Opioid suppression of an excitatory pontomedullary respiratory circuit by convergent mechanisms
Figures
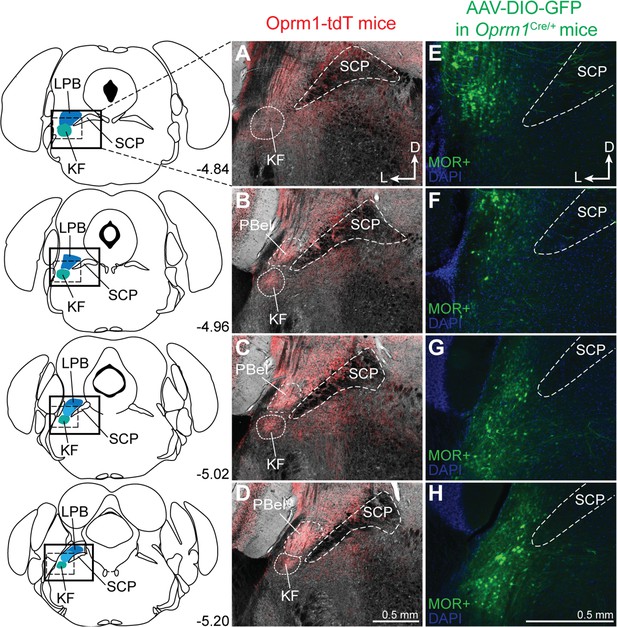
Dorsolateral pontine neurons express mu opioid receptors (MORs).
(A–D) Representative images of tdTomato expression, as an indicator of MOR expression, in coronal dorsolateral pontine slices from Oprm1-tdT mice (n = 3) across the rostral to caudal Kölliker-Fuse/lateral parabrachial area (KF/LPB) axis. Fluorescent tdTomato image is overlaid onto brightfield image to show landmarks. (E–H) Representative images of GFP expression, as an indicator of MOR expression, following injection of virus encoding Cre-dependent GFP into KF/LPB to label MOR+ neurons in adult Oprm1Cre/+ mice (n = 5). Left column are slice schematics corresponding to each row. The approximate levels caudal to bregma (in mm) are to the right of each schematic. The images correspond to the solid boxed area (A–D) or the dotted boxed area (E–H) of the slice schematic. The scale bar in (D) applies to images (A–D). The scale bar in (H) applies to images (E–H). PBel, external lateral subdivision of parabrachial; SCP, superior cerebellar peduncle.
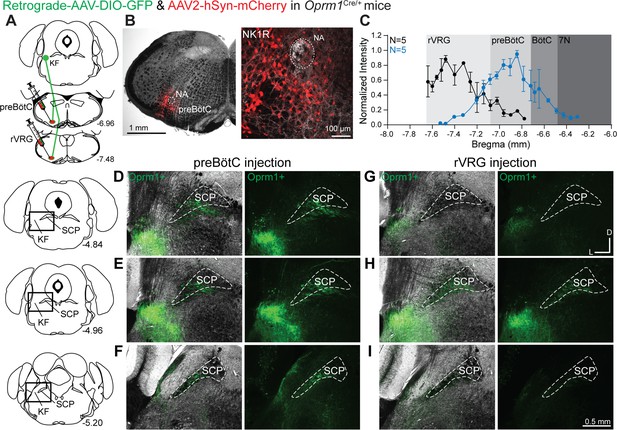
Oprm1+ Kölliker-Fuse (KF) neurons and neurites retrogradely labeled from the preBötzinger complex (preBötC) and rostral ventral respiratory group (rVRG).
(A) Schematic illustrating the approach to retrogradely label Oprm1+ KF neurons and neurites projecting to the preBötC or rVRG. (B) Images of coronal slices from the medulla with a control injection of AAV2-hSyn-mCherry into the preBötC of an Oprm1Cre/+ mouse to mark the injection site. Immunohistochemistry for the neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) was used as a marker for the preBötC and the nucleus ambiguous (NA). (C) Quantification of normalized AAV2-hSyn-mCherry fluorescence intensity along the rostral to caudal axis in the ventrolateral medulla of preBötC (n = 5) and rVRG (n = 5). Anatomical level relative to Bregma is indicated on the x-axis. (D–I) Representative images of GFP expression, as an indicator of retrograde-labeled Oprm1-expressing neurons and neurites, following injections into the preBötC (D–F) or the rVRG (G–I) across three levels of the dorsolateral pons. The bregma level is indicated on the schematics to the left of each row. The scale bar in (I) applies to all images (D–I). Higher magnification images of bregma –4.84 are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 2.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Quantification of spread at the injection sites.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81119/elife-81119-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
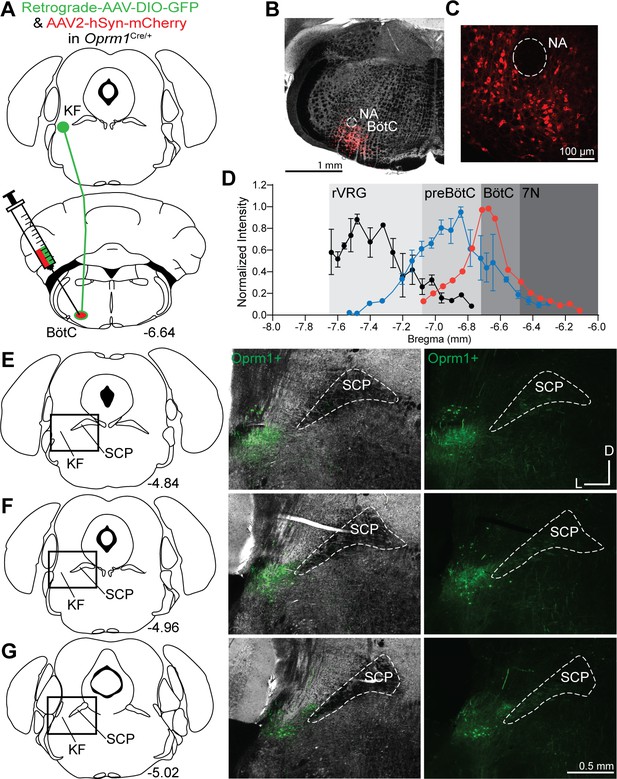
Oprm1+ Kölliker-Fuse (KF) neurons project to the Bötzinger complex (BötC).
(A) Schematic illustrating the approach to retrogradely label Oprm1+ KF neurons projecting to the BötC. (B–, C) Images of coronal slices from the medulla with a control injection of AAV2-hSyn-mCherry into the BötC of an Oprm1Cre/+ mouse to mark injection spread. The nucleus ambiguous (NA) was used as a medullary marker in both images. (D) Quantification of normalized AAV2-hSyn-mCherry spread along the rostral to caudal axis in the ventrolateral medulla of representative injection into BötC. Data from injections into preBötC (n = 5) and rostral ventral respiratory group (rVRG) (n = 5) are duplicated from Figure 2 for comparison. (E–G) Images of Oprm1+ expression following a BötC injection across three levels of the KF/lateral parabrachial area (LPB). The bregma coordinates and approximate location of KF/LPB are indicated. The scale bar in (G) applies to all images in (E–G).
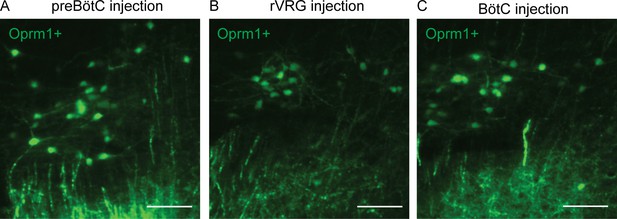
Higher magnification images of retrogradely labeled Kölliker-Fuse (KF) neurons.
Images of GFP expression, as an indicator of retrograde-labeled Oprm1-expressing neurons, following injections into preBötzinger complex (preBötC) (A), rostral ventral respiratory group (rVRG) (B), or BötC at bregma –4.84 of the dorsolateral pons. Scale bar is 100 µm.
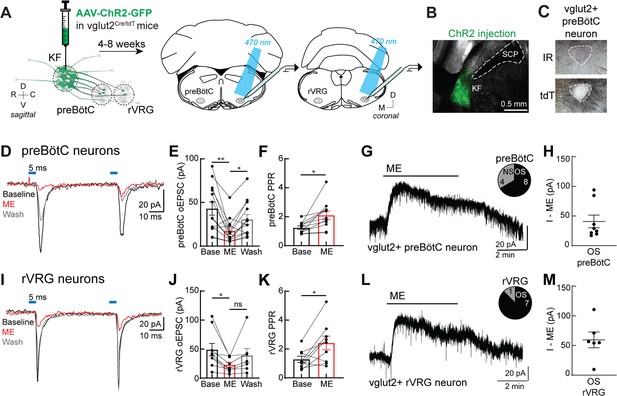
Presynaptic opioid receptors inhibit glutamate release from Kölliker-Fuse (KF) terminals onto excitatory preBötzinger complex (preBötC) and rostral ventral respiratory group (rVRG) neurons.
(A) Schematic of approach to optogenetically stimulate KF terminals and drive optogenetically evoke excitatory postsynaptic currents (oEPSCs) in excitatory preBötC and rVRG neurons in an acute brain slice. (B) Representative image of ChR2-GFP expression in the KF (injection area) of vglut2-tdT mouse. (C) tdTomato-expressing, excitatory vglut2-expressing preBötC (or rVRG) neurons were identified in acute brain slices. (D) Recording of pairs of oEPSCs (5 ms stimulation, 50 ms inter-stimulus interval) from an excitatory preBötC neuron in an acute brain slice at baseline (black), during perfusion of Met-enkephalin (ME, 3 μM) (red), and after wash (gray). (E) ME decreased oEPSC amplitude in preBötC neurons (n = 13; **p=0.007, *p=0.013 by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-test). (F) ME increased the paired-pulse ratio (P2/P1) in preBötC neurons (n = 11; *p=0.001 paired t-test). (G) ME (3 μM) induced outward currents in 8 of 12 preBötC neurons. OS, opioid-sensitive; NS, non-opioid-sensitive. (H) The amplitude of the outward current (I–ME, pA) in OS preBötC neurons. (I) Recording of pairs of oEPSCs (5 ms stimulation, 50 ms inter-stimulus interval) from an excitatory rVRG neuron in an acute brain slice at baseline (black), during perfusion of ME (3 μM) (red), and after wash (gray). (J) ME decreased oEPSC amplitude in rVRG neurons (n = 9; *p=0.027 by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-test). (K) ME increased the paired-pulse ratio (P2/P1) in rVRG neurons (n = 9; *p=0.043 by paired t-test). (L) ME-mediated outward currents were observed in 7 of 8 rVRG neurons. (M) The amplitude of the outward current (I–ME, pA) in OS rVRG neurons. For all graphs, bar/line and error represent mean ± SEM. Individual data points are from individual neurons.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Presynaptic opioid receptors inhibit glutamate release from Kölliker-Fuse (KF) terminals onto excitatory preBötzinger complex (preBötC) and rostral ventral respiratory group (rVRG) neurons.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81119/elife-81119-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
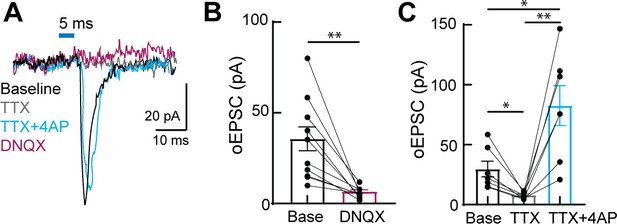
Kölliker-Fuse (KF) neurons send monosynaptic, glutamatergic projections to excitatory ventrolateral medullary neurons.
(A) Recording of optogenetically evoke excitatory postsynaptic currents (oEPSCs) from an excitatory (vglut2+) preBötzinger complex (preBötC) neuron in an acute brain slice at baseline (black), during perfusion of tetrodotoxin (TTX) (1 μM) (gray), during perfusion of TTX (1 μM) + 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) (100 μM) (cyan), and during perfusion of 6,7-dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (DNQX) (10 μM) (purple). (B) KF synapses onto medullary respiratory neurons are monosynaptic. TTX blocked oEPSCs (n = 7; *p=0.0207 by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-test), which were restored by perfusion of TTX + 4-AP (n = 7; **p=0.0086, *p=0.042 by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-test). (C) KF synapses onto medullary respiratory neurons are glutamatergic. AMPA-type glutamate receptor antagonist DNQX (10 μM) blocked oEPSCs (n = 11; **p=0.001 paired t-test).
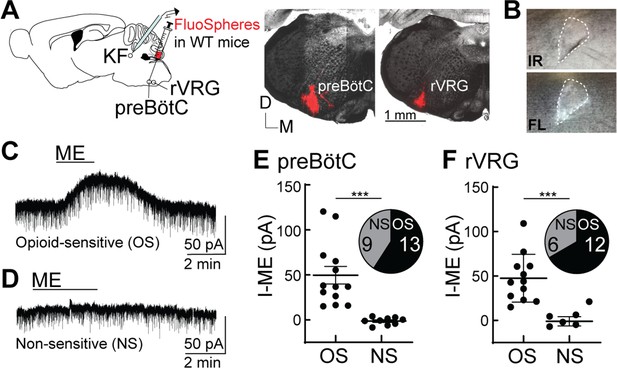
Opioids hyperpolarize Kölliker-Fuse (KF) neurons that project to the preBötzinger complex (preBötC) and rostral ventral respiratory group (rVRG).
(A) Schematic (left) of approach to retrogradely label KF neurons that project to the preBötC or rVRG with FluoSpheres in wild-type mice. Images (right) of FluoSpheres in the injection area (preBötC or rVRG). The scale bar applies to both injection images. (B) A KF neuron retrogradely labeled by FluoSpheres shown with IR-Dodt and epifluorescent (FL) illumination. (C, D) Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings from opioid-sensitive (‘OS’) and non-opioid-sensitive (‘NS’) retrogradely labeled KF neurons. Met-enkephalin (ME) (1 µM) induced an outward current in the opioid-sensitive (OS) neuron (C), but not the non-opioid-sensitive (NS) neuron (D). (E, F) Quantification of the amplitude of the ME-mediated current (I-ME [pA]) in OS and NS KF neurons that project to the preBötC (E; n = 22; ***p=0.0005; unpaired t-test) or the rVRG (F; n = 18; ***p=0.0007; unpaired t-test). ME induced an outward current in 13 of 22 KF neurons that project to the preBötC and 12 of 18 KF neurons that project to the rVRG. Individual data points are from individual neurons in separate slices. Line and error are mean ± SEM.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Opioid-mediated outward currents in Kölliker-Fuse (KF) neurons that project to the preBötzinger complex (preBötC) and rostral ventral respiratory group (rVRG).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81119/elife-81119-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
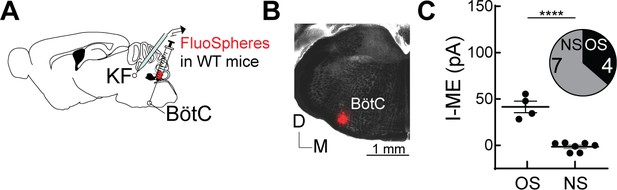
Opioids hyperpolarize Kölliker-Fuse (KF) neurons that project to the Bötzinger complex (BötC).
(A) Schematic of approach to retrogradely label KF neurons that project to the BötC with FluoSpheres in wild-type mice. (B) Image of FluoSpheres injection into the BötC. (C) Quantification of Met-enkephalin (ME)-mediated current in opioid-sensitive (OS) and non-opioid-sensitive (NS) KF neurons that project to the BötC (n = 11; p=0.0001; unpaired t-test). ME (1 µM) induced an outward current in 4 of 11 KF neurons that project to the BötC. Individual data points are from individual neurons in separate slices. Line and error are mean ± SEM.
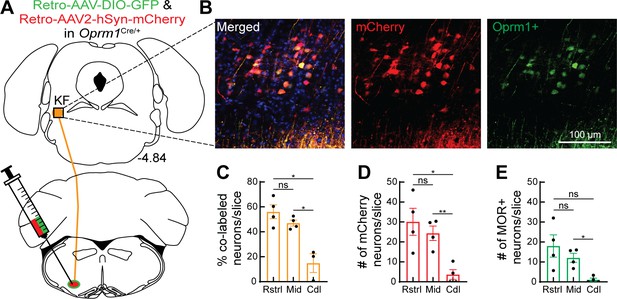
Oprm1+ and Oprm1- dorsolateral pontine neurons project to the ventrolateral medulla.
(A) Schematic of approach injecting retrograde virus encoding Cre-dependent GFP expression and a retrograde virus encoding mCherry expression into the ventrolateral medulla of Oprm1Cre/+ mice to label Oprm1+ and Oprm1- dorsolateral pontine neurons that project to these respiratory nuclei. (B) Representative images of mCherry expression (retrogradely labels neurons regardless of Oprm1 expression) and GFP expression (retrogradely labels Oprm1+ neurons) in a rostral dorsolateral pontine slice (bregma –4.84 mm). (C) Summary of percentage of retrograde-labeled neurons that were Oprm1+ (co-labeled with mCherry and GFP) in rostral (Rstrl, bregma –4.84 mm), mid-rostral (Mid, bregma –4.96 mm), and caudal (Cdl, bregma –5.2 mm) slices. (D, E) Summary of the average number of mCherry-expressing (D) or GFP-expressing MOR+ (E) dorsolateral pontine neurons per slice in rostral, mid-rostral, and caudal slices. Bar and error are mean ± SEM. Individual data points are from individual mice. N = 4 mice, three slices per region per mouse. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns = p>0.05 by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-test.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Oprm1+ and Oprm1- dorsolateral pontine neurons project to the ventrolateral medulla.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81119/elife-81119-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
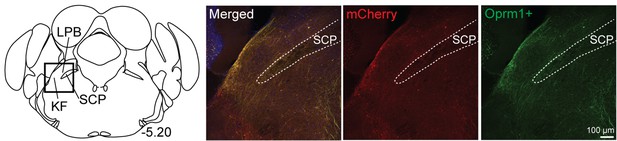
Medullary-projecting Oprm1+ neurons are mostly absent from the caudal Kölliker-Fuse (KF) and lateral parabrachial areas.
Retrograde-labeled neurons (both Oprm1+ and Oprm1-) were mostly lacking in caudal KF or lateral parabrachial area. The bregma coordinate and approximate location in KF/lateral parabrachial area (LPB) are indicated. The scale bar applies to all images.
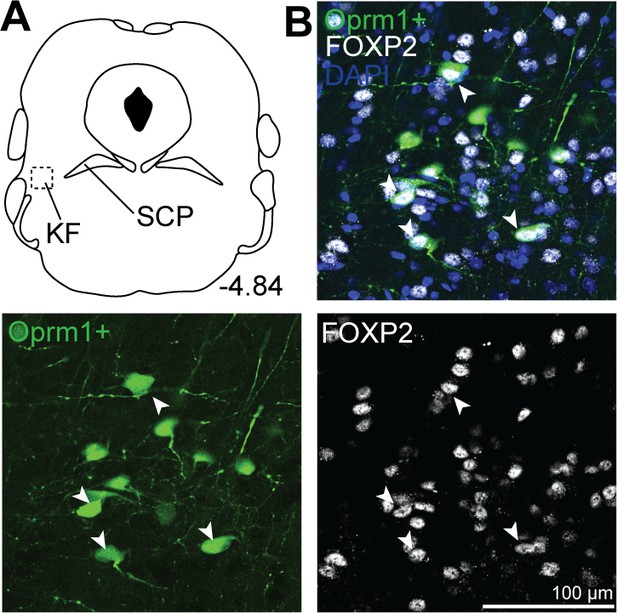
Oprm1+, medullary-projecting Kölliker-Fuse (KF) neurons express Forkhead box protein P2 (FoxP2).
Oprm1+ neurons that project to the ventrolateral medulla were retrogradely labeled by injection of retrograde AAV-DIO-GFP into Oprm1Cre/+ mice. Immunohistochemistry was used to label FoxP2. (A, B) In rostral slices (bregma –4.84), FoxP2 is expressed in Oprm1+ KF neurons that project to the ventrolateral medulla. Schematic (A) depicts the approximate bregma level and imaging area (dotted boxed area). The scale bar applies to all images. SCP, superior cerebellar peduncle.
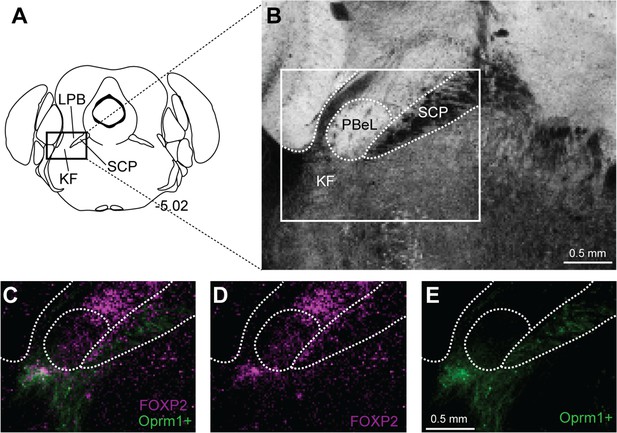
Forkhead box protein P2 (FoxP2) expression in caudal Kölliker-Fuse (KF), but not external lateral parabrachial subnucleus.
Oprm1+ neurons that project to the ventrolateral medulla were retrogradely labeled by injection of retrograde AAV-DIO-GFP into Oprm1Cre/+ mice. Immunohistochemistry was used to label FoxP2. (A) Schematic of approximate bregma level of the images. (B) Brightfield image of coronal slice used for imaging. (C–E) In caudal slices, FoxP2 is expressed in Oprm1+ KF neurons that project to the ventrolateral medulla and excluded from the outer portion of the external lateral parabrachial subnucleus (PBeL). Images in (C–E) are of the boxed area in (B). The scale bars apply to all images in each row. SCP, superior cerebellar peduncle.
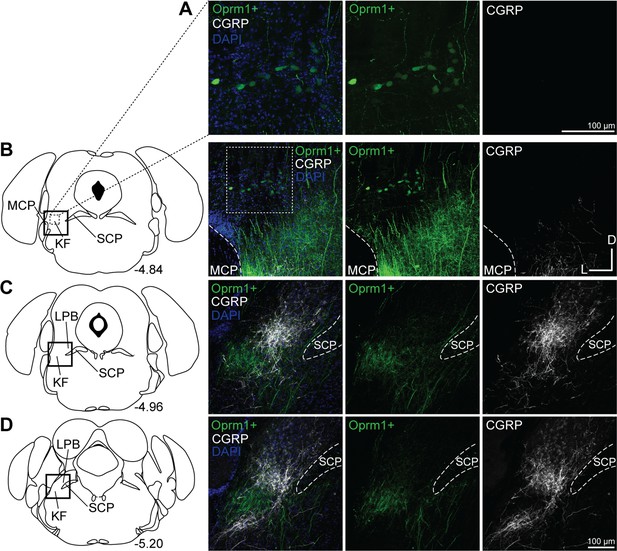
Oprm1+, medullary-projecting Kölliker-Fuse (KF) neurons do not express calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP).
Oprm1+ neurons that project to the ventrolateral medulla were retrogradely labeled by injection of retrograde AAV-DIO-GFP into Oprm1Cre/+ mice. Immunohistochemistry was used to label CGRP. (A, B) CGRP is absent from rostral KF and Oprm1+ KF neurons that project to the ventrolateral medulla (Oprm1+). (C, D) CGRP marks lateral parabrachial area (LPB) neurons and their axon fiber projections, but is absent from retrograde-labeled Oprm1+ axon fiber projections in mid-rostral (C) and caudal (D) slices. The approximate bregma levels are to the right of each schematic. The images correspond to the dotted boxed area (row A) or the solid boxed area (rows B–D) of the slice schematic. The images in (A) are zoomed into the dotted boxed area of the image in (B). The scale bar in (A) applies to the images in row (A). The scale bar in (D) applies to images in rows (B–D). SCP, superior cerebellar peduncle; MCP, medial cerebellar peduncle.
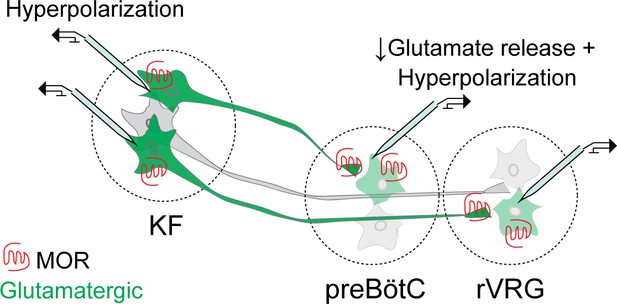
Summary schematic of mu opioid receptor (MOR) regulation of excitatory pontomedullary circuitry.
Kölliker-Fuse (KF): Somatodendritic MORs hyperpolarize KF neurons that project to the ventrolateral medulla. Ventrolateral medulla: presynaptic MORs inhibit glutamate release from KF axon terminals onto glutamatergic preBötzinger complex (preBötC) and rostral ventral respiratory group (rVRG )neurons. Somatodendritic MORs hyperpolarize glutamatergic preBötC and rVRG neurons that receive KF input. Glutamatergic neurons are in green.

Example intensity profile plots of the GFP, FoxP2 and DAPI signal across the neuron, indicated by the yellow line on the image.
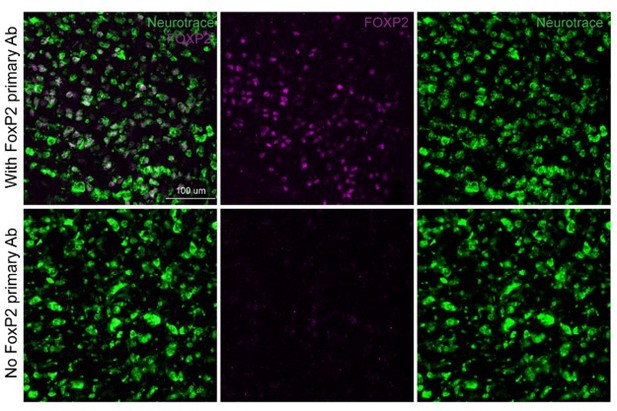
FoxP2 immunolabeling (magenta) in the KF area with (top row) and without (bottom row) the primary anti-FoxP2 antibody.
Neurotrace (green) is a fluorescent Nissl stain and labels neurons.
Tables
Mice used in this study.
| Strain | Reference | Source information | Key gene |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oprm1-cre | Liu et al., 2021. | Jax 035574 https://www.jax.org/strain/035574 Dr. Richard Palmiter (University of Washington) | Cre recombinase expressed in neurons with mu-opioid receptors |
| Vglut2-cre | Vong et al., 2011 | Jax 028863 https://www.jax.org/strain/028863 | Cre recombinase expressed in excitatory glutamatergic neurons |
| Ai9, tdTomato Cre-reporter | Madisen et al., 2010 | Jax 007909 https://www.jax.org/strain/007909 | LoxP-flanked STOP cassette preceding transcription of CAG promoter-driven red fluorescent protein variant (tdTomato) inserted into the Gt(ROSA)26Sor locus |
| C57BL/6J (wild-type) | Simon et al., 2013 | Jax 000664 https://www.jax.org/strain/000664 |
Key resources.
| Injectate | Strain used | Injection target | Figure | Source Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FluoSpheres 580/605, diameter: 0.04 µm | C57BL/6J | BötC, preBötC, or rVRG | Figure 4 and Figure 4—figure supplement 1 | Invitrogen |
| Retrograde AAV-hSyn-DIO-EGFP | Oprm1Cre/+ | BötC, preBötC, or rVRG | Figure 2 and Figure 2—figure supplement 1 | Addgene |
| AAV2-hSyn-mCherry | Oprm1Cre/+ | BötC, preBötC, or rVRG | Figure 2 and Figure 2—figure supplement 1 | UNC Vector Core |
| Retrograde AAV-hSyn-mCherry | Oprm1Cre/+ | BötC, preBötC, and rVRG | Figure 5 | Addgene |
| AAV2-hSyn-DIO-EGFP | Oprm1Cre/+ | KF/PB | Figure 1E–H | Addgene |
| AAV2-hSyn-hChR2(H134R)-EYFP-WPRE-PA | vglut2-tdT | KF/PB | Figure 3 | UNC Vector Core |
-
PreBötC, preBötzinger complex; rVRG, rostral ventral respiratory group; KF, Kölliker-Fuse; PB, parabrachial area.
Antibodies used in this study.
| Antigen | Immunogen description | Source, host species, RRID | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forkhead box P2 (FoxP2) | Targets human and mouse FoxP2 | R&D Systems, sheep polyclonal, Cat# AF5647, RRID:AB_2107133 | 1:1000 |
| Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) | Targets alpha-CGRP in canine, mouse, and rat | Peninsula, rabbit polyclonal, Cat# T-4032, RRID:AB_518147 | 1:1000 |
| Neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) | Targets C-terminal of NK1R in mouse, guinea pig, and human | Sigma-Aldrich, rabbit polyclonal, Cat# S8305 RRID:AB_261562 | 1:1000 |






