Rho GTPase signaling and mDia facilitate endocytosis via presynaptic actin
Figures
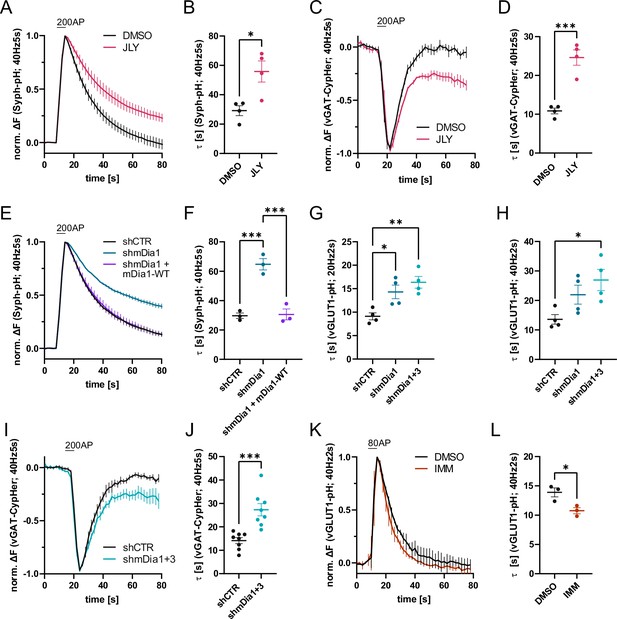
Actin dynamics and actin-nucleating mDia1/3 proteins facilitate synaptic vesicle (SV) endocytosis.
(A) Averaged normalized Synaptophysin-pHluorin (Syph-pH) fluorescence traces from transfected hippocampal neurons stimulated with 200 action potentials (APs) (40 Hz, 5 s) at physiological temperature (37.5 °C). Neurons were treated with 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or JLY cocktail (containing 8 µM Jasplakinolide, 5 µM Latrunculin A, and 10 µM Y-27632) as indicated. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from nDMSO = 23 videos; nJLY = 36 videos. (B) Endocytic decay constants (τ) of Synaptophysin-pHluorin traces in A: τDMSO = 29.1±3.4 s; τJLY = 55.8±7.2 s; p<0.05, two-tailed student’s t-test. Data shown represent mean ± SEM. (C) Averaged normalized bleach-corrected vGAT-CypHer fluorescence traces from hippocampal neurons treated with DMSO or JLY cocktail in response to 200 AP (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from nDMSO = 23 videos; nJLY = 29 videos. (D) Endocytic decay constants of vGAT-CypHer traces in C: τDMSO = 10.9±0.7 s, τJLY = 24.6±2.0 s; p<0.001, two-tailed unpaired student’s t-test. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM. (E) Averaged normalized Synaptophysin-pHluorin fluorescence traces from hippocampal neurons transfected with shRNA-encoding plasmids against no mammalian target (shCTR) or Diaph1 (shmDia1) in response to 200 AP (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. Neurons were co-transfected with mDia1-mCherry (mDia1-WT) or mCherry alone (shCTR & shmDia1) to exclude artifacts from overexpression. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nshCTR = 28 videos, nshmDia1=21 videos, nshmDia1 + mDia1-WT=21 videos. (F) Endocytic decay constants of Synaptophysin-pHluorin traces in E: τshCTR = 29.7±1.9 s; τshmDia1 = 64.7 ± 3.9 s; τshmDia1 + mDia1-WT = 30.6±3.7 s; pshCTR vs shmDia1 <0.001, pshmDia1 vs shmDia1 + mDia1-WT<0.001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test. Data shown represent mean ± SEM. (G) Endocytic decay constants of averaged normalized vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (vGLUT1)-pHluorin fluorescence traces (Figure 1—figure supplement 1I) from hippocampal neurons transduced with shCTR (τshCTR = 9.1±0.8 s), shmDia1 (τshmDia1 = 14.3±1.5 s), or shmDia1 +3 (τshmDia1+3 = 16.4±1.3 s) in response to 40 AP (20 Hz, 2 s) stimulation (pshCTR vs shmDia1 <0.05, pshCTR vs shmDia1+3 < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test). Data shown represent mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from nshCTR = 17 videos; nshmDia1=19 videos; nshmDia1+3 = 18 videos. (H) Endocytic decay constants of averaged normalized vGLUT1-pHluorin fluorescence traces (Figure 1—figure supplement 1K) of neurons transduced with lentiviral vectors encoding shCTR (τshCTR = 13.6±1.6 s), shmDia1 (τshmDia1 = 22.0±3.2 s) or shmDia1 +3 (τshmDia1+3 = 26.9±3.6 s) in response to 80 AP (40 Hz, 2 s) stimulation (pshCTR vs shmDia1+3 < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test). Data shown represent mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from nshCTR = 12 videos, nshmDia1=15 videos, nshmDia1+3 = 18 videos. (I) Averaged normalized bleach-corrected vGAT-CypHer fluorescence traces from hippocampal neurons transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 +3 in response to 200 AP (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM. N=8 independent experiments from nshCTR = 37 videos, nshmDia1+3 = 35 videos. (J) Endocytic decay constants of vesicular γ aminobutyric acid transporter (vGAT)-CypHer traces in I: τshCTR = 14.1±1.3 s; τshmDia1+3 = 27.3±2.6 s; p<0.001, two-tailed unpaired student’s t-test. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM. (K) Averaged normalized vGLUT1-pHluorin fluorescence traces from transduced neurons in response to 80 AP (40 Hz, 2 s) stimulation. Cells were treated with 0.1% DMSO or 10 µM mDia activator (IMM) in the imaging buffer. Data shown represent mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nDMSO = 18 videos; nIMM = 16 videos. (L) Endocytic decay constants of vGLUT1-pHluorin traces in K: τDMSO = 14.9±0.8 s; τIMM = 9.8±0.5 s; p<0.05, two-tailed unpaired student’s t-test. Data shown represent mean ± SEM.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Numerical source data for Figure 1A–L.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig1-data1-v2.zip
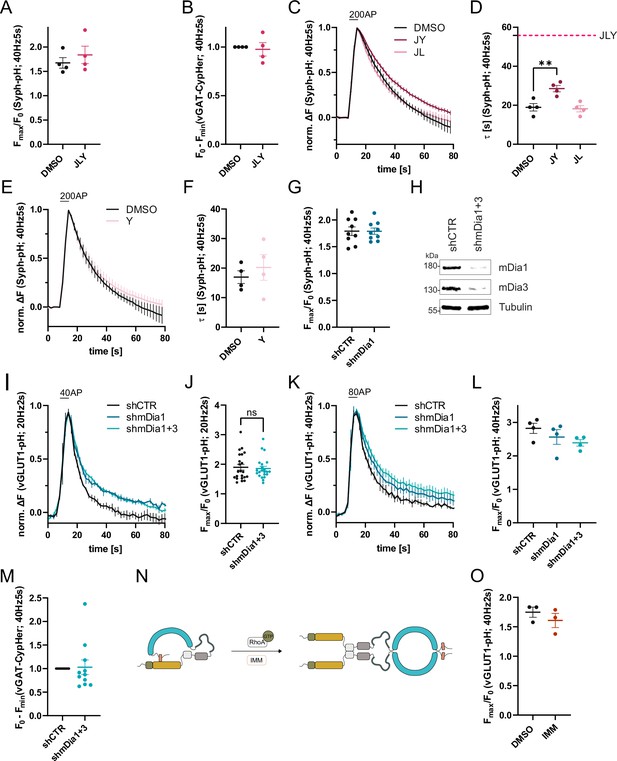
Role of formins and mDia1/3 in synaptic vesicle (SV) endocytosis.
(A) Maxima of background-corrected Synaptophysin-pHluorin (Syph-pHluorin) fluorescence traces (surface normalized) for neurons treated with 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (1.7 ± 0.1) or JLY cocktail (1.8 ± 0.2) in response to 200 action potential (AP) stimulation (40 Hz, 5 s). Data represent mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from nDMSO = 23 videos; nJLY = 36 videos. (B) Minima of background-corrected vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (vGAT)-CypHer fluorescence traces (surface normalization) for neurons treated with 0.1% DMSO or JLY cocktail (1.0± 0.1) in response to 200 AP stimulation (40 Hz, 5 s). Data represent mean ± SEM. Values for DMSO were set to 1. N=4 independent experiments from nDMSO = 23 videos; nJLY = 29 videos. (C) Averaged normalized Syph-pH fluorescence traces from transfected hippocampal neurons treated with 0.1% DMSO, JY or JL combinations (containing 8 µM Jasplakinolide, 5 µM Latrunculin A, and 10 µM Y-27632) stimulated with 200 APs (40 Hz, 5 s). Data shown represent the mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from nDMSO = 24 videos; nJY = 19 videos; nJL = 21 videos. (D) Endocytic decay constants of fluorescence traces in C: τDMSO = 19.0±1.9 s; τJY = 28.5±1.6 s; τJL = 18.2 ± 1.6 s; pDMSO vs JY <0.01, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test. Data shown represent mean ± SEM. (E) Averaged normalized Syph-pH fluorescence traces from transfected hippocampal neurons treated with 0.1% DMSO or 10 µM Y-27632 following 200 AP (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from nDMSO = 25 videos; nY = 18 videos. (F) Endocytic decay constants of fluorescence traces in E: τDMSO = 17.0±2.2 s; τY = 20.2±4.3 s. Data shown represent mean ± SEM. (G) Maxima of background-corrected Syph-pHluorin fluorescence traces (surface normalized) for neurons transfected with shCTR (1.8±0.1) or shmDia1 (1.8 ± 0.1) in response to 200 AP stimulation (40 Hz, 5 s). Data represent mean ± SEM. N=9 independent experiments from nshCTR = 49 videos; nshmDia1=42 videos. (H) Analysis of knockdown efficiency of lentiviral particles carrying shRNA against no mammalian target (shCTR) or Diaph1 and Diaph2 genes (shmDia1 +3) in mouse hippocampal cultures harvested 12 days after transduction. Protein abundance of mDia1, mDia3, and Tubulin were immunoblotted with specific antibodies. (I) Averaged normalized vGLUT1-pHluorin fluorescence traces from stimulated (40 APs; 20 Hz, 2 s) hippocampal neurons transduced with lentiviruses encoding shCTR, shmDia1, or both shmDia1 and shmDia3 combined (shmDia1 +3). Data represent mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from nshCTR = 17 videos, nshmDia1=19 videos, nshmDia1+3 = 18 videos. The corresponding endocytic decay constants are shown in Figure 1G. (J) Maxima of background-corrected vGLUT1-pHluorin fluorescence traces (surface normalized) for neurons transduced with shCTR (1.9±0.1) or shmDia1 +3 (1.9±0.1) in response to 40 AP stimulation (20 Hz, 2 s). Data represent mean ± SEM. N=22 independent experiments from nshCTR = 105 videos and nshmDia1+3 = 128 videos. (K) Averaged normalized vGLUT1-pHluorin fluorescence traces for neurons transduced with shCTR, shmDia1, or shmDia1 +3 in response to 80 AP stimulation (40 Hz, 2 s). Data represent mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from nshCTR = 12 videos; nshmDia1=15 videos; nshmDia1+3 = 18 videos. Corresponding endocytic decay constants are shown in Figure 1H. (L) Maxima of background-corrected vGLUT1-pHluorin fluorescence traces (surface normalized) for neurons transduced with shCTR (2.8±0.2), shmDia1 (2.6±0.2), or shmDia1 +3 (2.4±0.1) in response to 80 AP stimulation (40 Hz, 2 s). Data represent mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from nshCTR = 12 videos; nshmDia1=15 videos and nshmDia1+3 = 18 videos. (M) Minima of background-corrected vGAT-CypHer fluorescence traces (surface normalized) for neurons transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 +3 (1.0±0.2) in response to 200 AP stimulation (40 Hz, 5 s). Data represent mean ± SEM. Values for shCTR were set to 1. N=11 independent experiments from nshCTR = 45 videos and nshmDia1+3 = 42 videos. (N) Schematic representation of the regulation of mDia1. Binding of RhoA-GTP to the Rhotekin-Rho binding domain (RBD) (green) or application of mDia1 activator (IMM) competes with the intramolecular interaction of the N-terminal Diaphanous inhibitory domain (DID) (yellow) with the C-terminal Diaphanous autoinhibitory domain (DAD) (red) domain (see Figure 3A for domain structure). The release of autoinhibition leads to the dimerization of mDia formins in solution. (O) Maxima of background-corrected vGLUT1-pHluorin fluorescence traces (surface normalized) for neurons treated with 0.1% DMSO (1.7±0.1) or mDia activator (IMM; 1.6±0.1) in response to 80 AP stimulation (40 Hz, 2 s). Data represent mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nDMSO = 18 videos; nIMM = 16 videos.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Numerical source data of Figure 1—figure supplement 1A, B, C, D, E, F, G, I, J, K, L, M, O.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Original scan for the anti-mDia1 immunoblot from Figure 1—figure supplement 1H.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig1-figsupp1-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 3
Original scan for the anti-mDia3 immunoblot from Figure 1—figure supplement 1H.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig1-figsupp1-data3-v2.zip
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 4
Original scan for the anti-tubulin immunoblot from Figure 1—figure supplement 1H.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig1-figsupp1-data4-v2.zip
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 5
Original scans for immunoblots from Figure 1—figure supplement 1H with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig1-figsupp1-data5-v2.zip
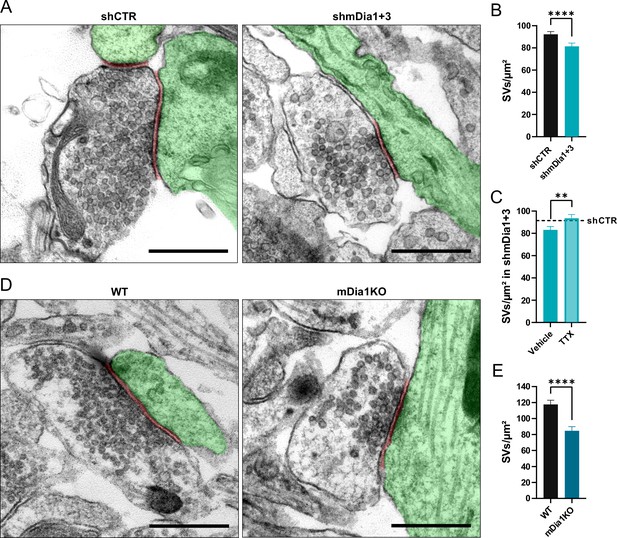
Loss of mDia1/3 causes an activity-dependent reduction of the synaptic vesicle (SV) pool.
(A) Representative synaptic electron micrographs from hippocampal neurons transduced with lentiviruses encoding shCTR or shmDia1 +3, targeting Diaph1/2 genes. Postsynapse and postsynaptic cleft are colored in green and maroon, respectively. Scale bar, 250 nm. (B) Average number of SVs per μm2 in boutons from shCTR (92.2±2.5) and shmDia1 +3 (81.4±2.9; p<0.0001, Mann-Whitney test) treated neurons. Data shown represent mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nshCTR = 326 synapses, nshmDia1+3 = 321 synapses. (C) Average number of SVs per μm2 in synaptic boutons from hippocampal neurons transduced with lentiviruses encoding shmDia1 +3 and treated with 0.1% Vehicle (10 µM NaOAc; 83.2±2.9) or 1 µM Tetrodotoxin (TTX; 93.8±3.1; p<0.01, Mann-Whitney test) for 36 hr before chemical fixation. Data shown represent mean ± SEM from two independent experiments and nVehicle = 225 synapses, nTTX = 221 synapses. Representative synaptic electron micrographs are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1A. The dotted line represents the average SV numbers/μm2 in shCTR boutons treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) from the same experiments as a reference (Figure 2—figure supplement 1A), (B). (D) Representative electron micrographs of synapses in hippocampal neurons from wild-type (WT) or Diaph1 (encoding mDia1) knockout (KO) mice. Postsynapse and postsynaptic cleft are colored in green and maroon, respectively. Scale bar, 250 nm. (E) Average number of SVs per μm2 in WT (117.6±5.3) and mDia1 KO (84.6±5.2; p<0.0001, Mann-Whitney test) boutons. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM from nWT = 103, nmDia1KO = 96 synapses (N=1).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Numerical source data for Figure 2C, D and G.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig2-data1-v2.zip
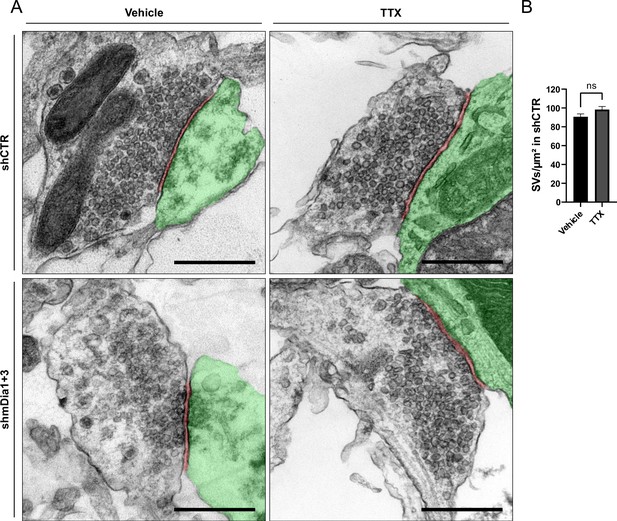
Synaptic vesicle (SV) depletion in mDia1/3-depleted neurons is activity-dependent.
(A) Representative synaptic electron micrographs from neurons transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 +3 and treated with 0.1% Vehicle or 1 µM TTX for 36 hr before fixation. Postsynapse and postsynaptic cleft are colored in green and maroon, respectively. Scale bar, 250 nm. (B) Average number of SV per μm2 in synaptic boutons of neurons transduced with shCTR and treated with 0.1% Vehicle (A; 90.7±3.1) or 1 µM TTX (B; 98.4±3.3) for 36 hr before chemical fixation. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM from two independent experiments and nVehicle = 180, nTTX = 204 synapses.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Numerical source data of Figure 2—figure supplement 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
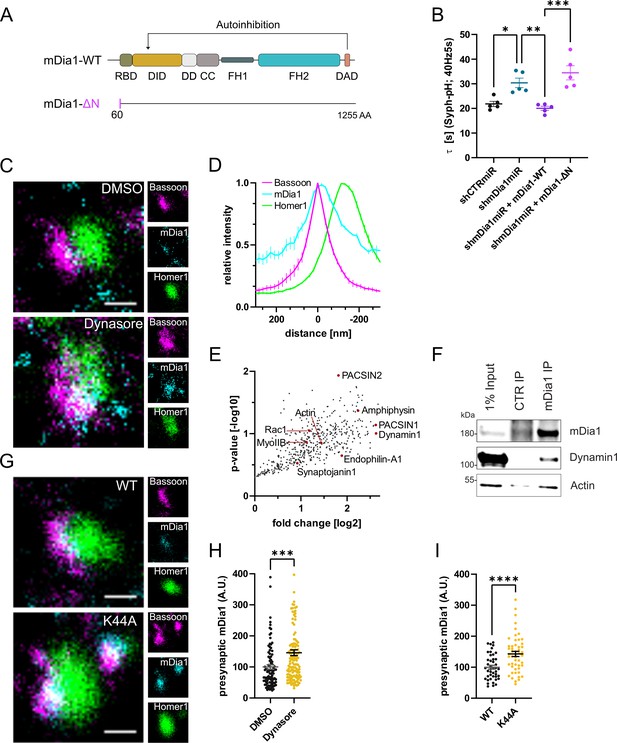
mDia1 associates with endocytic proteins and localizes to presynaptic sites.
(A) Schematic representation of functional domains of mDia1. Rho-binding domain (RBD), Diaphanous inhibitory domain (DID), Dimerization domain (DD), Coiled coil domain (CC), Formin homology domain 1 (FH1), Formin homology domain 2 (FH2), Diaphanous autoinhibitory domain (DAD). The unstructured N-terminus (first 60 amino acids) contains three basic stretches and was truncated in the ΔN mutant. (B) Endocytic decay constants of Synaptophysin-pHluorin traces (Figure 3—figure supplement 1C) from hippocampal neurons transfected with shRNAmiR against no mammalian target (shCTRmiR) or Diaph1 (shmDia1miR) in response to 200 action potential (AP) (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. For rescue experiments, neurons were co-transfected with plasmids encoding mDia1-WT-mCherry (τshmDia1miR + mDia1-WT=20.0±0.8 s), mDia1-ΔN-mCherry (τshmDia1miR + mDia1-ΔN=34.5±2.9 s), or mCherry alone (τshCTRmiR = 21.8±1.1 s, τshmDia1miR = 30.4±1.9 s) to exclude artifacts from overexpression (pshCTRmiR vs shmDia1miR < 0.05; pshmDia1miR vs shmDia1miR + mDia1-WT<0.01; pshmDia1miR + mDia1-WT vs shmDia1miR + mDia1-ΔN<0.01, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test). Data shown represent mean ± SEM. N=5 independent experiments from nshCTRmiR = 41 videos, nshmDia1miR = 51 videos, nshmDia1miR + mDia1-WT=35 videos, nshmDia1miR + mDia1-ΔN=37 videos. (C) Representative three-channel time-gated stimulated emission depletion (STED) images of synapses from hippocampal cultures treated with 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or 80 μM Dynasore for 10 min before fixation and immunostained for Bassoon (presynaptic marker, magenta), mDia1 (cyan) and Homer1 (postsynaptic marker, green). Scale bar, 250 nm. (D) Averaged normalized line profiles for synaptic distribution of mDia1 and Homer1 relative to Bassoon (Maximum set to 0 nm). Data represent mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from n=235 synapses. (E) Volcano plot of proteins associating with synaptic mDia1 analyzed by label-free proteomics of anti-mDia1 versus control (CTR) immunoprecipitates from detergent-extracted mouse synaptosomes (P2’ fraction). The logarithmic ratios of protein intensities are plotted against negative logarithmic p-values derived from a two-tailed student’s t-test. N=3 independent experiments. Each dot represents one protein. Selected cytoskeletal hits include: Actin, Myosin IIB (MyoIIB), and Rac1. Selected endocytic hits include Amphiphysin (p<0.05), Dynamin1, Endophilin-A1, PACSIN1, PACSIN2 (p<0.05), and Synaptojanin1. (F) Endogenous immunoprecipitation of mDia1 from detergent-extracted mouse synaptosomes (P2’ fraction) using mDia1-specific antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting for mDia1, Dynamin1, and β-Actin. (G) Representative three-channel time-gated STED images of synapses from hippocampal cultures transduced with wild-type Dynamin1 (WT) or GTPase-deficient Dynamin1 (K44A) in response to 200 AP (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. Cells were immunostained for Bassoon (magenta), mDia1 (cyan), and Homer1 (green). Scale bar, 250 nm. (H) Presynaptic mDia1 levels in synapses treated with 0.1% DMSO (100±7.3) or 80 µM Dynasore (145.8±9.3; p=0.0001; one sample Wilcoxon test) for 10 min in response to 200 AP (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. Absolute line profiles of mDia1 overlapping with Bassoon (presynapse) distribution were integrated. Data shown are normalized to DMSO (set to 100) and expressed as mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nDMSO = 92 synapses, nDynasore = 135 synapses. (I) Presynaptic mDia1 levels in synapses from hippocampal neurons transduced with wild-type Dynamin1 (WT; 100±6.2) or GTPase-deficient Dynamin1 (K44A; 142.9±8.3, p<0.0001, one sample Wilcoxon test) in response to 200 AP (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. Line profiles of mDia1 overlapping with Bassoon distribution were integrated. Data shown are normalized to Dynamin1-WT (set to 100) and expressed as mean ± SEM. N=2 independent experiments from nWT = 43 synapses, nK44A = 51 synapses.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Numerical source data for Figure 3B, D, E, H and K.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Original scan for the anti-mDia1 and anti-Dynamin1 immunoblots from Figure 3F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 3
Original scan for the anti-Actin immunoblot from Figure 3F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-data3-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 4
Original scans for immunoblots from Figure 3F with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-data4-v2.zip
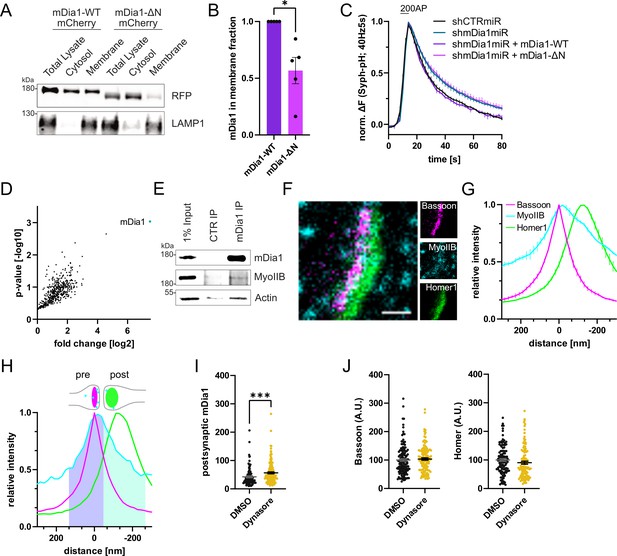
mDia1 binds membranes and localizes to presynaptic endocytic sites.
(A) Membrane levels of mDia1-WT-mCherry versus mDia1-ΔN-mCherry proteins overexpressed in HEK293T cells. Membrane and cytosolic cellular fractions were isolated by ultracentrifugation and analyzed by immunoblotting with specific antibodies (LAMP1) and in-gel fluorescence of mCherry tags. (B) Densitometric quantification of mDia1-WT versus mDia1-ΔN (0.6±0.1; p<0.05, one sample t-test) membrane-associated protein levels. Data shown are normalized to mDia1-WT (set to 1) and expressed as mean ± SEM. Representative immunoblot is shown in A. N=5 independent experiments. (C) Averaged normalized Synaptophysin-pHluorin fluorescence from stimulated (200 action potentials (APs), 40 Hz, 5 s) hippocampal neurons transfected with shCTRmiR or shmDia1miR. For rescue experiments, neurons were co-transfected with plasmids encoding mDia1-WT-mCherry, mDia1-ΔN-mCherry or mCherry alone (shCTRmiR & shmDia1miR). Endocytic decay constants are shown in Figure 3B. (D) Full volcano plot of proteins from Figure 3E associating with synaptic mDia1 analyzed by label-free proteomics of anti-mDia1 versus control (CTR) immunoprecipitates from detergent-extracted mouse synaptosomes (P2’ fraction). The cyan dot shows the specific enrichment of mDia1 as the bait protein of the immunoprecipitation (p<0.001, two-tailed student’s t-test). N=3 independent experiments. (E) Endogenous co-immunoprecipitation of Myosin IIB by mDia1 from detergent-extracted mouse synaptosomes (P2’ fraction). Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting using specific antibodies against mDia1, Myosin IIB (MyoIIB), and β-Actin. (F) Representative three-channel time-gated STED image of a synapse from hippocampal cultures fixed and immunostained for Bassoon (presynaptic marker, magenta), Myosin IIB (cyan), and Homer1 (postsynaptic marker, green). Scale bar, 250 nm. (G) Averaged normalized line profiles for synaptic distribution of Myosin IIB and Homer1 relative to Bassoon (Maximum set to 0 nm). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from n=267 synapses. (H) Rationale for quantification of presynaptic protein levels of interest. The presynapse was defined by the normalized Bassoon distribution (purple fraction, cut off at the cross-section with the Homer1 profile), and corresponding absolute individual synaptic line profiles were integrated. (I) Postsynaptic F-Actin levels in synapses treated with 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (42.6±3.4) or 80 µM Dynasore (56.5±3.3; p<0.001, Mann-Whitney test) for 10 min before fixation from Figure 3C and H. Data shown are normalized to presynaptic DMSO values from Figure 3H (set to 100) and expressed as mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nDMSO = 92 synapses, nDynasore = 135 synapses. (J) Quantification of Bassoon and Homer1 levels in synapses treated with 0.1% DMSO (100.0±4.5 for Bassoon; 100.0±4.3 for Homer1) or 80 µM Dynasore (103.7±4.1 for Bassoon; 98.6±5.3) for 10 min before fixation. Data shown are normalized to DMSO values (set to 100) and expressed as mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nDMSO = 132 synapses, nDynasore = 128 synapses.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original scan for in-gel mCherry fluorescence from Figure 3—figure supplement 1A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Original scan for the anti-LAMP1 immunoblot from Figure 3—figure supplement 1A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-figsupp1-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 3
Original scans from Figure 3—figure supplement 1A with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-figsupp1-data3-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 4
Numerical source data of Figure 3—figure supplement 1B, C, D, G, I, J.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-figsupp1-data4-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 5
Original scans for mCherry fluorescence in gels used for analysis are shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-figsupp1-data5-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 6
Original scans for mCherry fluorescence in gels used for analysis are shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1B with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-figsupp1-data6-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 7
Original scan for the anti-mDia1 immunoblot from Figure 3—figure supplement 1E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-figsupp1-data7-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 8
Original scan for the anti-Myosin IIB immunoblot from Figure 3—figure supplement 1E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-figsupp1-data8-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 9
Original scan for the anti-Actin immunoblot from Figure 3—figure supplement 1E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-figsupp1-data9-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 10
Original scans for immunoblots in Figure 3—figure supplement 1E with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig3-figsupp1-data10-v2.zip
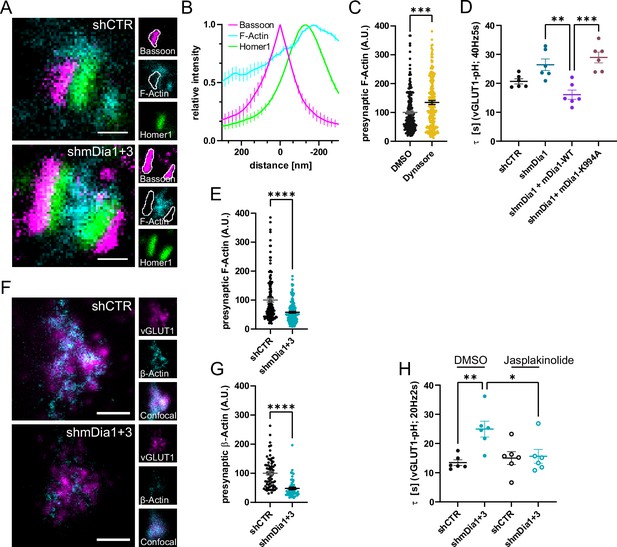
mDia facilitates synaptic vesicle (SV) endocytosis by regulating presynaptic F-actin.
(A) Representative three-channel time-gated stimulated emission depletion (STED) images of synapses from hippocampal cultures transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 +3, targeting Diaph1/2 genes, fixed and immunostained for Bassoon (presynaptic marker, magenta), F-Actin (cyan) and Homer1 (postsynaptic marker, green). Scale bar, 250 nm. (B) Averaged normalized line profiles for synaptic distribution of F-Actin and Homer1 relative to Bassoon (Maximum set to 0 nm). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from n=154 synapses. (C) Presynaptic F-Actin levels in synapses treated with 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (100±4.8) or 80 µM Dynasore (134.7±6.8; p=0.001, one sample Wilcoxon test) for 10 min before fixation (Representative images in Figure 4—figure supplement 1A). Cells were immunostained for Bassoon (magenta), F-Actin (cyan), and Homer1 (green). Absolute line profiles of F-Actin overlapping with Bassoon (presynapse) distribution were integrated. Data shown are normalized to DMSO (set to 100) and expressed as mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nDMSO = 207 synapses, nDynasore = 211 synapses. (D) Endocytic decay constants of vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (vGLUT1)-pHluorin traces from hippocampal neurons transduced with lentiviral particles encoding shCTR (τshCTR = 20.7 ± 0.9 s) or shmDia1 (τshmDia1 = 26.4±2.0 s) in response to 200 action potential (AP) (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. For rescue experiments, neurons were co-transduced with lentiviruses encoding mDia1-WT-SNAP (τshmDia1 + mDia1-WT=16.1±1.9 s) or mDia1-K994A-SNAP (τshmDia1 + mDia1-K994A=29.0±1.9 s) (pshmDia1 vs shmDia1 + mDia1-WT<0.01; pshmDia1 + mDia1-WT vs shmDia1 + mDia1-K994A<0.001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. N=6 independent experiments from nshCTR = 21 videos; nshmDia1=21 videos, nshmDia1 + mDia1-WT=16 videos, nshmDia1 + mDia1-K994A=19 videos. (E) Presynaptic F-Actin levels in synapses from hippocampal cultures transduced with shCTR (100±6.4) or shmDia1 +3 (58.1±2.9; p<0.001, one sample Wilcoxon test). Line profiles of F-Actin overlapping with Bassoon (presynapse) distribution were integrated. Data shown are normalized to shCTR (set to 100) and expressed as mean ± SEM. N=4 independent experiments from nshCTR = 155 synapses, nshmDia1+3 = 158 synapses. (F) Representative confocal and two-channel time-gated STED images of endogenous β-Actin (cyan) in vGLUT1 (magenta) positive boutons from hippocampal neurons transduced with lentiviruses encoding shCTR or shmDia1 +3. Scale bar, 250 nm. (G) Analysis of presynaptic endogenous β-Actin levels in vGLUT1 positive boutons from shCTR (100±6.3) and shmDia1 +3 (47.7±4.3; p<0.0001 one-sample Wilcoxon test) transduced neurons. β-Actin STED mean intensity was measured using a confocal vGLUT1 signal as a mask. Data shown are normalized to shCTR (set to 100) and expressed as mean ± SEM from two independent experiments and nshCTR = 67 synapses, nshmDia1+3 = 53 synapses. (H) Endocytic decay constants of vGLUT1-pHluorin traces (Figure 4—figure supplement 1H) for neurons transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 +3 in response to 40 AP (20 Hz, 2 s) stimulation. Neurons were pre-incubated with 0.1% DMSO or 1 µM Jasplakinolide (Jasp) for 30 min in the media before imaging (τshCTR + DMSO = 13.4±1.0 s, τshCTR + Jasp = 15.0±2.2 s, τshmDia1+3 + DMSO=25.0±2.7 s, τshmDia1+3 + Jasp=15.6±2.4 s; pshCTR vs shmDia1+3 < 0.01; pshmDia1+3 + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + Jasp<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. N=6 independent experiments from nshCTR + DMSO = 32 videos, nshmDia1+3 + DMSO=35 videos, nshCTR + Jasp = 33 videos; nshmDia1+3 + Jasp=34 videos.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Numerical source data for Figure 4B, C, D, E, G and H.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig4-data1-v2.zip
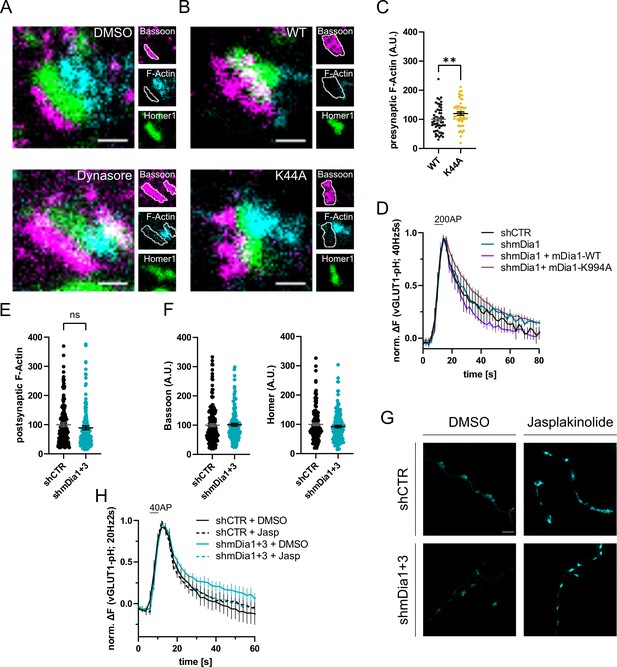
mDia1 regulates presynaptic actin and synaptic vesicle (SV) endocytosis.
(A) Representative three-channel time-gated stimulated emission depletion (STED) images of synapses from hippocampal cultures treated with 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or 80 µM Dynasore for 10 min. Cells were fixed and stained for Bassoon (magenta), F-Actin (cyan), and Homer1 (green). Scale bar, 250 nm. Corresponding analysis of presynaptic F-Actin levels is shown in Figure 4C. (B) Representative three-channel time-gated STED images of synapses from hippocampal cultures transduced with Dynamin1-WT or Dynamin1-K44A. Cells were fixed and stained for Bassoon (magenta), F-Actin (cyan), and Homer1 (green). Scale bar, 250 nm. (C) Presynaptic F-Actin levels in synapses from neurons transduced with Dynamin1-WT (100±5.9) or Dynamin1-K44A (119.8±6.2, p<0.01, one sample t-test) in B. Absolute line profiles of F-Actin overlapping with Bassoon (presynapse) distribution were integrated. Data shown are normalized to WT (set to 100) and expressed as mean ± SEM. nWT = 54 synapses, nK44A = 49 synapses. (D) Averaged normalized vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (vGLUT1)-pHluorin fluorescence traces for neurons transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 in response to 200 action potential (AP) (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. For rescue purposes, cells were co-transduced with mDia1-WT-SNAP or mDia1-K994A-SNAP. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. N=6 independent experiments from nshCTR = 21 videos; nshmDia1=21 videos; nshmDia1 + mDia1-WT=16 videos; nshmDia1 + mDia1-K994A=19 videos. Corresponding endocytic decay constants are shown in Figure 4D. (E) Postsynaptic F-Actin levels in synapses transduced with shCTR (100.0±6.4) or shmDia1 +3 (89.3±6.4) from Figure 4A and E. Data shown are normalized to shCTR values (set to 100) and expressed as mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nshCTR = 206 synapses, nshmDia1+3 = 135 synapses. (F) Quantification of Bassoon and Homer1 levels in synapses transduced with shCTR (100.0±4.7 for Bassoon; 100.0±4.5 for Homer1) or shmDia1 +3 (101.4±4.8 for Bassoon; 92.4±4.0). Data shown are normalized to DMSO values (set to 100) and expressed as mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nshCTR = 158 synapses and nshmDia1+3 = 159 synapses. (G) Representative STED images of endogenous β-Actin in vGLUT1 positive synapses in hippocampal neurons transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 +3 and treated with 0.1% DMSO or 1 µM Jasplakinolide for 45 min. Neurons were co-transfected with pOrange-GFP-β-Actin knock-in and vGLUT1-mCherry plasmids before fixation and immunostaining. Scale bar, 2.5 µm. (H) Averaged normalized vGLUT1-pHluorin fluorescence traces for neurons transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 +3 in response to 40 AP (20 Hz, 2 s) stimulation. Neurons were pre-incubated with 0.1% DMSO or 1 µM Jasplakinolide (Jasp) for 30 min in the cell media before imaging. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. N=6 independent experiments from nshCTR + DMSO = 32 videos, nshmDia1+3 + DMSO=35 videos, nshCTR + Jasp = 33 videos; nshmDia1+3 + Jasp=34 videos. The corresponding endocytic decay constants are shown in Figure 4I.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Numerical source data of Figure 4—figure supplement 1C, D, E, F, H.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
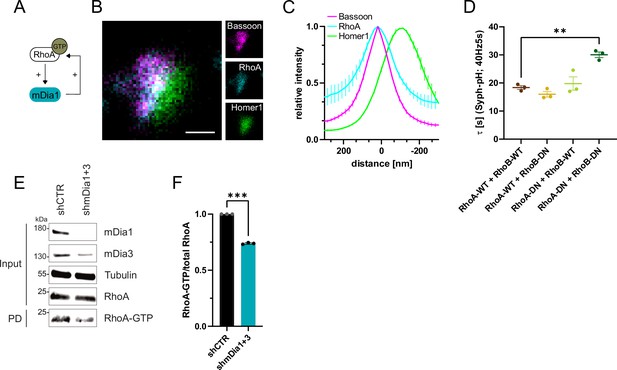
RhoA/B facilitates presynaptic endocytosis and are regulated by mDia1/3.
(A) Schematic representation of activation of mDia1 by RhoA-GTP and positive feedback loop of mDia1 on RhoA-GTP levels through GEF stimulation. (B) Representative three-channel time-gated STED image of synapses from hippocampal cultures, fixed and immunostained for Bassoon (magenta), RhoA (cyan), and Homer1 (green). Scale bar, 250 nm. (C) Averaged normalized line profiles for synaptic distribution of RhoA and Homer1 relative to Bassoon (Maximum set to 0 nm). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. N=5 independent experiments from n=230 synapses. (D) Endocytic decay constants of averaged normalized Synaptophysin-pHluorin fluorescence traces (Figure 5—figure supplement 1A) in response to 200 action potential (AP) (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. Neurons were transfected with the annotated combinations of plasmids encoding wild-type (WT) or dominant-negative (DN, T19N mutation) RhoA and RhoB (τRhoA-WT + RhoB-WT=18.4±0.7 s, τRhoA-WT + RhoB-DN = 16.0±1.0 s, τRhoA-DN + RhoB-WT=19.8±2.4 s, τRhoA-DN + RhoB-DN=30.1±1.0 s; pRhoA-WT + RhoB-WT vs RhoA-DN + RhoB-DN<0.01, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test). Data shown represent mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nRhoA-WT + RhoB-WT=21 videos, nRhoA-DN + RhoB-WT=31 videos, nRhoA-WT + RhoB-DN=23 videos, nRhoA-DN + RhoB-DN=22 videos. (E) Analysis of RhoA activity by RhoA-GTP pulldown (PD) from whole-cell lysates (input) of mouse hippocampal neurons expressing shCTR or shmDia1 +3 using immobilized Rhotekin as a bait. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting for mDia1, mDia3, RhoA, and Tubulin using specific antibodies. Input, 10% of material used for the pulldown. The contrast of pulldown and input blots was seperately adjusted for visualization purposes. (F) Densitometric quantification of RhoA-GTP normalized to total RhoA levels (input) in lysates from neurons transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 +3 (0.7±0.0, p<0.001, one sample t-test) from immunoblots exemplified in E. Values for shCTR were set to 1. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from N=3 independent experiments.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Numerical source data for Figure 5C, D and F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig5-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Original scans for the anti-mDia1, anti-Tubulin, anti-RhoA, and anti-mDia3 immunoblots from Figure 5E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig5-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 3
Original scans for immunoblots from Figure 5E with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig5-data3-v2.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 4
Original scans for the anti-RhoA immunoblots used for analysis are shown in Figure 5F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig5-data4-v2.zip
-
Figure 5—source data 5
Original scans for immunoblots used for analysis are shown in Figure 5F with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig5-data5-v2.zip
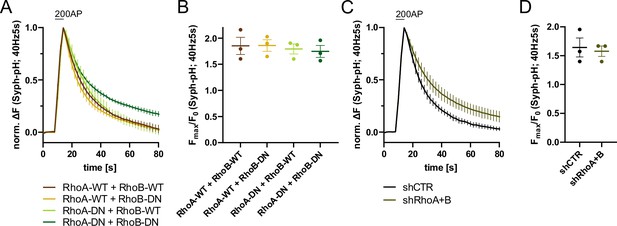
RhoA/B regulates synaptic vesicle (SV) endocytosis.
(A) Averaged normalized Synaptophysin-pHluorin fluorescence traces from stimulated (200 APs; 40 Hz, 5 s) hippocampal neurons transfected with plasmids encoding the indicated combinations of wild-type (WT) or DN RhoA and RhoB variants. Data represent mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nRhoA-WT + RhoB-WT=21 videos, nRhoA-DN + RhoB-WT=31 videos, nRhoA-WT + RhoB-DN=23 videos, nRhoA-DN + RhoB-DN=22 videos. Endocytic decay constants are shown in Figure 5D. (B) Maxima of background-corrected Syph-pHluorin fluorescence traces (surface normalized) for neurons transfected with indicated combinations of WT or DN RhoA and RhoB variants (1.9±0.2 for RhoA-WT+RhoB WT; 1.9±0.1 for RhoA-WT+RhoB DN; 1.8±0.1 for RhoA-DN +RhoB WT; 1.7±0.1 for RhoA-DN +RhoB DN) in response to 200 AP stimulation (40 Hz, 5 s). Data represent mean ± SEM. (C) Averaged normalized Synaptophysin-pHluorin fluorescence traces from stimulated (200 APs; 40 Hz, 5 s) hippocampal neurons transfected with shRNA against no mammalian target (shCTR) or against Rhoa and Rhob genes (shRhoA +B). Data represent mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nshCTR = 27 videos, nshRhoA+B = 25 videos. (D) Maxima of background-corrected Syph-pHluorin fluorescence traces (surface normalized) for neurons transfected with shCTR (1.6±0.2) or shRhoA +B (1.6±0.1) in response to 200 AP stimulation (40 Hz, 5 s). Data represent mean ± SEM.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Numerical source data of Figure 5—figure supplement 1A–D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
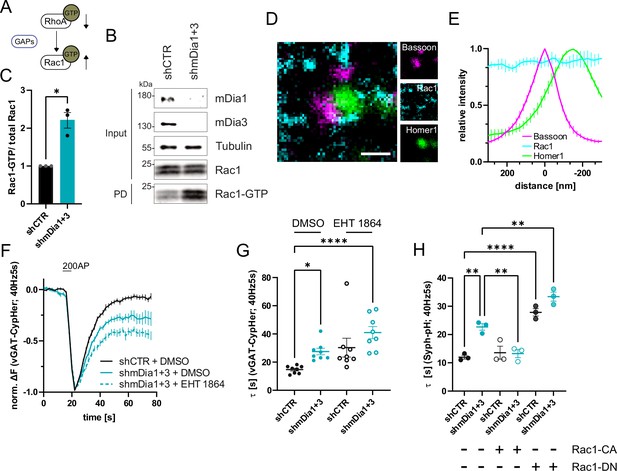
mDia1/3-Rho and Rac1 signaling facilitates presynaptic endocytosis.
(A) Schematic of the interplay between RhoA and Rac1 signaling via GTPase regulatory proteins (e.g. GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) among others) common for RhoA and Rac1. (B) Analysis of Rac1 activity by Rac1-GTP pulldown (PD) from whole-cell lysates (input) of mouse hippocampal neurons expressing shCTR or shmDia1 +3 utilizing immobilized PAK as a bait. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting for mDia1, mDia3, Rac1, and Tubulin using specific antibodies. Input, 10% of material used for the pulldown. The contrast of pulldown and input blots was seperately adjusted for visualization purposes. (C) Densitometric quantification of Rac1-GTP normalized to total Rac1 levels (input) in lysates from neurons transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 +3 (2.2±0.2; p<0.05, one sample t-test) from immunoblots exemplified in (B). Values for shCTR were set to 1. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from N=3 independent experiments. (D) Representative three-channel time-gated stimulated emission depletion (STED) image of synapses from hippocampal cultures, fixed and immunostained for Bassoon (magenta), Rac1 (cyan), and Homer1 (green). Scale bar, 250 nm. (E) Averaged normalized line profiles for synaptic distribution of Rac1 and Homer1 relative to Bassoon (Maximum set to 0 nm). Data represent mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from n=79 synapses. (F) Averaged normalized vGAT-CypHer fluorescence traces for neurons transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 +3 in response to 200 AP (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. Cells were acutely treated with 0.1% DMSO or 10 µM Rac1 Inhibitor (EHT 1864) in the imaging buffer. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM. N=8 independent experiments from nshCTR + DMSO = 46 videos, nshmDia1+3 + DMSO = 45 videos, nshCTR + EHT 1864 = 42 videos, nshmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 = 43 videos. (G) Endocytic decay constants of vGAT-CypHer traces in F: τshCTR + DMSO = 14.7±0.9 s, τshmDia1+3 + DMSO=27.5±2.3 s, τshCTR + EHT 1864 = 30.3±6.7 s, τshmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 = 41.0±4.3 s; pshCTR + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + DMSO<0.05, pshCTR + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 < 0.0001, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test. Data represent mean ± SEM. (H) Endocytic decay constants of Synaptophysin-pHluorin traces (Figure 6—figure supplement 1E) of neurons transduced with shCTR (τshCTR = 12.0±0.7 s) or shmDia1 +3 (τshmDia1+3 = 22.7±2.0 s) and transfected with constitutively active Rac1 (Rac1-CA; Q61L variant; τshCTR + Rac1-CA=13.6±1.2 s, τshmDia1+3 + Rac1-CA=13.3±1.4 s) or dominant negative Rac1 (Rac1-DN; T17N variant; τshCTR + Rac1-DN = 27.8±1.3 s, τshmDia1+3 + Rac1-DN = 33.4±1.6 s) in response to 200 AP (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation (pshCTR vs shmDia1+3 < 0.01; pshCTR vs shCTR + Rac1-DN<0.0001, pshCTR vs shmDia1+3 + Rac1-DN<0.01, pshmDia1+3 vs shmDia1+3 + Rac1-DN<0.01, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nshCTR = 12 videos, nshmDia1+3 = 23 videos; nshCTR + Rac1-CA=10 videos, nshmDia1+3 + Rac1-CA=14 videos, nshCTR + Rac1-DN = 9 videos; nshmDia1+3 + Rac1-DN = 13 videos.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Original scans for the anti-mDia3, anti-Tubulin, and anti-Rac1 immunoblots from Figure 6B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Original scan for the anti-mDia1 immunoblot from Figure 6B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 3
Original scans for immunoblots from Figure 6B with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-data3-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 4
Numerical source data for Figure 6C, E, F, G and H.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-data4-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 5
Original scans for the anti-Rac1 immunoblots used for analysis are shown in Figure 6C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-data5-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 6
Original scans for immunoblots used for analysis are shown in Figure 6C with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-data6-v2.zip
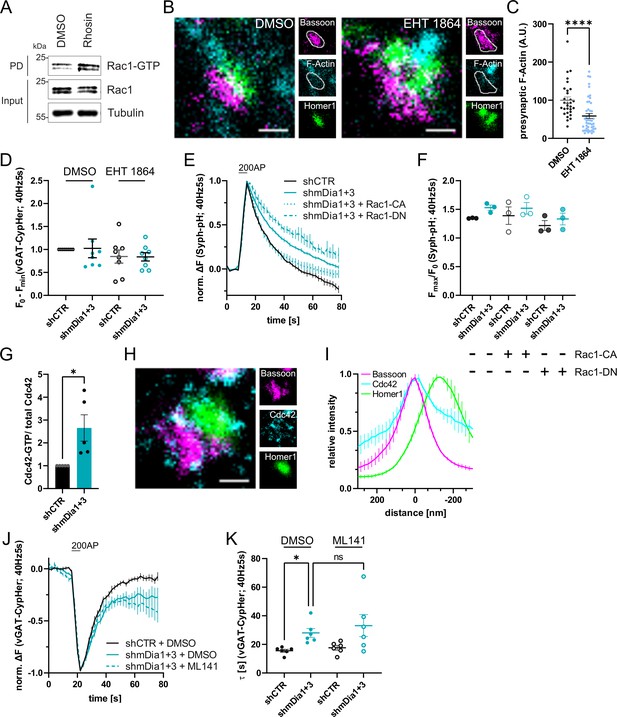
Cooperative action of mDia1/3 and Rac1 pathways in presynaptic endocytosis.
(A) Analysis of Rac1 activity by Rac1-GTP pulldown (PD) from whole-cell lysates (input) of mouse hippocampal cultures upon inhibition of Rho activity utilizing immobilized PAK as bait. Cells were treated with 0.1% DMSO or 10 µM Rho Inhibitor (Rhosin) for 2 hr before harvest. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting for Rac1 and Tubulin using specific antibodies. Input, 10% of material used for the pulldown. The contrast of pulldown and input blots was seperately adjusted for visualization purposes. (B) Representative three-channel time-gated STED images of synapses from hippocampal cultures treated with 0.1% DMSO or 10 µM Rac1 Inhibitor (EHT 1864) for 2 hr. Cells were fixed and stained for Bassoon (magenta), F-Actin (cyan), and Homer1 (green). Scale bar, 250 nm. (C) Presynaptic F-Actin levels in synapses of neurons treated with 0.1% DMSO (100±8.5) or 10 µM Rac1 Inhibitor (EHT 1864; 58.6±6.5; p<0.0001, one sample Wilcoxon test) for 2 hr. Line profiles of F-Actin overlapping with Bassoon (presynapse) distribution were integrated. Data shown are normalized to DMSO (set to 100) and expressed as mean ± SEM. nDMSO = 30, nEHT 1864 = 46 from two independent experiments. (D) Minima of background-corrected vGAT-CypHer fluorescence traces (surface normalized) for neurons treated with 0.1% DMSO (1.0±0.2 for shmDia1 +3) or 10 µM Rac1 Inhibitor (EHT 1864; 0.8±0.1 for shCTR; 0.8±0.1 for shmDia1 +3) in response to 200 AP stimulation (40 Hz, 5 s). Data represent mean ± SEM. Values were normalized to DMSO-treated shCTR (set to 1). N=8 independent experiments from nshCTR + DMSO = 46 videos, nshmDia1+3 + DMSO=45 videos, nshCTR + EHT 1864 = 42 videos, nshmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 = 43 videos. (E) Averaged normalized Synaptophysin-pHluorin fluorescence traces from stimulated (200 APs; 40 Hz, 5 s) hippocampal neurons transduced with lentiviruses encoding shCTR or shmDia1 +3 and transfected with plasmids for expression of constitutively-active Rac1 (Rac1-CA; Q61L variant) or dominant-negative Rac1 (Rac1-DN; T17N variant). Data represent mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nshCTR = 12 videos, nshmDia1+3 = 23 videos, nshCTR + Rac1-CA=10 videos, nshmDia1+3 + Rac1-CA=14 videos, nshCTR + Rac1-DN = 9 videos; nshmDia1+3 + Rac1-DN = 13 videos. The corresponding endocytic decay constants are shown in Figure 6H. (F) Maxima of background-corrected Synaptophysin-pHluorin fluorescence traces (surface normalized maximum values of traces shown in E) from stimulated (200 APs; 40 Hz, 5 s) hippocampal neurons transduced with lentiviruses encoding shCTR (Fmax/F0=1.3±0.0) or shmDia1 +3 (Fmax/F0=1.5±0.0) and transfected with plasmids encoding CA (Fmax/F0 shCTR + Rac1-CA=1.4±0.2; Fmax/F0 shmDia1+3 + Rac1-CA=1.5±0.1) or DN versions (Fmax/F0 shCTR + Rac1-DN = 1.2±0.1; Fmax/F0 shmDia1+3 + Rac1-DN = 1.3±0.1) of Rac1. Data represent mean ± SEM. (G) Densitometric quantification of Cdc42-GTP normalized to total Cdc42 levels in lysates from shmDia1 +3 transduced neurons (2.7±0.6; p<0.05, one sample t-test). Values for shCTR were set to 1. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from N=3 independent experiments. (H) Representative three-channel time-gated stimulated emission depletion (STED) image of synapses from hippocampal mouse cultures, fixed and immunostained for Bassoon (magenta), Cdc42 (cyan), and Homer1 (green). Scale bar, 250 nm. (I) Averaged normalized line profiles for synaptic distribution of Cdc42 and Homer1 relative to Bassoon (Maximum set to 0 nm). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (N=3; n=96 synapses). (J) Averaged normalized vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (vGAT)-CypHer fluorescence traces for neurons transduced with shCTR or shmDia1 +3 in response to 200 AP (40 Hz, 5 s) stimulation. Cells were acutely treated with 0.1% DMSO or 10 µM Cdc42 Inhibitor (ML141) in the imaging buffer. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM. N=6 independent experiments from nshCTR + DMSO = 31 videos, nshmDia1+3 + DMSO=33 videos, nshmDia1+3 + ML141=32 videos. (K) Endocytic decay constants of vGAT-CypHer traces in J: τshCTR + DMSO = 15.6±1.0 s, τshmDia1+3 + DMSO=28.0±3.1 s, τshCTR + ML141=17.6±1.6 s, τshmDia1+3 + ML141=33.1 ± 7.7 s; pshCTR + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + DMSO<0.01, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM. N=6 independent experiments from nshCTR + DMSO = 31 videos, nshmDia1+3 + DMSO=33 videos, nshCTR + ML141=29 videos, nshmDia1+3 + ML141=32 videos.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original scan for the anti-Rac1 immunoblots from Figure 6—figure supplement 1A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Original scan for the anti-Tubulin immunoblot from Figure 6—figure supplement 1A.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-figsupp1-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 3
Original scans for immunoblots in Figure 6—figure supplement 1A with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-figsupp1-data3-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 4
Numerical source data of Figure 6—figure supplement 1C, D, E, F, G, I, J, K.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-figsupp1-data4-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 5
Original scans for anti-Cdc42 immunoblots used for analysis are shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 1G.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-figsupp1-data5-v2.zip
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 6
Original scans for anti-Cdc42 immunoblots used for analysis are shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 1G with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig6-figsupp1-data6-v2.zip
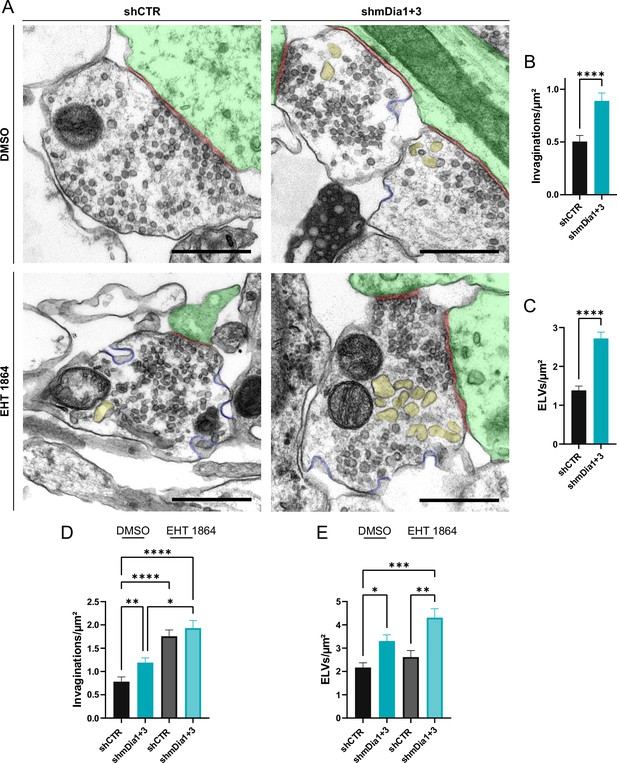
Defects in presynaptic ultrastructure induced by interference with mDia1/3-Rho and Rac1 signaling.
(A) Representative synaptic electron micrographs from hippocampal neurons transduced with lentiviruses encoding shCTR or shmDia1 +3, targeting Diaph1/2 genes, and treated with 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or 10 µM Rac1 Inhibitor (EHT 1864) for 2 hr before fixation. Invaginations and endosome-like vacuoles (ELVs) are colored in blue and yellow, while postsynapse and synaptic cleft are colored in green and maroon, respectively. Scale bar, 250 nm. (B) Average number of invaginations per μm2 in shCTR (0.5±0.1) and shmDia1 +3 (0.9±0.1; p<0.0001, Mann-Whitney test) boutons. Data represent mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nshCTR = 326 synapses, nshmDia1+3 = 323 synapses. (C) Average number of ELVs per μm2 in shCTR (1.4±0.1) and shmDia1 +3 (2.7±0.2; p<0.0001, Mann-Whitney test) boutons. Data represent mean ± SEM. N=3 independent experiments from nshCTR = 326 synapses, nshmDia1+3 = 323 synapses. (D) Average number of invaginations per μm2 in shCTR and shmDia1 +3 boutons treated with 0.1% DMSO (0.8±0.1 for shCTR; 1.2±0.1 for shmDia1 +3, pshCTR + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + DMSO<0.01) or 10 µM EHT 1864 (1.8±0.1 for shCTR, pshCTR + DMSO vs shCTR + EHT 1864 < 0.0001; 1.9±0.2 for shmDia1 +3, pshCTR + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 < 0.0001, pshmDia1+3 + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test) for 2 hr before fixation. Data represent mean ± SEM from nshCTR + DMSO = 144 synapses, nshmDia1+3 + DMSO=143 synapses, nshCTR + EHT 1864 = 136 synapses, nshmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 = 153 synapses. (E) Average number of ELVs per μm2 in shCTR and shmDia1 +3 boutons treated with 0.1% DMSO (2.2±0.2 for shCTR; 3.3±0.3 for shmDia1 +3, pshCTR + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + DMSO<0.05) or 10 µM EHT 1864 (2.6±0.3 for shCTR; 4.3±0.4 for shmDia1 +3, pshCTR + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 < 0.001, pshCTR + EHT 1864 vs shmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 < 0.01, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test) for 2 hr before fixation. Data represent mean ± SEM from nshCTR + DMSO = 144 synapses, nshmDia1+3 + DMSO=143 synapses, nshCTR + EHT 1864 = 136 synapses, nshmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 = 153 synapses.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Numerical source data from Figure 7B–E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig7-data1-v2.zip
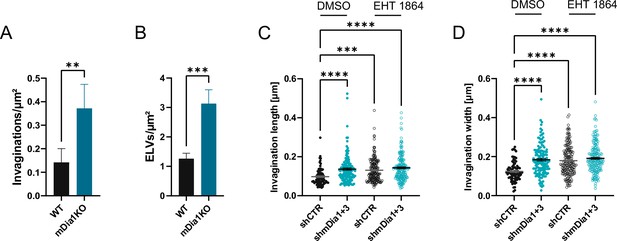
mDia1/3 and Rac1 cooperatively regulate the synaptic vesicle (SV) cycle and presynaptic ultrastructure.
(A) Average number of invaginations per μm2 in WT (0.1±0.1) and Diaph1 KO (mDia1KO; 0.4±0.1; p<0.01, Mann-Whitney test) boutons. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM from nWT = 103 synapses, nmDia1KO = 96 synapses. (B) Average number of endosome-like vacuoles (ELVs) per μm2 in wild-type (WT) (1.3±0.2) and mDia1KO (3.1±0.5; p<0.001, Mann-Whitney test) boutons. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM from nWT = 103 synapses, nmDia1KO = 96 synapses. (C) Average invagination length in shCTR and shmDia1 +3 boutons treated with 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (97.6±4.5 nm for shCTR; 136.8±6.0 nm for shmDia1 +3, pshCTR + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + DMSO<0.0001) or 10 µM EHT 1864 (130.9±4.5 nm for shCTR, pshCTR + DMSO vs shCTR + EHT 1864 < 0.001; 143.1±4.9 nm for shmDia1 +3, pshCTR + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 < 0.0001, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test) for 2 hr before chemical fixation. Data represent mean ± SEM from nshCTR + DMSO = 77 invaginations, nshmDia1+3 + DMSO=141 invaginations, nshCTR + EHT 1864 = 176 invaginations, nshmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 = 189 invaginations. (D) Average invagination width in shCTR and shmDia1 +3 boutons treated with 0.1% DMSO (124.5±5.6 nm for shCTR; 184.1±6.6 nm for shmDia1 +3, pshCTR + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + DMSO<0.0001) or 10 µM EHT 1864 (179.0±5.8 nm for shCTR, pshCTR + DMSO vs shCTR + EHT 1864 < 0.0001; 191.0±5.4 nm for shmDia1 +3, pshCTR + DMSO vs shmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 < 0.0001, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test) for 2 hr before chemical fixation. Data represent mean ± SEM from nshCTR + DMSO = 77 invaginations, nshmDia1+3 + DMSO=141 invaginations, nshCTR + EHT 1864 = 176 invaginations, nshmDia1+3 + EHT 1864 = 189 invaginations.
-
Figure 7—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Numerical source data of Figure 7—figure supplement 1A–D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-fig7-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip

Based on this analysis postsynaptic mDia1 levels were also elevated upon Dynasore treatment (new Figure 3-Supplement 1I).
In spite of this and consistent with the fact that the majority of mDia1 is localized at the presynapse, we found that postsynaptic F-actin levels were unchanged in mDia1/3depleted neurons (p = 0.0966; One sample t-test) (new Figure 4-Supplement 1E,F).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | C57BL/6 N wild-type | Leibniz Research Institute for Molecular Pharmacology | RRID:IMSR_JAX:000664 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | mDia1 KO | Bartolini Lab, Columbia University | Peng et al., 2003; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00170–2 | Genetic knockout of Diaph1 |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293T | American Type Culture Collection | Cat# CRL-3216; RRID:CVCL_0063 | |
| Antibody | β-Actin (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# A5441; RRID:AB_476744 | IB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Bassoon (guinea pig monoclonal) | Synaptic Systems | Cat# 141 318; RRID:AB_2927388 | IC (1:100) |
| Antibody | CDC42 (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab64533; RRID:AB_1310067 | IB (1:1000); IC (1:100) |
| Antibody | Dynamin1 (rabbit polyclonal) | Pietro D. Camilli | Shupliakov et al., 2002; DOI: 10.1126/science.276.5310.29 | IB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | GFP (mouse monoclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A-11120; RRID:AB_221568 | IC (1:2500) |
| Antibody | Homer1 (mouse monoclonal) | Synaptic Systems | Cat# 160 011; RRID:AB_2120992 | IC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Homer1 (rabbit polyclonal) | Synaptic Systems | Cat# 160 003; RRID:AB_887730 | IC (1:200) |
| Antibody | LAMP1 (rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9091; RRID:AB_2687579 | IB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | mDia1 (mouse monoclonal) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 610848; RRID:AB_398167 | IB (1:500); IP (2 µg) |
| Antibody | mDia1 (rabbit monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab129167; RRID:AB_11143749 | IC (1:100) |
| Antibody | mDia3 (rabbit polyclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# HPA005647; RRID:AB_1078657 | IB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Myosin IIb (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab684; RRID:AB_305661 | IC (1:100) |
| Antibody | Myosin IIb (rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 3404; RRID:AB_126421 | IB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | Rac1 (mouse monoclonal) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 610650; RRID:AB_397977 | IB (1:1000); IC (1:50) |
| Antibody | RFP (rabbit polyclonal) | Takara Bio | Cat# 632496; RRID:AB_10013483 | IC (1:500) |
| Antibody | RhoA (rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2117; RRID:AB_10693922 | IB (1:1000); IC (1:100) |
| Antibody | α-Tubulin (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# T9026; RRID:AB_47759 | IB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | IgG control (mouse monoclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 31903; RRID:AB_10959891 | IP (2 μg) |
| Antibody | vGAT-CypHer5E (rabbit polyclonal) | Synaptic Systems | Cat# 131 103CpH; RRID:AB_2189809 | Live-imaging (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgG Atto542 (donkey polyclonal) | Martin Lehmann | Gonschior et al., 2022; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32533-4 | IC (1:400) |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit IgG Atto542 (donkey polyclonal) | Martin Lehmann | Gonschior et al., 2022; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32533-4 | IC (1:400) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 594 (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A-11032; RRID:AB_2534091 | IC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 594 (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A-11037; RRID:AB_2534095 | IC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-guinea pig Atto647N (camelid monoclonal) | Synaptic Systems | Cat# N0602-At647N-S; RRID:AB_2744576 | IC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 647 (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A-21235; RRID:AB_2535804 | IC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IRDye 680RD (goat polyclonal) | LI-COR Biosciences | Cat# 925–68070; RRID:AB_2651128 | IB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit IRDye 680RD (goat polyclonal) | LI-COR Biosciences | Cat# 926–68071; RRID:AB_10956166 | IB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgG, IRDye 800CW (goat polyclonal) | LI-COR Biosciences | Cat# 926–32210; RRID:AB_621842 | IB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit IgG, IRDye 800CW (goat polyclonal) | LI-COR Biosciences | Cat# 926–32211; RRID:AB_621843 | IB (1:10000) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Phalloidin-Alexa Fluor 594 | AAT Bioquest | Cat# ABD-23158 | IC (1:1000) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Synaptophysin-pHluorin | Leon Lagnado | Gonschior et al., 2022; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32533-4 | Expresses rat Synaptophysin-2xpHluorin (inserted between Asn183 – Thr184) under a CMV promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | vGlut1-pHluorin | Volker Haucke | Bolz et al., 2023; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2023.08.016 | Expresses rat vGlut1-pHluorin (inserted between Gly99 – Gly100) under a hSyn1 promotor; lentiviral plasmid |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mCherry | Clontech | Cat# 632523 | Expresses mCherry under a CMV promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mDia1-WT-mCherry | This study | - | Expresses mouse mDia1-WT-mCherry under a CMV promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mDia1-ΔN -mCherry | This study | - | Expresses truncation (first 60 AA) variant of mouse mDia1-mCherry under a CMV promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mDia1-WT-SNAP | This study | - | Expresses mouse mDia1-WT-SNAP under a hSyn1 promotor; lentiviral plasmid |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mDia1-K994A-SNAP | This study | - | Expresses K994A variant of mDia1-SNAP under a hSyn1 promotor; lentiviral plasmid |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Dynamin1-WT-SNAP | This study | - | Expresses mouse Dynamin1-WT-SNAP under a hSyn1 promotor; lentiviral plasmid |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Dynamin1-K44A-SNAP | This study | - | Expresses K44A variant of mouse Dynamin1-SNAP under a hSyn1 promotor; lentiviral plasmid |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | vGlut1-mCherry | Franck Polleux | Kwon et al., 2016; https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002516 | Expresses rat vGlut1-mCherry under a CAG promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Rac1-CA | Addgene | Cat# 12983; RRID:Addgene_12983 | Expresses Q61L variant of human myc-Rac1 under a CMV promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Rac1-DN | Addgene | Cat# 12984; RRID:Addgene_12984 | Expresses T17N variant of human myc-Rac1 under a CMV promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | RhoA-WT | Theofilos Papadopoulos | Reddy-Alla et al., 2010; https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07149.x | Expresses human 3xHA-RhoA-WT under a CMV promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | RhoA-DN | Theofilos Papadopoulos | Reddy-Alla et al., 2010; https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07149.x | Expresses T19N variant of human 3xHA-RhoA under a CMV promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | RhoB-WT | Harry Mellor | Mellor, 1998; https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.9.4811 | Expresses human myc-RhoB-WT under a CMV promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | RhoB-DN | Harry Mellor | Mellor, 1998; https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.9.4811 | Expresses T19N variant of human myc-RhoB under a CMV promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | shCTR (transfected) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# SHC016 | No murine targets |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | shmDia1 (transfected) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# TRCN0000108685 | Targets 3'UTR of NM_007858 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | shRhoA (transfected) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# TRCN0000302388 | Targets CDS of NM_016802 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | shRhoB (transfected) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# TRCN0000294874 | Targets CDS of NM_007483 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | shCTRmiR | This study | - | Expresses rat Synaptophysin-2xpHluorin under a CMV promotor and shRNA embedded into a microRNA (shRNAmiR) with no murine targets |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | shmDia1miR | This study | - | Expresses rat Synaptophysin-2xpHluorin under a CMV promotor and shRNAmiR against the CDS of mouse Diaph1 (mDia1) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | shCTR (transduced) | Christian Rosenmund | Watanabe et al., 2014; https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13846 | Expresses NLS-RFP or BFP under a hSyn1 promotor and shRNA against no murine target (msClathrin scrambled) under a U6 promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | shmDia1 (transduced) | This study | - | Expresses NLS-RFP or BFP under a hSyn1 promotor and shRNA against the 3'UTR of mouse Diaph1 (mDia1) under a U6 promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | shmDia3 (transduced) | This study | - | Expresses NLS-RFP or BFP under a hSyn1 promotor and shRNA against the CDS of mouse Diaph2 (mDia3) under a U6 promotor |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | MD2.G | Addgene | Cat# 12259; RRID:Addgene_12259 | Expresses lentiviral VSV-G envelope protein |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | psPAX2 | Addgene | Cat# 12260; RRID:Addgene_12260 | Expresses lentiviral packaging protein |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pOrange GFP-β-Actin KI | Addgene | Cat#131479; RRID:Addgene_131479 | gRNA and GFP donor for endogenous N-terminal tagging of β-Actin (amino acid position: D2) by targeting Actb |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dynasore | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# D7693 | 80 μM 10 min |
| Chemical compound, drug | EHT 1864 | MedChemExpress | Cat# HY-16659 | 10 μM acute (CypHer); 2 h (IC/EM) |
| Chemical compound, drug | IMM-01 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# SML1064 | 10 μM acute |
| Chemical compound, drug | Jasplakinolide | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# J4580 | 8 μM acute (JLY); 1 μM 30 min |
| Chemical compound, drug | Latrunculin A | Cayman Chemical | Cat# CAY10684 | 5 µM acute (JLY) |
| Chemical compound, drug | ML141 | MedChemExpress | Cat# HY-12755 | 10 µM acute |
| Chemical compound, drug | Rhosin | MedChemExpress | Cat# HY-12646 | 10 µM 2 h |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tetrodotoxin | Carl Roth | Cat# 6973.1 | 1 µM 36 h |
| Chemical compound, drug | Y-27632 | Tocris | Cat# 1254 | 1 µM acute (JLY) |
| Commercial assay or kit | Rhotekin-Rho binding domain (RBD) beads | Cytoskeleton Inc | Cat# RT02 | 60 μg |
| Commercial assay or kit | PAK-p21 binding domain (PBD) beads | Cytoskeleton Inc | Cat# PAK02 | 20 μg |
| Commercial assay or kit | ProFection Mammalian Transfection System – Calcium Phosphate | Promega | Cat# E1200 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Gibson Master Mix | New England Biolabs Inc | Cat# E2611L | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Q5 site-directed mutagenesis kit | New England Biolabs Inc | Cat# E0552S | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | NIH | RRID:SCR_002285 | |
| Software, algorithm | Prism | GraphPad | RRID:SCR_002798 | Version 9.5.1. |
| Software, algorithm | Image Lab Software | Bio-Rad | RRID:SCR_014210 | Version 6.0.1 |
| Software, algorithm | Image Studio Lite | LI-COR Biosciences | RRID:SCR_013715 | Version 5.2.5 |
| Software, algorithm | pHluorin ROI sector | Github | https://github.com/DennisVoll/pHluorin_ROI_selector/; Voll, 2020 | |
| Software, algorithm | SynActJ | Martin Lehmann | Schmied et al., 2021; https://doi.org/10.3389/fcomp.2021.777837 | |
| Software, algorithm | Macro_plot_lineprofile_multicolor | Kees Straatman | Gerth et al., 2017; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2019.03.020 | |
| Software, algorithm | MaxQuant | Jürgen Cox | https://www.maxquant.org/maxquant/ | Version 1.6.1.0 |
| Software, algorithm | Perseus | Jürgen Cox | https://www.maxquant.org/perseus/ | Version 1.6.7.0 |
| Sequence-based reagent | see Supplementary file 1 |
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 1
List of oligonucleotides used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92755/elife-92755-supp1-v2.xlsx






