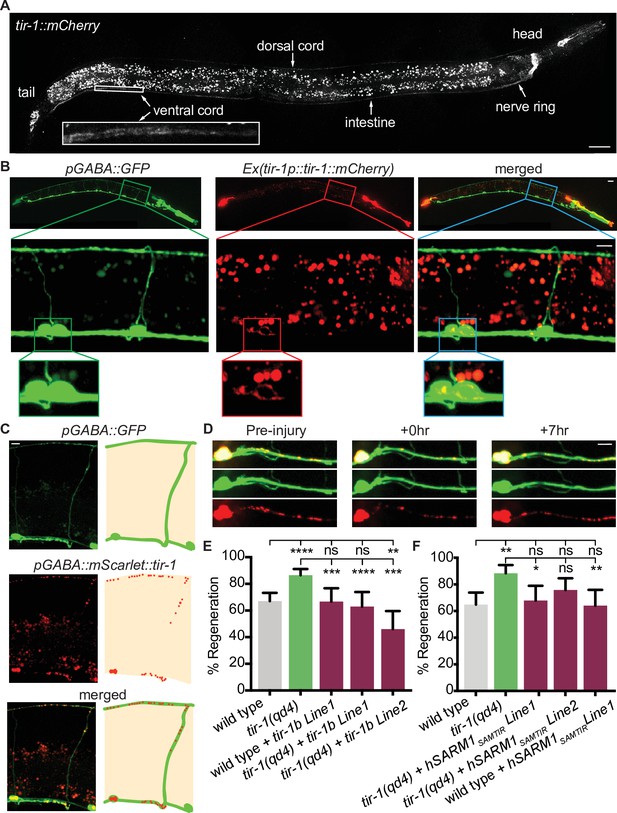
TIR-1 functions cell-autonomously to inhibit regeneration.
(A) Endogenous TIR-1 is expressed faintly in the nervous system, particularly in neurons along the dorsal and ventral (enlarged box) nerve cords. Note the intestinal expression significantly overlaps with autofluorescent gut granules and therefore is not an accurate representation of endogenous tir-1 expression in the intestine. Scale bar:25 μm. (B) Representative micrographs of transgenic animals expressing tir-1b::mCherry under its endogenous promoter indicates TIR-1b::mCherry is expressed in GABA neurons. Enlarged boxes show TIR-1b::mCherry expression in the cell bodies of GABA neurons. Scale bars: upper images, 25 μm; insets, 10 μm. (C,D) When expressed specifically in GABA neurons, mScarlet::tir-1b is expressed in a punctate pattern in the cell bodies and axons of GABA neurons before, immediately after and 7 hr after injury. Scale bars: 5 μm. (E) GABA-specific expression of tir-1b rescues axon regeneration in tir-1(qd4) animals but not wild-type animals. N = 197, 148, 62, 50, 69. (F) GABA-specific expression of human SARM1SAM-TIR lacking the N-terminal autoinhibitory domain rescues axon regeneration in single cut tir-1(qd4) mutants and not in wild-type animals. N = 91, 60, 53, 66, 50. Significance relative to wild type or tir-1(qd4) is indicated by *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
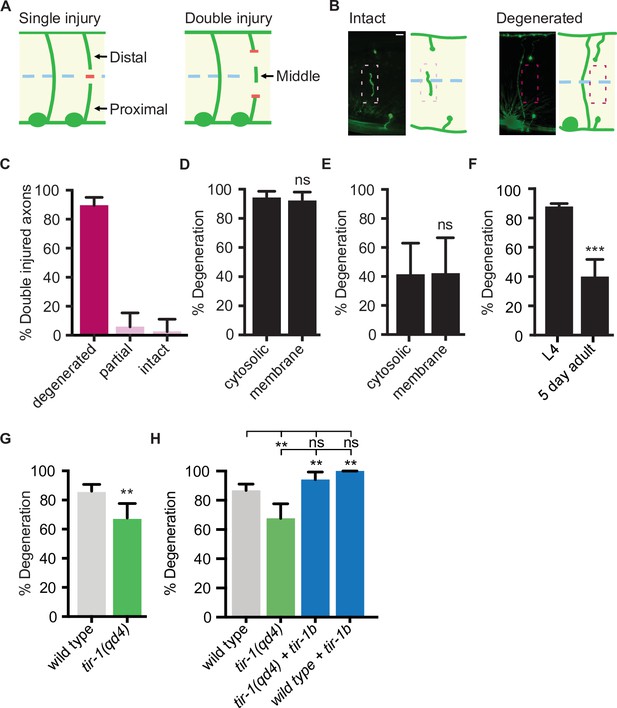
TIR-1 promotes axon degeneration in injured GABA motor neurons.
(A) Single and double injury models. After being severed once, GABA axons do not degenerate. Severing an axon twice creates a middle fragment that degenerates. (B) Micrographs of intact and degenerated middle fragments 24 hr post axotomy. Boxes with dashed lines highlight intact (pink) and degenerated (red) middle fragments. Scale bar: 5 μm. (C) Most middle fragments degenerate 24 hr after double injury. N = 61. (D) No significant difference in middle fragment degeneration was observed between axons expressing membrane tagged- or cytosolic GFP 24 hr (N = 19, 14) and (E) 1.5 hr after injury. (F) Middle fragments degenerate less frequently in aged adult animals compared to animals in the fourth larval stage (L4). N = 70, 44. (G) tir-1 promotes middle fragment degeneration. N = 63, 68. (H) Expression of tir-1b specifically in GABA motor neurons restores regeneration to tir-1(qd4) animals. N = 211, 68, 34, 37. Significance relative to control is indicated by *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
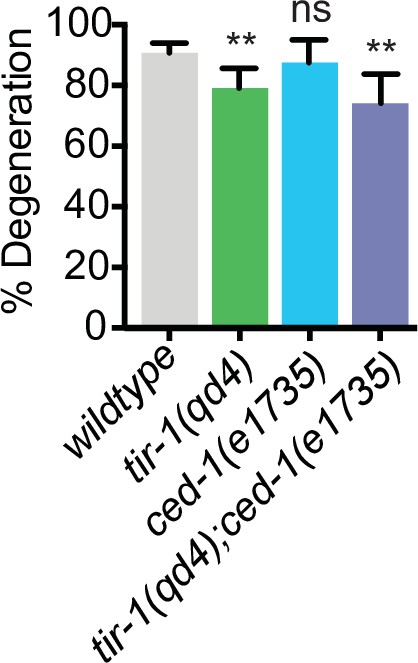
CED-1 does not regulate middle fragment degeneration.
tir-1 functions independently from ced-1 to regulate degeneration of the middle fragment after injury. N = 125, 37, 40, 58. Significance relative to wild type is indicated by **p≤0.01, Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
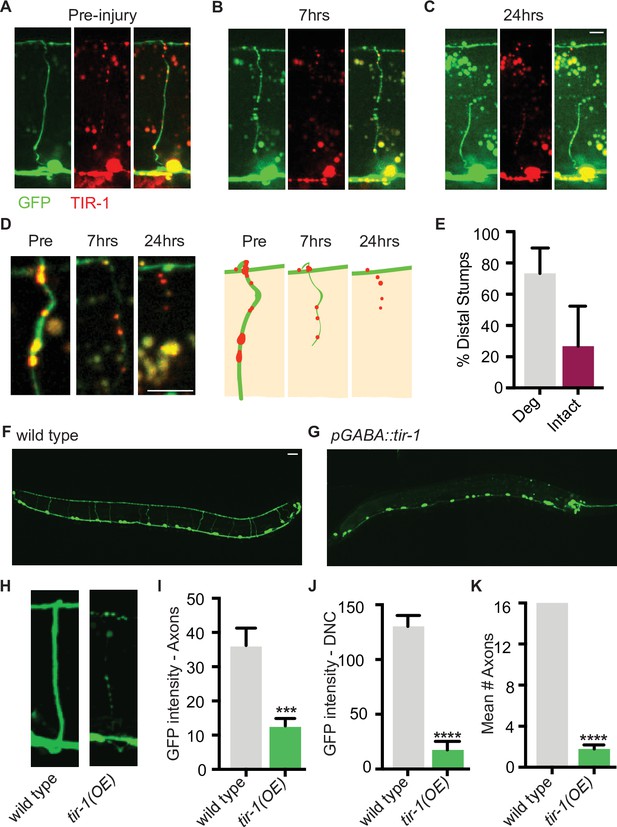
TIR-1 expression causes spontaneous axon degeneration in GABA motor neurons.
(A–C) Expression of mScarlet::tir-1b in GFP-labeled GABA motor neurons is sufficient to induce degeneration of the distal stump after a single axotomy. Micrographs and representative drawings demonstrate mScarlet::TIR-1b is localized in the cytoplasm in GABA cell bodies and along their axons in the ventral nerve cord, commissures, and dorsal nerve cord. Three timepoints are represented: (A) before injury, (B) immediately after injury, and (C) 7 hr after injury. At 7 hr, the distal stump has degenerated while the proximal stump remains intact. Scale bar: 5 μm. (D) Magnified image of a degenerating distal stump before injury, 7 hr after injury and 24 hr after injury. Scale bar: 5 μm. (E) Most distal stumps degenerate within 24 hr after a single injury in animals expressing mScarlet::tir-1b. (F, G) Individual GABA motor axons (seen in F) degenerate in transgenic animals expressing unc-47p::tir-1b::mCherry (G). Scale bar: 20 μm. (H) Magnified image of a wild-type axon and one that degenerates in animals that express unc-47p::tir-1b::mCherry. There is less (I) GFP intensity along the axon commissures (N = 18, 14), (J) GFP intensity along the dorsal nerve cord and (K) number of intact axons in animals that overexpress tir-1 in GABA neurons compared to wild-type animals (N = 6, 9), indicating tir-1 promotes axon degeneration. For categorical data, significance relative to wild type is indicated by ****p≤0.0001, Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. For continuous data, significance relative to wild type is indicated by ***p≤0.001, Student’s t-test. Error bars represent SEM.
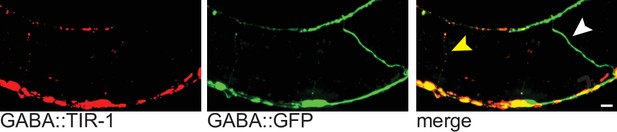
TIR-1 expression induces degeneration.
Representative micrographs indicating axons that express the unc-47p::tir-1::mCherry transgene degenerate, whereas neighboring axons that do not express the transgene remain intact. Transgenic axons labeled with yellow arrow and non-transgenic axons labeled with white arrow. Cytosolic GFP is expressed from an integrated unc-47p::GFP construct, and therefore is expressed throughout the GABA nervous system. Scale bar: 10 μm.
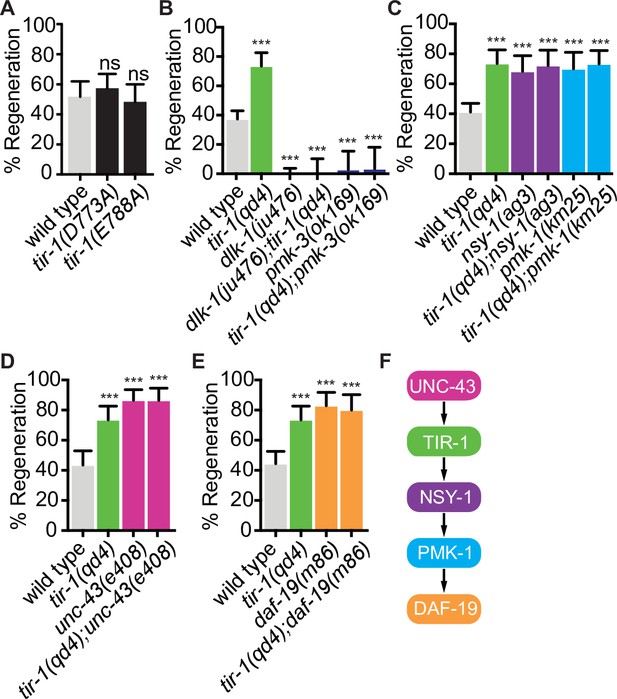
TIR-1 functions independently of its NADase activity and with the NSY-1 signaling pathway to inhibit axon regeneration.
(A) Conserved residues E788A/E642A, which is required for the NADase function of TIR-1 and SARM1, and D773A/D627 are not required to inhibit axon regeneration. (B) DLK-1 and TIR-1 function in the same or parallel pathways to regulate axon regeneration. N = 288, 68, 122, 41, 36, 30. (C) Axon regeneration is significantly increased in predicted null alleles of nsy-1/ASK1 and pmk-1/p38 following double injury, in both the presence and absence of tir-1 function. Double mutants are not statistically different from single mutants. N = 289, 68, 60, 50, 54, 71. (D) Null mutation of unc-43/CAMKII enhances axon regeneration after double injury in the presence and absence of tir-1. N = 89, 68, 39, 37. (E) Loss of the transcription factor daf-19/RFX1-3 increases axon regeneration after double injury in the presence and absence of tir-1. N = 142, 68, 41, 35. (F) Components of the TIR-1–NSY-1 signaling cascade. Significance relative to wild type is indicated by *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
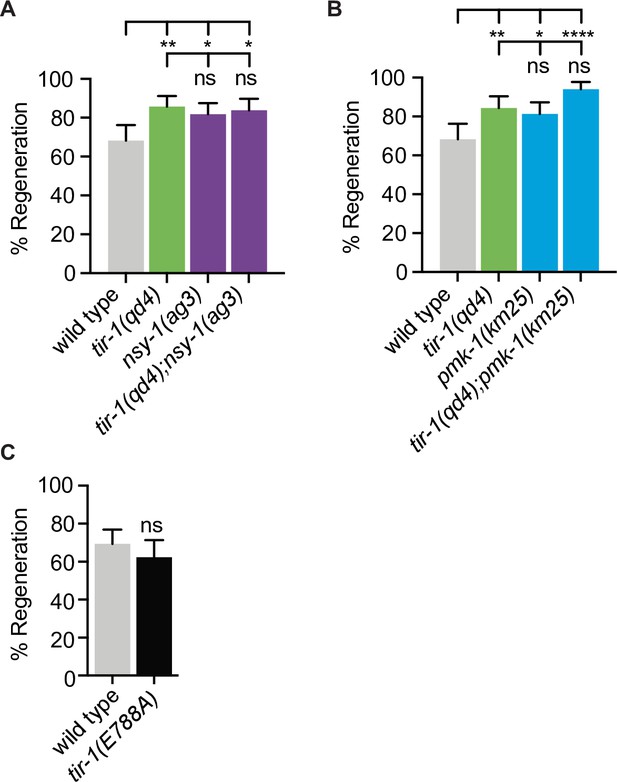
TIR-1 inhibits regeneration with the NSY-1/ASK1 and PMK-1/p38 MAPK after a single injury.
Axon regeneration is significantly increased in predicted null alleles of (A) nsy-1/ASK1 and (B) pmk-1/p38 following a single injury, in both the presence and absence of tir-1 function. Double mutants are not statistically different from single mutants. N = 110, 112, 132, 105 and 126, 96, 123, 84. (C) Mutation of conserved residue E788A/E642A, which is required for the NADase function of TIR-1 and SARM1, does not affect axon regeneration. Significance relative to wild type was determined using Fisher’s exact text and is indicated by *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ****p≤0.0001. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
The ATF-7 transcription factor does not regulate axon regeneration.
(A) Axon regeneration is not significantly different between atf-7(gk715) mutants and wild type controls 24 hr after laser surgery. N = 90, 68, 35. Significance relative to wild type or tir-1(qd4) is indicated by **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
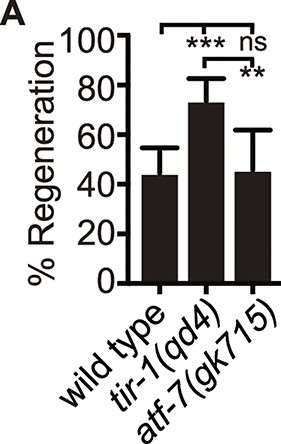
TIR-1 is capable of NADase-independent and -dependent axon degeneration.
(A) Mutation of conserved residue E788A/E642A, which is required for the NADase function of TIR-1 and SARM1, does not affect axon degeneration after double axotomy. D773A/D627A modestly suppresses degeneration. N = 97, 106, 64. (B) Conserved residues E788A/E642A and D773A/D627A are required for chronic axon degeneration. Lines represent independently generated transgenic strains that were generated by injecting equal concentrations of the same tir-1b::mCherry expression plasmid into separate tir-1(qd4) animals and isolating transgenic lines from each animal. N = 34, 32, 33, 23, 1211, 17. (C) Equivalent amounts of wild-type tir-1b, tir-1b(e788a), and tir-b(d773A) transgenes are expressed, as quantified by total mCherry fluorescence in the cell bodies of tir-1(qd4) animals, which were identified by expression of an integrated GABA-specific GFP marker, oxIs12 (N = 63, 70, 70). Significance relative to wild type was determined by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s test and is indicated by ****p≤0.0001. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
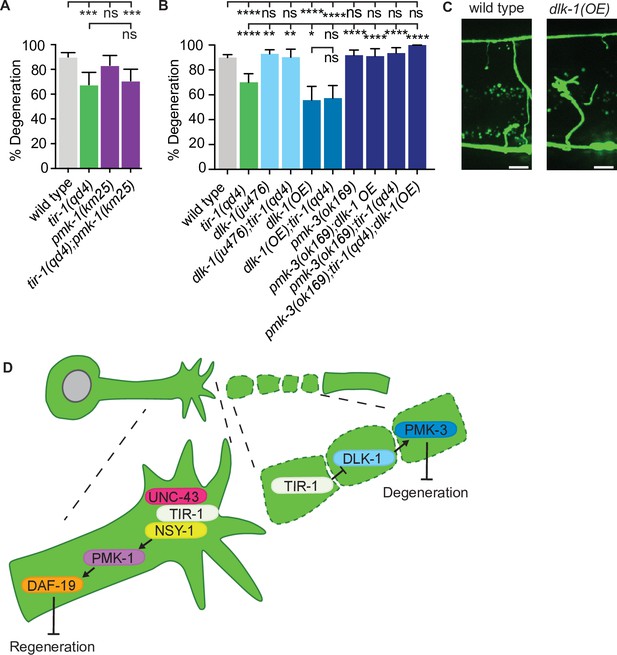
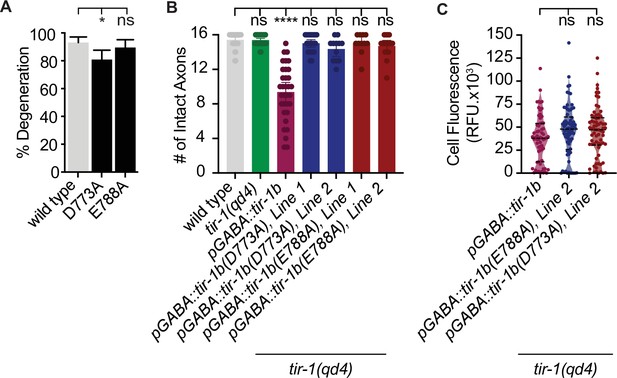
TIR-1 functions with the DLK-1 signaling pathway to regulate axon degeneration.
(A) Loss of pmk-1/p38 does not affect degeneration with or without tir-1 function. N = 198, 68, 54, 71. (B) Loss of dlk-1 function suppresses the decreased degeneration of tir-1(qd4) animals and overexpression of dlk-1 in GABA motor neurons inhibits degeneration, indicating DLK-1 negatively regulates axon degeneration. Loss of pmk-3 function rescues degeneration in all backgrounds, indicating PMK-3 is epistatic to both dlk-1 and tir-1. N = 517, 140, 142, 41, 70, 82, 98, 45, 62, 23. Significance relative to wild type is indicated by *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, ****p≤0.0001. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. (C) Representative micrographs of double injured wild type and dlk-1(OE) axons in which the respective middle fragments did and did not (asterisk) degenerate. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) TIR-1 inhibits axon regeneration and promotes axon degeneration in the same injured axon. In the proximal fragment, TIR-1 functions with the NSY-1 signaling cascade to modify gene transcription and inhibit axon regeneration. In the severed fragment, TIR-1 promotes degeneration by antagonizing the inhibitory DLK-1 signaling cascade. Significance relative to wild type or tir-1(qd4) is indicated by *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
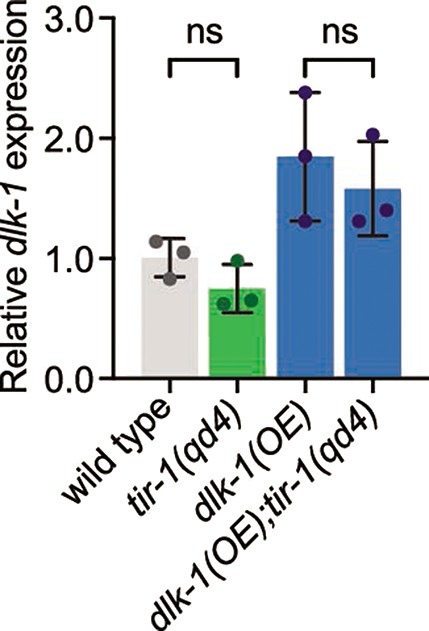
Expression of endogenous dlk-1 mRNA did not significantly differ between tir-1(-) and wild-type animals.
Similarly, mRNA expression from the integrated pGABA::dlk-1 transgene was not changed by the loss of tir-1 function. Significance determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple corrections test. Error bars represent standard deviation.
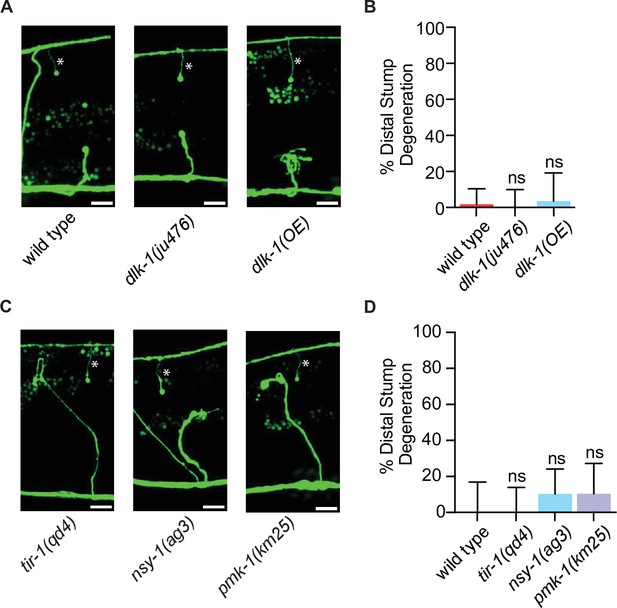
DLK-1 does not inhibit distal axon fragment degeneration after a single injury.
(A) Representative micrographs of severed distal stumps in wild type, dlk-1(-) loss-of-function mutants, and dlk-1(oe) overexpression mutants. (B) Distal axon stumps do not readily degenerate 24 hr after a single injury in wild type, dlk-1(-), or dlk-1(oe) animals. N = 56, 42, 28. (C) Representative micrographs of severed distal stumps in tir-1(-), or nsy-1(-), and pmk-1(-) loss-of-function mutants. (D) Distal axon stumps do not readily degenerate 24 hr after a single injury in wild type, tir-1(-), or nsy-1(-), or pmk-1(-) animals. N = 23, 29, 39, 29. No significant difference was observed relative to wild-type controls, Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. Scale bars: 10 μm.
Tables
Motor axon degeneration is dependent on expression of tir-1, but not mCherry.
tir1(qd4) animals were injected with the indicated expression constructs and the number of degenerating GABA motor axons was quantified. Expression of GFP or mCherry in motor axons is not sufficient to induce axon degeneration on their own. However, expression of untagged tir-1 or GFP-tagged tir-1 does induce axon degeneration.
| Description | Expression Plasmid | % Damaged Axons |
|---|---|---|
| control | unc-47p::GFP | 0 |
| control | unc-47p::mCherry | 0 |
| untagged line 1 | unc-47p::tir-1 | 9 |
| untagged line 2 | unc-47p::tir-1 | 6 |
| untagged line 3 | unc-47p::tir-1 | 11 |
| untagged line 4 | unc-47p::tir-1 | 17 |
| GFP tagged line 1 | unc-47p::tir-1::GFP | 13 |
| GFP tagged line 2 | unc-47p::tir-1::GFP | 31 |
| GFP tagged line 3 | unc-47p::tir-1::GFP | 6 |





