How honey bees make fast and accurate decisions
Figures
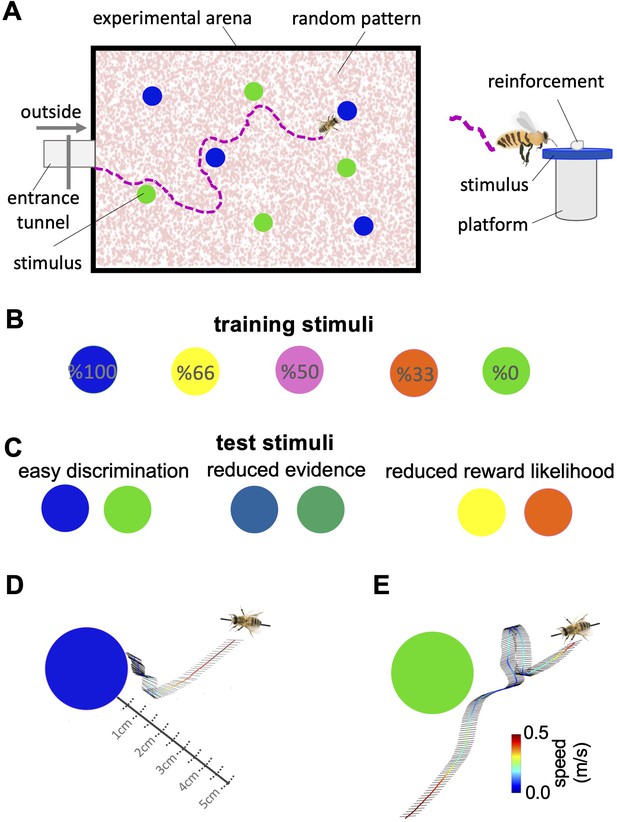
Bees’ behaviour in a colour discrimination task.
(A & B) Each bee was given 18 training trials in which she could choose between two different colours: one rewarded and the other punished. The bee was free to select each colour and return to the hive when satiated marking the end of a trial. Stimuli positions in the arena were changed in each trial in a pseudo-random manner. Stimuli were 2 cm diameter-coloured disks on a small platform (5 cm tall). On the top of each colour was placed either 10 μl reward (50% sucrose) or punishment (quinine) in training, or distilled water in tests. Two different colours, four disks of each colour, were presented in each training trial and test. Five different colours were used in the training. The colours differed in the proportion of training bouts in which they offered reward and punishment (rewarded at 100, 66, 50, 33, and 0% of training trials). Two groups of bees were trained with different likelihoods of reward and punishment from each colour (see Materials and methods section and Figure 1—source data 1). (C) Following training, the bee was given three unreinforced tests where the positive or negative reinforcements were replaced with distilled water. Bees’ responses were analysed from video recordings of the first 120 s in the flight arena. In the easy colour discrimination test, bees were presented with three pairs of the 100% and 0% rewarded colours (blue and green). In the reduced reward likelihood test, bees were examined with 66% and 33% rewarded colours (yellow and orange). In the reduced evidence test. bees were given two colours intermediate between green and blue (D & E) Examples of flight paths showing the inspection activity of a bee during the easy discrimination test in accepting blue (D) and rejecting green (E). Each black line on the flight path corresponds to the bee’s body orientation in a single video frame with 4ms intervals between frames. Line colour: flight speed 0.0–0.5 m/s (See Video 1).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Bees’ choices during the training trials.
Tables show the number of bees’ correct and incorrect choices to the high and low rewarded stimuli during two different sequences of training trials were used (A: Protocol 1; B: Protocol 2). The blue cells indicate the number of reward bees received, whereas the red cells indicate the number of punishment bees received.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86176/elife-86176-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
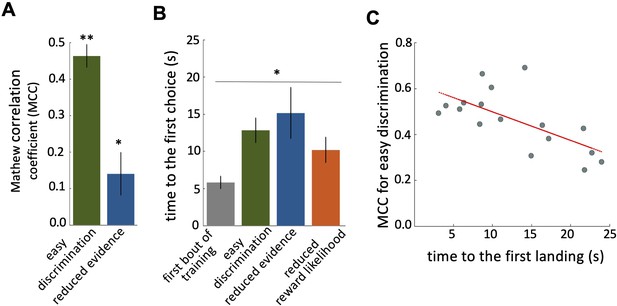
Characteristics of bee decision making.
(A) Matthew correlation coefficients (MCC) (mean ± SEM) for the easy discrimination and reduced evidence tests. In the both easy discrimination and reduced evidence tests, this correlation is computed with respect to choosing the high-rewarded colours for each bee. A positive correlation (max at +1) indicates perfect correct performance while zero indicates chance level performance. Correlation coefficients were significantly greater than zero for both tests. (B) Average time to the first choices for three tests and the first training trial. Bees naive to the stimuli made their first choice faster than bees trained on the stimuli (p=1.55e-3). (C) Scatter plot showing a negative correlation between the MCC and the time to first acceptance in the easy discrimination test. A rapid first choice correlated with higher performance. Values for each individual bee are shown by small circles. n=20, **p<0.005 and *p<0.05.
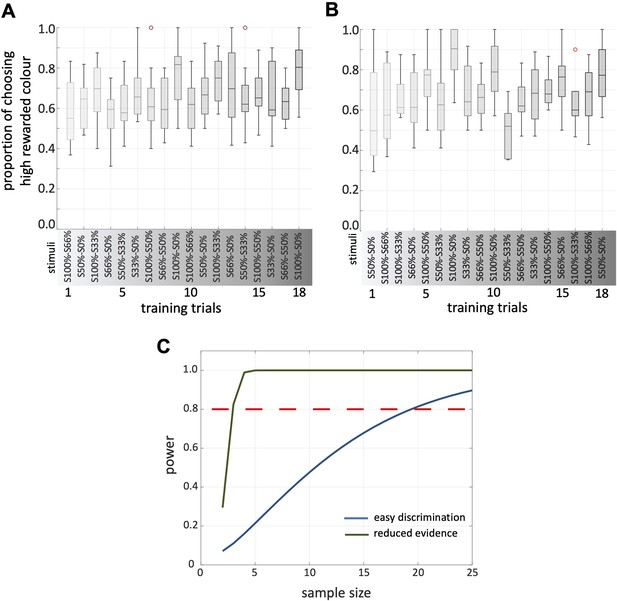
Bees’ performance during the training.
(A, B) Bar graphs show the proportion of bees’ responses to high rewarded stimuli at each training trials (A: bees in Protocol 1; B: bees in Protocol 2). Below exhibit the stimuli presented at each training trails. (C) Results of power analyses for both easy discrimination and reduced evidence tests, assuming the mean and variance in MCC seen in this study (Figure 2A). It indicates that our sample size of 20 bee provided us with a power level that exceeded the commonly accepted threshold of 80%.
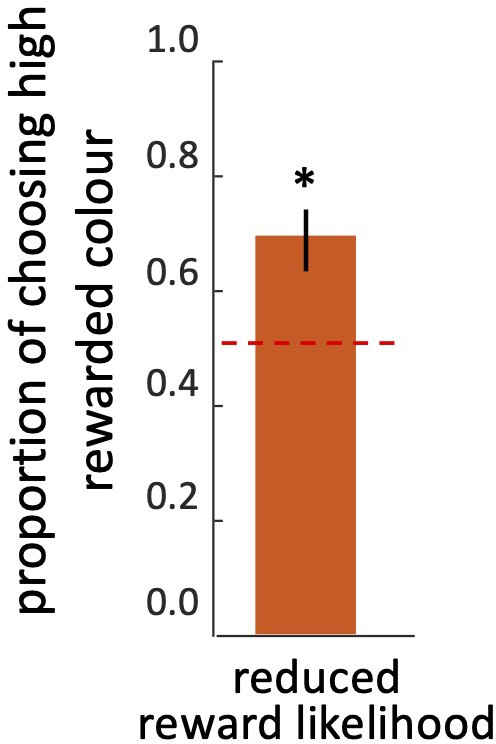
Bees’ performance on the reduced reward likelihood test.
Bar shows mean proportion of choosing high-rewarded colour. Dashed line indicates performance expected at random. n=20.
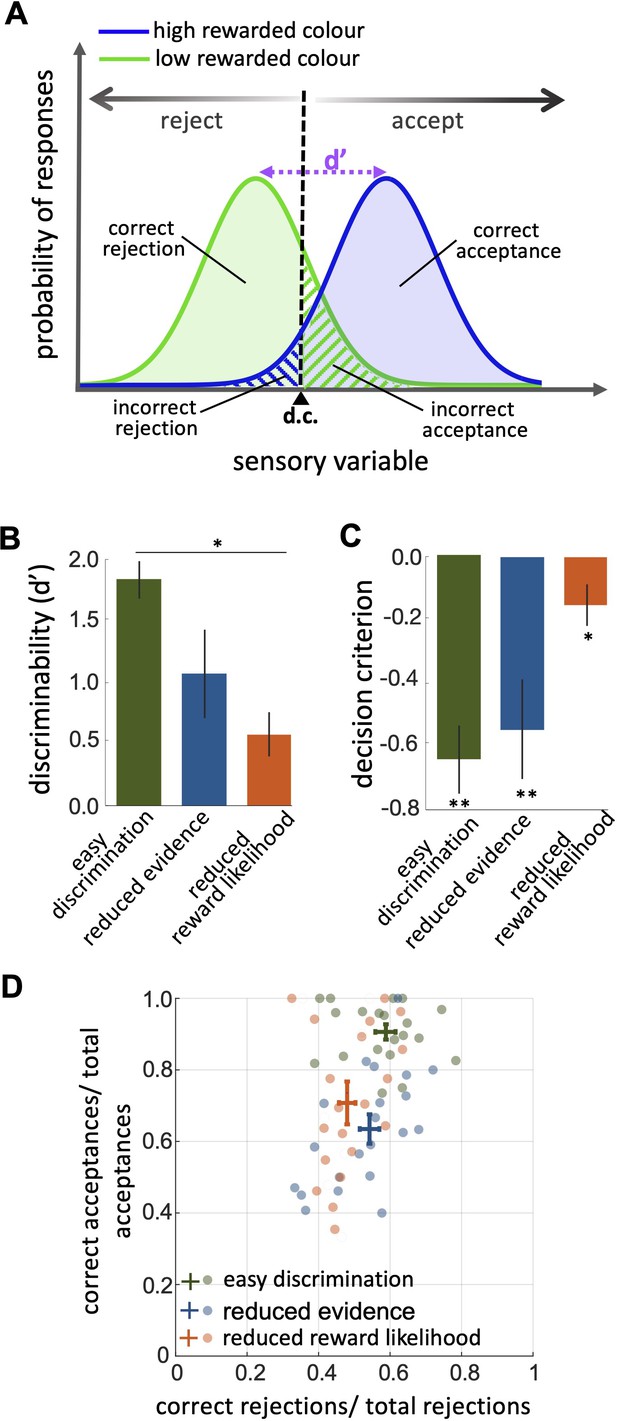
An investigation by classical signal detection theory.
(A) Probability of responding to the high (blue) and low (green) rewarded stimuli at different levels of sensory input. For a trained bee we recognise a threshold (decision criterion, d.c.) at which their behaviour shifts from rejection to acceptance. As a result, we have four types of behavioural responses. d’ is the discriminability of the two stimuli. (B) Discriminability was greatest in the easy discrimination task and was reduced in both reduced evidence and reduced reward likelihood tests. (C) The decision criterion was negative for the easy discrimination and reduced evidence tests indicating fewer incorrect acceptances than incorrect rejections in these tests. The decision criterion was closer to zero in the reduced reward likelihood test indicating similar accuracy of acceptance and rejection in this test. (D) Plotting the ratio of correct to incorrect acceptances and rejections (crosses show the mean and SEM) for the three tests show that generally, bees were more accurate in acceptance than rejection responses. Acceptance accuracy fell in the reduced evidence and reduced reward likelihood tests. n = 20, **p<0.005 and *p<0.05.
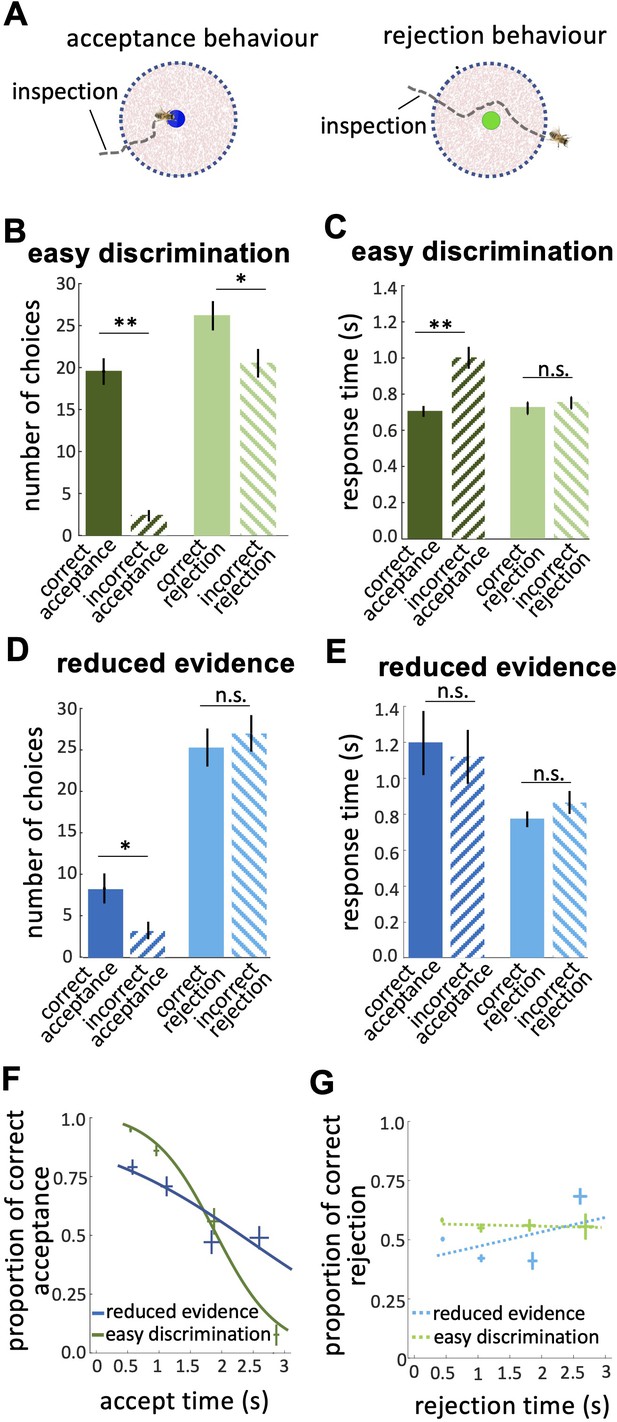
Response times of bee decisions.
(A) Bees inspected the coloured stimuli prior to accepting or rejecting a colour. (B) The number of rejections was higher than the number of acceptances in the easy discrimination test. The difference between the correct and incorrect acceptances was larger than the difference between correct and incorrect rejections. (C) In the easy discrimination test bees accepted correct colours faster than incorrect colours, but there was no difference in the response time for correct and incorrect rejections. (D) In the reduced evidence test there were still more correct acceptances than incorrect acceptances, but the number of correct acceptances decreased. (E) Acceptance times for the correct colour were increased in the reduced evidence test. Bees took longer to accept stimuli with reduced evidence comparing to rejection responses, for both correct or incorrect choices. (F) Conditional Accuracy Function (CAF) plot for acceptance responses in the reduced evidence and easy discrimination tests. Lines show the best fit of piece-wise logistic regressions to the bee’s response time. Acceptance accuracy declined with increasing response time. The vertical and horizontal lines at each cross indicate the standard deviation of the proportion of correct acceptance and accept time, respectively. (G) CAF curve for rejections in both easy discrimination and reduced evidence tests. The accuracy of rejection did not change significantly with response time. The vertical and horizontal lines at each cross indicate the standard deviation of the proportion of correct rejection and rejection time, respectively. n=20, **p<0.005, *p<0.05 and n.s., p>0.05.
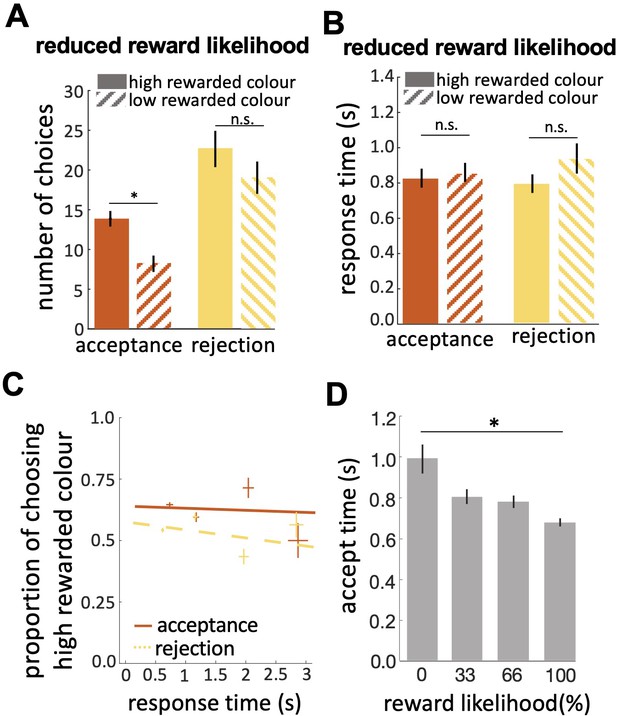
Bees’ performance in the reduced reward likelihood test.
(A) In the reduced reward likelihood test bees made more rejection than acceptance responses. Bees accepted the highly-rewarded colour more than the low-rewarded colour, but there was no difference in rejections of the two colours. (B) Response times did not differ for either colour or response. (C) CAF curves for acceptance and rejection response. The accuracy of acceptance or rejection responses did not change with response time in the reduced reward likelihood test (see Figure 4F&G). (D) Comparing acceptance times in the easy discrimination and reduced evidence tests allowed us to compare acceptance times for stimuli with different likelihoods of reward in training. Bees accepted the stimuli with higher reward likelihood faster. n=20, *p<0.05 and n.s., p>0.05.
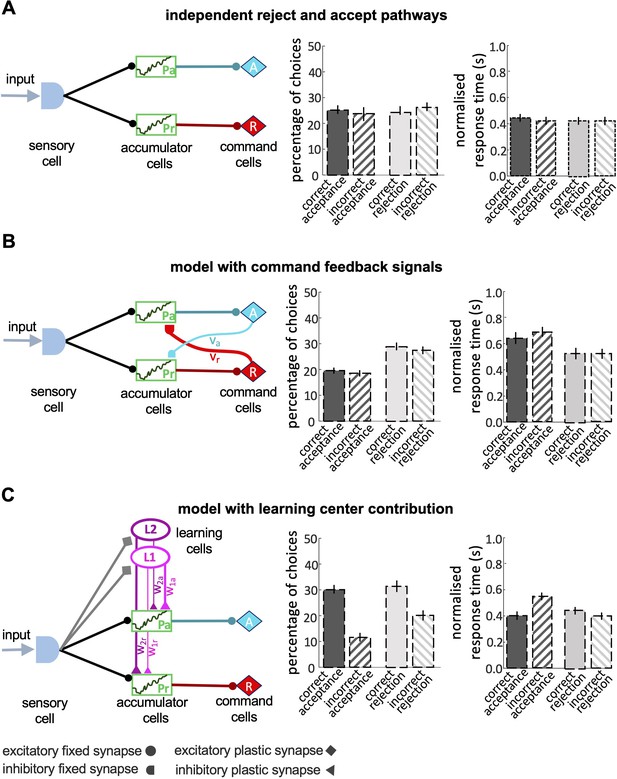
Models of decision-making.
(A) A simple model with independent accumulators and command cells for acceptance and rejection was not able to reproduce the features of bee decisions. Correct and incorrect choices were made at equal frequency. (B) When cross-inhibitory feedback from the command cells was added to the model, the model was still not able to discriminate between the correct and incorrect choices, despite the number of rejections now being higher than acceptances. (C) A model with parallel pathways and learning cells that inhibit the accumulators with different values (i.e. ) had the ability to discriminate between stimuli, but the proportion of accepting correct colours and rejecting the incorrect colours are equal.
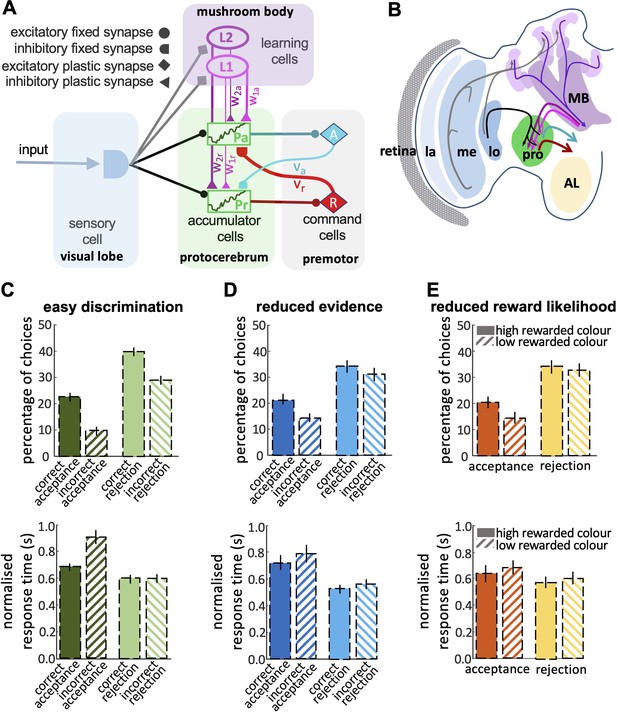
Neurobiologically-plausible model for honey bee foraging choices.
(A) The model shows the connectivity of the components of the minimum circuitry of bee decision-making, including sensory cells, two parallel accumulators, learning cells and motor commands (See Materials and Methods). Synaptic connection classes are represented at the left-hand side. (B) The diagram shows a part of the insect brain involved in the decision-making process. The photoreceptors provide input from the eye to the lamina, which then sends its projections to the medulla. The medulla connects to the protocerebrum and, in parallel, to a third-order visual processing centre, the lobula, which then sends inputs via several tracts into the protocerebrum. In parallel, neurons in the optic lobe region (medulla and lobula) branch in the mushroom body. The anterior portions of the protocerebrum receive outputs from mushroom body output neurons (MBONs), supporting learning and memory. The output from the protocerebrum are premotor neurons. MB: mushroom bodies; AL: antennal lobe; la & me: lamina and medulla neuropils; lo: lobula; pro: protocerebrum. Our model reproduces the bees’ responses to easy discrimination (C), reduced evidence (D), and reduced reward likelihood tests (E). The average percentage of correct choices (acceptance or rejection) made by the model bees within blocks of 25 trials. All non-overlapping SEM error bars are significantly different (p<0.05).
Videos
Sample video of honeybee in the test.
The video was captured from an overhead perspective, providing a clear view of the bees' movements within the flight arena, showcasing their reactions to various stimuli. The black lines depict the orientation of the bee’s body at each frame of the video, offering further observations of their positioning and behaviour during the experiment.
Tables
Two different sequences of training trials were used.
10 bees were trained with the protocol P1 and 10 with the protocol P2.
| Protocol P1 | Protocol P2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #trials | colours at each trial | #trials | colours at each trial |
| 1 | S100% vs S66% | 1 | S50% vs S0% |
| 2 | S50% vs S0% | 2 | S100% vs S66% |
| 3 | S100% vs S33% | 3 | S100% vs S33% |
| 4 | S66% vs S0% | 4 | S66% vs S0% |
| 5 | S50% vs S33% | 5 | S100% vs S50% |
| 6 | S100% vs S50% | 6 | S50% vs S33% |
| 7 | S33% vs S0% | 7 | S100% vs S0% |
| 8 | S66% vs S50% | 8 | S33% vs S0% |
| 9 | S100% vs S0% | 9 | S66% vs S50% |
| 10 | S100% vs S66% | 10 | S100% vs S0% |
| 11 | S50% vs S0% | 11 | S50% vs S33% |
| 12 | S100% vs S33% | 12 | S66% vs S50% |
| 13 | S66% vs S0% | 13 | S33% vs S0% |
| 14 | S50% vs S33% | 14 | S100% vs S50% |
| 15 | S100% vs S50% | 15 | S66% vs S0% |
| 16 | S33% vs S0% | 16 | S100% vs S33% |
| 17 | S66% vs S50% | 17 | S100% vs S66% |
| 18 | S100% vs S0% | 18 | S50% vs S0% |





