X-chromosome target specificity diverged between dosage compensation mechanisms of two closely related Caenorhabditis species
Figures
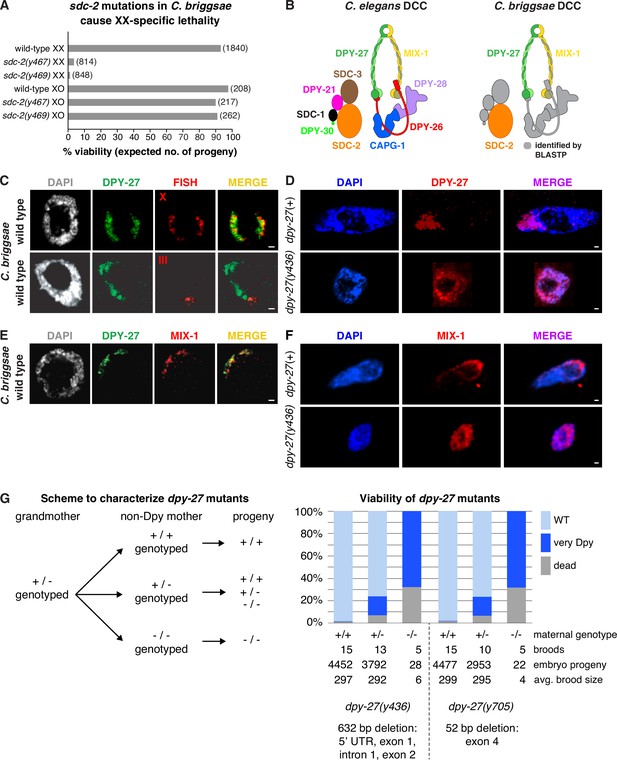
Conservation of X-chromosome dosage compensation machinery between C. briggsae and C. elegans.
(A) sdc-2 mutations cause XX-specific lethality in C. briggsae. Graph shows percent viability of wild-type and Cbr sdc-2 mutant XX and XO adults. Viability of homozygous XX and hemizygous XO Cbr sdc-2 mutants is expressed as the percentage of live adults for each karyotype relative to the number expected (shown in parentheses) in the progeny of a cross if all mutant animals were viable. Crosses and calculations are described in Materials and methods. Sequence changes of sdc-2 mutations derived from genome editing using zinc-finger nucleases are shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 3A. (B) Schematic of the C. elegans dosage compensation complex (left) and C. briggsae orthologs identified by BLASTP (right). The C. elegans dosage compensation complex (DCC) includes homologs of all core condensin subunits (MIX-1, DPY-27, DPY-26, DPY-28, and CAPG-1). C. briggsae DCC components identified and characterized in this study are shown in color; other orthologs are in gray. DPY-27 and MIX-1 belong to the SMC (Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes) family of chromosomal ATPases. Each has nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs) at its N- and C-termini that are linked by two long coiled-coil domains separated by a hinge domain. Each SMC protein folds back on itself to form a central region of two anti-parallel coiled coils flanked by the NBDs and the hinge. DPY-27 and MIX-1 dimerize through interactions between their hinge domains and their NBD domains. The globular NBDs bind to the three non-SMC condensin DCC subunits (DPY-26, DPY-28, and CAPG-1) (See Meyer, 2022a). (C) Condensin subunit DPY-27 binds X chromosomes and mediates dosage compensation in C. briggsae. Confocal images of C. briggsae hermaphrodite gut nuclei co-stained with the DNA dye DAPI (gray), antibodies to Cbr DPY-27 (green), and FISH probes to either 5% of X (red, top), or 1% of chromosome III (red, bottom) show that Cbr DPY-27 co-localizes with X but not III, consistent with a role in dosage compensation. Scale bars, 1 μm. (D) Confocal images of C. briggsae gut nuclei from dpy-27(+) or dpy-27(y436) mutant XX adult hermaphrodites co-stained with DAPI (blue) and the Cbr DPY-27 rabbit antibody (red). DPY-27 shows subnuclear localization in a dpy-27(+) gut nucleus (top), as expected for X localization. The mutant gut nucleus (bottom) shows diffuse nuclear distribution of DPY-27, as anticipated for a mutant SMC-4 condensin ortholog that lacks most of the N-terminal part of the ATPase domain and, therefore, has no ATP binding or hydrolysis. Scale bars, 1 μm. (E) Confocal images of a C. briggsae gut nucleus from wild-type adult hermaphrodites co-stained with DAPI (gray) and antibodies to Cbr DPY-27 (green) and Cbr MIX-1 (red) show that Cbr MIX-1 co-localizes with Cbr DPY-27 on X in wild-type hermaphrodites. Scale bars, 1 μm. (F) Association of Cbr MIX-1 (red) with X found in a dpy-27(+) nucleus (top) is disrupted in a Cbr dpy-27(y436) nucleus (bottom), in accord with participation of Cbr MIX-1 in a protein complex with Cbr DPY-27. Scale bars, 1 μm. (G) Viability of dpy-27 mutant XX C. briggsae animals. The left panel shows the genetic scheme to characterize the effect of maternal genotype on viability of dpy-27 null XX mutants. Comparison is made between homozygous null dpy-27 progeny from heterozygous or homozygous non-Dpy mutant mothers. The genotype of non-DPY mothers was established through PCR analysis. The right panel shows the percent viability of progeny from wild-type hermaphrodites and heterozygous or homozygous dpy-27 mutant hermaphrodites. The maternal genotype, number of broods, total number of embryo progeny from all broods, and average brood size are provided for two null alleles of dpy-27. Molecular characterization of mutations is shown below the graph and in Figure 1—figure supplement 3B. Almost all progeny of dpy-27 null mutant mothers are dead; a homozygous dpy-27 null strain cannot be propagated. More than 20% of progeny of dpy-27/+heterozygous mutant mothers are very Dpy or dead, indicating that a wild-type DPY-27 maternal contribution has minimal effect on suppressing the deleterious effect of the homozygous null zygotic genotype. The complete XX lethality is consistent with a major role for condensin subunit DPY-27 in dosage compensation.
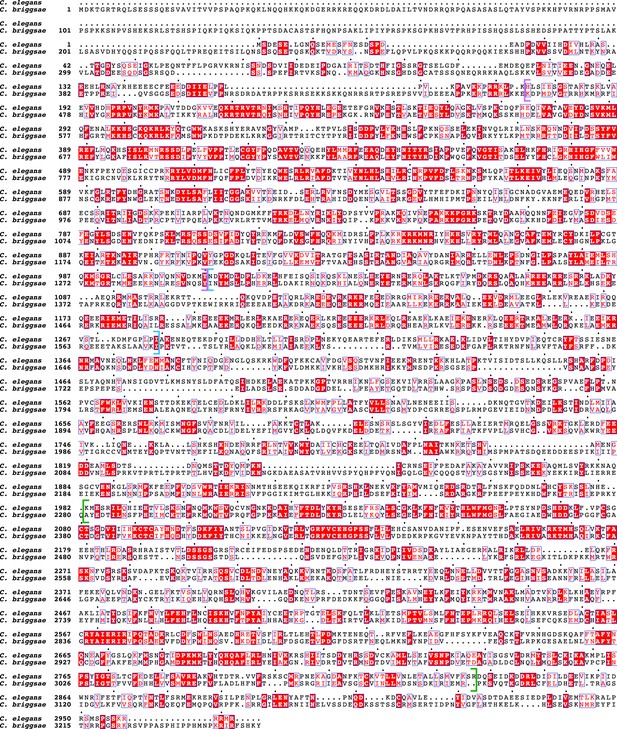
Protein sequence alignment comparing SDC-2 proteins in C. elegans and C. briggsae.
In the sequence alignment, the red background indicates amino acid identity, and the red characters demark similarity. The predicted coiled-coil regions are delineated by blue brackets. The alignment reveals two regions that show conservation between C. elegans and C. briggsae. They are also present in SDC-2 from C. japonica, C. brenneri, and C. tropicalis (Figure 1—figure supplement 2). The first region (purple brackets) is N-terminal to the coiled-coil domains. The second conserved region (green brackets) is in the C-terminal part of SDC-2 proteins. Between Cbr and Cel, the entire SDC-2 protein shows 26% identity and 43% similarity, the N-terminal region shows 38% identity and 58% similarity, and the C-terminal region shows 32% identity and 51% similarity.
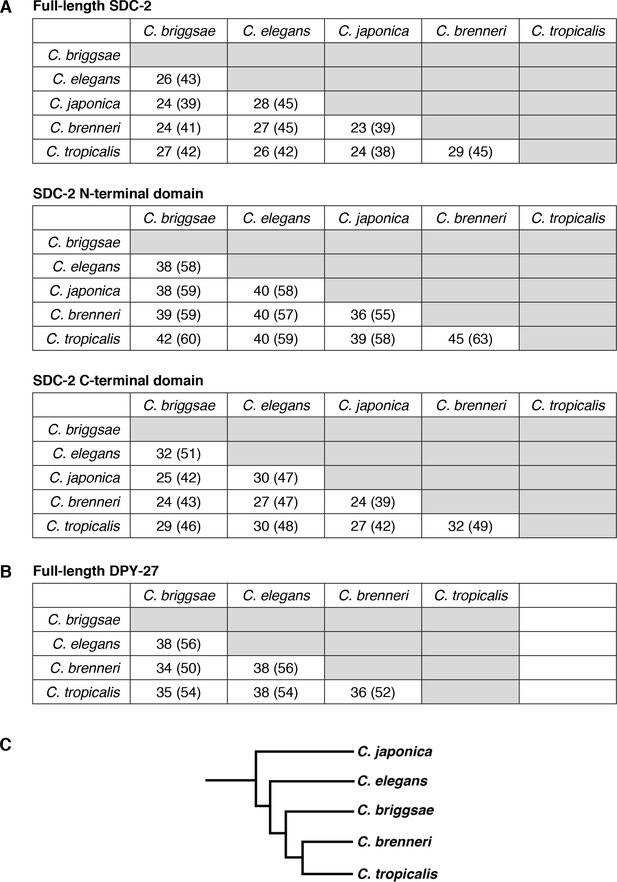
Conservation of SDC-2 and DPY-27 proteins in the Caenorhabditis genus.
Pairwise sequence comparisons between Caenorhabditis species show the percent of amino acid identity and similarity (in parenthesis) for (A) SDC-2 full-length protein, SDC-2 N-terminal domain, and SDC-2 C-terminal domain and (B) DPY-27 full-length protein. (C) Phylogeny of Caenorhabditis species.
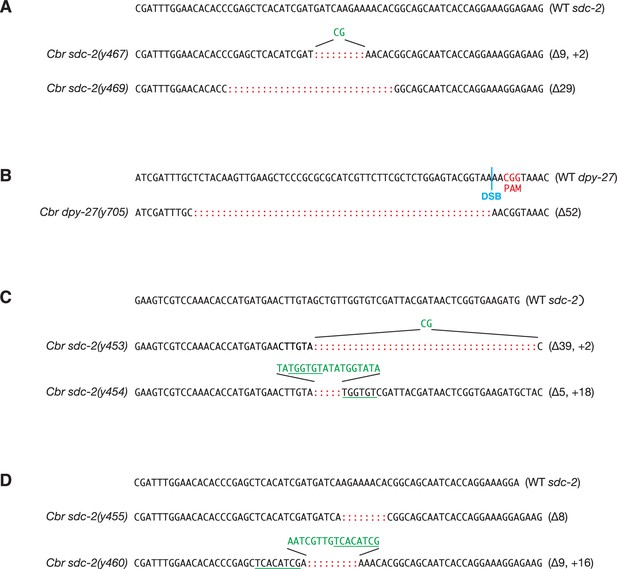
DNA sequence changes mediated by genome editing.
(A) DNA sequences of mutant Cbr sdc-2 alleles that were created by genome editing using zinc-finger nucleases, as described in Wood et al., 2011. Mutations include short insertions (green) and deletions (red colons) that generate in-frame deletions and frame-shift mutations. Inserted sequences (green) frequently share homology (underlined in green) with sequences flanking the break site, as is typical of NHEJ-mediated repair. The deletions in both sdc-2(y467) and sdc-2(y469) create premature translation stop codons, thereby preventing the formation of full-length SDC-2 proteins and causing a complete loss of gene function. For y467, the wild-type sequence ends at codon 926-Asp. The deletion and insertion cause 18 incorrect amino acids to be translated, and a stop codon occurs in place of codon 945. For y469, the wild-type sequence ends at codon 921-Thr. The deletion causes 26 incorrect amino acids to be translated, and a stop codon occurs in place of codon 948. (B) DNA sequence of mutant Cbr dpy-27(y705) allele created by genome editing using CRISPR/Cas9. The Cas9 target sequence was 5' CGCTCTGGAGTACGGTAAAA 3'. The PAM is the CGC (red) immediately 3’ of the target sequence. The double-strand break (DSB) site is indicated by a blue line. The mutation is a 52 bp deletion (red colons) in exon 4 that creates a premature translation stop codon and prevents the formation of the full-length DPY-27 protein. The deletion starts at codon 689, and the in-frame stop codon is two codons past the 3’ end of the deletion. (C, D) DNA sequences of mutant Cbr sdc-2 alleles that were obtained as suppressors of the XO-specific lethality caused by a xol-1 mutation. Alleles sdc-2(y453), sdc-2(y454), sdc-2(y455), and sdc-2(y460), were created by genome editing using zinc-finger nucleases, as described in Wood et al., 2011. The mutations in both sdc-2(y453) and sdc-2(y454) create premature translation stop codons, thereby preventing the formation of full-length SDC-2 proteins and causing a complete loss of gene function. For sdc-2(y453), the wild-type sequence ends at codon 563-Val. The deletion and insertion cause six incorrect amino acids to be translated, and a stop codon occurs in place of codon 570 (554). For sdc-2(y454), the wild-type sequence ends at codon 563-Val. The deletion and insertion cause 11 incorrect amino acids to be translated, and a stop codon occurs in place of codon 575. The mutations in both sdc-2(y455) and sdc-2(y460) create premature translation stop codons, thereby preventing the formation of full-length SDC-2 proteins. For sdc-2(y455), the wild-type sequence ends at codon 927-His. The deletion causes 27 incorrect amino acids to be translated, and a stop codon occurs in place of codon 955. For sdc-2(y460), the wild-type sequence ends at codon 925-Ile. The deletion and insertion cause 34 incorrect amino acids to be translated, and a stop codon occurs in place of codon 960.
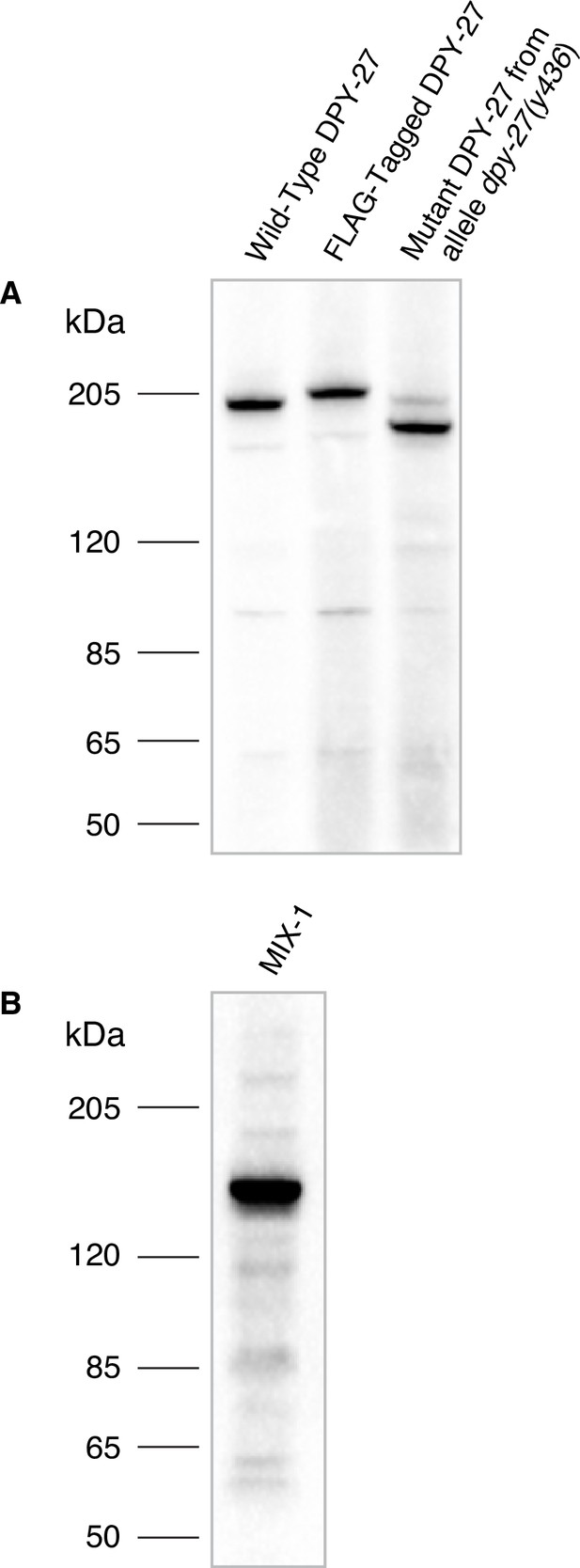
Specificity of Cbr DPY-27 and MIX-1 antibodies.
(A) Western blot analysis comparing DPY-27 proteins in extracts made from twenty wild-type adult C. briggsae XX hermaphrodites (lane 1), adult XX hermaphrodites encoding a 3xFLAG-tagged version of DPY-27 (lane 2), or mutant adult XX hermaphrodites carrying the dpy-27(y436) allele (lane 3) demonstrated the specificity of the anti-DPY-27 polyclonal rabbit antibody. Antibody was raised to the Cbr DPY-27 C-terminal peptide DVQSEAPSAGRPVETDREGSYTNFD. The antibody recognizes the full-length wild-type DPY-27 protein, a 3xFLAG-tagged protein expected to be 3 kDa larger than the wild-type protein, and a mutant protein expected to be 20 kDa shorter than the wild-type protein if translation starts at the internal start codon at position 179, just after the y436 deletion endpoint. Proteins run slower than expected for their calculated molecular weights, but correspond to the relative molecular weights calculated for the three proteins: 179 kDa for the wild-type protein, 182 kDa for the 3xFLAG-tagged protein, 159 kDa for the mutant protein. The dpy-27(y436) mutant lane also shows a faint band at the size expected for the wild-type protein, likely because homozygous dpy-27(y436) mutant adults were picked from a plate of dpy-27(y436)/+mothers, and contaminating +/+ or + /y436 larvae or embryos might have adhered to Dpy adults that were picked. (B) Western blot analysis of an extract from twenty wild-type adult C. briggsae XX hermaphrodites probed with anti-Cbr-MIX-1 polyclonal rabbit antibody raised against the Cbr MIX-1 C-terminal peptide EATKKPSKKSAKKAVQNTDDEME. The calculated molecular weight of MIX-1 is 139 kDa.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 4—source data 1
Source data for DPY-27 and MIX-1 antibody specificity.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85413/elife-85413-fig1-figsupp4-data1-v2.zip
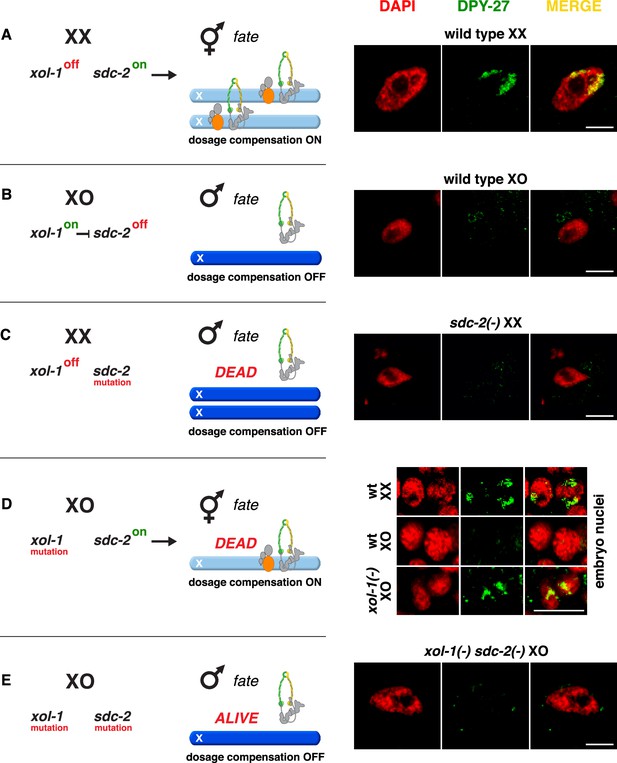
Conserved genetic hierarchy targets the C. briggsae dosage compensation complex (DCC) to the X chromosomes of hermaphrodites.
(A–E) Schematic depiction of the genetic hierarchy controlling sex-specific DCC recruitment to C. briggsae X chromosomes (left) paired with representative immunofluorescence experiments exemplifying DCC localization (right). Scale bars, 5 μm. Gut nuclei (A, B, C, E) or embryos (D) were co-stained with DAPI (red) and antibodies to Cbr DPY-27 (green). In wild-type XX, but not XO gut nuclei (A, B), DPY-27 co-localizes with X chromosomes, consistent with a role for condensin subunit DPY-27 in dosage compensation (see also Figure 1C). (C) SDC-2 is required for recruitment of DPY-27 to the X chromosomes of hermaphrodites. Failure of the DCC to bind X chromosomes of sdc-2 XX mutants underlies the XX-specific lethality. Shown is the gut nucleus of a rare XX sdc-2 mutant escaper near death. sdc-2 mutant XX escaper animals are masculinized. (D) Lethality of Cbr xol-1(y430) XO animals corresponds to inappropriate binding of the DCC to the single X in embryos. (E) Mutation of the DCC recruitment factor Cbr sdc-2 in a Cbr xol-1 XO mutant prevents DCC recruitment to X and suppresses the XO lethality. See Figure 3B for quantification.
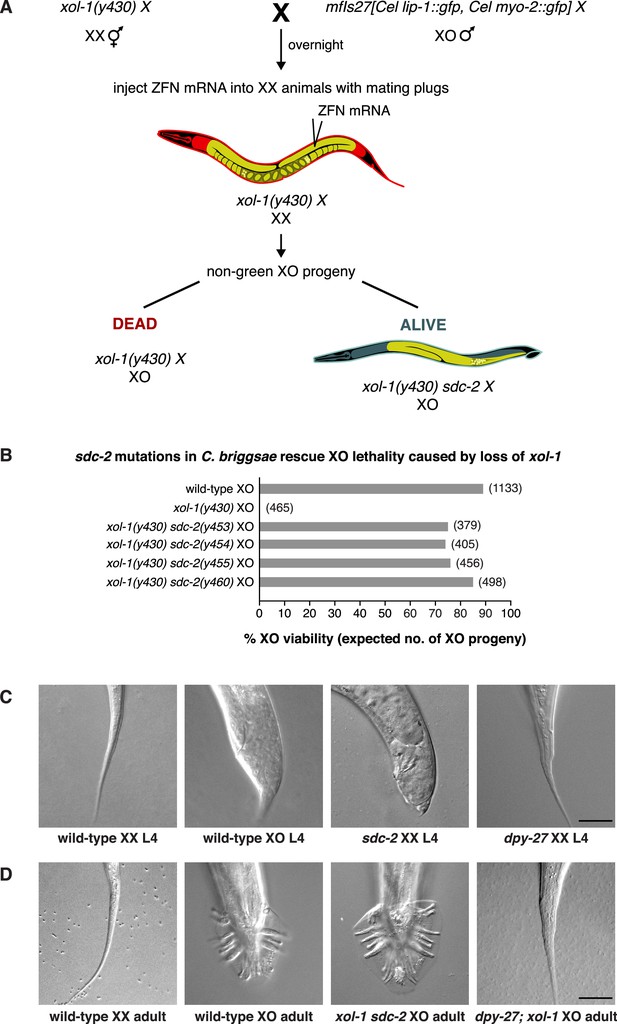
sdc-2 controls dosage compensation and sex determination in C. briggsae.
(A) Diagram of the screening strategy to recover Cbr sdc-2 mutations as suppressors of the XO-specific lethality caused by a xol-1 mutation. Cbr xol-1 XX hermaphrodites were mated with males carrying a gfp-marked X chromosome to allow F1 XO males to be monitored for the parental origin of the X chromosome. Animals with mating plugs (indicating successful mating) were injected with mRNAs to sdc-2 zinc-finger nucleases, and all F1 males were examined for GFP fluorescence. Non-green males necessarily inherited an X chromosome carrying a Cbr-xol-1 mutation and, assuming conservation of the dosage compensation complex (DCC) regulatory hierarchy, would be inviable without a concomitant Cbr sdc-2 mutation. GFP-positive males arose at low frequency from fertilization of nullo-X oocytes (caused by non-disjunction of the maternal X chromosome) with gfp-X-bearing sperm. These false positives were discarded from further study. (B) Cbr sdc-2 mutations rescue Cbr xol-1(y430) XO lethality. Graph shows percent viability of wild-type XO animals and mutant XO animals carrying combinations of Cbr xol-1 and Cbr sdc-2 mutations. The % XO viability is expressed as the percentage of live XO adults relative to the number expected (shown in parentheses) in the progeny of the cross. Formulae for viability calculations are given in the Materials and methods. Sequence changes of sdc-2 mutations are shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 3C and D. (C) sdc-2 activates the program for Cbr hermaphrodite sexual development. DIC images show the comparison of tail morphologies for Cbr L4 animals of different genotypes. sdc-2 mutations, but not dpy-27 mutations, cause masculinization of XX animals. Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) DIC images show tail morphologies of wild-type or doubly mutant Cbr adults. An sdc-2 mutation suppresses both the XO lethality and feminization caused by a xol-1 mutation, consistent with a role for sdc-2 in controlling both dosage compensation and sex determination. xol-1 sdc-2 XO animals are viable, fertile males, indicating that the sdc-2 mutation suppressed the lethality and feminization caused by xol-1 mutations in XO animals. A dpy-27 mutation suppresses the XO lethality but not feminization caused by a xol-1 mutation, consistent with a role for dpy-27 in dosage compensation but not sex determination. dpy-27; xol-1 XO animals are fertile hermaphrodites. Scale bar, 20 μm.
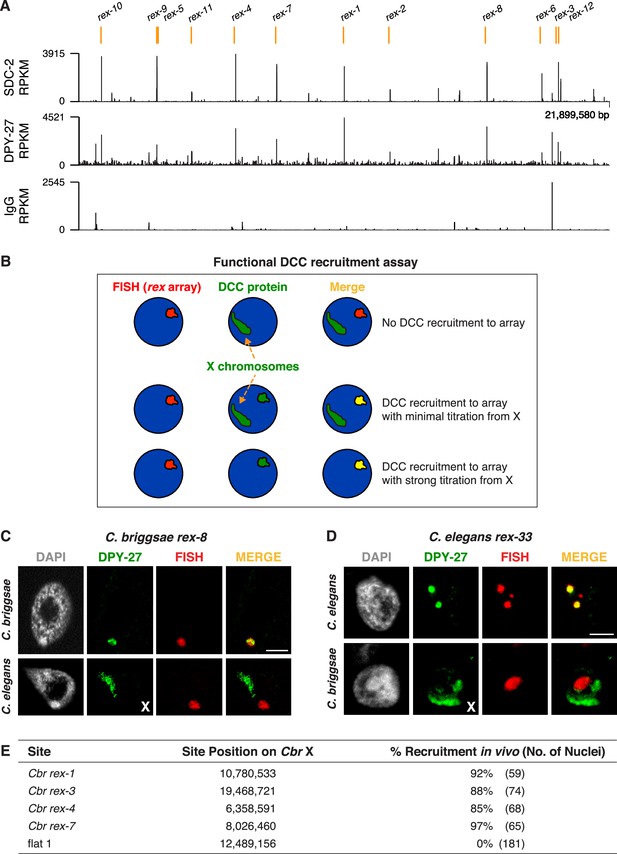
Identification of C. briggsae dosage compensation complex (DCC) recruitment elements on X.
(A) ChIP-seq profiles of Cbr SDC-2 and Cbr DPY-27 binding to X chromosomes. ChIP-seq experiments were performed using an anti-FLAG antibody to immunoprecipitate SDC-2 from a strain encoding FLAG-tagged SDC-2, and the same anti-FLAG antibody was used in ChIP-seq experiments to immunoprecipitate DPY-27 from a strain encoding FLAG-tagged DPY-27. The control IgG ChIP-seq profile on X is also shown. Peaks that correspond to recruitment elements on X (rex sites), as determined by the assay in (B), are indicated in orange above the ChIP-seq profiles. RPKM is the abbreviation for reads per kilobase per million reads mapped. (B) Assay performed in vivo to determine whether DNAs from ChIP-seq peaks recruit the DCC when detached from X. XX embryos carrying extrachromosomal arrays with multiple copies of DNA from a ChIP-seq peak in (A) were stained with a DNA FISH probe to the array (red) and DPY-27 antibody (green). If the DNA from a peak failed to recruit the DCC, DPY-27 staining would identify X chromosomes but not the array. If DNA from a peak encoded a recruitment site (rex site), DPY-27 staining would co-localize with the array and the X chromosome. In the merged image, the array would appear yellow and the X chromosome would appear green. Often, an array carries enough copies of a rex site that it titrates most of the DCC from X, and only the array itself shows evidence of DCC binding, appearing yellow in the merged image. In that case, the X chromosome is not detectable by DPY-27 antibody staining. XX strains carrying rex arrays that titrate the DCC from X cannot be propagated due to the defect in dosage compensation caused by DCC titration. (C) C. briggsae rex sites recruit the C. briggsae DCC but not the C. elegans DCC. Shown is a C. briggsae or C. elegans XX gut nucleus carrying an extrachromosomal array containing multiple copies of the C. briggsae DCC recruitment site rex-8. Nuclei were stained with appropriate species-specific C. briggsae or C. elegans antibodies to the DCC subunit DPY-27 (green), DAPI (gray), and an array FISH probe (red). In C. briggsae, DPY-27 bound to arrays in about 40% of the 52 scored nuclei carrying a Cbr rex-8 array, and the DCC was titrated from X. In C. elegans, DPY-27 bound to arrays in 0% of the 27 scored nuclei carrying a Cbr rex-8 array, and DPY-27 binding to the C. elegans X was evident. Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) C. elegans rex sites do not recruit the C. briggsae DCC. Shown is a C. elegans or C. briggsae XX gut nucleus carrying an extrachromosomal array containing multiple copies of the C. elegans recruitment site rex-33 with three MEX motifs (ln[P] scores of −13.13,–15.33, –15.35). Nuclei were stained with C. elegans or C. briggsae antibodies to DCC subunit DPY-27 (green), DAPI (gray), and an array FISH probe (red). In C. elegans, DPY-27 bound to arrays in 100% of the 63 scored nuclei carrying a Cel rex-33 array, and the DCC was titrated from X. In C. briggsae, DPY-27 bound to arrays in 0% of the 53 scored nuclei carrying a Cel rex-33 array, but did bind to Cbr X chromosomes in the same nuclei (Table 2). Scale bar, 5 μm. (E) Quantification of exemplary Cbr recruitment assays in vivo using extrachromosomal arrays containing multiple copies of DNA from Cbr DCC ChIP-seq peaks that define rex sites. Data are shown for DPY-27 recruitment to DNA from four strong Cbr ChIP-seq peaks and a control region of DNA lacking a DCC peak (flat one containing the gene mom-1). Shown are the locations of the sites on X, the total number of embryonic nuclei scored for DPY-27 recruitment to the array, and the percent of nuclei recruiting the DCC. Arrays carrying rex sites recruit the DCC but arrays carrying the control flat region fail to recruit the DCC. Results of DCC recruitment assays in vivo for all rex sites are presented in Table 2.
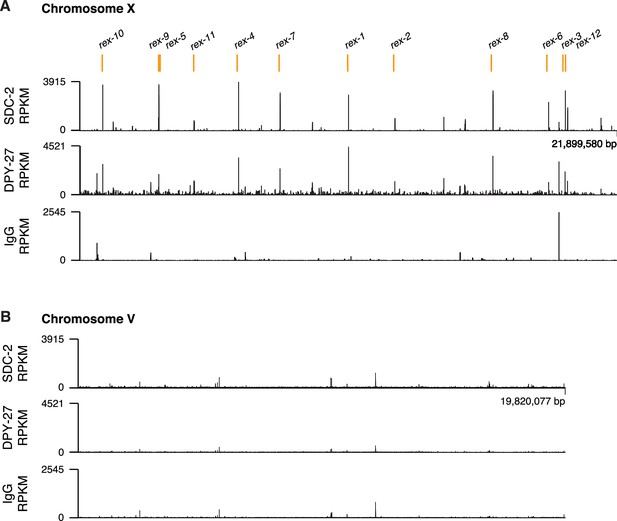
ChIP-seq profiles of Cbr SDC-2 and Cbr DPY-27 binding to chromosomes X and V.
For ChIP-seq profiles of Cbr SDC-2 and Cbr DPY-27 binding to chromosomes X (A) and V (B), experiments were performed using an anti-FLAG antibody to immunoprecipitate SDC-2 from a strain encoding FLAG-tagged SDC-2, and the same anti-FLAG antibody was used to immunoprecipitate DPY-27 from a strain encoding FLAG-tagged DPY-27. Control IgG ChIP-seq profiles on X and V are also shown. Peaks that correspond to recruitment elements on X (rex sites) are indicated in orange above the ChIP-seq profiles. RPKM is the abbreviation for reads per kilobase per million reads mapped.
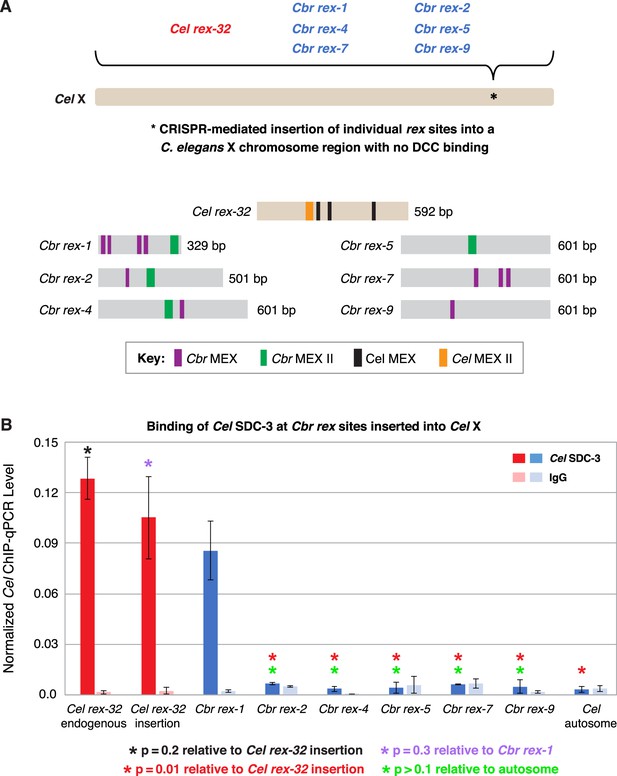
C. briggsae rex sites integrated into the C. elegans X chromosome by genome editing failed to recruit the C. elegans dosage compensation complex (DCC).
Binding of C. elegans DCC protein Cel SDC-3 and an IgG control were examined by ChIP-qPCR for Cel rex-32 at its endogenous location on X, and for six C. briggsae rex sites (Cbr rex-1, Cbr rex-2, Cbr rex-4, Cbr rex-5, Cbr rex-7, and Cbr rex-9) plus the control Cel rex-32 that were inserted by Cas9 genome editing into position 15,574,674 bp of the C. elegans X chromosome. (A) Schematic shows the location of Cbr rex insertions in the Cel X chromosomes and shows the different combinations of Cbr MEX and MEX II motifs in the inserted Cbr rex sites. (B) The graph of Cel SDC-3 ChIP-qPCR data shows that all Cbr rex sites except rex-1 exhibited SDC-3 binding that was not significantly different from that of the autosomal negative control. Cbr rex-1 contains a Cel Motif C variant within each Cbr MEX motif, thereby accounting for the exceptional SDC-3 binding. The Motif C variants within Cbr rex-1 MEX include GGGCAGGGT (–11.68), GGGCAGGGG (–14.16), GCGCAGGGC (–12.06), and CGGCAGGGG (–10.72). A fifth Motif C variant lies between the –14.16 and –12.06 variants: TCCAAGGGG (–9.84). Cel SDC-3 levels for each replicate were normalized to the average levels at the five Cel rex sites: Cel rex-8, Cel rex-16, Cel rex-32, Cel rex-48, and Cel rex-35. Error bars represent the SD for three replicates of Cel rex-32 and Cbr rex-1 and two replicates for each of Cbr rex-2, Cbr rex-4, Cbr rex-5, Cbr rex-7, and Cbr rex-9. Cel SDC-3 binding to the endogenous Cel rex-32 site and the inserted rex-32 site were not significantly different (p=0.2). Cel SDC-3 binding to all Cbr rex sites except Cbr rex-1 was significantly lower than binding to the Cel rex-32 insertion (p=0.01, Student’s t-test). Cel SDC-3 binding at Cel rex-32 versus Cbr rex-1 is not significantly different (p=0.3).
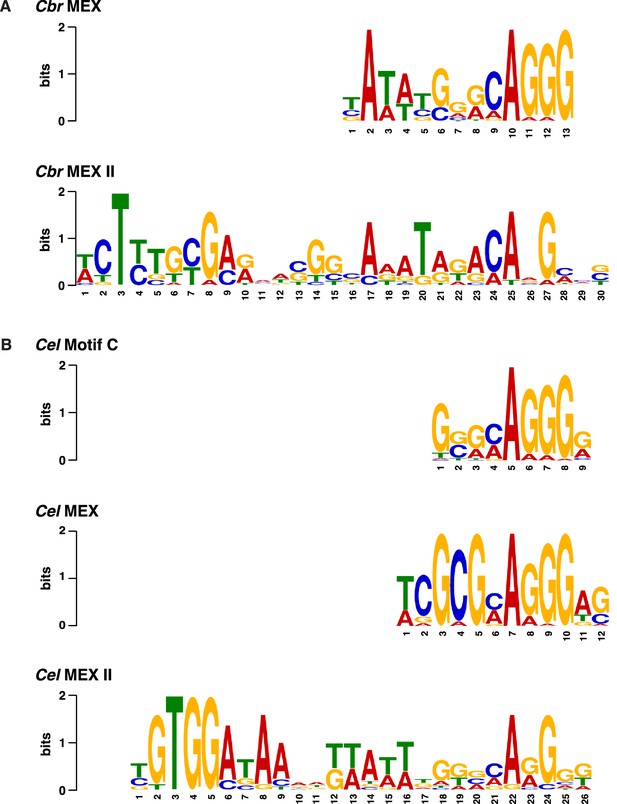
Comparison of C. briggsae and C. elegans DNA motifs on X that occur within respective rex sites and recruit respective dosage compensation complex (DCC) complexes.
(A) Shown are the C. briggsae consensus motifs for the 13 bp MEX and 30 bp MEX II variants that recruit the DCC. Also shown are the C. elegans consensus motifs for the 12 bp MEX, 26 bp MEX II, and 9 bp Motif C variants that recruit the Cel DCC (B). The sequences were aligned relative to the conserved adenine in the 5'-CAGGG-3' common core of the motifs. Predominantly, the Cel MEX motif has a cytosine in the fourth position of the motif. Mutating it to a guanine (C4G) severely reduced DCC binding in assays conducted in vivo and in vitro. The consensus Cbr MEX motif has a guanine at the equivalent position relative to the CAGGG core. Hence, the Cbr MEX motif is predicted not to function as a DCC recruitment motif in C. elegans.
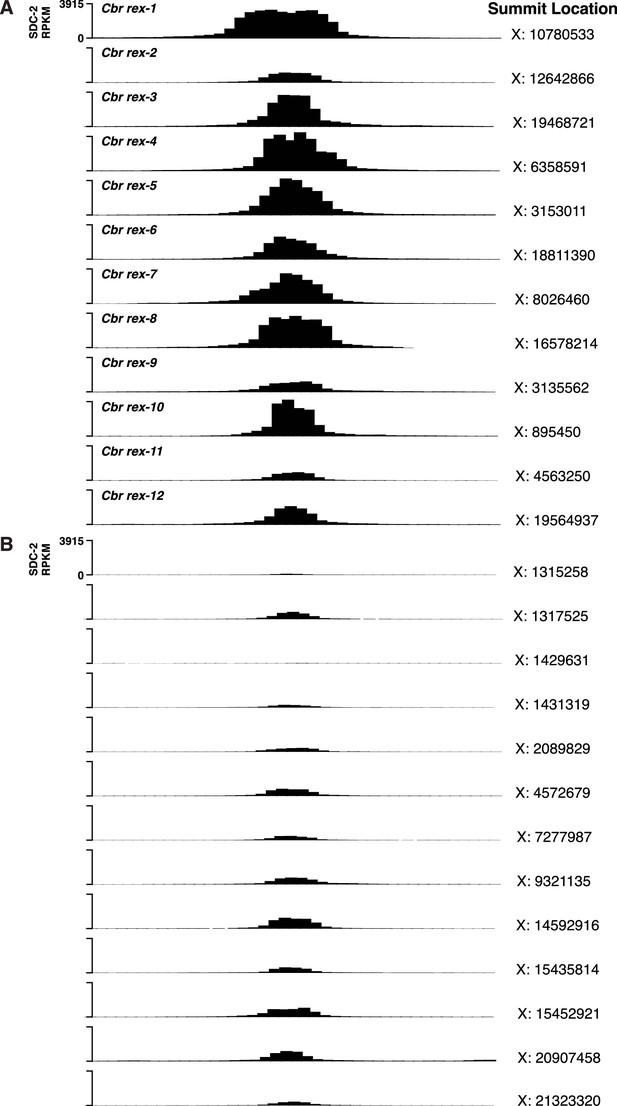
C. briggsae SDC-2 ChIP-seq peak profiles for rex sites and non-rex sites on X.
(A, B) Each profile represents 2,000 bp centered on summit locations. (A) SDC-2 ChIP-seq profiles for all twelve Cbr rex sites. X coordinates for the peak summit locations are shown on the right, and the name of each rex site is shown on the left. The y-axis shows the SDC-2 signal in RPKM (reads per kilobase per million reads mapped). (B) SDC-2 ChIP-seq peak profiles for the thirteen non-rex sites that were analyzed for motif candidates. No motif candidates that correlate with SDC-2 binding were found. The profiles show intermediate levels of SDC-2 binding that are equivalent to or lower than that at rex-2. Peak summit locations are shown on the right, and the y-axis shows the SDC-2 RPKM signal.
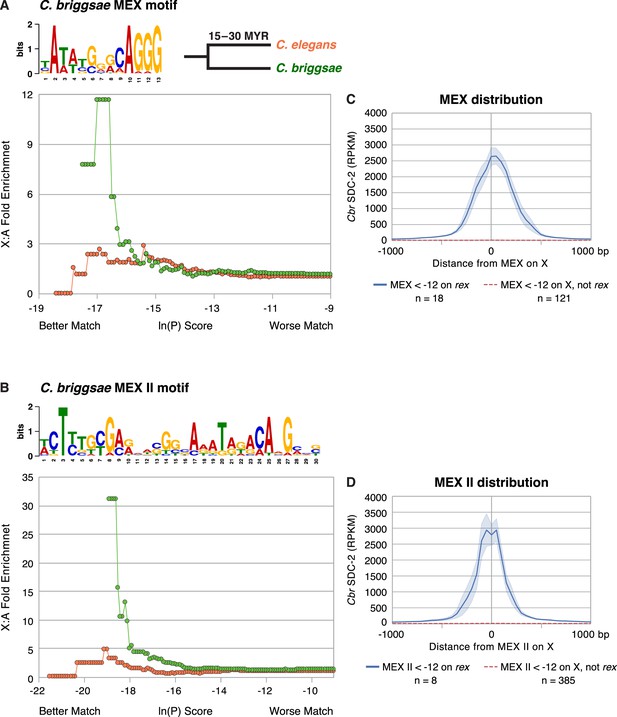
Enrichment of Cbr MEX and Cbr MEX II motifs on X chromosomes between C. briggsae and C. elegans.
(A, B) Graphs show the enrichment (y-axis) of Cbr MEX (A) or Cbr MEX II (B) variants (x-axis) on X chromosomes compared to autosomes in the C. briggsae (green circles) and C. elegans (orange circles) genomes. For MEX, the ln(P) is the natural log of the probability that a 13-mer matches the MEX consensus motif matrix (shown above the graphs) as calculated by the Patser program. For MEX II, the ln(P) is the natural log of the probability that a 30-mer matches the MEX II consensus motif matrix (shown above the graphs) as calculated by Patser. The lower the score, the better the match. The maximum theoretical ln(P) value for MEX is –18.7 and for MEX II is –29.3. The best MEX score found on Cbr X is –18.7 and for MEX II is - 27.58. The graphs reflect cumulative scores. For example, the 12-fold X:A enrichment of MEX for C. briggsae at –17.58 reflects all motifs with ln(P) ≤ –17.58. The C. elegans X chromosome is not enriched for the Cbr MEX or MEX II consensus motifs that are enriched on Cbr X chromosomes and that are pivotal for Cbr DCC recruitment to Cbr X, as we show subsequently. (C) The graph plots the mean (dark blue) and standard error (light blue) of Cbr SDC-2 ChIP-seq signal (RPKM) at various distances from MEX motifs (< –12) in rex sites versus the mean (dashed red) and standard error (light red) of SDC-2 signal at varying distances from MEX motifs (< –12) on X but not in rex sites. Abundant SDC-2 binding was found at MEX motifs in rex sites, but negligible SDC-2 binding was found at individual MEX motifs on X that were not in rex sites or at MEX motifs on autosomes. n, total number of MEX motifs in each category. (D) The graph plots the mean (dark blue) and standard error (light blue) of Cbr SDC-2 ChIP-seq signal (RPKM) at various distances from MEX II motifs (< –12) in rex sites versus the mean (dashed red line) and standard error (light red) of SDC-2 signal at varying distances from MEX II motifs (< –12) on X but not in rex sites. Abundant SDC-2 binding was found at MEX II motifs in rex sites, but negligible SDC-2 binding was found at individual MEX II motifs on X that were not in rex sites or at MEX II motifs on autosomes. n, total number of MEX II motifs in each category.
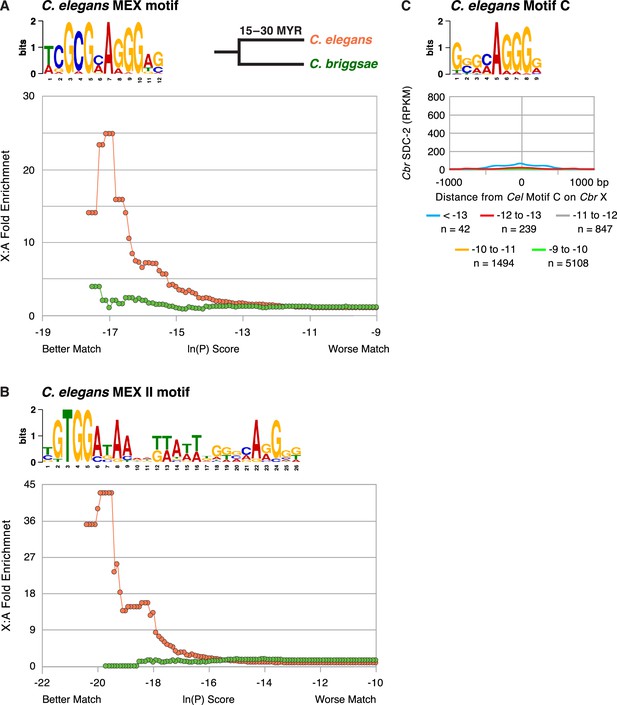
The C. briggsae X chromosome is not enriched for the C. elegans MEX (A) or MEX II (B) motifs that are highly enriched on Cel X chromosomes and pivotal for DCC binding to Cel X chromosomes in vivo.
The descriptions of these graphs are the same as those presented in the legend to Figure 7. (C) Graph shows the Cbr SDC-2 RPKM signal from ChIP-seq experiments as a function of the distance from Cel Motif C variants of different matches (ln[P] score) to the consensus motif found on Cbr X chromosomes. Cbr SDC-2 binding is negligible at most Cel Motif C variants, indicating that Cel Motif C fails to participate in Cbr dosage compensation complex (DCC) recruitment to X chromosomes. The slight increase in SDC-2 signal at Motif C (< –13) variants is due to their location within MEX and MEX II motifs.
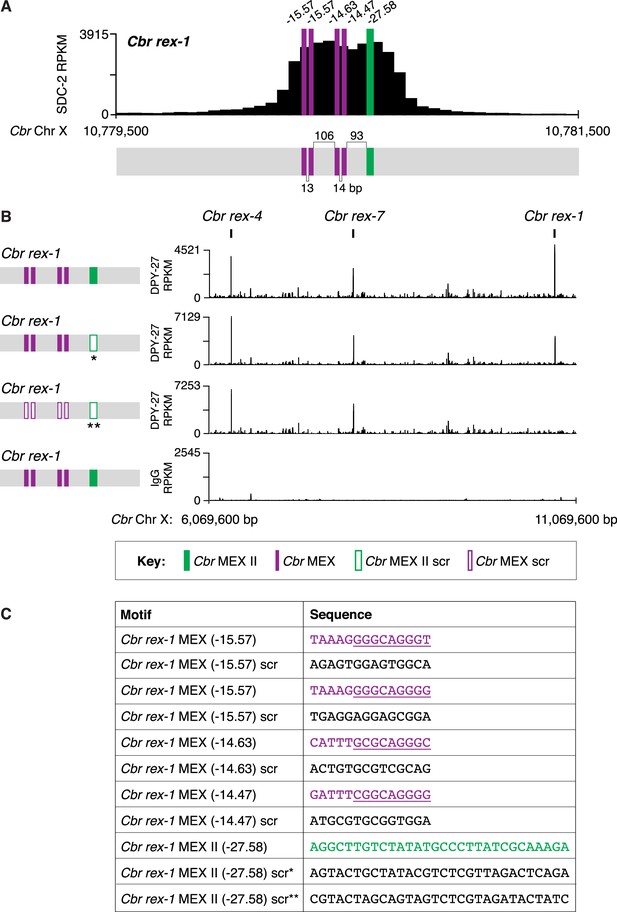
Combinatorial clustering of MEX and MEX II motifs in Cbr rex-1 facilitates dosage compensation complex (DCC) binding to the endogenous rex-1 site on X.
(A) Shown is an enlargement of the SDC-2 ChIP-seq peak profile for Cbr rex-1 with its associated MEX (purple) and MEX II (green) motifs and their ln(P) scores. (B) DPY-27 ChIP-seq analysis was performed using anti-FLAG antibody on an otherwise genetically wild-type C. briggsae strain encoding FLAG-tagged DPY-27 and on FLAG-tagged DPY-27 C. briggsae mutant variants carrying either a scrambled (scr) version of MEX II or a scrambled version of MEX II and all four MEX motifs. The control IgG ChIP-seq analysis was performed on the C. briggsae strain encoding FLAG-tagged DPY-27 carrying wild-type copies of all rex sites. DPY-27 and control IgG ChIP-seq profiles are also shown for Cbr sites rex-7 and rex-4 as an internal standard since DPY-27 binding was not disrupted at these sites. (C) Sequences of the wild-type Cbr rex-1 MEX motifs and their scrambled versions. Underlined is the Cel Motif C variant within each Cbr MEX motif. For analyzing MEX II, two different MEX II mutant variants were used, as indicated by asterisks. Numbers between motifs indicate the base pairs separating the motifs. ChIP-seq profiles reveal that mutating only MEX II reduces some DCC binding at rex-1, and mutating MEX II and all MEX motifs eliminates DCC binding. The motifs act cumulatively to recruit the DCC.

Clustering of MEX and MEX II motifs in Cbr rex-1 confers dosage compensation complex (DCC) binding in vivo.
(A) Shown is an enlargement of the SDC-2 ChIP-seq peak profile for Cbr rex-1 with its associated MEX and MEX II motifs and their ln(P) scores. Numbers between motifs indicate the base pairs separating the motifs. (B) Cbr DPY-27 binding to wild-type and mutant versions of rex-1 was assayed using extrachromosomal arrays carrying multiple copies of wild-type rex-1 or mutant rex-1 variants with either a scrambled MEX II sequence, four scrambled MEX sequences, or a scrambled MEX II sequence and four scrambled MEX sequences. Shown is the total number of array-bearing nuclei that were assayed and the percentage of those nuclei exhibiting DPY-27 binding. The assays show that mutating only MEX II or only the four MEX motifs reduces DPY-27 binding, while mutating both MEX and MEX II motifs virtually eliminates DPY-27 binding. These results indicate that both MEX and MEX II motifs are important for DCC binding at rex sites in vivo. The p-values were determined using the Student’s t-test and are relative to DPY-27 recruitment to arrays carrying wild-type rex-1 sequences. (C) Sequences of wild-type Cbr rex-1 motifs and their scrambled versions are shown.
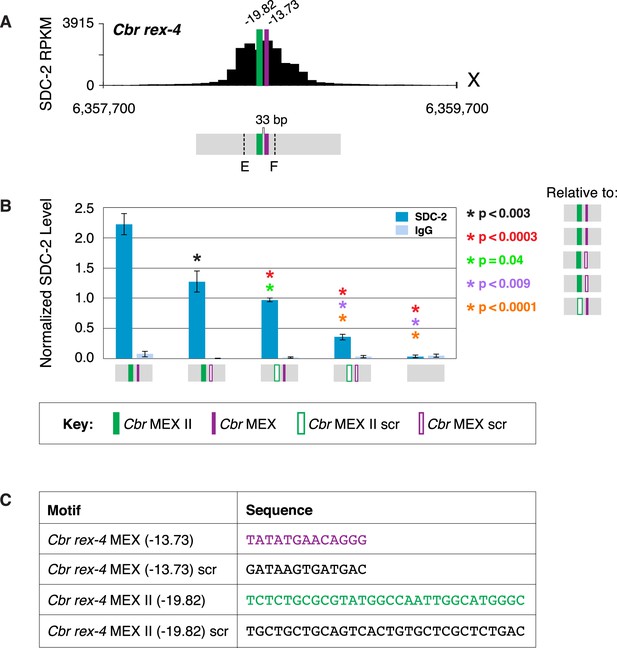
MEX and MEX II motifs are critical for dosage compensation complex (DCC) binding to Cbr rex-4 in vivo.
(A) Shown is an enlargement of the SDC-2 ChIP-seq profile for rex-4, a schematic of the MEX (purple) and MEX II (green) motifs in rex-4, and the location of primers (E and F, dashed lines) to evaluate DCC binding in vivo using ChIP-qPCR. Motifs are separated by 33 bp. (B) The graph shows ChIP qPCR levels for SDC-2 (dark blue) and control IgG (light blue) at endogenous wild-type rex-4, at endogenous rex-4 with different combinations of motif mutations created by genome editing, and at a negative control site on X of 107 bp that lacks DCC binding centered at (7,000,213 bp). Strains carrying wild-type and mutant motifs encoded FLAG-tagged SDC-2. SDC-2 levels for each replicate were normalized to the average level of five endogenous non-edited rex sites (Cbr rex-1, Cbr rex-2, Cbr rex-5, and Cbr rex-9). Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. Asterisks of the same color specify data compared using the Student’s t-test. If more than two motif combinations are compared, the schematic to the right of the p-value indicates the motif combination to which the other combinations were compared. (C) DNA sequences of wild-type and mutant motifs (scr) are shown below the graph. Both MEX and MEX II motifs are critical for DCC binding at rex-4. Mutating each motif independently causes an equivalent reduction in DCC binding, and mutating both motifs is necessary to eliminate DCC binding. ChIP-qPCR analysis of SDC-2 binding at intervals across the entire peak is presented in Figure 9—figure supplement 1.
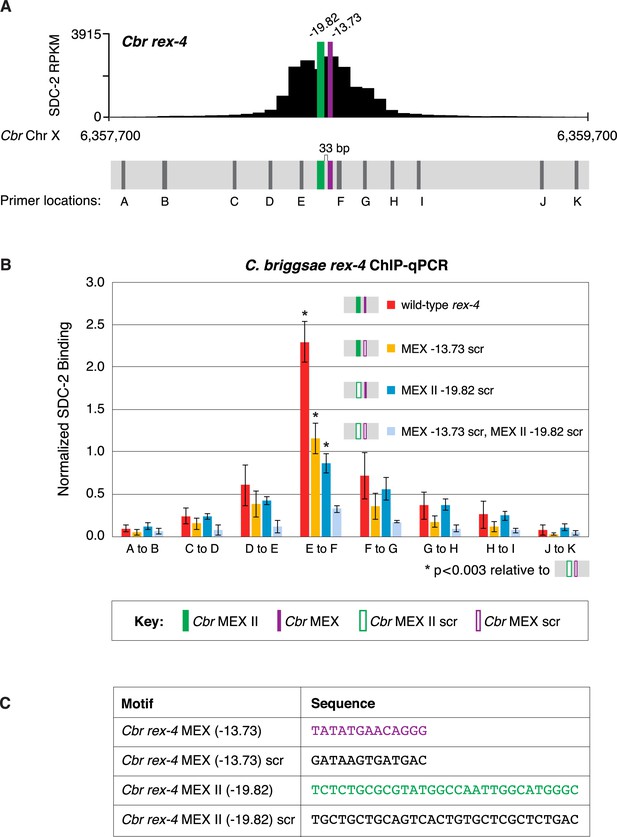
MEX and MEX II motifs are critical for SDC-2 binding to Cbr rex-4 in vivo.
This figure extends the analysis of SDC-2 binding at rex-4 in wild-type and rex-4 mutant strains presented in Figure 9 by including SDC-2 ChIP-qPCR analysis at intervals extending all along the entire SDC-2 peak. (A) The schematic showing motifs in rex-4 include the locations of primers (gray) used for the PCR analysis presented in the graph (B) below it. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. The asterisks highlight the SDC-2 binding values that are significantly different in the E-F interval of the rex-4 site that is mutant for both MEX and MEX II versus wild-type rex-4 or rex-4 with either MEX or MEX II scrambled. Statistics were determined using the Student’s t-test. All other aspects of the figure resemble those explained in the legend to Figure 9. (C) Sequences of wild-type rex-4 motifs and their scrambled versions are shown.
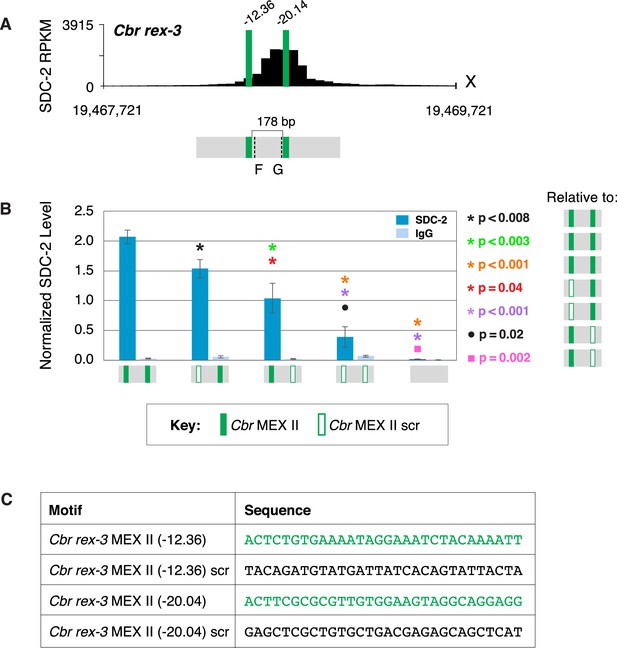
Both MEX II motifs are critical for dosage compensation complex (DCC) binding to Cbr rex-3 in vivo.
(A) Shown is an enlargement of SDC-2 ChIP-seq profile for Cbr rex-3 with its associated MEX II motifs (green) and their ln(P) scores. Motifs are separated by 178 bp. Locations of primers (F and G, dashed lines) to evaluate DCC binding in vivo using ChIP-qPCR are shown. (B) The graph shows ChIP qPCR levels for SDC-2 (dark blue) and control IgG (light blue) at endogenous wild-type rex-3, at endogenous rex-3 with different combinations of motif mutations created by genome editing, and at a negative control site on X that lacks DCC binding. Strains carrying wild-type and mutant motifs encoded FLAG-tagged SDC-2. SDC-2 levels for each replicate were normalized to the average level of five endogenous non-edited rex sites (Cbr rex-1, Cbr rex-2, Cbr rex-5, and Cbr rex-9). Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. Symbols of the same color specify data compared using the Student’s t-test. If more than two motif combinations are compared, the schematic to the right of the p-value indicates the motif combination to which the other combinations were compared. (C) DNA sequences of wild-type and mutant motifs (scr). Both MEX II motifs are critical for DCC binding at rex-3. Mutating each motif independently causes an equivalent reduction in DCC binding, and mutating both motifs is necessary to eliminate DCC binding. ChIP-qPCR analysis of SDC-2 binding at intervals across the entire peak is presented in Figure 10—figure supplement 1.
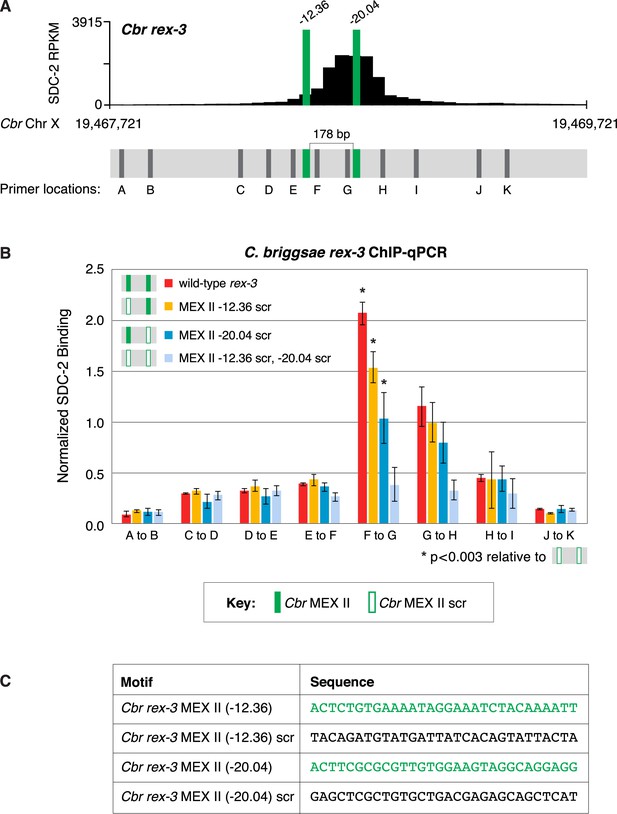
Both MEX II motifs are critical for dosage compensation complex (DCC) binding to Cbr rex-3 in vivo.
This figure extends the analysis of SDC-2 binding at rex-3 in wild-type and rex-3 mutant strains in Figure 10 by including SDC-2 ChIP-qPCR analysis at intervals extending all along the SDC-2 entire peak. (A) The schematic of motifs in rex-3 includes the locations of primers (gray) used for the PCR analysis presented in the graph (B) below it. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. The asterisks highlight the SDC-2 binding values that are significantly different in the F-G interval of the rex-3 site that is mutant for both MEX II motifs versus wild-type rex-3 or rex-3 with one scrambled MEX II motif. Statistics were determined using the Student’s t-test. All other aspects of the figure resemble those explained in the legend to Figure 10. (C) Sequences of wild-type rex-3 motifs and their scrambled versions are shown.
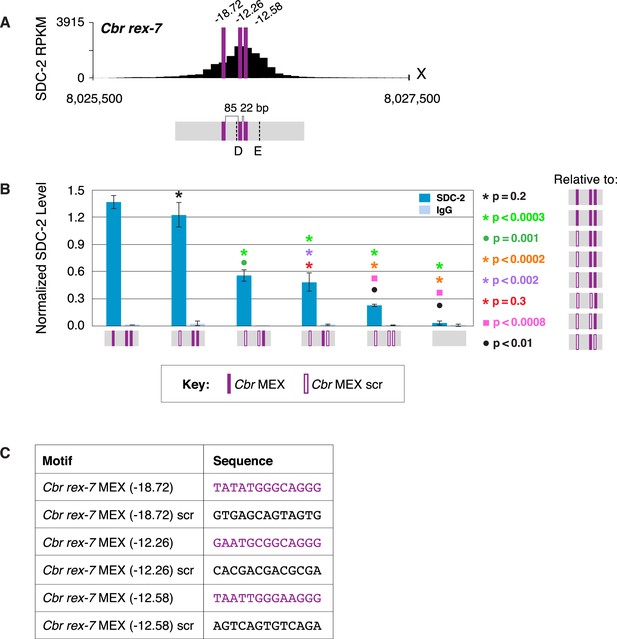
Multiple MEX motifs in Cbr rex-7 contribute to dosage compensation complex (DCC) binding in vivo.
(A) Shown is an enlargement of SDC-2 ChIP-seq profile for Cbr rex-7 with its associated MEX motifs (purple) and their ln(P) scores. Motifs are separated by 85 bp and 22 bp. Locations of primers (D and E, dashed lines) to evaluate DCC binding in vivo using ChIP-qPCR are shown. (B) The graph shows ChIP qPCR levels for SDC-2 (dark blue) and control IgG (light blue) at endogenous wild-type rex-7, at endogenous rex-7 with different combinations of motif mutations created by genome editing, and at a negative control site on X that lacks DCC binding. Strains carrying wild-type and mutant motifs encoded FLAG-tagged SDC-2. SDC-2 levels for each replicate were normalized to the average level of five endogenous non-edited rex sites (Cbr rex-1, Cbr rex-2, Cbr rex-5, and Cbr rex-9). Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. Symbols of the same color specify data compared using the Student’s t-test. If more than two motif combinations are compared, the schematic to the right of the p-value indicates the motif combination to which the other combinations were compared. (C) Sequences of wild-type and mutant motifs (scr). Multiple MEX motifs contribute to DCC binding at rex-7. Mutating the first MEX motif has an insignificant effect on DCC binding, but mutating the first MEX motif and either of the other two motifs reduces binding equivalently. Mutating all three MEX motifs eliminates DCC binding. ChIP-qPCR analysis of SDC-2 binding at intervals across the entire peak is presented in Figure 11—figure supplement 1.
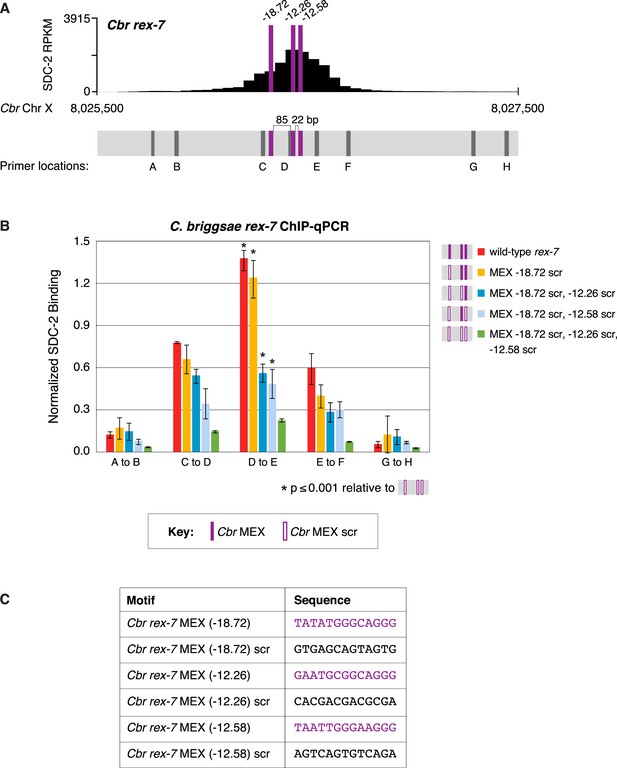
Multiple MEX motifs in Cbr rex-7 contribute to dosage compensation complex (DCC) binding in vivo.
This figure extends the analysis of SDC-2 binding at rex-7 in wild-type and rex-7 mutant strains in Figure 11 by including SDC-2 ChIP-qPCR analysis at intervals extending all along the SDC-2 entire peak. (A) The schematic of motifs in rex-7 includes the locations of primers (gray) used for the PCR analysis presented in the graph (B) below it. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. The asterisks highlight the SDC-2 binding values that are significantly different in the D-E interval of the rex-7 site that is mutant for all three MEX motifs versus wild-type rex-7 or rex-7 with different combinations of scrambled MEX motifs. Statistics were determined using the Student’s t-test. All other aspects of the figure resemble those explained in the legend to Figure 11. (C) Sequences of wild-type rex-7 motifs and their scrambled versions are shown.
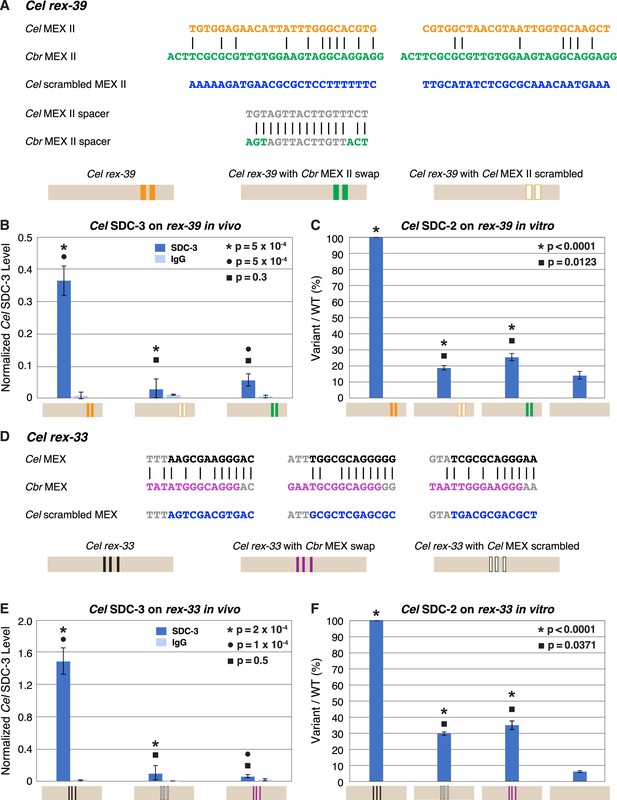
Functional divergence of X motifs demonstrated by C. elegans dosage compensation complex (DCC) binding studies in vivo and in vitro to Cel rex sites engineered to replace Cel motifs with Cbr MEX and MEX II motifs.
(A) Comparison of DNA sequences for the two MEX II motifs in wild-type Cel rex-39 (Cel ln[P] of –21.23 and –20.74) with the Cbr MEX II motifs (Cbr ln[P] of –20.04 and Cel ln[P] > –9 for both) that replaced them. DNA sequences of the spacer region between wild-type Cel MEX II motifs and inserted Cbr MEX II motifs are shown, as are sequences of the scrambled Cel MEX II motifs used as negative controls. Schematics show keys for rex sites analyzed for Cel SDC-3 binding in vivo and Cel SDC-2 binding in vitro: wild-type Cel rex-39 (orange, MEX II motifs), Cel rex-39 with Cbr MEX II motifs (green), Cel rex-39 with scrambled Cel MEX II motifs (orange outline). (B) Graph shows ChIP qPCR levels for Cel SDC-3 (dark blue) and control IgG (light blue) at wild-type Cel rex-39 and mutant rex-39 with Cbr MEX II motifs in vivo. Cel SDC-3 binds in vivo to endogenous Cel rex-39 sites with wild-type MEX II motifs but not to mutant Cel rex-39 sites with either scrambled Cel MEX II motifs or Cbr MEX II motif replacements. SDC-3 levels for each replicate were normalized to the average SDC-3 level at 7 control rex sites (Cel rex-8, Cel rex-14, Cel rex-16, Cel rex-32, Cel rex-35, Cel rex-36, and Cel rex-48). Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. Statistical comparisons were calculated using the Student’s t-test. (C) Graph of in vitro assay assessing Cel SDC-2 binding to a wild-type Cel rex-39 DNA template and a mutant rex-39 template with Cbr MEX II motifs. Cel SDC-2 binds to the Cel rex-39 template with wild-type MEX II motifs but not to mutant rex-39 templates with either scrambled Cel MEX II motifs or Cbr MEX II motif replacements. Cel SDC-2 does not bind to the control template (beige) made of DNA from a site on the Cel X that lacks SDC-2 binding in vivo. SDC-2 levels detected for the mutant variants of rex-39 templates are shown as the percentage (%) of SDC-2 binding to the wild-type rex-39 template. The plot represents the average of three independent experiments, with error bars indicating SD. Statistical comparisons were calculated using the Student’s t-test. (D) Comparison of DNA sequences for the three MEX motifs in wild-type Cel rex-33 and the Cbr MEX motifs that replaced them. Also shown are sequences for the scrambled Cel MEX motifs used as negative controls. Schematics show keys for rex sites analyzed for Cel SDC-3 binding in vivo and Cel SDC-2 binding in vitro: wild-type Cel rex-33 (black, MEX motifs), Cel rex-33 with Cbr MEX motifs (purple), Cel rex-39 with scrambled Cel MEX motifs (black outline). (E) Graph shows ChIP qPCR levels for Cel SDC-3 (dark blue) and control IgG (light blue) at wild-type Cel rex-33 and mutant rex-33 with Cbr MEX motifs in vivo. Cel SDC-3 binds to endogenous Cel rex-33 sites with wild-type MEX motifs but not to mutant Cel rex-33 sites with either scrambled Cel MEX motifs or Cbr MEX motif replacements. Details of the experiment and graph are the same as in (B). (F) Graph of in vitro assay assessing Cel SDC-2 binding to a wild-type Cel rex-33 DNA template and a mutant rex-33 template with Cbr MEX motifs. Cel SDC-2 binds to the Cel rex-33 template with wild-type MEX motifs but not to mutant Cel rex-33 templates with either scrambled Cel MEX motifs or Cbr MEX motif replacements. Cel SDC-2 does not bind to the control template (beige). SDC-2 levels detected for the mutant variant rex-33 templates are shown as the percentage (%) of SDC-2 binding to the wild-type rex-33 template. The plot represents the average of three independent experiments, with error bars indicating SD. Statistical comparisons were calculated using the Student’s t-test.
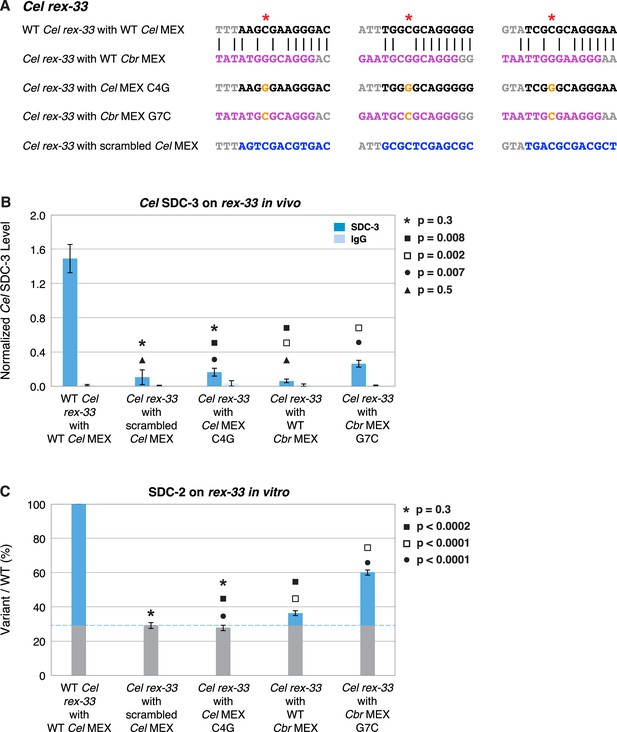
A nucleotide position in the consensus Cbr MEX motif can act as a critical determinant for whether Cel dosage compensation complex (DCC) binds in vivo and in vitro.
(A) Shown are DNA sequences of three wild-type or mutant Cel or Cbr MEX motifs within Cel rex-33 assayed for Cel SDC-3 binding in vivo (B) and Cel SDC-2 binding in vitro (C). The ln(P) scores for the wild-type Cel MEX motifs in rex-33 are −13.13, –15.33, and –15.35. The Cel ln(P) scores for the 3 substituted Cbr MEX motifs are all greater than –9. The three Cbr ln[P] scores for those substituted Cbr MEX motifs are −18.72, –12.26, and −12.58. The Cel ln(P) scores for the 3 Cel MEX motifs with the C4G change are −9.58, –11.20, and –11.26. The Cel ln(P) scores for the three Cbr MEX motifs with the G7C change are −12.20, –11.16, and –10.84. The Cel ln(P) scores for the Cel rex-33 scrambled MEX motifs are all greater than –9. (B) Graph shows normalized ChIP qPCR levels for Cel SDC-3 (dark blue) and control IgG (light blue) in vivo at endogenous Cel rex-33 with wild-type or mutant Cel MEX motifs and wild-type or mutant Cbr MEX motifs. Replacing the critical cytosine (red asterisk) in each of the three MEX motifs of endogenous Cel rex-33 with a guanine (C4G) eliminates Cel SDC-3 binding, as does scrambling the three Cel MEX motifs. Substituting three Cbr MEX motifs for Cel MEX motifs also severely reduces Cel DCC binding. Each Cbr MEX motif has a guanine instead of a cytosine in the critical location. Replacing the guanine with a cytosine (G7C) in each of the Cbr MEX motifs increased Cel SDC-3 binding 4.2-fold, resulting in a Cel SDC-3 binding level representing 18% of that at wild-type rex-33. SDC-3 levels for each replicate were normalized to the average SDC-3 level at seven control rex sites (Cel rex-8, Cel rex-14, Cel rex-16, Cel rex-32, Cel rex-35, Cel rex-36, and Cel rex-48). Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. Statistical comparisons were calculated using the Student’s t-test. (C) Graph of the in vitro Cel SDC-2 binding assay shows that replacing the critical cytosine (red asterisk) in each of the three MEX motifs of Cel rex-33 with a guanine (C4G) eliminates Cel SDC-2 binding, as does scrambling the three MEX motifs. Substituting three Cbr MEX motifs for Cel MEX motifs severely reduces Cel DCC binding. Each Cbr MEX motif has a guanine instead of a cytosine in the critical location. Replacing the guanine with a cytosine (G7C) in each of the Cbr MEX motifs increases specific Cel SDC-2 binding 4.3-fold and restores it to 44% of that at the wild-type rex-33 DNA template. SDC-2 levels detected for the mutant variants of rex-33 templates are shown as the percentage (%) of SDC-2 binding to the wild-type rex-33 template. The plot represents the average of three independent experiments, with error bars indicating SD. Statistical comparisons were calculated using the Student’s t-test.
Tables
MALDI-TOF identification of Cbr MIX-1 peptides.
| m/z Submitted | MH+ Matched | Delta ppm | Peptide | MissedCleavage | Database Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 916.47 | 916.46 | 9.5 | 674–680 | 0 | (K)YHENVVR(L) |
| 1163.59 | 1163.58 | 3.3 | 375–384 | 1 | (K)LRGELEGMSR(G) |
| 1214.65 | 1214.66 | –3.6 | 631–641 | 0 | (R)VLIESQCLPGR(R) |
| 1224.63 | 1224.62 | 8.8 | 713–723 | 1 | (R)EVAYTDGVKSR(T) |
| 1263.74 | 1263.74 | –0.87 | 524–534 | 0 | (R)DVEGLVLHLIR(L) |
| 1285.69 | 1285.69 | –2.8 | 631–641 | 0 | (R)VLIESQCLPGR(R) |
| 1350.69 | 1350.70 | –8.9 | 656–666 | 0 | (R)YTIINDQSLQR(A) |
| 1881.97 | 1881.98 | –2.3 | 134–150 | 0 | (R)GVGLNVNNPHFLIMQGR(I) |
| 1886.89 | 1886.91 | –6.8 | 86–101 | 0 | (K)QSPFGMDHLDELVVQR(H) |
| 2064.01 | 2064.00 | 3.4 | 460–477 | 0 | (K)ITQQVQSLGYNADEDVQR(R) |
| 2377.18 | 2377.16 | 5.6 | 385–415 | 1 | (R)GTVTNDKGEHVSLETYIQETR(A) |
-
This table lists the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of measured peptides, the predicted masses (MH+ Matched), and the deviation from predicted masses (Delta ppm). The ID of each measured peptide is described by the residue range within full-length MIX-1 (Peptide) and its corresponding amino acid sequence (Database Sequence). The number of uncut tryptic peptide bonds is listed for each peptide (Missed Cleavage).
-
In addition to MIX-1, MALDI-TOF analysis of excised protein bands in the molecular weight range of condensin subunits excised from an SDS-PAGE gel revealed peptides corresponding to four common high-molecular weight contaminants: the three vitellogenin yolk proteins VIT-2, VIT-4, VIT-5, and CBG14234, an ortholog of VIT-4. No protein bands corresponding to the molecular weights of SDC-2 or SDC-3 were visible on the SDS-PAGE gel.
Results of DCC recruitment assays in vivo.
(A) Cbr rex DNA fragments assayed in C. briggsae and (B) Identical Cel rex DNA fragments assayed in C. elegans and in C. briggsae.
| (A) C. briggsae DCC binds C. briggsae DCC recruitment sites. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cbr rex Site | Cbr Chr X Peak Position | Cbr SDC-2 RPKM | Cbr Array Assay in vivo % Recruitment (No. of Nuclei) | ||
| rex-1 | 10,780,533 | 2890 | 92% | (59) | |
| rex-2 | 12,642,866 | 999 | 90% | (101) | |
| rex-3 | 19,468,721 | 3219 | 88% | (74) | |
| rex-4 | 6,358,591 | 3915 | 85% | (68) | |
| rex-5 | 3,153,011 | 3562 | 98% | (45) | |
| rex-6 | 18,811,390 | 2203 | 74% | (68) | |
| rex-7 | 8,026,460 | 2964 | 97% | (65) | |
| rex-8 | 16,578,214 | 3217 | 37% | (52) | |
| rex-9 | 3,135,562 | 1029 | 85% | (62) | |
| rex-10 | 895,450 | 3605 | 80% | (55) | |
| rex-11 | 4,563,250 | 830 | 89% | (54) | |
| rex-12 | 19,564,937 | 1786 | 79% | (77) | |
| flat 2 | 11,762,995 | 2890 | 6% | (48) | |
| flat 3 | 20,918,257 | 999 | 0% | (144) | |
| (B) C. briggsae DCC does not bind C. elegans DCC recruitment sites. | |||||
| Cel rex Site | Cel Chr X Peak Position | Cel Array Assay in vivo % Recruitment (No. of Nuclei) | Cbr Array Assay in vivo % Recruitment (No. of Nuclei) | ||
| rex-4 | 11,522,205 | 100% | (16) | 1% | (116) |
| rex-33 | 6,296,501 | 100% | (63) | 0% | (53) |
-
(A) Extrachromosomal arrays composed of DNA fragments (2 kb) that were PCR-amplified from C. briggsae X chromosome regions corresponding to Cbr SDC-2 ChIP-seq peaks were tested for their ability to recruit the Cbr DCC. Gut nuclei from C. briggsae transgenic lines were scored for the presence of the array using a FISH probe against the myo-2::gfp vector and the presence or absence of DCC binding to the array by immunofluorescence signal using Cbr DPY-27 antibodies. The % recruitment is the percentage of total scored array-bearing nuclei that showed DPY-27 bound to the array.
-
(B) Identical DNA fragments encoding individual C. elegans DCC recruitment sites (rex) were injected into C. elegans and C. briggsae to create extrachromosomal arrays containing multiple copies of the rex site. Gut nuclei from C. elegans or C. briggsae transgenic lines were scored for the presence of the array using a FISH probe against the myo-2::gfp vector and for the presence or absence of DCC binding to the array by immunofluorescence signal from the species-matched DPY-27 antibody. The % recruitment is the percentage of total scored array-bearing nuclei that showed DCC binding to the array.
Motifs within rex sites.
The ln(P) values for MEX II motifs are underlined, and the values for MEX motifs are not underlined.
| Cbr rex Site | Chr X Peak Position | SDC-2 RPKM | Cbr MEX motif ln(P) < –12 Cbr MEX II ln(P) < –12 |
|---|---|---|---|
| rex-1 | 10,780,533 | 2890 | –15.57 (13 bp) –15.57 (106 bp) –14.63 (14 bp) –14.47 (93 bp) –27.58 |
| rex-2 | 12,642,866 | 999 | –14.25 (73 bp) –22.69 |
| rex-3 | 19,468,721 | 3219 | –12.36 (178 bp) –20.04 |
| rex-4 | 6,358,591 | 3915 | –19.09 (33 bp) –13.80 |
| rex-5 | 3,153,011 | 3562 | –18.98 |
| rex-6 | 18,811,390 | 2203 | –15.43 (289 bp) –13.35 |
| rex-7 | 8,026,460 | 2964 | –18.72 (85 bp) –12.26 (22 bp) –12.58 |
| rex-8 | 16,578,214 | 3217 | –13.00 (60 bp) –14.31 (69 bp) –13.22 (23 bp) –13.52 |
| rex-9 | 3,135,562 | 1029 | –12.8 |
| rex-10 | 895,450 | 3605 | –12.60 (63 bp) –14.68 |
| rex-11 | 4,563,250 | 830 | |
| rex-12 | 19,564,937 | 1786 |
-
Listed are the rex sites analyzed in this study and their motifs. Motif cutoffs used include MEX with ln(P) < –12 and MEX II with ln(P) < –12. The distances between adjacent motifs (in bp) is listed in parenthesis between motifs. Also listed are the coordinates (in bp) with the maximum SDC-2 ChIP-seq signal in each rex site and the maximum SDC-2 ChIP signal in reads per kilobase per million reads mapped (RPKM) within a 50 bp window. MEX and MEX II are not likely to be the only DNA sequence features within rex sites that contribute to DCC binding, since rex-11 and rex-12 lack these motifs with ln(P) values < –12.
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85413/elife-85413-mdarchecklist1-v2.pdf
-
Supplementary file 1
List of alleles and strains used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85413/elife-85413-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
List of primers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85413/elife-85413-supp2-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Chromosome-specific BACs used to generate FISH probes.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85413/elife-85413-supp3-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
List of target-specific sequences for guide RNAs used in CRISPR / Cas9 genome editing experiments.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85413/elife-85413-supp4-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 5
DNA sequences of repair templates used in CRISPR / Cas9 genome editing experiments.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85413/elife-85413-supp5-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 6
DNA templates used for in vitro DCC binding assays.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85413/elife-85413-supp6-v2.docx





