Multi-tiered actions of Legionella effectors to modulate host Rab10 dynamics
Figures
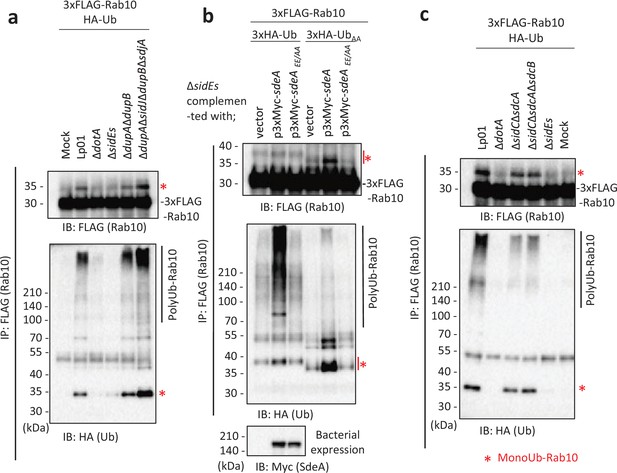
The SidE- and SidC-family proteins differentially contribute toward ubiquitination of Rab10.
HEK293T-FcγRII cells transiently expressing 3xFLAG-Rab10 and HA-Ub were infected with the indicated L. pneumophila strains for 1 hr at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 20. Rab10 was isolated from cell lysate by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with anti-FLAG and with anti-HA antibodies (a-c). Triple-HA-Ub (3xHA-Ub) or Ub in which the C-terminal GG were replaced with AA (3xHA-UbAA) was expressed instead of HA-Ub in (b). Bacterial lysates were probed with anti-Myc antibody in (b). The asterisks indicate the postion of monoubiquitinated Rab10.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 1a (anti-FLAG and anti-HA).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 1—source data 2
PDF containing Figure 1a and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG and anti-HA), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig1-data2-v1.pdf
-
Figure 1—source data 3
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 1b (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-Myc).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig1-data3-v1.zip
-
Figure 1—source data 4
PDF containing Figure 1b and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-Myc), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig1-data4-v1.pdf
-
Figure 1—source data 5
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 1c (anti-FLAG and anti-HA).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig1-data5-v1.zip
-
Figure 1—source data 6
PDF containing Figure 1c and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG and anti-HA), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig1-data6-v1.pdf
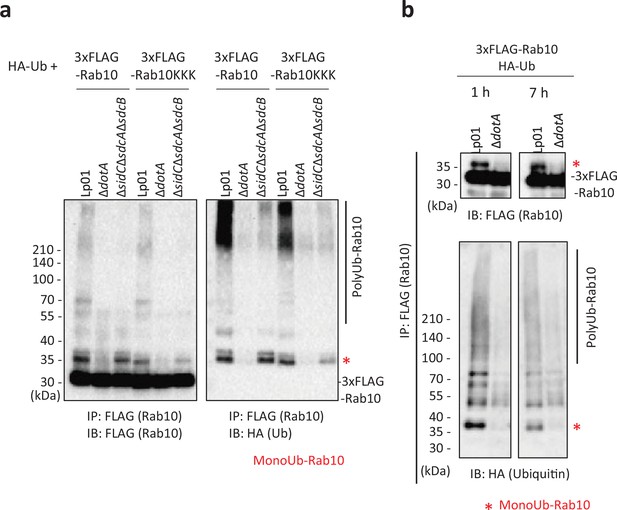
Mutation of Lys102, Lys136, and Lys154 on Rab10 did not eliminate ubiquitination of Rab10 upon infection.
HEK293T-FcγRII cells transiently expressing 3xFLAG-Rab10 or 3xFLAG-Rab10 K102A K136A L154A (KKK) (a) with HA-Ub were infected with the indicated L. pneumophila strains for 1 hr (a) or 7 hr (b) at an MOI of 20. Rab10 was isolated from cell lysate by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with anti-FLAG and with anti-HA antibodies. The asterisks indicate the postion of monoubiquitinated Rab10.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 1—figure supplement 1a (anti-FLAG and anti-HA).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 2
PDF containing Figure 1—figure supplement 1a and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG and anti-HA), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig1-figsupp1-data2-v1.pdf
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 3
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 1—figure supplement 1b (anti-FLAG and anti-HA).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig1-figsupp1-data3-v1.zip
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 4
PDF containing Figure 1—figure supplement 1b and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG and anti-HA), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig1-figsupp1-data4-v1.pdf

The SidE- and SidC-family proteins differentially contribute toward recruitment of Rab10 to the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV).
HeLa-FcγRII cells transiently expressing RFP-Rab10 were infected with the indicated L. pneumophila strains at an MOI of 5 for 4 hr (a) and for the indicated time (b). (a) Representative images of infected cells. Fixed cells were stained for L. pneumophila (green) and DNA (blue) and visualized with RFP-Rab10 (red). Magnified images in the white squares are shown in merged and in each channel. Arrows indicate the Rab10-positive LCVs. Scale bars, 10 μm. (b) Quantitation of Rab10-positive LCVs (%). Infections were performed in triplicate and each value represents scoring from 200 LCVs. Significance was determined using Student’s t-test.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Raw images of micrographs in Figure 2a.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig2-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Counting data in Figure 2b.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig2-data2-v1.zip
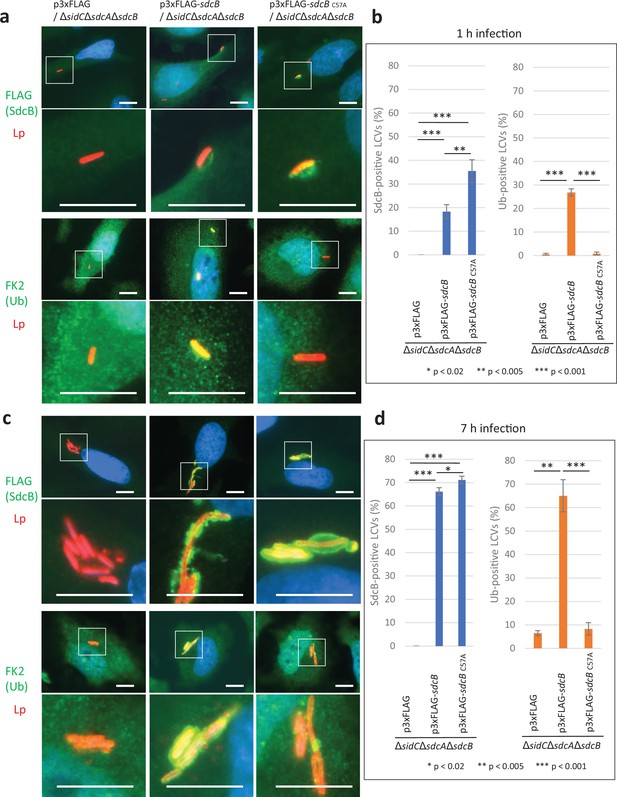
SdcB associates with the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV) and plays a major role in Ub recruitment to the LCV at late stages of infection.
HeLa-FcγRII cells were infected with the indicated L. pneumophila strains at an MOI of 2 for 1 hr (a, b) and for 7 hr (c, d). (a, c) Representative images of infected cells. Fixed cells were stained for FLAG-SdcB or Ub (green), L. pneumophila (red), and DNA (blue). Magnified images in the white squares are shown in the lower panels. Scale bars, 10 μm. (b, d) Quantitation of SdcB-positive (left) and of Ub-positive (right) LCVs (%). Infections were performed in triplicate and each value represents scoring from 200 LCVs. Significance was determined using Student’s t-test.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Raw images of micrographs in Figure 3a.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig3-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Raw images of micrographs in Figure 3c.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig3-data2-v1.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 3
Counting data in Figure 3, d.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig3-data3-v1.zip

The catalytic activity of SdcB enhances retention of Rab10 on the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV).
(a) HEK293T-FcγRII cells transiently expressing 3xFLAG-Rab10 Q68L (QL) or Rab10 T23N (TN) with HA-Ub were infected with the indicated L. pneumophila strains for 1 hr at an MOI of 50. Rab10 was isolated from cell lysate by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with anti-FLAG antibody. (b) HeLa-FcγRII cells transiently expressing RFP-Rab10QL were infected with the indicated L. pneumophila strains at an MOI of 10 for 1 hr (see Figure 4—figure supplement 2). Rab10-positive LCVs (%) were quantified. Infections were performed in triplicate and each value represents scoring from 50 LCVs. Significance was determined using Student’s t-test and represented as: ****p < 0.0002. (c) HEK293T-FcγRII cells transiently expressing 3xFLAG-Rab10QL and HA-Ub were infected with the L. pneumophila strains expressing Myc-tagged SdcB or its catalytic mutant for 7 hr at an MOI of 20. Rab10 was isolated from cell lysate by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with anti-FLAG and with anti-HA antibodies. For detection of translocated SdcB, it was isolated from cell lysate by immunoprecipitation using anti-Myc magnetic beads and was probed with anti-Myc antibody. Note that apparent reduction of the wild-type SdcB was caused by its auto-ubiquitination leading to the molecular weight shift (see text). (d, e) HeLa-FcγRII cells transiently expressing RFP-Rab10 were infected with the indicated L. pneumophila strains at an MOI of 2 for 7 hr. (d) Representative images of infected cells. Fixed cells were stained for FLAG-SdcB (green) and L. pneumophila (blue) and visualized with RFP-Rab10 (red). Magnified images in the white squares are shown in each channel. White arrows indicate the position of a bacterium. The red arrow indicates a Rab10 signal surrounding an LCV. Scale bars, 10 μm. (e) Quantitation of Rab10-positive LCVs (%) out of SdcB-positive ones. Infections were performed in triplicate and each value represents scoring from 200 SdcB-positive LCVs. Significance was determined using Student’s t-test.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 4a (anti-FLAG).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig4-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 2
PDF containing Figure 4a and an original scan of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig4-data2-v1.pdf
-
Figure 4—source data 3
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 4c (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-Myc).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig4-data3-v1.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 4
PDF containing Figure 4c and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-Myc), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig4-data4-v1.pdf
-
Figure 4—source data 5
Raw images of micrographs in Figure 4d.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig4-data5-v1.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 6
Counting data in Figure 4b, e.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig4-data6-v1.zip
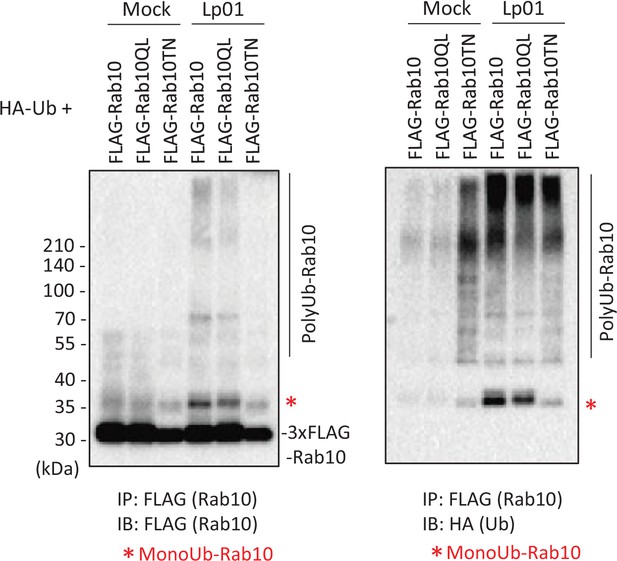
Active Rab10 is preferentially targeted for infection-induced ubiquitination.
HEK293T-FcγRII cells transiently expressing 3xFLAG-Rab10 Q68L (QL) or Rab10 T23N (TN) with HA-Ub were infected with the wild-type L. pneumophila strain or treated with media containing anti-Legionella antiserum (mock infection) for 1 hr at an MOI of 20. Rab10 was isolated from cell lysate by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with anti-FLAG and with anti-HA antibodies.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 4—figure supplement 1 (anti-FLAG and anti-HA).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 2
PDF containing Figure 4—figure supplement 1 and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG and anti-HA), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig4-figsupp1-data2-v1.pdf
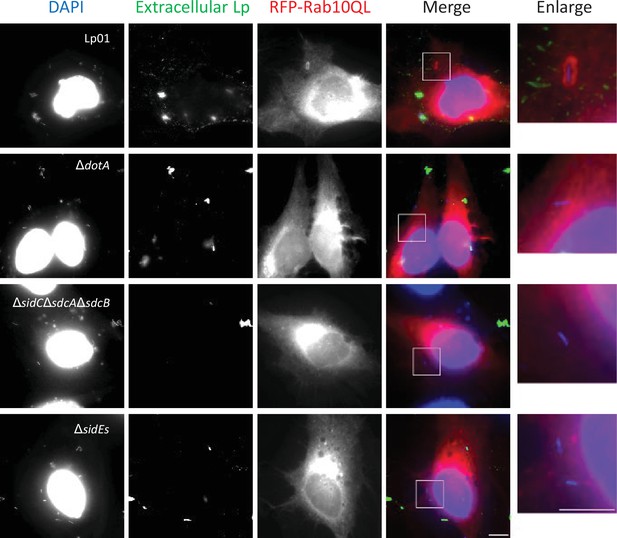
The SidE- and SidC-family proteins contribute toward retaining active Rab10 to the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV).
HeLa-FcγRII cells transiently expressing RFP-Rab10QL were infected with the indicated L. pneumophila strains at an MOI of 10 for 1 hr. Cells were fixed and stained with anti-Legionella antiserum (green) before permeabilization of cells for detection of extracellular bacteria. Permeabilized cells were stained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue) for detection of intracellular bacteria (and nuclei) and with RFP-Rab10 (red). Representative images of infected cells were shown. Magnified merged images in the white squares are shown as enlarged images. Scale bars, 5 μm.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw images of in micrographs in Figure 4—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig4-figsupp2-data1-v1.zip

The transglutaminase activity of MavC can mediate a unique Ub conjugation to SdcB.
(a) 3xFLAG-SdcB, HA-Ub, and GFP-MavC were coexpressed in HEK293T-FcγRII cells. SdcB was isolated from cell lysates by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with the indicated antibodies. The asterisks indicate the Ub-conjugated form of SdcB. (b) 3xFLAG-SdcB and GFP-MavC were coexpressed in HEK293T-FcγRII cells. SdcB was isolated from cell lysates by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with the indicated antibodies. The asterisks indicate the Ub-conjugated form of SdcB. (c) In vitro transglutaminase assay was performed using purified proteins. The samples were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) followed by silver staining (top) or by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies (middle and bottom). The asterisks indicate the Ub-conjugated form of SdcB. (d) 3xFLAG-SdcA or SidC, GFP-MavC, and HA-Ub were coexpressed in HEK293T-FcγRII cells. SdcA or SidC was isolated from cell lysates by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with the indicated antibodies. The asterisks indicate the Ub-conjugated form of SdcA. (e) 3xFLAG-SdcB, GFP-MavC, and HA-Ub or Ub without any Lys residues (Ub No K) were coexpressed in HEK293T-FcγRII cells. SdcB was isolated from cell lysates by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with the indicated antibodies. The asterisks indicate the Ub-conjugated form of SdcB. (f) 3xFLAG-SdcB, GFP-MavC, and HA-Ub or Ub in which the C-terminal GG were replaced with AA (Ub AA) were coexpressed in HEK293T-FcγRII cells. SdcB was isolated from cell lysates by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with the indicated antibodies. The asterisks indicate the Ub-conjugated form of SdcB.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 5a (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-GFP).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 2
PDF containing Figure 5a and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-GFP), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data2-v1.pdf
-
Figure 5—source data 3
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 5b (anti-FLAG, anti-FK2, and anti-GFP).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data3-v1.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 4
PDF containing Figure 5b and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG, anti-FK2, and anti-GFP), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data4-v1.pdf
-
Figure 5—source data 5
Original files for the silver stained gel and western blot analysis in Figure 5c (anti-FK2 and anti-His).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data5-v1.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 6
PDF containing Figure 5c and original scans of the relevant silver stained gel and western blot analysis (anti-FK2 and anti-His), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data6-v1.pdf
-
Figure 5—source data 7
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 5d (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-GFP).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data7-v1.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 8
PDF containing Figure 5d and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-GFP), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data8-v1.pdf
-
Figure 5—source data 9
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 5e (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-GFP).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data9-v1.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 10
PDF containing Figure 5e and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-GFP), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data10-v1.pdf
-
Figure 5—source data 11
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 5f (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, anti-P4D1, and anti-GFP).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data11-v1.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 12
PDF containing Figure 5f and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, anti-P4D1, and anti-GFP), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-data12-v1.pdf
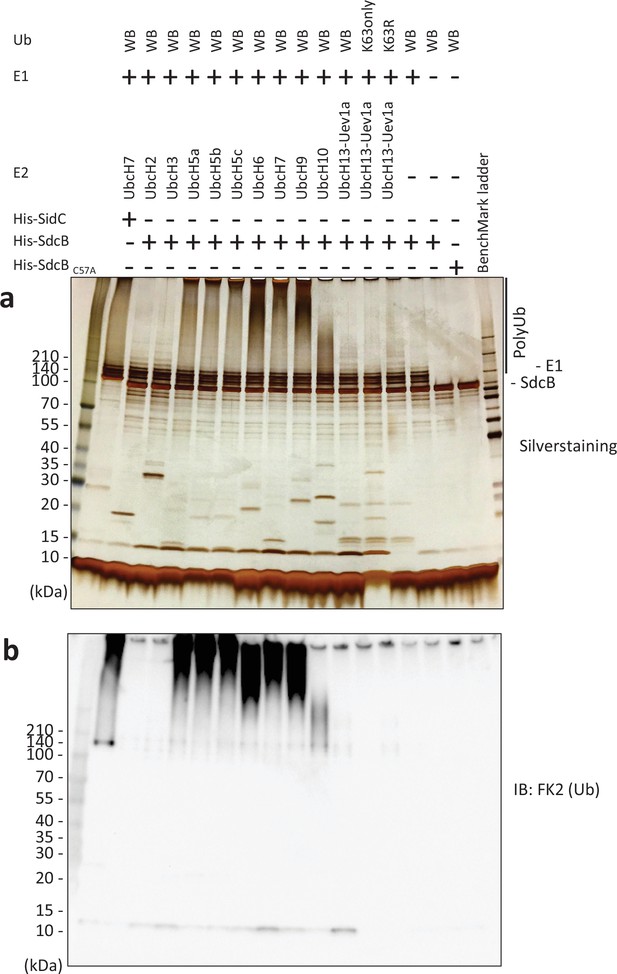
SdcB has a catalytic activity of self-ubiquitination with preference of various E2 enzymes.
Ub, E1 enzyme, indicated E2 enzymes, and purified His-SdcB or His-SidC were mixed in the reaction buffer in the presence of ATP and incubated at 30°C for 120 min. The samples were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) followed by silver staining (a) or by immunoblotting using the anti-Ub antibody (b).
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original files for the silver staining and the western blot analysis in Figure 5—figure supplement 1 (silver staining and anti-FK2).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 2
PDF containing original scans of the silver stained gel and the western blot analysis in Figure 5—figure supplement 1 (anti-FK2) with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-figsupp1-data2-v1.pdf
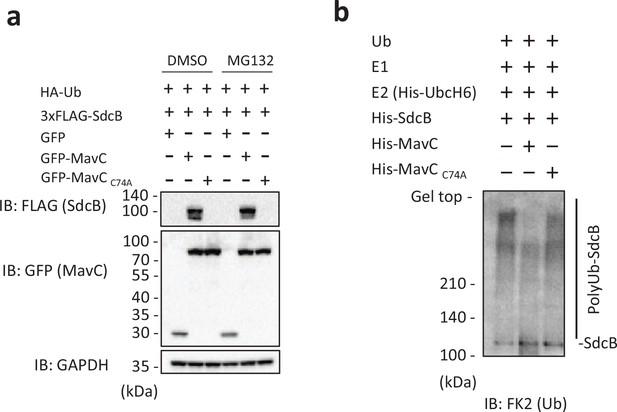
The catalytic activity of MavC negatively impacts on auto-ubiquitination of SdcB.
(a) 3xFLAG-SdcB, HA-Ub and GFP-MavC were coexpressed in HEK293T-FcγRII cells. After 24 hr transfection, cell media was replaced with media containing 10 μM of MG132 or equivalent amount of dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), and incubation of cells was resumed for additional 6 hr. The cell lysates were probed with the indicated antibodies. (b) The in vitro reaction was performed with recombinant Ub, E1 enzyme, His-UbcH6, purified His-SdcB and His-MavC in the reaction buffer in the presence of ATP by incubation at 30°C for 120 min. The samples were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) followed by immunoblotting using the anti-Ub antibody.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 5—figure supplement 2a (anti-FLAG, anti-GFP and anti-GAPDH).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-figsupp2-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 2—source data 2
PDF containing Figure 5—figure supplement 2a and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG, anti-GFP, and anti-GAPDH), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-figsupp2-data2-v1.pdf
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 2—source data 3
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 5—figure supplement 2b (anti-FK2).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-figsupp2-data3-v1.zip
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 2—source data 4
PDF containing Figure 5—figure supplement 2b and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FK2), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig5-figsupp2-data4-v1.pdf

Identification of residues on Ub and SdcB between which MavC can crosslink.
(a) MavC catalyzes the formation of an isopeptide bond between the Gln41 of Ub and the Lys518 of SdcB. The indicated proteins were expressed in HEK293T-FcγRII cells and SdcB was isolated from cell lysates by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads. The samples were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE). The Ub-conjugated SdcB was detected by immunoblotting and by CBB staining. The gel slices of areas of the bands shown with the red squares were subjected to mass spectrometric analysis. Product ion spectrum was shown for Ub peptide – AKIQDKEGIPPDQQR crosslinked with SdcB peptide – VLLDKEVNDEGIAEAVASK. (b, c) The indicated proteins were coexpressed in HEK293T-FcγRII cells. SdcB was isolated from cell lysates by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with the indicated antibodies. The asterisks indicate the Ub-conjugated form of SdcB.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Original files for the CBB stained gel and western blot analysis in Figure 6a (anti-HA).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig6-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 2
PDF containing Figure 6a and original scans of the relevant CBB stained gel and western blot analysis (anti-HA), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig6-data2-v1.pdf
-
Figure 6—source data 3
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 6b (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-GFP).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig6-data3-v1.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 4
PDF containing Figure 6b and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-GFP), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig6-data4-v1.pdf
-
Figure 6—source data 5
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 6c (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-GFP).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig6-data5-v1.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 6
PDF containing Figure 6c and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-GFP), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig6-data6-v1.pdf
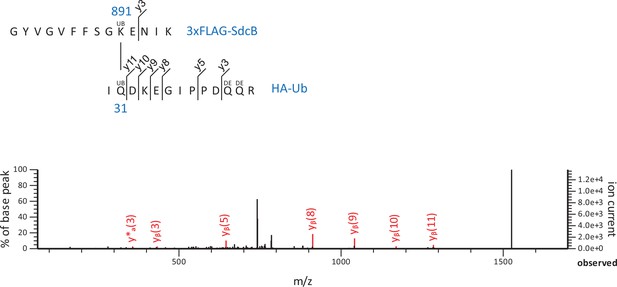
Mass spectrometry analysis identified additional residues forming a covalent linkage between Ub and SdcB.
Product ion spectrum was shown for Ub peptide – IQDKEGIPPDQQR crosslinked with SdcB peptide – GYVGVFFSGKENIK.
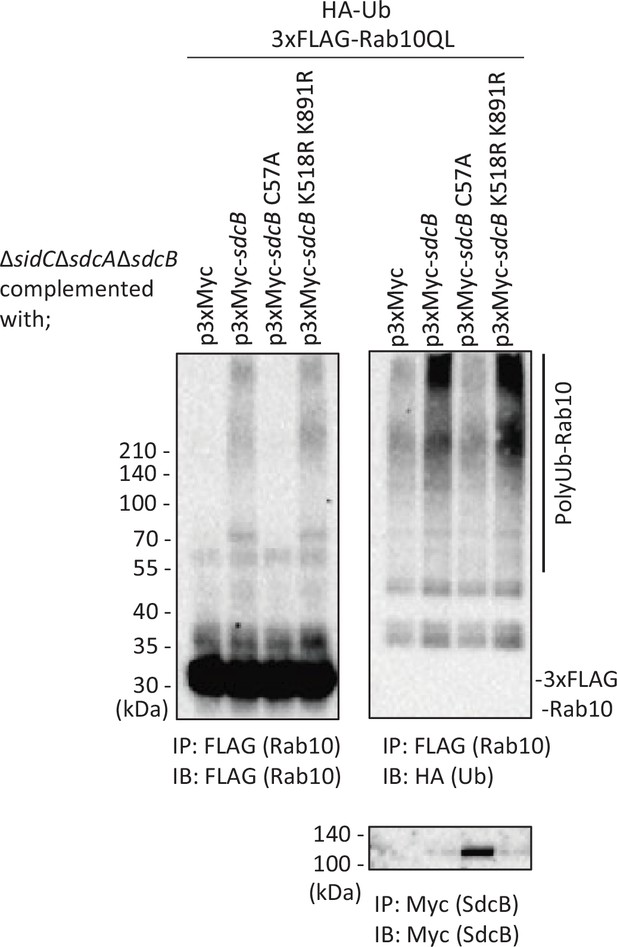
Mutations on Lys518 and Lys891 of SdcB did not affect ubiquitination of Rab10.
HEK293T-FcγRII cells transiently expressing 3xFLAG-Rab10QL and HA-Ub were infected with the L. pneumophila ΔsidCΔsdcAΔsdcB strain expressing Myc-tagged SdcB, its catalytic mutant (SdcB C57A) or SdcB K518R K891R for 7 hr at an MOI of 20. Rab10 was isolated from cell lysate by immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG magnetic beads and was probed with anti-FLAG and with anti-HA antibodies. For detection of translocated SdcB, it was isolated from cell lysate by immunoprecipitation using anti-Myc magnetic beads and was probed with anti-Myc antibody. Note that apparent loss of SdcB was caused by its auto-ubiquitination leading to the molecular weight shift.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 6—figure supplement 2 (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-Myc).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig6-figsupp2-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 2—source data 2
PDF containing Figure 6—figure supplement 2 and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-FLAG, anti-HA, and anti-Myc), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig6-figsupp2-data2-v1.pdf

Catalytic activity of MavC negatively regulates the Rab10 localization to the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV).
(a, b) HeLa-FcγRII cells transiently expressing RFP-Rab10 and HA-MavC or its catalytic mutant were infected with the Lp01 ΔsidCΔsdcAΔsdcB strain complemented with the plasmid expressing 3xFLAG-SdcB or its catalytic mutant at an MOI of 2 for 4 hr. (a) Representative images of cells infected with the Lp01 ΔsidCΔsdcAΔsdcB strain complemented with the plasmid expressing 3xFLAG-SdcB. Fixed cells were stained for FLAG-SdcB (green) and DNA (blue), and visualized with RFP-Rab10 (red). Magnified images in the white squares are shown in each channel. White arrows indicate the position of a bacterium. The red arrow indicates a Rab10 signal surrounding an LCV. Scale bars, 10 μm. (b) Quantitation of Rab10-positive LCVs (%) out of SdcB-positive ones. Infections were performed in triplicate and each value represents scoring from 200 SdcB-positive LCVs. Significance was determined using Student’s t-test. (c) HeLa-FcγRII cells transiently expressing RFP-Rab10 were infected with the indicated Lp01 strains at an MOI of 2 for 9 hr, and Rab10-positive LCVs (%) were quantified. Infections were performed in triplicate and each value represents scoring from 200 LCVs. Significance was determined using Student’s t-test. (d) The schematic of roles of SidE- and SidC-family ligases in Rab10 localization to the LCV and of negative regulation of SdcB-dependent Rab10 retention by the transglutaminase activity of MavC. Red arrows indicate canonical Ub conjugation by SidC, SdcA, and SdcB. Purple arrows indicate the noncanonical Ub conjugation. In the early stage of infection, Rab10 is recruited and retained to the LCV. This event is linked to its phosphoribosylated (PR) ubiquitination catalyzed by the SidE effectors. The PR ubiquitination of Rab10 provides a platform of its polyubiquitination in a manner depending on SidC and SdcA. In later stages, SdcB contributes toward sustained Ub accumulation on the LCV, enabling the LCV to maintain Rab10 on the vacuole. MavC-mediated crosslinking between Ub and SdcB disrupts the catalytic activity of SdcB, eventually releasing Rab10 from the LCV.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Raw images of micrographs in Figure 7a.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig7-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 7—source data 2
Counting data in Figure 7b, c.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig7-data2-v1.zip
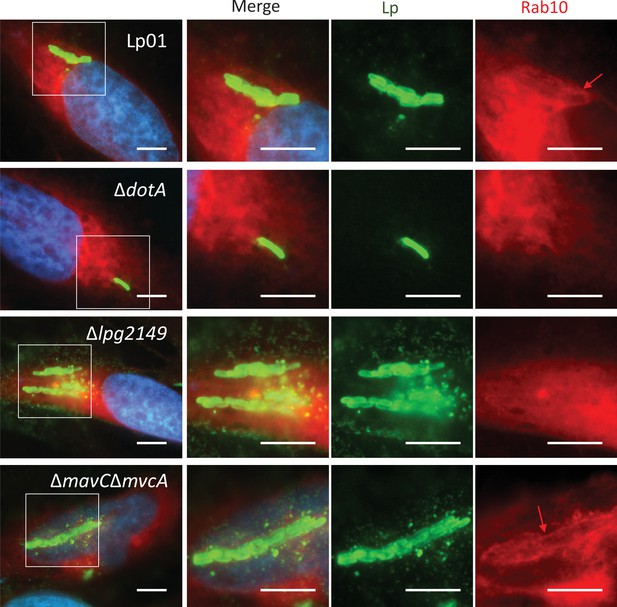
Bacterially delivered MavC mediates elimination of Rab10 from the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV).
Representative images of cells infected with the indicated Lp01 strains at an MOI of 2 for 9 hr (Rab10-positive LCVs (%) were quantified in Figure 7c). Fixed cells were stained for L. pneumophila (green) and DNA (blue), and visualized with RFP-Rab10 (red). Magnified images in the white squares are shown in each channel. Red arrows indicate the Rab10 signal surrounding an LCV. Scale bars, 10 μm.
-
Figure 7—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw images of in micrographs in Figure 7—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig7-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
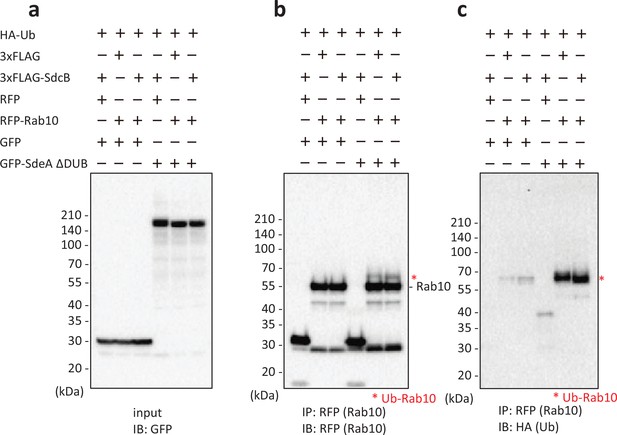
Ectopic expression of SdcB does not proceed Rab10 polyubiquitination even in the presence of SdeA.
Indicated proteins were coexpressed in HEK293T-FcγRII cells. Rab10 was isolated from cell lysates by immunoprecipitation using anti-RFP magnetic beads and was probed with the indicated antibodies. The asterisks indicate the Ub-conjugated form of Rab10.
-
Figure 7—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Original files for the western blot analysis in Figure 7—figure supplement 2 (anti-GFP, anti-RFP, and anti-HA).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig7-figsupp2-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 7—figure supplement 2—source data 2
PDF containing Figure 7—figure supplement 2 and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-GFP, anti-RFP, and anti-HA), with cropped areas.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-fig7-figsupp2-data2-v1.pdf
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Legionella pneumophila) | Philadelphia-1 (Lp01) | Berger and Isberg, 1993 | NC_002942.5 | |
| Strain, strain background (Legionella pneumophila) | Lp01ΔicmV ΔdotA (ΔdotA) | Zuckman et al., 1999 | N/A | |
| Strain, strain background (Legionella pneumophila) | Lp01 ΔsidCΔsdcA | This study | N/A | Constructed in Nagai lab |
| Strain, strain background (Legionella pneumophila) | Lp01 ΔsidCΔsdcAΔsdcB | This study | N/A | Constructed in Nagai lab |
| Strain, strain background (Legionella pneumophila) | Lp01 ΔsidEΔsdeAΔsdeBΔsdeC (ΔsidEs) | This study | N/A | Constructed in Nagai lab |
| Strain, strain background (Legionella pneumophila) | Lp01 ΔdupAΔdupB | This study | N/A | Constructed in Nagai lab |
| Strain, strain background (Legionella pneumophila) | Lp01 ΔdupAΔsidJΔdupBΔsdjA | This study | N/A | Constructed in Nagai lab |
| Strain, strain background (Legionella pneumophila) | Lp01 Δlpg2149 | This study | N/A | Constructed in Nagai lab |
| Strain, strain background (Legionella pneumophila) | Lp01 ΔmavCΔmvcA | This study | N/A | Constructed in Nagai lab |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | DH5α | TOYOBO | Cat# DNA-903 | Competent cells |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | DH5αλpir | Zuckman et al., 1999 | N/A | Competent cells |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | BL21(DE3) | NOVAGEN-MERK | Cat# 69450 | Competent cells |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HeLa‐FcγRII | Arasaki et al., 2017 | Established from ATCC CCL-2 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293T‐FcγRII | Arasaki and Roy, 2010 | Established from ATCC CRL-3216 | |
| Antibody | anti-FLAG (M2) (Mouse monoclonal) | Sigma | Cat# F1804 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-HA (Mouse monoclonal) | MBL | Cat# M132-3 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-HA (Rabbit monoclonal) | MBL | Cat# 561 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-Ub (FK2) (Mouse monoclonal) | Enzo | Cat# BML-PW8810 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-Ub (P4D1) (Mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | Cat# sc-8017 | WB (1:200) |
| Antibody | anti-GFP (Rabbit polyclonal) | MBL | Cat# 598 | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | anti-His (Mouse monoclonal) | Novagen | Cat# 70796-3 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-Myc (Mouse monoclonal) | Roche | Cat# 11 667 203 001 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-RFP (Rabbit polyclonal) | MBL | Cat# PM005 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-GAPDH (Mouse monoclonal) | Proteintec | Cat# 60004-1-Ig | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | anti-Legionella pneumophila (Rabbit polyclonal) | BioAcademia | Cat# 64-100 | IF (1:5000) Opsonization (1:3000) |
| Antibody | Goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary, HRP | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 62-6520 | WB (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) secondary, HRP | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 65-6120 | WB (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse | Thermo Fisher | Cat#A-11029 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit | Thermo Fisher | Cat#A-11034 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Rhodamine RedX goat anti-rabbit | Thermo Fisher | Cat# R6349 | IF (1:1000) |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Ubiquitin, human recombinant | Boston Biochem | Cat# U-100H | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Ubiquitin K63R, human recombinant | Boston Biochem | Cat# UM-K63R | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Ubiquitin mutant with K63 only, human recombinant | Boston Biochem | Cat# UM-K630 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | UBE1, human recombinant | Boston Biochem | Cat# E-305 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Ubc (E2) Enzyme Kit | Boston Biochem | Cat# K-980B | |
| Chemical compound, drug | N-(2-Acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid (ACES) | Sigma | Cat# 7365-82-4 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | N-Ethylmaleimide (NEM) | Sigma | Cat# E3876 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | cOmplete protease inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA free) | Roche (Merk) | Cat# 11873580001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SigmaFast Protease Inhibitor Cocktail | Sigma | Cat# S8830 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) | Nacarai | Cat# 27327-94 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | MG132 | Calbiochem | Cat# 474791 | |
| Commercial assay kit | Silver Stain MS Kit | FUJIFILM Wako | Cat# 299-58901 | |
| Commercial assay kit | QuickChange II site-directed mutagenesis kit | Agilent | Cat# 200523 | |
| Commercial assay kit | Gibson assembly kit | New England Biolabs | Cat# E2611 | |
| Commercial assay kit | EndoFree Plasmid MAXI prep kits | QIAGEN | Cat# 12362 | |
| Other | 4,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) | DOJINDO | Cat# GW094 | 1:10,000 |
| Other | Lipofectamine 2000 | Invitrogen | Cat# 11668-019 | Transfection reagent |
| Other | Polyethylenimine (PEI) | Polysciences | Cat# 24765-2 | Transfection reagent |
| Other | Poly-L-lysine | Sigma | Cat# P4707 | 0.01% |
| Other | Paraformaldehyde (PFA) | Sigma | Cat# 441244 | 4% |
| Other | ProLongTM Diamond Antifade Mountant | Thermo Fisher | Cat# P36961 | Antifade moutant |
| Other | Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) agarose | QIAGEN | Cat# 30210 | Affinity matrix |
| Other | FLAG M2 magnetic beads | Sigma | Cat# M8823 | Affinity beads |
| Other | Myc-Trap magnetic beads | chromotek | Cat# ytma | Affinity beads |
| Other | RFP-Trap magnetic beads | chromotek | Cat# rtma | Affinity beads |
| Other | Minimum essential medium α (MEMα) | Gibco | Cat# 12571-063 | Medium |
| Other | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) | Gibco | Cat# 11885-084 | Medium |
| Other | Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Sigma | Cat# 172012 | Heat inactivated, 10% |
| Other | Goat serum | Gibco | Cat# 16210-064 | 2% |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Plasmids used in this study are listed.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-supp1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Primers used in this study are listed.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-supp2-v1.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89002/elife-89002-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf





