Precise control of neural activity using dynamically optimized electrical stimulation
Figures
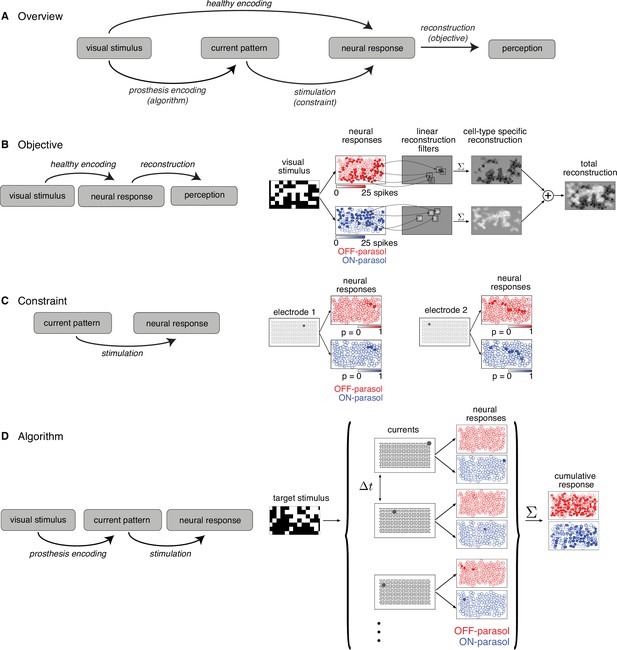
Algorithmic components of the proposed framework for electrical stimulation.
(A) In a healthy retina, the visual stimulus is encoded in the neural response pattern of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs; top row). In a retina with an implant, the visual stimulus is encoded into current patterns, which generate neural response patterns (bottom row). In either case, the neural responses are eventually processed by the brain to elicit perception, through a process assumed to involve reconstruction of the image. Selecting the appropriate electrical stimulation can be framed as an optimization problem, in which the goal is to identify an algorithm (prosthesis encoding) that achieves an objective (reconstruction error) while operating under constraints (electrical stimulation). (B) Objective: Linear reconstruction of visual stimulus by summing cell-specific spatial filters, weighted by spike counts. Receptive fields of ON (blue) and OFF (red) parasol cells in a population are shown. (C) Constraint: Characterizing electrically evoked RGC responses with a dictionary of stimulation patterns. Example dictionary elements, with cells shaded according to evoked response probability. A single-electrode stimulated multiple cells, indicating poor selectivity. (D) Algorithm: Run-time usage of the artificial retina. Exploiting the slow visual integration time, distant electrodes are stimulated in fast sequence. The resulting neural response is the summation of spikes elicited in each time step.
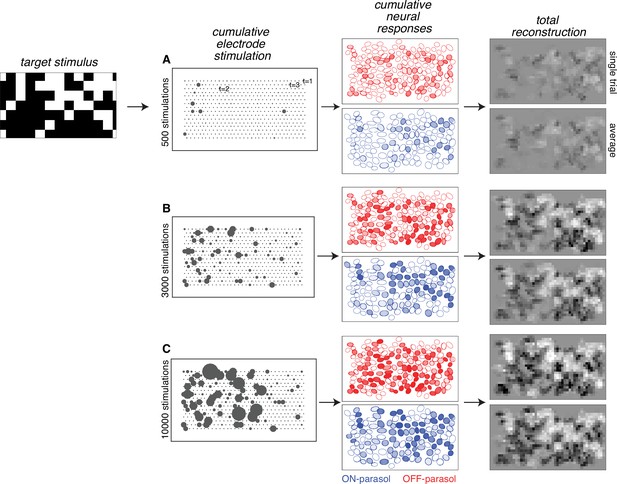
Visual stimulus reconstruction achieved using the greedy temporal dithering algorithm.
White noise target image shown on left. First column: cumulative stimulation count across electrodes after 500, 3000, and 10,000 electrical stimuli (A, B, and C, respectively). Second column: responses for ON (blue) and OFF (red) parasol cells, sampled according to the single-electrode calibration data. Shade indicates the cumulative number of spikes. Third column: single-trial and trial-averaged reconstruction of the target stimulus.
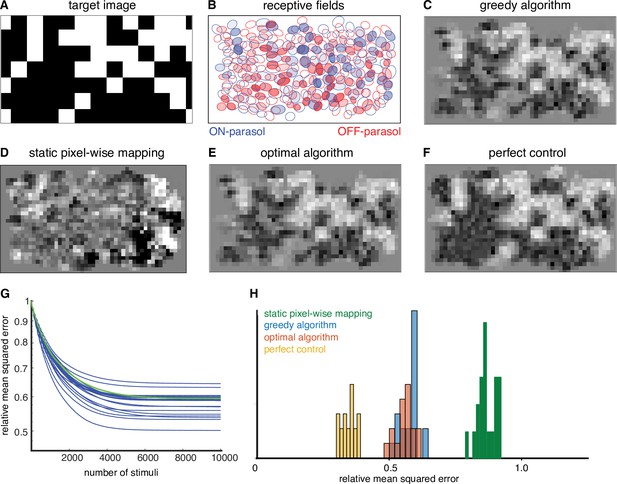
Quantifying the performance of dynamically optimized stimulation.
(A) A sample target checkerboard image. (B) ON and OFF receptive fields shaded with the expected summed response from greedy temporal dithering. Achieved reconstructions are shown for (C) greedy temporal dithering using calibrated responses to single-electrode stimulation (8448 electrical stimuli), (D) static pixel-wise mapping approximating existing open-loop systems (5023 stimuli), (E) a lower error bound on the optimal algorithm for a single-electrode dictionary (1850 stimuli), and (F) perfect control with the available reconstruction filters. (G) Reconstruction error (relative mean squared error) between target and the expected achieved perception for 20 different targets (blue lines), with the example from C indicated with the green line. (H) Histogram of relative performance of the above approaches across 20 target images.

Experimental validation of dynamically optimized stimulation in the rat retina.
(A) Four sample target checkerboard images. Achieved reconstructions for these images are shown (B) assuming perfect control of retinal ganglion cell (RGC) firing with the available reconstruction filters, (C) using greedy temporal dithering based on calibrated single-electrode responses, and (D) and using the RGC responses evoked during electrical stimulation with greedy temporal dithering. (E, F) ON and OFF receptive fields shaded with the total number of evoked spikes. (G) Reconstruction error (relative mean squared error) across 20 target images for perfect control vs. greedy temporal dithering using calibrated responses (top) and for greedy temporal dithering using calibrated responses vs. evoked responses (bottom). Red points correspond to the four targets shown. Evoked RGC responses are averaged over 25 trials for each target (D–G).
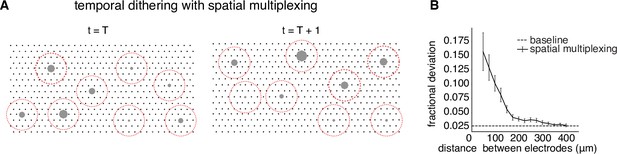
Spatial multiplexing by simultaneous stimulation of distant electrodes.
(A) Visualization of temporally dithered and spatially multiplexed stimulation. At each time step, multiple single-electrode stimuli are chosen greedily (gray circles) across the electrode array (black dots), separated by a spatial exclusion radius (red circles). (B) Estimation of the spatial exclusion radius using 754 total electrode pairs across 7 parasol cells from 4 peripheral macaque retina preparations (see Methods). Interaction between electrodes is measured by fractional deviation in activation threshold for a given cell on a primary electrode (ordinate) resulting from simultaneous stimulation of another electrode with identical current amplitude at varying separations (abscissa). Baseline represents the variability associated with estimating single-electrode activation thresholds.
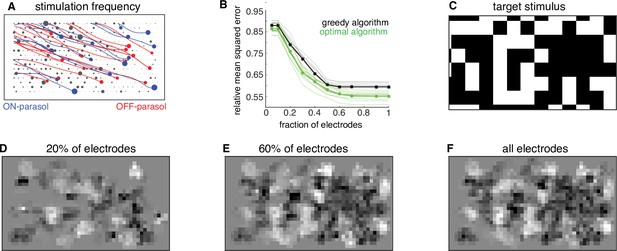
Subsampling electrodes for hardware efficiency.
(A) Frequency of stimulating different electrodes (size of gray circles), overlaid with axons (lines), and somas (colored circles) inferred from spatiotemporal spike waveform across the electrode array recorded from each cell. (B) Reconstruction error as a function of the fraction of electrodes included in the dictionary (black, thin lines correspond to different target images) and average over 20 target images (black, thick line). Different collections of target stimuli were used for electrode selection and reconstruction performance evaluation. Lower bound on error of any algorithm for the subsampled dictionaries for individual targets (green, thin lines) and averaged across targets (green, thick line). (C) Example target image. (D–F) Reconstructed images using the dictionary with most frequently used 20%, 60%, and 100% of electrodes, respectively.
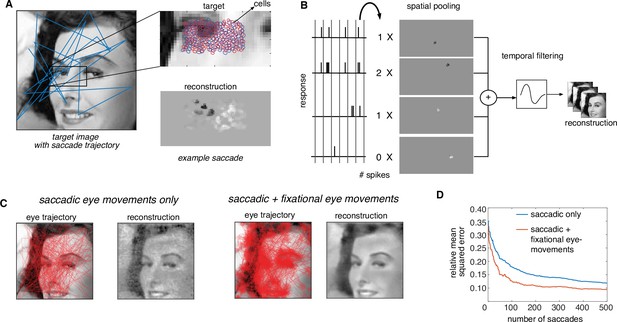
Extension of dynamically optimized stimulation to naturalistic conditions with eye movements.
(A) Conversion of a visual scene into dynamic stimulus. A target visual scene (left), with sample eye movement trajectory (blue). For each eye position, the population of ganglion cells accessible by the implant views a small portion of the visual scene (top right). The reconstructed stimulus for each patch captures the local stimulus information (bottom right). (B) Spike trains passed through a spatiotemporal reconstruction filter of the dynamic stimulus video. For simplicity, a rank one filter was used, which spatially filtered each spike bin independently, and then filtered the reconstructed stimulus video in time. (C) Final reconstruction performance over a sequence of saccades, in the absence (left) and the presence (right) of small fixational eye movements. (D) Reduction in reconstruction error of the visual scene as a function of the number of saccades, in the absence (blue) and the presence (orange) of fixational eye movements.
Greedy temporal dithering and spatial multiplexing in natural viewing conditions.
Top row: operation of the proposed approach when only saccadic eye movements are used. Left: target visual scene with overlaid eye movement trajectory (red). Middle: target stimulus for the cells underneath the retinal implant. Right: the assembled visual scene after generating responses with the selected stimulation sequence. Bottom row: similar to top, with fixational eye movements in addition to saccadic eye movements.






