Evaluating hippocampal replay without a ground truth
Figures
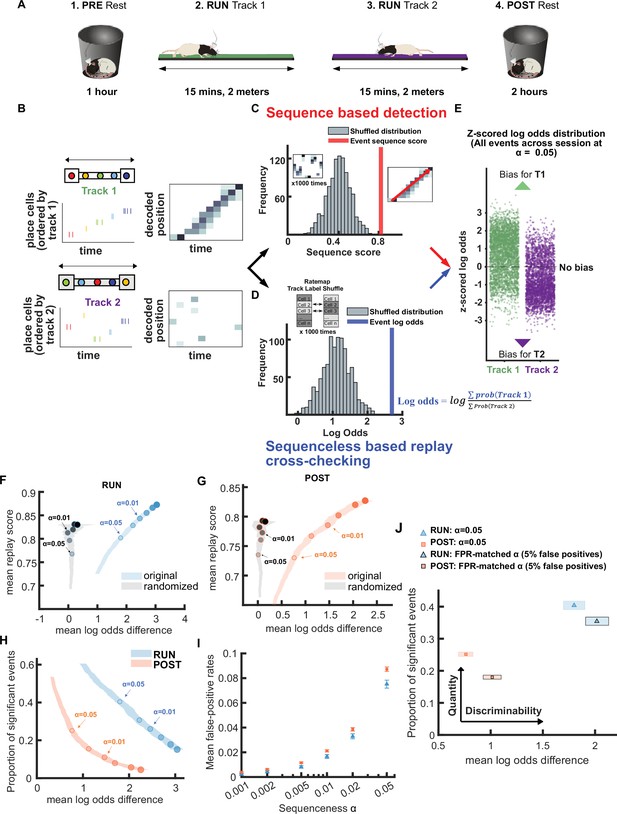
Demonstration of novel replay analysis framework for comparing sequence fidelity with track discriminability.
(A) Experimental design. For each recording session, the animal ran back and forth on two novel linear tracks (RUN) with resting sessions before (PRE) and afterward (POST). Rat schematic in A was adapted with permission from SciDraw.io (Asiminas, 2020b; Asiminas, 2020a). (B–E) Schematic of sequence-based and sequenceless decoding framework. (B) Each candidate replay event spike train was fed into a naïve Bayesian decoder to calculate the decoded posterior probabilities across time and space. (C) Then, for the sequence-based analysis, the sequence score for each candidate event was determined from the weighted correlation of the posterior probability matrix. Significance was determined by comparing the replay score relative to a shuffled distribution (alpha level = 0.05). (D) For sequenceless decoding, a Bayesian decoding similar to sequence-based approach was used, with the exception that only place cells with stable place fields on both tracks were used as template to avoid any track discrimination bias. Then, the logarithmic ratio of the summed posterior probabilities within each replay event for each track is calculated (log odds). The event log odds were z-scored relative to a shuffled distribution where each place cell’s track 1 and 2 place fields were randomly shuffled between tracks. (E) The difference between track 1 and track 2 replay events’ log odds can be used as a metric to cross-check the performance of sequence-based replay detection. (F,G) The relationship between the mean log odds difference and mean replay score for the significant events detected at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) using a weighted correlation replay scoring with two different shuffling procedures (place field circular shuffle and time bin permutation shuffle). The shaded region indicates the 95% bootstrap confidence interval for the mean log odds difference. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represent the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (F) Significant events detected during RUN using original candidate events (blue) and cell-id randomized spurious events (gray). (G) Significant events detected during POST using original candidate events (orange) and cell-id randomized spurious events (gray). (H) The relationship between the mean log odds difference and the proportion of significant events detected at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) during RUN (blue) and POST (orange).The shaded region indicates the 95% bootstrap confidence interval for mean log odds difference. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represent the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (I) The mean proportion of significant cell-id randomized events (mean false-positive rate) at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001). The error bar indicates the 95% bootstrap confidence interval for mean false-positive rates. (J) The replay detection performance at the original alpha level = 0.05 and the FPR-matched alpha level when the mean false-positive rate was 5%. The shaded box indicates a 95% bootstrap confidence interval for both proportion of significant events detected and mean log odds difference. The box with a light outline represents the values at an alpha level = 0.05 and the box with black outline represents the values at the FPR-matched alpha level. (Number of candidate replay events: RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283). The 95% confidence interval for the proportion of significant events, mean log odds difference, mean false-positive rates, and the FPR-matched alpha level for replay events detected during RUN and POST are available in Figure 1—source data 1.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Summary of replay detection performance for weighted correlation method with two shuffles.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85635/elife-85635-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
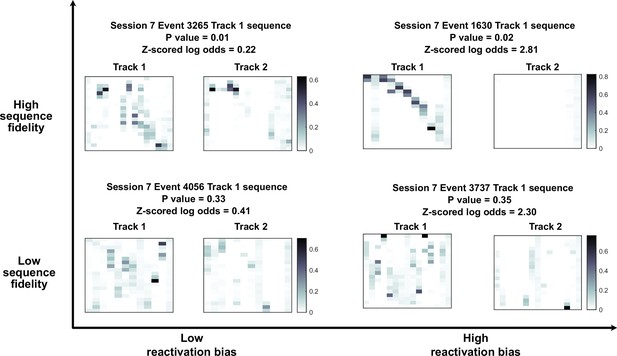
Individual examples of decoded trajectories with different sequence fidelity and reactivation bias.
Each panel is the posterior probabilities of a candidate event decoded against track 1 template (left) or track 2 template (right), with the y axis representing position and the x axis representing time (each pixel corresponds to 20 cm and 20 ms in space and time). The four panels are arranged such that the events on the bottom left have low track 1 reactivation bias and low sequence fidelity and top right have high track 1 reactivation bias and high sequence fidelity.
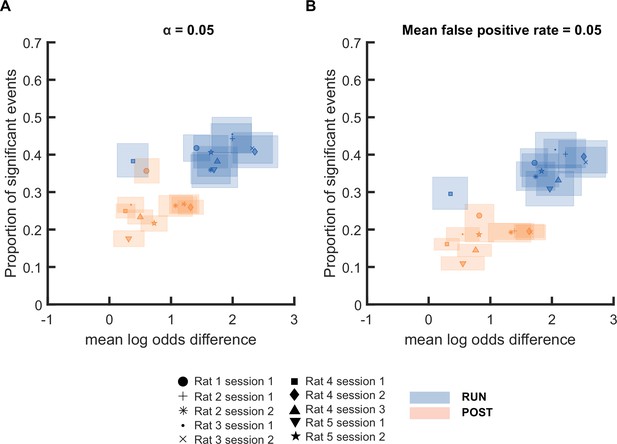
Mean log odds difference and proportion of significant events detected hold across 10 sessions.
(A,B) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at (A) an alpha level of 0.05 and (B) an FPR-matched alpha level with a mean false-positive rate of 5%.
The shaded box indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. Different colors are used to indicate different behavioral states: RUN (blue) and POST (orange). Different symbols are used to indicate different sessions. (Number of candidate replay events for sessions 1-10 : RUN n = 579, 559, 500, 388, 483, 400, 466, 459, 388 and 421 and POST n = 778, 1228, 969, 1770, 1578, 1986, 1793, 1687, 1278 and 1259, respectively)
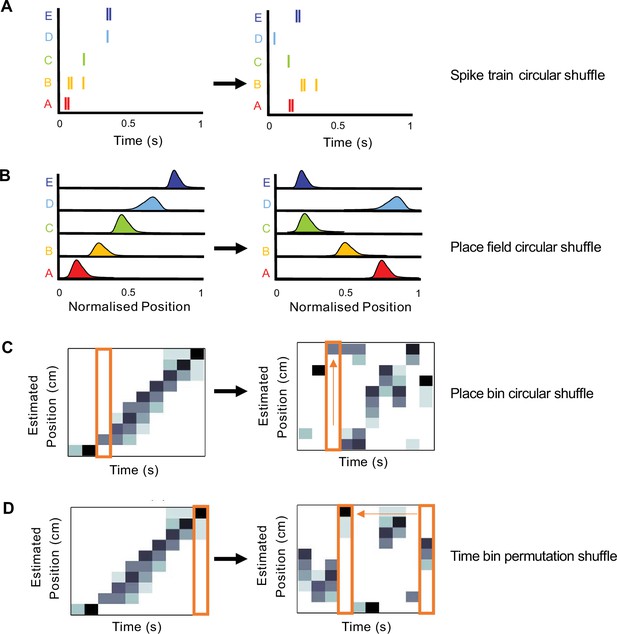
Schematics of shuffling procedures performed to obtain four null distributions for replay detection.
(A) A spike train circular shuffle (dark blue) in which each cell’s spike train was independently circularly shifted in time by a random amount within each replay event. (B) A place field circular shuffle (light blue) in which each cell’s ratemap was circularly shifted in space by a random amount. (C) A place bin circular shuffle (orange) in which the posterior probability distribution for each time bin was independently circularly shifted by a random amount. (D) A time bin permutation shuffle (red) in which the order of the time bin was permuted randomly.
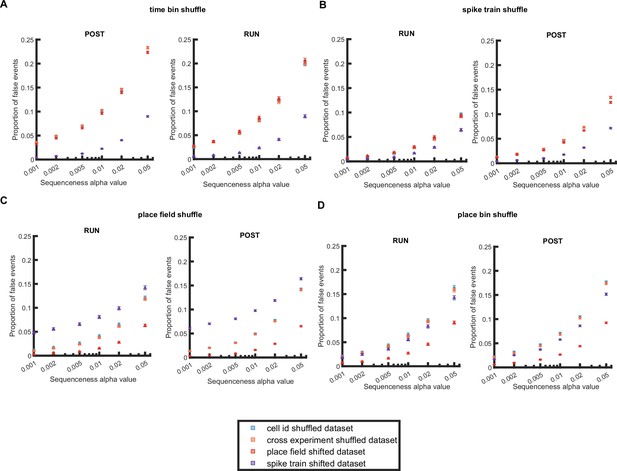
Proportion of false-positive events detected when using different shuffle methods and randomized datasets for a null distribution.
The detection during RUN and POST was based on single shuffle - (A) time bin permutation shuffle, (B) spike train circular shift shuffle, (C) place field circular shift shuffle, and (D) place bin circular shift shuffle. Methods for data randomization included - within experiment cell-id randomization (blue squares), and cross experiment cell-id randomization (orange squares), place field randomization (red squares) and spike train randomization (purple squares).
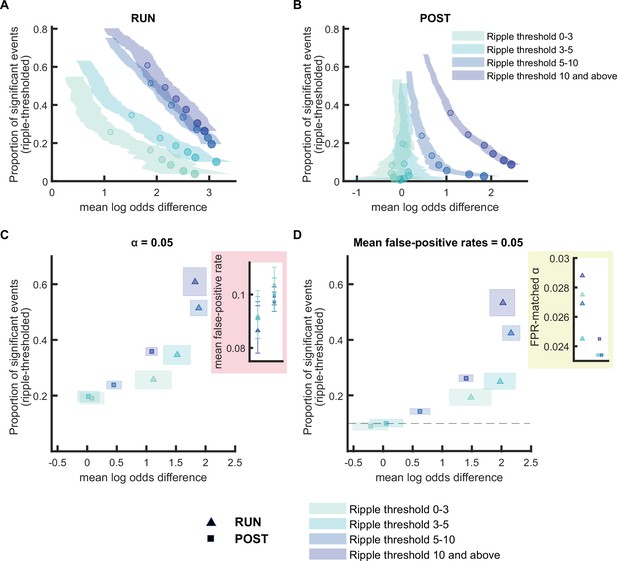
Replay detection performance improves with ripple power.
(A,B) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) as ripple power increases (0–3, 3–5, 5–10, 10, and above). The shaded region indicates the 95% bootstrapped confidence interval for mean log odds difference. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represent the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (A) Replay events detected during RUN. (B) Replay events detected during POST. (C,D) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds differences at (C) an alpha level = 0.05 and (D) an FPR-matched alpha level with a mean false-positive rate of 5%. The shaded box indicates a 95% bootstrap confidence interval for both the proportion of significant events detected and mean log odds difference. The triangle symbol is used to represent replay events during RUN and the square symbol is used to represent replay events during POST. The dashed line represents the approximate chance level at mean false-positive rate of 5%. (Number of candidate replay events for ripple range 0-3, 3-5, 5-10 and 10 and above: RUN n = 782,1091,1982 and 788 and POST n = 1667, 2136, 4904 and 5619, respectively). The 95% confidence interval for the proportion of significant events, mean log odds difference, mean false-positive rates, and the FPR-matched alpha level for replay events with different ripple power range are available in Figure 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Summary of replay detection performance at different ripple power thresholds.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85635/elife-85635-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
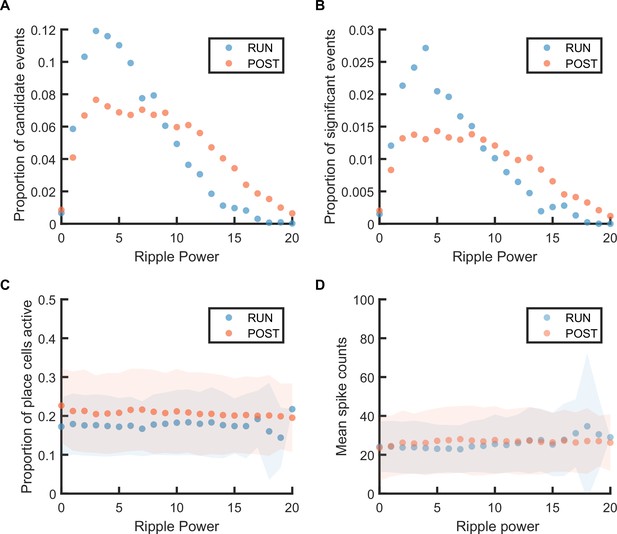
The replay event distribution, number of active place cells, and total spikes during replay event at different ripple powers.
(A) The distribution of candidate replay events across different ripple powers. (B) The proportion of significant events (out of all candidate events) at p-value≤0.05 at different ripple powers. (C) The mean number of active place cells during significant replay events. The shaded region indicated the standard deviation of the number of active place cells at each ripple power range. (D) The mean number of spikes fired by the active place cells during significant replay events. The shaded region indicated the standard deviation of the spike count at each ripple power range.
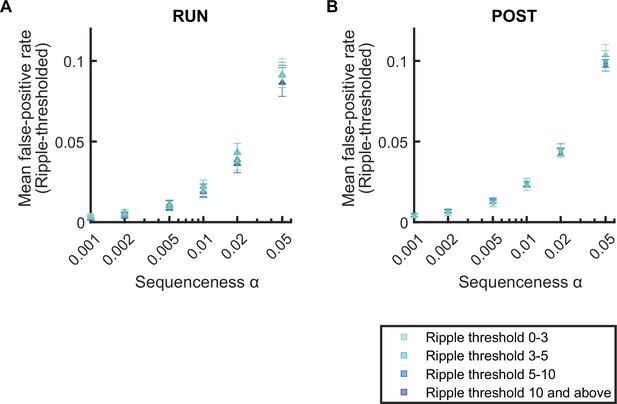
The mean false-positive rate across both tracks for replay events detected with different ripple power range.
(A,B) The mean false-positive rate calculated at different alpha levels (i.e. 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, 0.001) as ripple power increased (i.e. 0–3, 3–5, 5–10,10, and above). The error bar indicated the 95% bootstrap confidence interval. (A) Replay events detected during RUN. (B) Replay events detected during POST.
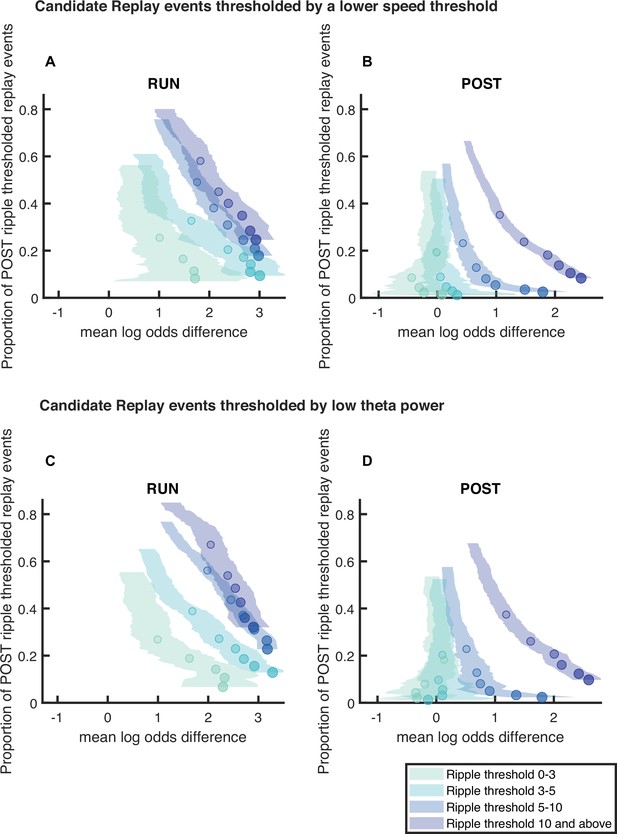
Replay detection performance improves with ripple power using stricter criteria for candidate events.
The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) as ripple power increases (0–3, 3–5, 5–10, 10, and above). (A,B) A stricter replay event criterion for the animal’s speed is used (<1 cm/s). (Number of candidate replay events for ripple range 0-3, 3-5, 5-10 and 10 and above: RUN n = 256, 435, 878 and 421 and POST n = 1214, 1736, 4203 and 4746, respectively) (C,D) An additional replay event criterion (z-score of theta power <0) is used. (Number of candidate replay events for ripple range 0-3, 3-5, 5-10 and 10 and above: RUN n = 389, 666, 1243 and 445 and POST n = 1061, 1287, 2347 and 2335, respectively). The shaded region indicates the 95% bootstrapped confidence interval for mean log odds difference. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represent the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (A,C) Replay events detected during RUN. (B,D) Replay events detected during POST.
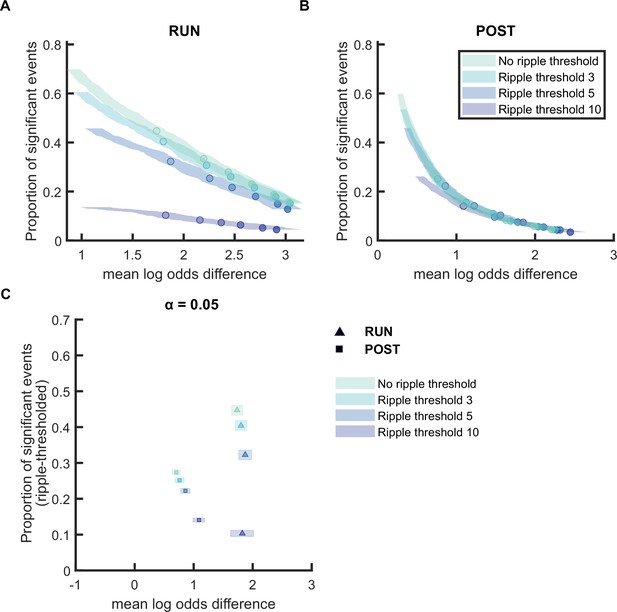
Replay detection performance improves with ripple threshold for POST but not RUN.
(A,B) The proportion of significant events (out of all candidate events based on multi-unit activity [MUA] criteria alone) and mean log odds difference at different alpha level (0.2–0.001) as ripple threshold increases (0, 3, 5, and 10). The shaded region indicates the 95% bootstrapped confidence interval for mean log odds difference. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represent the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (A) Replay events detected during RUN. (B) Replay events detected during POST. (C) The proportion of significant events (out of all candidate events based on MUA criteria alone) and mean log odds differences at the alpha level of 0.05. The shaded box indicates a 95% bootstrap confidence interval for both the proportion of significant events detected and mean log odds difference. The triangle symbol is used to represent replay events during RUN and the square symbol is used to represent replay events during POST. (Number of candidate replay events: RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283).
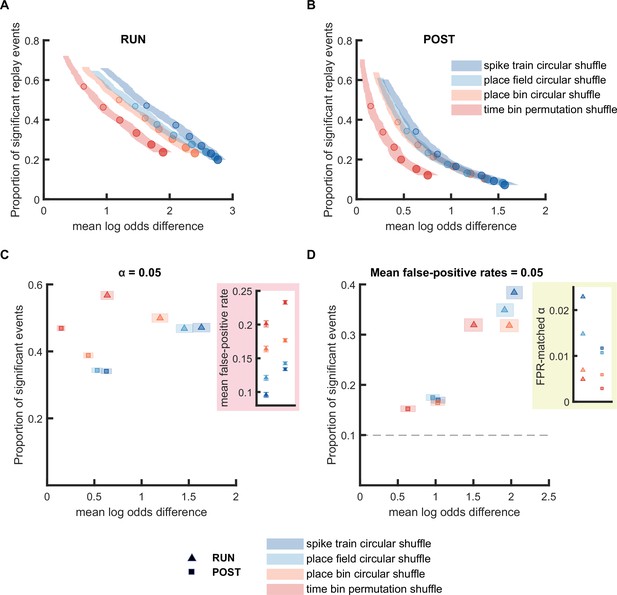
Replay detection performance was sensitive to the shuffling method applied.
(A,B) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) when using four different shuffling methods: (1) spike train circular shuffle (dark blue), (2) place field circular shuffle (light blue), (3) place bin circular shuffle (orange), and (4) time bin permutation shuffle (red). The shaded region indicates the 95% bootstrapped confidence interval for mean log odds difference. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represent the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (A) Replay events detected during RUN. (B) Replay events detected during POST. (C,D) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at (C) an alpha level = 0.05 and (D) an FPR-matched alpha level with a mean false-positive rate of 5%. The shaded box indicates the 95% bootstrap confidence interval for both the proportion of significant events detected and mean log odds difference. The triangle symbol is used to represent replay events during RUN and the square symbol is used to represent replay events during POST. The dashed line represents the approximate chance level at mean false-positive rate of 5%. (Number of candidate replay events: RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283). The 95% confidence interval for the proportion of significant events, mean log odds difference, mean false-positive rates, and the FPR-matched alpha level for replay events detected using different shuffling methods are available in Figure 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Summary of replay detection performance using four different shuflling methods.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85635/elife-85635-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
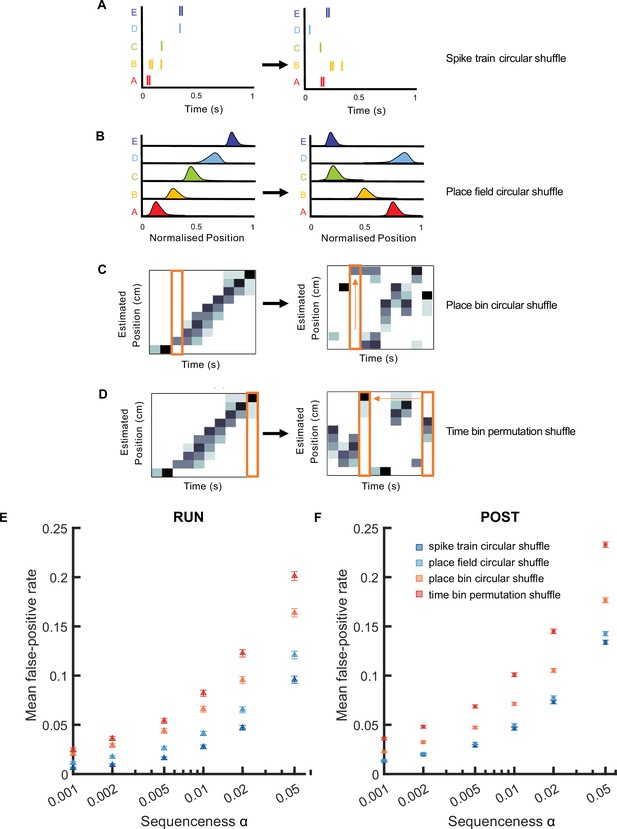
The mean false-positive rate across both tracks for replay events detected using different shuffling methods.
(A) A spike train circular shuffle (dark blue) in which each cell’s spike train was independently circularly shifted in time by a random amount within each replay event. (B) A place field circular shuffle (light blue) in which each cell’s ratemap was circularly shifted in space by a random amount. (C) A place bin circular shuffle (orange) in which the posterior probability distribution for each time bin was independently circularly shifted by a random amount. (D) A time bin permutation shuffle (red) in which the order of the time bin was permuted randomly. (E,F) The mean false-positive rate calculated at different alpha levels (i.e. 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, 0.001) using four shuffles. The error bar indicated the 95% bootstrap confidence interval. (E) Replay events detected during RUN. (F) Replay events detected during POST.
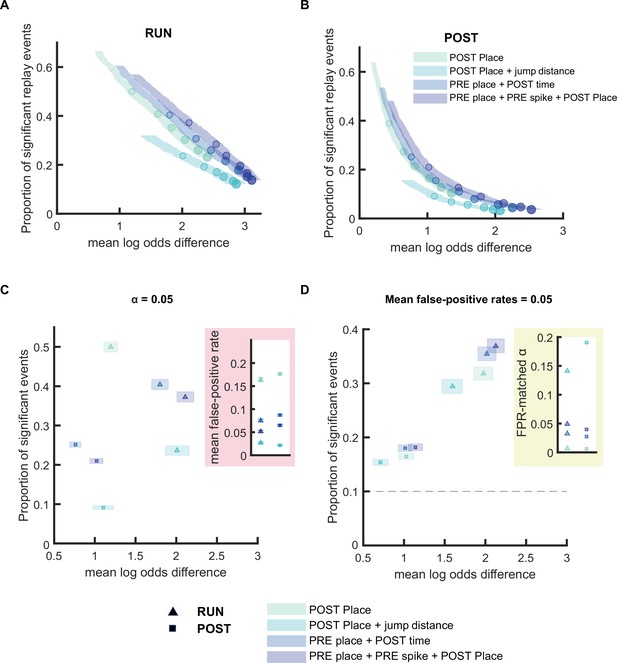
Replay detection performance can be improved by adding stricter detection criteria.
(A,B) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) with four different detection criteria: (1) Only a post-decoding place bin circular shuffle, (2) a post-decoding place bin circular shuffle with jump distance threshold at normalized track length 0.4, (3) a pre-decoding place field circular shuffle and a post-decoding time bin permutation shuffle, (4) a pre-decoding place field circular shuffle, a pre-decoding spike train circular shuffle, and a post-decoding place bin circular shuffle. The shaded region indicates a 95% bootstrap confidence interval for mean log odds difference. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represent the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (A) Replay events detected during RUN. (B) Replay events detected during POST. (C,D) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at (C) an alpha level = 0.05 and (D) an FPR-matched alpha level with a mean false-positive rate of 5%. The shaded box indicates a 95% bootstrap confidence interval for both the proportion of significant events detected and mean log odds difference. The triangle symbol represents replay events during RUN and the square symbol represents replay events during POST. The dashed line represents the approximate chance level at mean false-positive rate of 5%. (Number of candidate replay events: RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283). The 95% confidence interval for the proportion of significant events, mean log odds difference, mean false-positive rates, and the alpha level for replay events detected using different detection criteria are available in Figure 4—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Summary of replay detection performance when adding stricter detection criteria.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85635/elife-85635-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
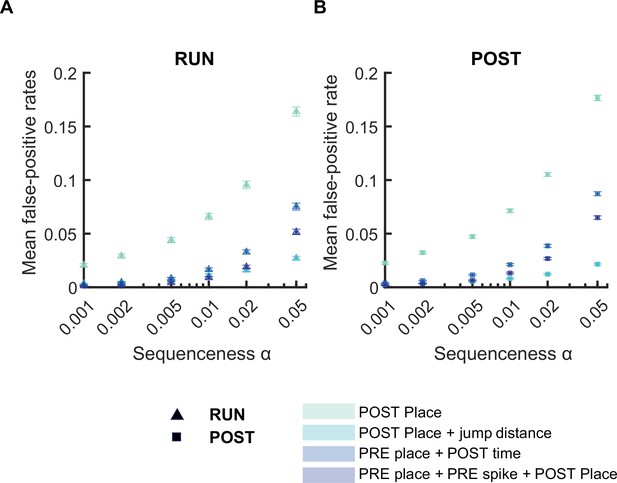
The mean false-positive rate across both tracks for replay events detected using different detection criteria.
(A,B) The mean false-positive rate calculated at different alpha levels (i.e. 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, 0.001) using four different detection criteria: (1) Only a place bin circular shuffle, (2) a place bin circular shuffle with jump distance threshold (40% of the track length), (3) a place field circular shuffle and a time bin permutation shuffle, (4) a place bin circular shuffle, a spike train circular shuffle, and a place bin circular shuffle. The error bar indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. (A) Replay events detected during RUN. (B) Replay events detected during POST.
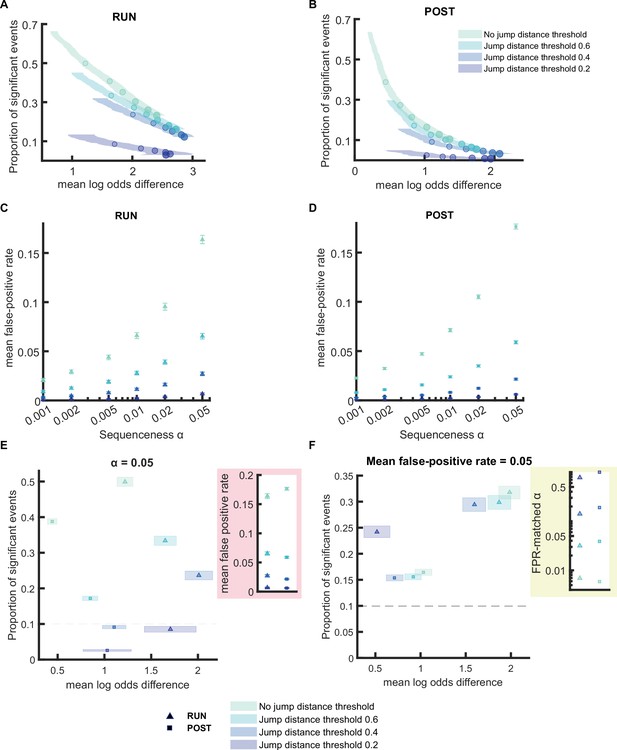
Comparison of the replay detection performance when applying different jump distance thresholds.
(A,B) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) using place bin circular shuffle plus jump distance threshold ranging from 0.2 to 1 (normalized track length). The shaded region indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represented the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (A) Replay events detected during RUN. (B) Replay events detected during POST. (C,D) The mean false-positive rate calculated at different alpha levels (i.e. 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, 0.001) using four different jump distance threshold. The error bar indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. For jump distance, due to the extremely low false-positive even at alpha level = 0.2, we quantified the replay detection performance up until alpha level = 1. (C) Replay events detected during RUN. (D) Replay events detected during POST. (E,F) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at (E) an alpha level = 0.05 and (F) an FPR-matched alpha level with mean false-positive rate of 0.05. The shaded box indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. The triangle symbol was used to represent replay events during RUN and the square symbol was used to represent replay events during POST. The dashed line represented the approximate chance level at mean false-positive rate of 5%. (Number of candidate replay events: RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283). The 95% confidence interval for the proportion of significant events, mean log odds difference, mean false-positive rates, and the FPR-matched p-value across all methods are available in Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85635/elife-85635-fig4-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
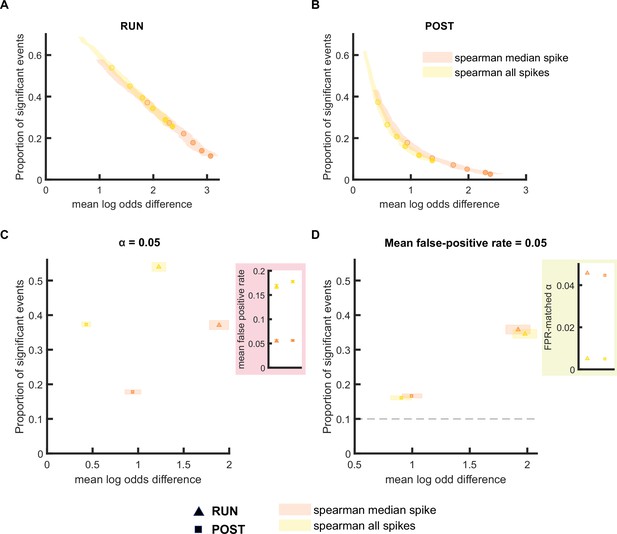
The performance of rank-order-based replay detection method depends on the selection of spikes for analysis.
(A,B) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) when (1) all spikes or (2) only the median spike fired by each place cell was included for rank-order-based replay analysis. The shaded region indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval for mean log odds difference. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represent the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (A) Replay events detected during RUN. (B) Replay events detected during POST. (C,D) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at (C) an alpha level = 0.05 and (D) an FPR-matched alpha level with a mean false-positive rate of 5%. The shaded box indicates a 95% bootstrap confidence interval for both the proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference. The triangle symbol is used to represent replay events during RUN and the square symbol was is to represent replay events during POST. The dashed line represents the approximate chance level at mean false-positive rate of 5%. (Number of candidate replay events: RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283). The 95% confidence interval for the proportion of significant events, mean log odds difference, mean false-positive rates, and the FPR-matched alpha level for rank-order-based methods using all spikes or only median spike within the replay event are available in Figure 5—source data 1.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Summary of replay detection performance for rank-order-based methods.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85635/elife-85635-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
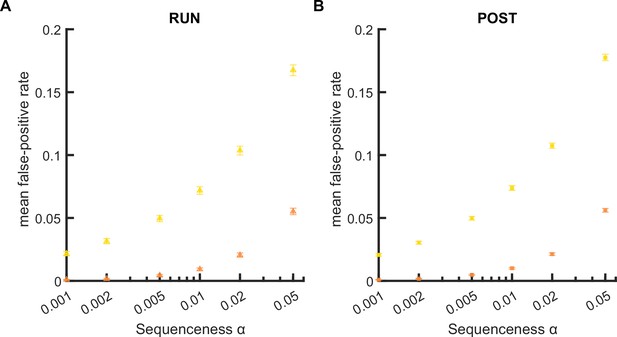
The mean false-positive rate across both tracks when all spikes or median spike fired by each place cell was included for Spearman’s rank-order-based analysis.
(A,B) The mean false-positive rate calculated at different alpha levels (i.e. 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, 0.001) when (1) all spikes or (2) only the median spike fired by each place cell was included for rank-order-based replay analysis. The error bar indicated the 95% bootstrap confidence interval. (A) Replay events detected during RUN. (B) Replay events detected during POST.
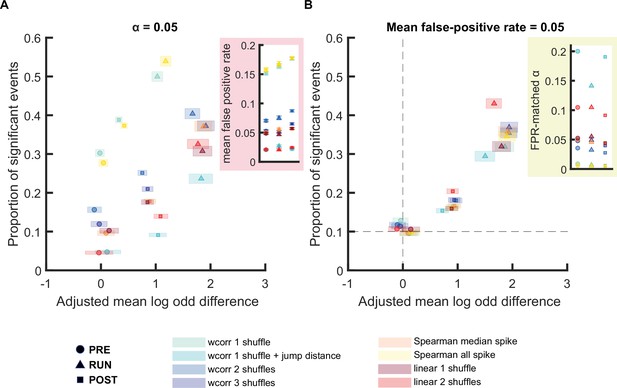
Comparison of different replay detection methods for replay events during PRE, RUN, and POST.
(A,B) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at (A) an alpha level = 0.05 and (B) an FPR-matched alpha level with a mean false-positive rate of 5% using a range of different methods: (1) weighted correlation with place bin circular shuffle, (2) weighted correlation with place bin circular shuffle and jump distance threshold at normalized track length 0.4, (3) weighted correlation with place field circular shuffle and time bin permutation shuffle, (4) weighted correlation with place field circular shuffle, spike train circular shuffle, and time bin permutation, (5) Spearman’s rank-order based correlation using only median spike fired by each place cell, (6) Spearman’s rank-order based correlation using all spikes fired by each place cell, (7) linear fitting with place bin circular shuffle, (8) linear fitting with place field circular shuffle and time bin permutation shuffle. The shaded box indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. The circle symbol was used to represent replay events during PRE. The triangle symbol was used to represent replay events during RUN and the square symbol was used to represent replay events during POST. Inset plots are (A) the mean false-positive rate across shuffling methods and (B) the FPR-matched alpha level across shuffling methods. The dashed line in (B) represented the approximate chance level detection rate and track discriminability at mean false-positive rate of 5%. (Number of candidate replay events: PRE n = 8485, RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283). The 95% confidence interval for the proportion of significant events, mean shuffled-corrected log odds difference, mean false-positive rates, and the FPR-matched p-value across all methods are available in Figure 6—source data 1.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Summary of replay detection performance across multiple detection methods.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85635/elife-85635-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
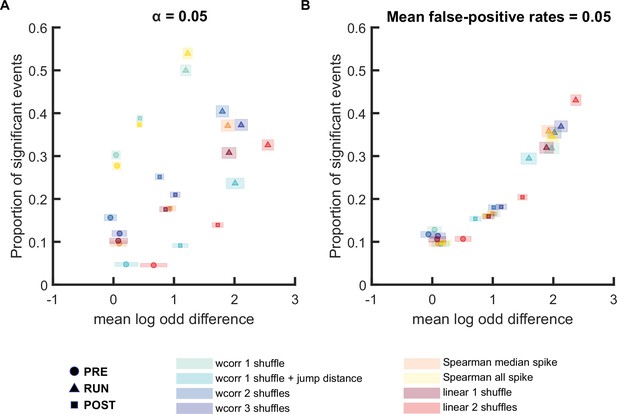
Comparison of different replay detection methods for replay events during PRE, RUN, and POST when log odds difference was not shuffle-subtracted.
(A,B) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at (A) an alpha level = 0.05 and (B) an FPR-matched alpha level with a mean false-positive rate of 5% using a range of different methods: (1) weighted correlation with place bin circular shuffle, (2) weighted correlation with place bin circular shuffle and jump distance threshold at normalized track length 0.4, (3) weighted correlation with place field circular shuffle and time bin permutation shuffle, (4) weighted correlation with place field circular shuffle, spike train circular shuffle, and time bin permutation, (5) Spearman’s rank-order-based correlation using only median spike fired by each place cell, (6) Spearman’s rank-order-based correlation using all spikes fired by each place cell, (7) linear fitting with place bin circular shuffle, (8) linear fitting with place field circular shuffle and time bin permutation shuffle. The shaded box indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. The circle symbol was used to represent replay events during PRE. The triangle symbol was used to represent replay events during RUN and the square symbol was used to represent replay events during POST. (Number of candidate replay events: PRE n = 8485, RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283).
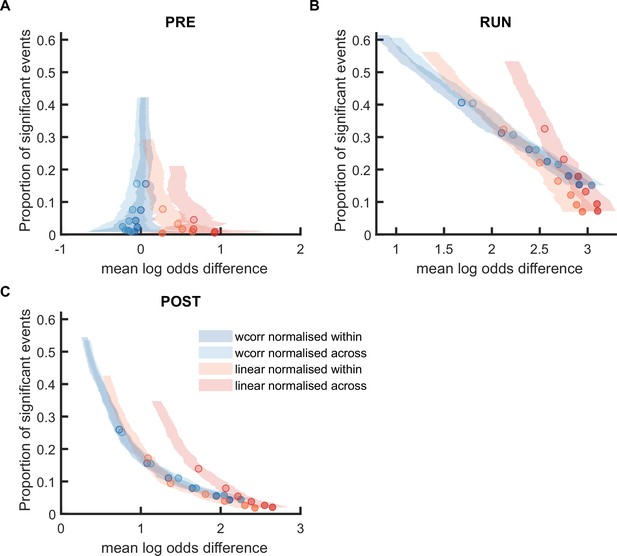
Comparison of mean log odds difference using weighted correlation and linear fitting when the posterior probabilities were normalized within track or cross-track.
(A,B) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) when using weighted correlation and linear fitting where the posterior probabilities were normalized within track or across both tracks. The shaded region indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represented the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (A) Replay events detected during RUN. (B) Replay events detected during POST. (Number of candidate replay events: PRE n = 8485, RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283).
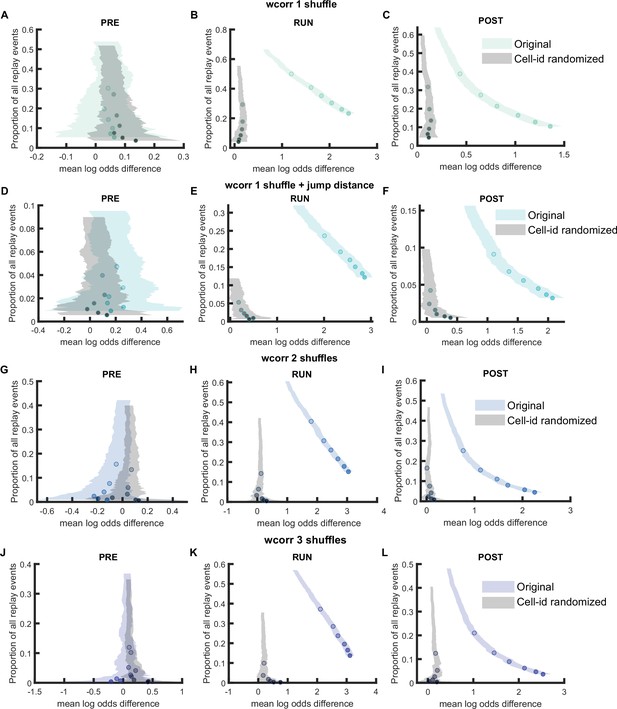
Comparison of replay detection performance using weighted correlation for replay events during PRE, RUN, and POST.
(A–J) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) when using weighted correlation with different detection criteria. (A–C) Only post-decoding place bin circular shuffle. (D–F) Post-decoding place bin circular shuffle with jump distance threshold at normalized track length 0.4. (G–I) Pre-decoding place field circular shuffle and post-decoding time bin permutation shuffle. (J–L) Pre-decoding place field circular shuffle, pre-decoding spike train circular shuffle, and post-decoding time bin permutation. The shaded region indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represented the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (A,D,G,J) Replay events detected during PRE. (B,E,H,L) Replay events detected during RUN. (C,F,I,L) Replay events detected during POST. (Number of candidate replay events: PRE n = 8485, RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283)
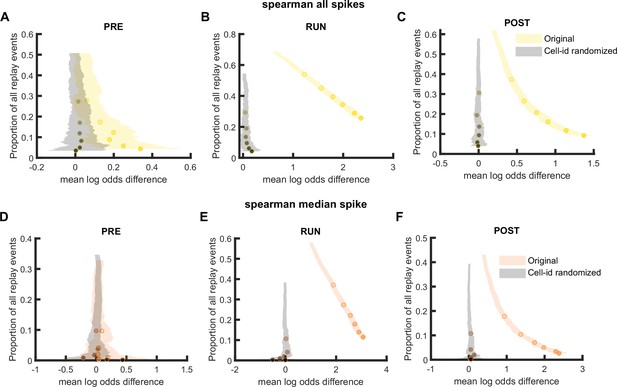
Comparison of replay detection performance using Spearman’s rank-order-based correlation for replay events during PRE, RUN, and POST.
(A–F) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) when (A–C) all spikes or (D–F) only the median spike fired by each place cell was included for rank-order-based replay analysis. The shaded region indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represented the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (A,D) Replay events detected during PRE. (B,E) Replay events detected during RUN. (C,F) Replay events detected during POST. (Number of candidate replay events: PRE n = 8485, RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283).
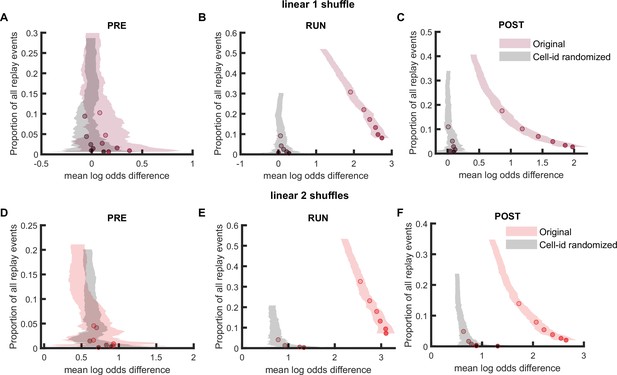
Comparison of replay detection performance using linear fitting for replay events during PRE, RUN, and POST.
(A–F) The proportion of significant events and mean log odds difference at different alpha levels (0.2–0.001) when using linear fitting approach with (A–C) only post-decoding place bin circular shuffle or (D–F) both pre-decoding place field circular shuffle and post-decoding time bin permutation shuffle. The shaded region indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. The six dots with increasing color intensity for each distribution represented the data at an alpha level of 0.05, 0.02, 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.001. (A,D) Replay events detected during PRE. (B,E) Replay events detected during RUN. (C,F) Replay events detected during POST. (Number of candidate replay events: PRE n = 8485, RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283).
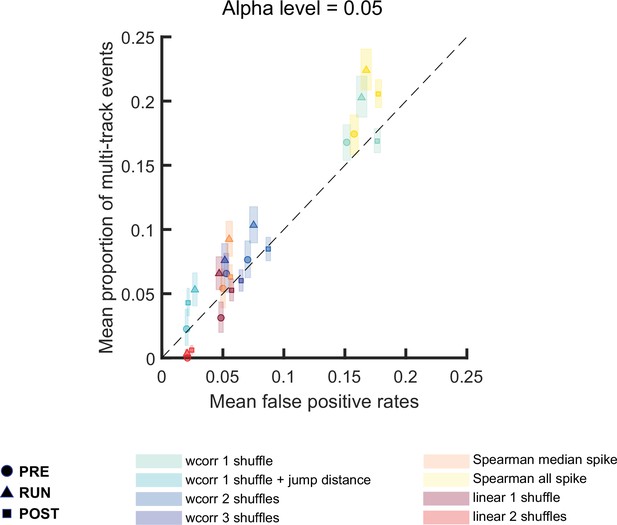
Comparison of the proportion of multi-track events and mean false-positive rate for different replay detection methods, and for replay events during PRE, RUN, and POST.
Multi-track events are replay events that pass all shuffling tests and/or additional replay criteria used for both tracks. At an alpha level = 0.05, shuffling methods tested include: (1) weighted correlation with place bin circular shuffle, (2) weighted correlation with place bin circular shuffle and jump distance threshold at normalized track length 0.4, (3) weighted correlation with place field circular shuffle and time bin permutation shuffle, (4) weighted correlation with place field circular shuffle, spike train circular shuffle, and time bin permutation, (5) Spearman’s rank-order-based correlation using only median spike fired by each place cell, (6) Spearman’s rank-order-based correlation using all spikes fired by each place cell, (7) linear fitting with place bin circular shuffle, (8) linear fitting with place field circular shuffle and time bin permutation shuffle. The shaded box indicated 95% bootstrap confidence interval. The circle symbol was used to represent replay events during PRE. The triangle symbol was used to represent replay events during RUN and the square symbol was used to represent replay events during POST. (Number of candidate replay events: PRE n = 8485, RUN n = 4643 and POST n = 15283)

Distribution of Spearman’s rank order correlation score and p value for false events with random sequence where each neuron fires one (left), two (middle) or three (right) spikes.

Distribution of Spearman’s rank order correlation score and p value for mixture of 20% true events and 80% false events where each neuron fires one (left), two (middle) or three (right) spikes.
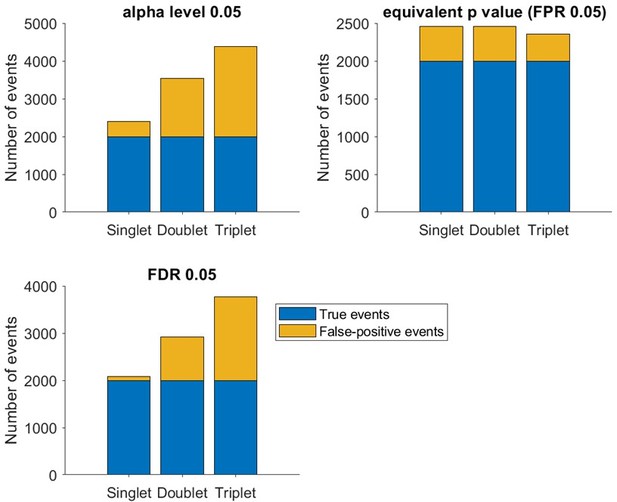
Number of true events (blue) and false events (yellow) detected based on α level 0.
05 (upper left), empirical false positive rate 5% (upper right) and false discovery rate 5% (lower left, based on BH method).
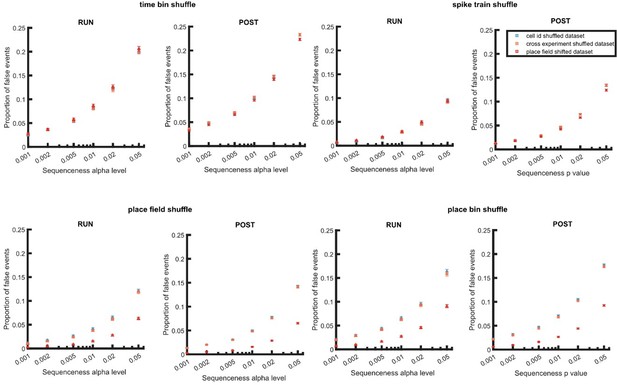
Proportion of false events detected when using dataset with within and cross experiment cell-id randomization and place field randomization.
The detection was based on single shuffle including time bin permutation shuffle, spike train circular shift shuffle, place field circular shift shuffle, and place bin circular shift shuffle.
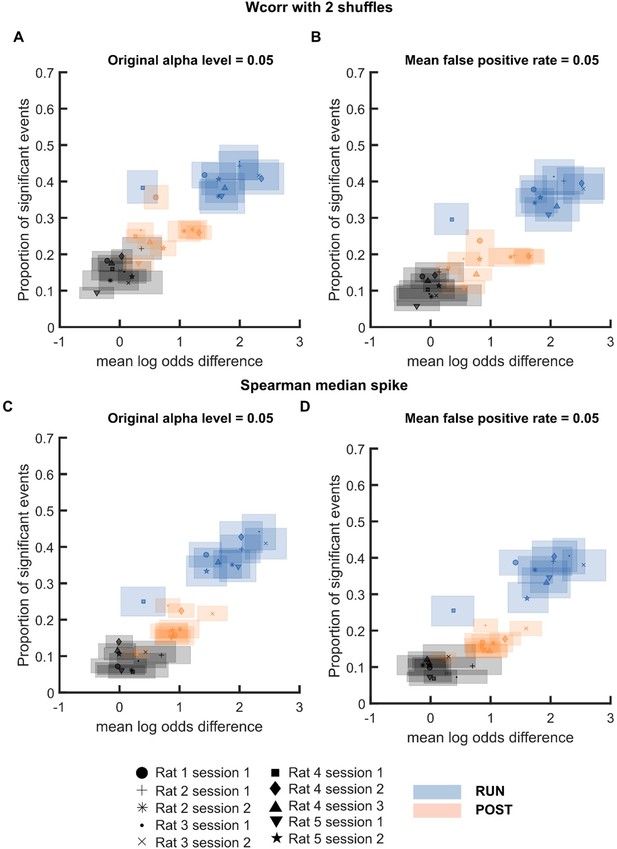
Mean log odds and proportion of significant events at α level 0.
05 or FDR-matched α level for individual sessions when replay events were detected using (A-B) weighted correlation with two shuffles and (C-D) Spearman correlation using only each cell’s median spike. Different color is used to indicate different behavioural states: PRE (black), RUN (blue) and POST (orange). Different symbol is used to indicate different sessions..





