Organization, functions, and mechanisms of the BBSome in development, ciliopathies, and beyond
Figures
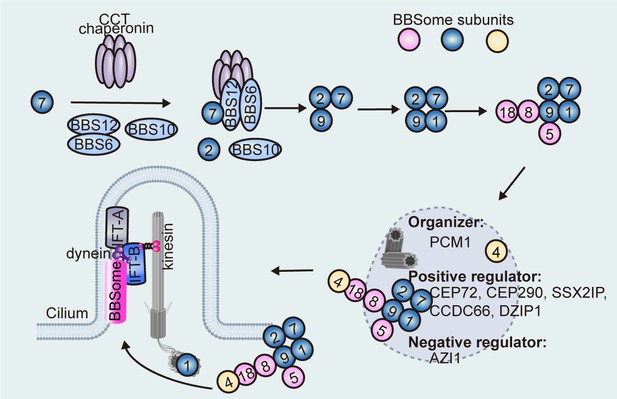
Sequential assembly model of the BBSome.
The CCT chaperonin complex and BBS6/10/12 stabilize BBS7 to form the BBS-chaperonin complex, which recruits BBS2 for BBS7 binding. BBS2 directly interacts with BBS9 and BBS7 to form a ternary core complex before subsequent recruitment of other BBSome subunits. BBS4, which localizes on the centriolar satellites, is presumably the last subunit to be incorporated into the BBSome, whereas the basal body-localized BBS1 facilitates transfer of the BBSome into the cilium. BBSome transfer from centriolar satellites to the basal body (and then to the cilium) is regulated by centriolar satellite proteins (e.g. CEP72, CEP290, SSX2IP, CCDC66, DZIP1, and AZI1).
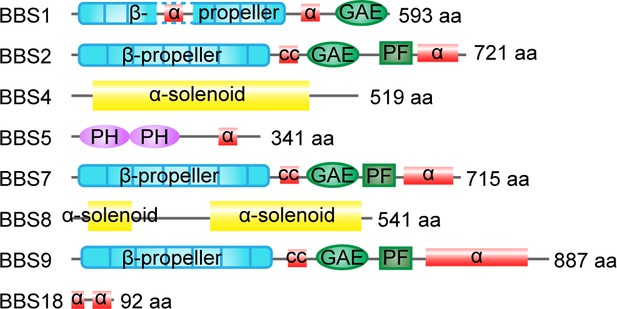
Domain organization of homo BBSome subunits.
The number of residues and the domain structures are indicated. α, alpha helices; GAE, gamma-adaptin ear domain; cc, coiled-coil domain; PF, platform domain; PH, pleckstrin-homology domain.
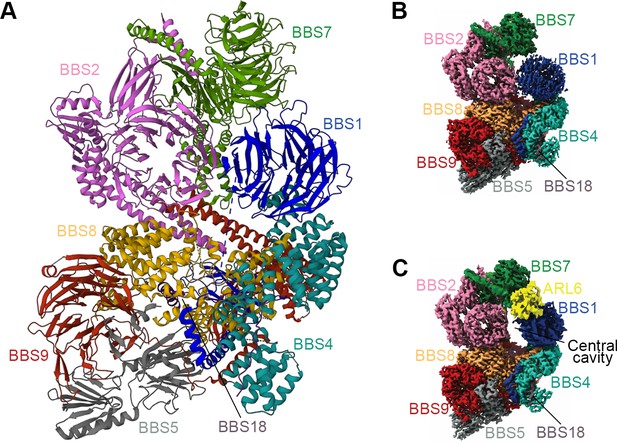
Structure of the mammalian BBSome.
(A) Atomic models of the eight subunits of the bovine BBSome. (B) Cryo-EM structure of the bovine BBSome. (C) Cryo-EM structure of the BBSome:ARL6:GTP complex in the same orientations as the map in panel B. Images are adapted from Singh et al., 2020, where it was published under a CC BY 4.0 license.
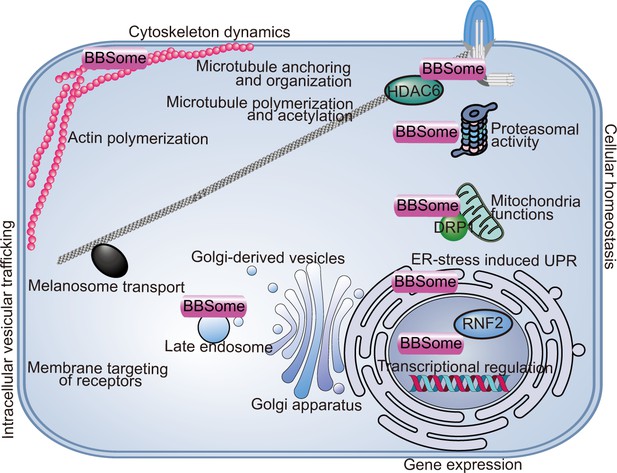
Non-ciliary functions of the BBSome.
The BBSome is involved in a wide range of cellular functions including intracellular vesicular transport, cytoskeletal dynamics, gene expression, and cellular and organelle homeostasis. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; UPR, unfolding protein response.
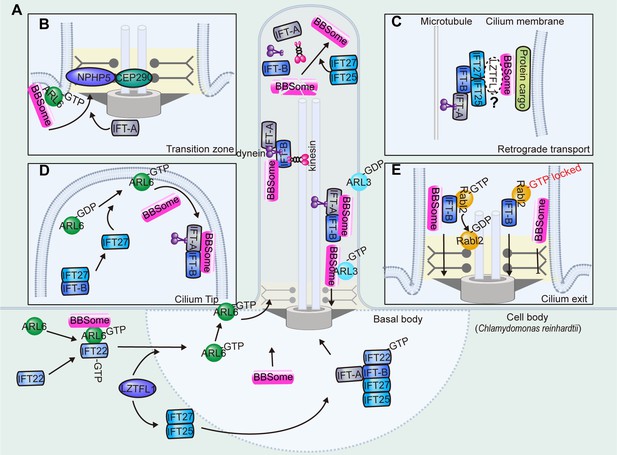
Ciliary transport of the BBSome.
(A) The BBSome is recruited to the basal body through ARL6-GTP and IFT22-GTP. LZTFL1 also facilitates basal body recruitment of the BBSome. At the ciliary tip, IFT25/27 promotes BBSome reassembly for retrograde transport. At the proximal ciliary region above the transition zone, a portion of cargo-laden BBSome sheds off retrograde IFT and acts as the effector of ARL3 for ciliary retrieval. (B) The BBSome is recruited to the membrane as an effector of ARL6-GTP. Ciliary entry of the BBSome is facilitated by IFT-A and transition zone proteins NPHP5 and CEP290. (C) The BBSome rides on the retrograde transport train, probably mediated by the IFT-B components IFT27 and IFT25. Whether the adaptor protein LZTFL1 functions as the linker between the BBSome and IFT-B remains to be demonstrated (D) At the ciliary tip, IFT27 disassociates from IFT-B to activate ARL6. Then, ARL6-GTP arranges the BBSome onto the membranes for retrograde transport. (E) During ciliary exit, the BBSome is transported across the transition zone on IFT-B, where Rabl2-GTP hydrolyses to the Rabl2-GDP form to dissociate from IFT trains. The BBSome sheds off from the IFT-B trains and fails to pass through the transition zone when the IFT-B is persistently bound by the GTP-locked Rabl2.
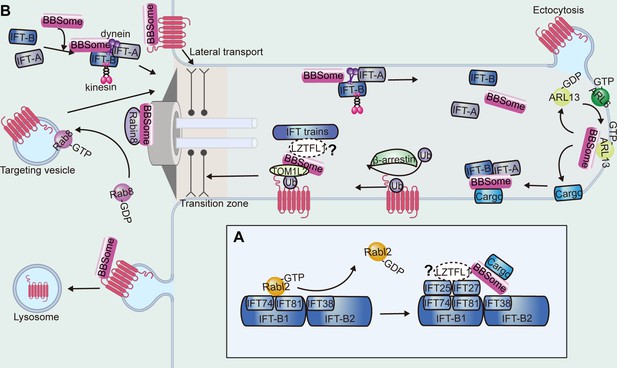
Functions of the BBSome in the cilium.
(A) The anchoring of the BBSome on IFT trains. The BBSome interacts with IFT-B through IFT38. The Rabl2 GTPase and the IFT25-IFT27 dimer bind to IFT74-IFT81 of IFT-B in a mutually exclusive manner and may regulate BBSome-mediated cargo loading. (B) During the cargo’s ciliary entry, the BBSome either regulates vesicle targeting in a Rab8-Rabin8-dependent manner or regulates the cargo’s lateral transport between the plasma and ciliary membrane. At the ciliary base and at the ciliary tip, the BBSome may regulate IFT assembly to ensure their ciliary entry and turnaround and hold them together during transport. At the ciliary tip, ARL6 and ARL13 regulate cargo pickup by the BBSome for retrieval. During the cargo’s exit, β-arrestin arranges the cargo for ubiquitin modification, followed by BBSome-mediated exit across the transition zone. TOM1L2 may function as an adapter between the BBSome and ubiquitin sidechains. The BBSome facilitates endocytic sorting of select membrane proteins at the base of the cilium. The unretrieved GPCRs can also be shed into ectocytosis vesicles for disposal.
Tables
Characteristics and functions of BBS genes.
| No | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Protein | Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BBS1 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 1 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 1 protein | Member of the BBSome complex | Mykytyn et al., 2002 |
| 2 | BBS2 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 2 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 2 protein | Member of the BBSome complex | Nishimura et al., 2001 |
| 3 | ARL6 | ADP ribosylation factor like GTPase 6 | ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 6 | Small GTPase; Facilitate BBSome assembly and recruitment to the cilium | Chiang et al., 2004; Fan et al., 2004 |
| 4 | BBS4 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 4 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 4 protein | Member of the BBSome complex | Mykytyn et al., 2001 |
| 5 | BBS5 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 5 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 5 protein | Member of the BBSome complex | Woods et al., 1999; Young et al., 1999 |
| 6 | MKKS | MKKS centrosomal shuttling protein | McKusick-Kaufman/Bardet-Biedl syndromes putative chaperonin | Chaperonin protein for BBSome complex assembly | Katsanis et al., 2000; Slavotinek et al., 2000 |
| 7 | BBS7 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 7 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 7 protein | Member of the BBSome complex | Badano et al., 2003a |
| 8 | TTC8 | Tetratricopeptide repeat domain 8 | Tetratricopeptide repeat protein 8 | Member of the BBSome complex | Ansley et al., 2003 |
| 9 | BBS9 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 9 | Protein PTHB1 | Member of the BBSome complex | Nishimura et al., 2005 |
| 10 | BBS10 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 10 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 10 protein | Chaperonin protein for BBSome complex assembly | Stoetzel et al., 2006 |
| 11 | TRIM32 | Tripartite motif containing 32 | E3 ubiquitin protein ligase TRIM32 | E3 ubiquitin ligase | Chiang et al., 2006 |
| 12 | BBS12 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 12 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 12 protein | Chaperonin protein for BBSome complex assembly | Stoetzel et al., 2007 |
| 13 | MKS1 | MKS transition zone complex subunit 1 | Meckel syndrome type 1 protein | Transition zone component; Regulates ciliary trafficking | Leitch et al., 2008 |
| 14 | CEP290 | Centrosomal protein 290 | Centrosomal protein of 290 kDa (Cep290) | Transition zone component; Regulates ciliary entry | Leitch et al., 2008 |
| 15 | WDPCP | WD repeat containing planar cell polarity effector | WD repeat containing and planar cell polarity effector protein fritz homolog (hFRTZ) | Component of the CPLANE (ciliogenesis and planar polarity effectors) complex; regulates ciliogenesis | Kim et al., 2010 |
| 16 | SDCCAG8 | SHH signaling and ciliogenesis regulator SDCCAG8 | Serologically defined colon cancer antigen 8 | Regulates ciliogenesis and Hedgehog signaling pathway | Otto et al., 2010 |
| 17 | LZTFL1 | Leucine zipper transcription factor like 1 | Leucine zipper transcription factor-like protein 1 | Regulates the BBSome trafficking | Marion et al., 2012b |
| 18 | BBIP1 | BBSome interacting protein 1 | BBSome-interacting protein 1 | Member of the BBSome complex | Loktev et al., 2008 |
| 19 | IFT27 | Intraflagellar transport 27 | Intraflagellar transport protein 27 homolog | IFT-B complex component; Required for ciliary trafficking | Aldahmesh et al., 2014 |
| 20 | IFT172 | Intraflagellar transport 172 | Intraflagellar transport protein 172 homolog | IFT-B complex component | Bujakowska et al., 2015 |
| 21 | CFAP418 | Cilia And Flagella Associated Protein 418 | Cilia- and flagella-associated protein 418 | A ciliary protein of unknown function | Khan et al., 2016; Heon et al., 2016 |
| 22 | IFT74 | Intraflagellar transport 74 | Intraflagellar transport protein 74 homolog | IFT-B complex component | Lindstrand et al., 2016 |
| 23 | NPHP1 | Nephrocystin 1 | Nephrocystin-1 | Transition zone component | Lindstrand et al., 2014 |
| 24 | SCAPER | S-phase cyclin A associated protein in the ER | S phase cyclin A-associated protein in the endoplasmic reticulum (S phase cyclin A-associated protein in the ER) | Regulates ciliary dynamics | Wormser et al., 2019 |
| 25 | CCDC28B | Coiled-coil domain containing 28B | Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 28B | Centrosomal protein that regulates ciliogenesis | Badano et al., 2006 |
| 26 | SCLT1 | Sodium channel and clathrin linker 1 | Sodium channel and clathrin linker 1 | Distal appendage component that regulates ciliogenesis | Morisada et al., 2020 |





