Improving PD-1 blockade plus chemotherapy for complete remission of lung cancer by nanoPDLIM2
Figures
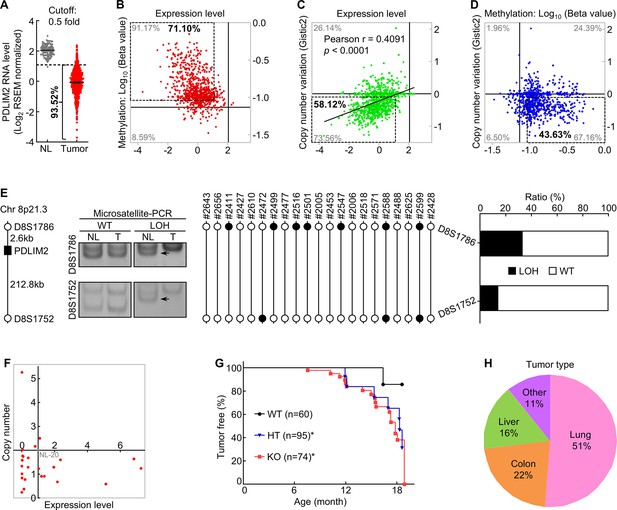
PDLIM2 repression in human lung cancer involves both epigenetic alteration and genetic deletion, and Pdlim2 genetic deletion in mice leads to development of spontaneous tumors, majorly lung tumors.
(A) TCGA data showing PDLIM2 repression in over 90% of lung tumors if using 50% of the expression level in normal lung tissues as the cut-off (NL, n=110; Tumor, n=1019). (B) TCGA data showing PDLIM2 promoter hypermethylation and expression repression (dashed box) in over 70% of lung tumors when using 125% of the methylation level in normal lung tissues as the cut-off (n=827). (C) TCGA data showing positive associations between PDLIM2 expression and its gene copy numbers as well as PDLIM2 genetic deletion and expression repression (dashed box) in about 58% of lung tumors using the copy number variation of –0.1 as the cut-off (n=1010). (D) TCGA data showing simultaneous promoter hypermethylation and genomic deletion of PDLIM2 (dashed box) in about 44% of lung tumors (n=816). (E) Microsatellite-PCR showing PDLIM2 loss in human lung tumors (n=21). (F) qPCR showing PDLIM2 loss in human lung cancer cell lines with known copy number of the PDLIM2 gene (n=25). (G) Kaplan-Meier tumor-free survival curve showing increased spontaneous tumors in Pdlim2-/- and Pdlim2+/- mice compared to WT mice. Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test was performed. *<0.05. (H) Percentage of tumor types spontaneously developed in Pdlim2-/- and Pdlim2+/- mice showing a majority of lung tumors.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Excel file for the data shown in Figure 1A-G.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Original files for the DNA gel images shown in Figure 1E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig1-data2-v1.zip
-
Figure 1—source data 3
PDF file for the DNA gel images shown in Figure 1E with the relevant bands clearly labelled.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig1-data3-v1.zip
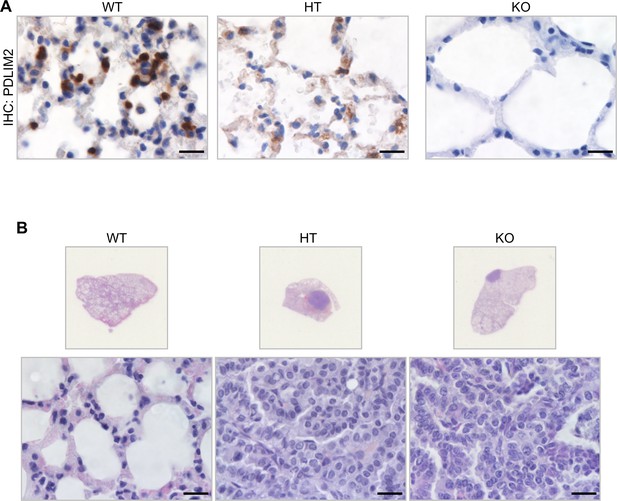
Mice with PDLIM2 deletion develop spontaneous tumors, majorly lung tumors.
(A) IHC assays showing decreased and complete loss of PDLIM2 protein expression in the lungs of PDLIM2+/- and PDLIM2-/- mice, respectively. Scale bar, 20 µm. (B) H&E staining of the lung tissues showing spontaneous lung tumors in PDLIM2+/- and PDLIM2-/- mice. Scale bar, 20 µm.

Systemic administration of PDLIM2 plasmid nanoparticles shows efficacy in mouse model of refractory lung cancer.
(A) Schedule of lung cancer induction and treatment. (B) Urethane model showing efficacy of intravenous administration of PDLIM2-expression plasmid nanoparticles for refractory lung cancer (n≥6). Nanoparticles with an empty vector plasmid (Vec) that was employed to express PDLIM2 were used as a control. (C) IHC staining showing decreased nuclear expression of STAT3 and RelA in lung tumors by PDLIM2 nanotherapy (n=6). (D) IHC staining showing decreased Bcl-xL and increased apoptosis marker cleaved caspase –3 in lung tumors by PDLIM2 nanotherapy (n=6). (E) IHC staining showing decreased Cyclin D1 and proliferation (BrdU incorporation) in lung tumors by PDLIM2 nanotherapy (n=6). Scale bar in (C–E), 20 μm. Student’s t test was performed (two tailed, unpaired) and data represent means ± SEM in (B–E). **p<0.01; ns, not statistically significant.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Excel file for the data shown in Figure 2B-E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig2-data1-v1.zip
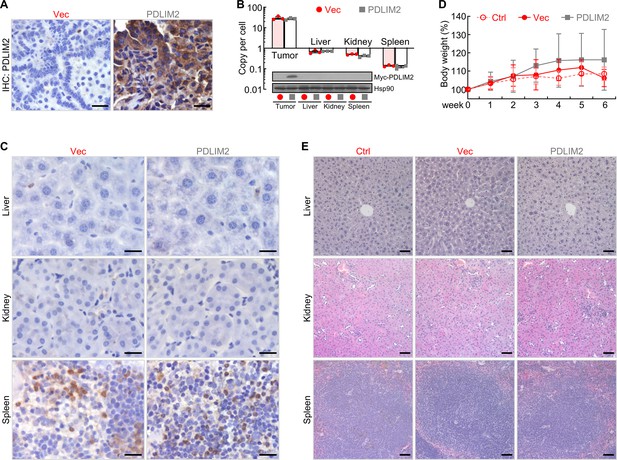
PDLIM2 nanotherapy shows high tumor specificity and low toxicity.
(A) IHC staining showing high PDLIM2 re-expression in lung tumors after PDLIM2 nanotherapy. (B) PCR and IB assays showing lung tumor-specific plasmids delivery and PDLIM2 expression by PDLIM2 nanotherapy (n=3). (C) IHC staining showing comparable expression of PDLIM2 in the indicated tissues of mice treated with PDLIM2 expression plasmid or empty vector plasmid nanoparticles. (D) No significant changes in animal body weight by nanoPDLIM2 (n=5). (E) H&E staining showing no noticeable changes in major organs by nanoPDLIM2. Scale bar: (A and C) 20 μm; (E) 50 μm.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Excel file for the data shown in Figure 3B, D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig3-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Original files for the Western blot images shown in Figure 3B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig3-data2-v1.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 3
PDF file for the Western blot images shown in Figure 3B with the relevant bands clearly labelled.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig3-data3-v1.zip
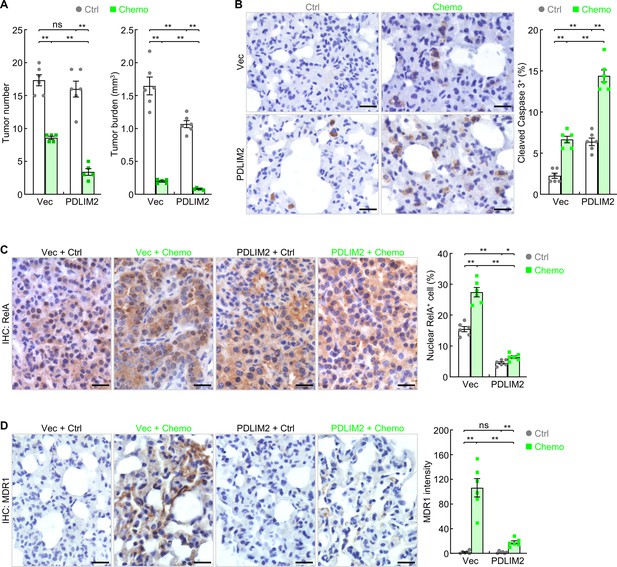
PDLIM2 nanotherapy renders lung cancers more vulnerable to chemotherapy.
(A) Urethane model showing synergy of PDLIM2 nanotherapy and chemotherapy in lung cancer treatment (n≥5). (B) IHC staining showing increased lung tumor cell apoptosis by PDLIM2 nanotherapy, chemotherapy, and further increase by their combination (n=6). (C) IHC staining showing RelA activation by chemotherapy and blockage of chemo activation of RelA by PDLIM2 nanotherapy (n=6). (D) IHC staining showing strong MDR1 induction by chemotherapy and blockage of MDR1 induction by PDLIM2 nanotherapy (n=6). Scale bar in (B–D), 20 μm. Student’s t test was performed (two tailed, unpaired) and data represent means ± SEM. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ns, not statistically significant.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Excel file for the data shown in Figure 4A-D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig4-data1-v1.zip
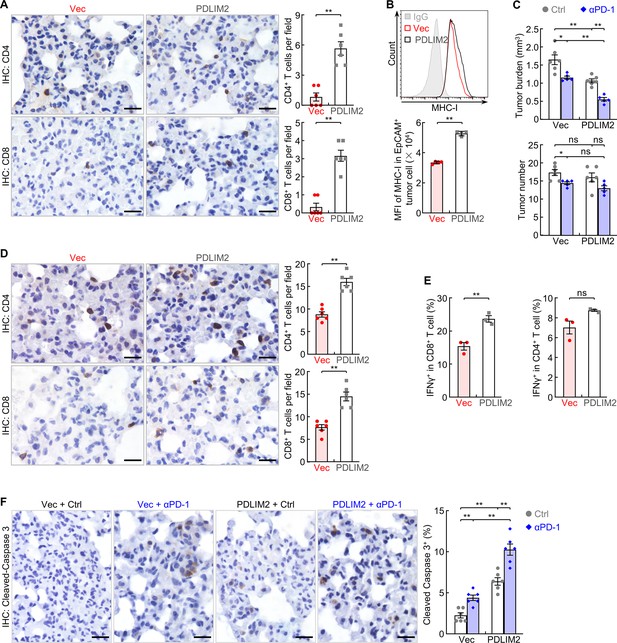
PDLIM2 nanotherapy increases the efficacy of PD-1 blockade immunotherapy for refractory lung cancer.
(A) IHC staining showing increased TILs in lung tumors by PDLIM2 nanotherapy (n=6). (B) FACS showing increased MHC-I expression in lung tumor cells by PDLIM2 nanotherapy (n=4). (C) Urethane model showing PDLIM2 nanotherapy enhancing PD-1 immunotherapy efficacy in lung cancer treatment (n≥5). (D) IHC staining showing increased TILs by PDLIM2 nanotherapy in the context of immunotherapy (n=6). (E) FACS showing increased activation of CD8+ T cells by PDLIM2 nanotherapy in the context of immunotherapy (n=3). (F) IHC staining showing increased lung tumor cell apoptosis by PDLIM2 nanotherapy, immunotherapy, and further increase by their combination (n=6). Scale bar in (A, D, F), 20 μm. Student’s t test was performed (two tailed, unpaired) and data represent means ± SEM. **p<0.01; ns, not statistically significant.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Excel file for the data shown in Figure 5A-F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig5-data1-v1.zip
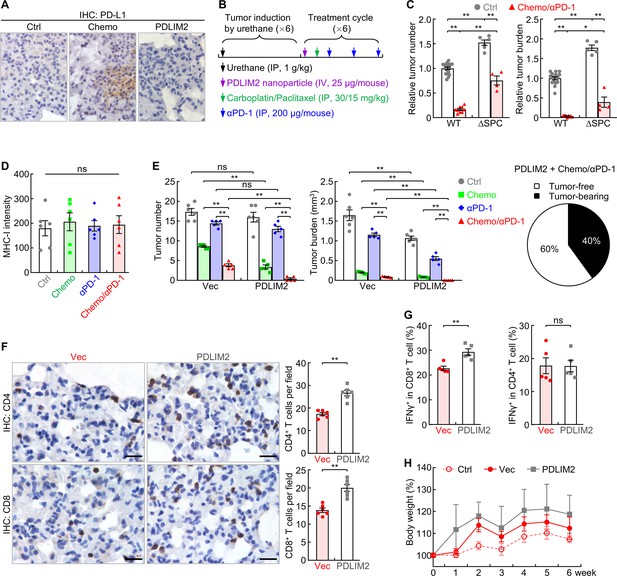
Combination of PDLIM2 nanotherapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy shows great efficacy in lung cancer treatment.
(A) IHC staining showing PD-L1 induction by chemotherapy but not PDLIM2 nanotherapy. (B) Schedule of lung cancer induction and treatment. (C) Urethane model showing high resistance of lung tumors to the chemo and αPD-1 combination therapy in lung epithelial specific PDLIM2 deletion mice (ΔSPC) (n≥4). (D) IHC staining showing no MHC-I induction by chemotherapy, PD-1 immunotherapy or their combination (n=6). (E) Tumor examination showing complete remission of all lung tumors in 60% of mice by combination of the three therapies (n≥5). (F) IHC staining showing increased TILs by PDLIM2 nanotherapy in mice treated with anti-PD-1 and chemotherapeutic drugs (n=6). (G) FACS analysis showing increased lung CD8+ T-cell activation by PDLIM2 nanotherapy in mice treated with anti-PD-1 and chemotherapeutic drugs (n=5). (H) No significant effect of PDLIM2 nanotherapy on the body weight of mice treated with anti-PD-1 and chemotherapeutic drugs (n=5). Scale bar in (A and F), 20 μm. Student’s t test was performed (two tailed, unpaired) and data represent means ± SEM in (c–g). *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ns, not statistically significant.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Excel file for the data shown in Figure 6C-H.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig6-data1-v1.zip
PDLIM2 nanotherapy causes no obvious toxicity in major organs.
(H & E) staining showing comparable toxicity in lung, liver, kidney, and spleen between Vec and PDLIM2 group in the context of combinational chemotherapy and PD-1 blockade immunotherapy (n=5). Scale bar: 50 µm.
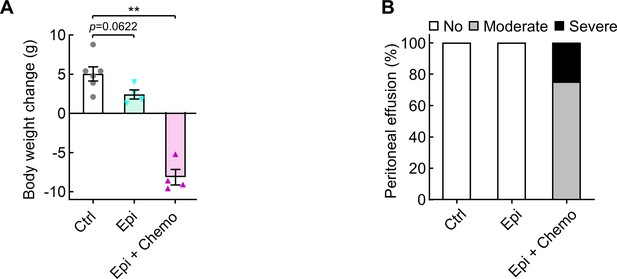
Epigenetic drugs cause body weight loss in mice with lung cancer.
Mice were i.p. injected with urethane (1 g/kg) for 6 weeks to induce lung tumors, and then treated for 6 weeks with 5-aza-dC and MS-275 (Epi, i.p., 1 mg/kg each, twice per week), carboplatin and paclitaxel (Chemo, i.p., 30 mg/kg and 15 mg/kg, respectively, once per week), or their combinations. (A) Body weight change between prior to the first treatment and the sacrifice endpoint. (B) Percentage of mice with peritoneal effusion (n ≥ 4). Excel file for the data shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 3.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Excel file for the data shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig6-figsupp2-data1-v1.zip
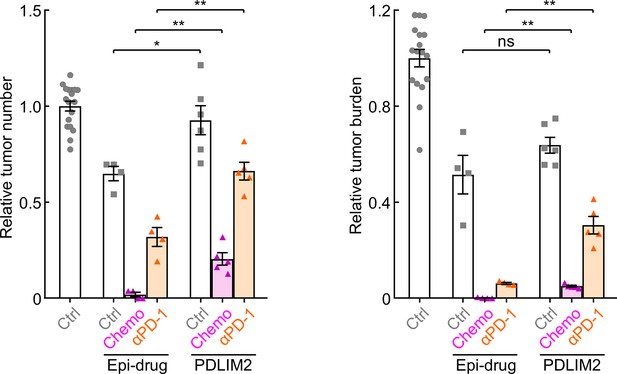
Epigenetic drugs show better efficacy in lung cancer treatment.
Mice were i.p. injected with urethane (1 g/kg) for 6 weeks to induce lung tumors, and then treated with 5-aza-dC and MS-275 (Epi, i.p., 1 mg/kg each, twice per week), carboplatin and paclitaxel (Chemo, i.p., 30 mg/kg and 15 mg/kg, respectively, once per week), anti-PD-1 antibody (aPD-1, i.p., 200 µg/mouse, three times per week), PDLIM2-expression plasmids containing nanoparticles (i.v., 25 µg plasmid/mouse, once per week), or their combinations for 6 weeks before they were sacrificed for tumor examination (n≥4).
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Excel file for the data shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-fig6-figsupp3-data1-v1.zip
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Homo sapiens) | PDLIM2 | GenBank | 64236 | |
| Gene (Mus musculus) | Pdlim2 | GenBank | 213019 | |
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | FVB/N | Ref# 6, 28 | Pdlim2flx/flx/SP-C-rtTAtg/−/(tetO)7CMV-Cretg/tg (ΔSPC) | |
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | BAB/c | Ref# 6, 19, 21, 22 | Pdlim2-/- | |
| Commercial assay or kit | in vivo-jetPEI | Polyplus Transfection | 101000030 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCMV-myc-Pdlim2 | This paper | PDLIM2 plasmid | PDLIM2 expression plasmid |
| Chemical compound, drug | Carboplatin | AdipoGen | AG-CR1-3591 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Paclitaxel | AdipoGen | AG-CN2-0045 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | Lung cancer cell lines | Ref# 6 | Calu-6 (RRID:CVCL_0236) H727 (RRID:CVCL_1584) H23 (RRID:CVCL_1547) H358 (RRID:CVCL_1559) SKLU-1 (RRID:CVCL_0629) SW1573 (RRID:CVCL_1720) CALU-1 (RRID:CVCL_0608) 128-88 T (RRID:CVCL_A2AG) H1299 (RRID:CVCL_0060) 273T (RRID:CVCL_Y296) HCC827 (RRID:CVCL_2063) H1650 (RRID:CVCL_1483) H3255 (RRID:CVCL_6831) 343T (RRID:CVCL_A2AK) Calu-3 (RRID:CVCL_0609) H1435 (RRID:CVCL_1470) H1793 (RRID:CVCL_1496) H596 (RRID:CVCL_1571) H838 (RRID:CVCL_1594) H1838 (RRID:CVCL_1594) A-549 (RRID:CVCL_0023) H1975 (RRID:CVCL_1511) | Cell lines maintained in the laboratories of Dr. Gutian Xiao and Dr Zhaoxia Qu |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | nontumorigenic bronchial epithelial cell line from normal adult | ATCC | NL20 (RRID:, CVCL_3756, ATCC# CRL-2503) | |
| Software | Flow data acquisition and analysis | BD Biosciences | Accuri C6 | |
| Software | Flow data acquisition | BD Biosciences | FACSDiva | |
| Software | Flow data analysis | FlowJo | FlowJo | |
| Software | Data statistical analysis and graph presentation | GraphPad | Graphpad Prism |
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 1
Antibodies and primers used.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/89638/elife-89638-supp1-v1.docx





