Brain-derived and in vitro-seeded alpha-synuclein fibrils exhibit distinct biophysical profiles
Figures
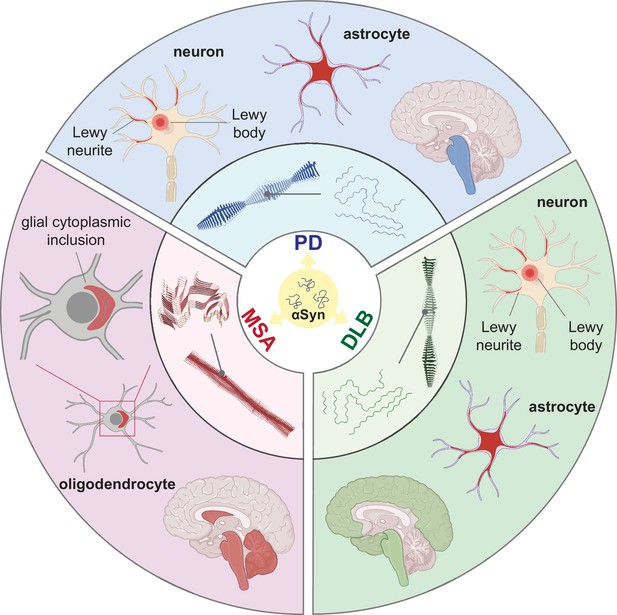
Distinct alpha-synuclein (αSyn) strains are associated with different neuropathological and clinical hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA).
αSyn misfolds and aggregates into fibrils with characteristic conformations. At the atomic level, PD and DLB strains share a ‘Lewy fold’ structure at the fibrillar core and comprise a single protofilament (Yang et al., 2022). MSA strains are twisted with two protofilaments intertwined, forming a different core structure to the ‘Lewy fold’ (Schweighauser et al., 2020). At a cellular level, PD is characterized by significant neuronal loss at the brainstem, especially substantia nigra (SN), highlighted in blue. Lewy body (LB) and Lewy neurite (LN) accumulate in neurons. αSyn also accumulates in astrocytes, forming astroglial pathology. In DLB, the brainstem and neocortex are the most affected regions, highlighted in green. Here, LB and LN accumulate in neurons, and astroglial pathology is also observed. In MSA, the cerebellum, basal ganglia, and brainstem are the most affected, highlighted in red. Here, αSyn accumulates as glial cytoplasmic inclusions (GCIs) in the oligodendrocytes. The 3D structures of the αSyn fibrillar cores were generated using PyMOL, and the PDB structures from Schweighauser et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2022.
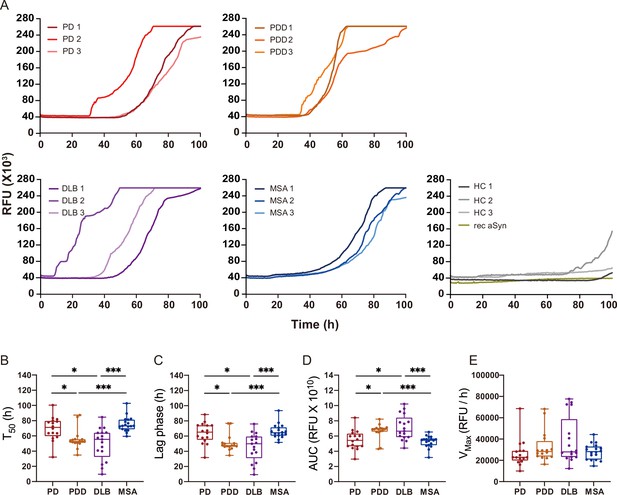
Alpha-synuclein (αSyn) seeding amplification assay (SAA) seeded with αSyn fibrils from Parkinson’s disease (PD), Parkinson’s disease with dementia (PDD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA) brains.
(A) SAA was performed with sarkosyl insoluble fractions of PD (n=3), PDD (n=3), DLB (n=3), MSA (n=3), and HC (n=3) brains. The curves represent an average of six replicates. Rec αSyn indicates an unseeded control reaction. (B) Time to reach 50% of the maximum fluorescence (). (C) The lag phase was taken at the time point where each positive reaction exceeded the threshold (RFU ≥ 5 SD). (D) Area under the curve (AUC). (E) The largest increase of fluorescence per unit of time (VMAX). (B–E) Plotted values represent the six replicates of the three cases for each disease (n=18). RFU, relative fluorescence unit; SD, standard deviation. *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.005.
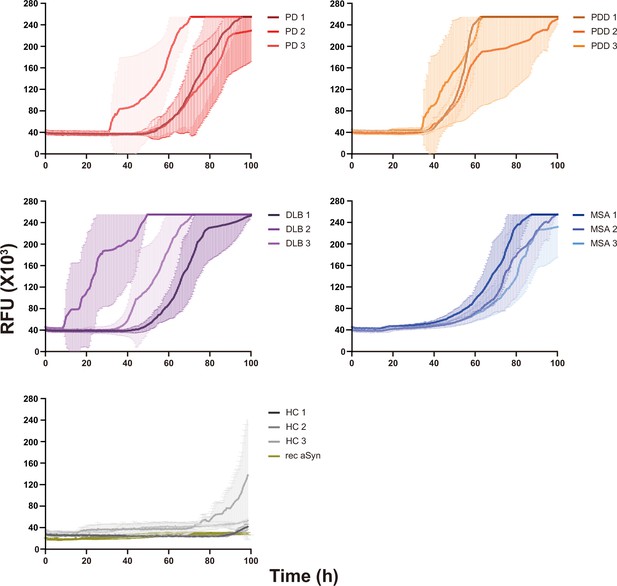
Raw data of the alpha-synuclein (αSyn) seeding amplification assay (SAA) reaction seeded with αSyn fibrils from Parkinson’s disease (PD), Parkinson’s disease with dementia (PDD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), multiple system atrophy (MSA), and healthy control brains.
The curves represent the average of 6 replicates, and error bars indicate ± one standard deviation (SD). RFU, relative fluorescence unit.
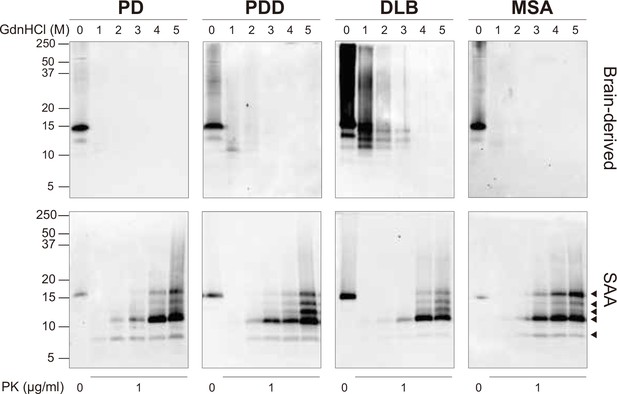
Brain-derived and SAA alpha-synuclein (αSyn) fibrils exhibited distinct biochemical profiles.
Brain-derived and SAA αSyn fibrils were subjected to denaturation with increasing concentrations of GdnHCl (0–5 M) and to PK digestion (1 μg/ml). The antibody clone 42 (BD Biosciences) was used to reveal the PK-resistant peptides. Immunoblots of one representative case from Parkinson’s disease (PD), Parkinson’s disease with dementia (PDD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA) are presented. The brain-derived and SAA fibrils are on the top and bottom rows, respectively. The molecular weights of the protein standards are shown in kilodaltons (kDa). Black arrows mark the five PK-resistant peptides revealed in the SAA fibrils. SAA, seeding amplification assay; GndHCl, guanidine-hydrochloride; PK, proteinase-K.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Unedited western blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-fig3-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Labelled unedited western blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-fig3-data2-v1.zip
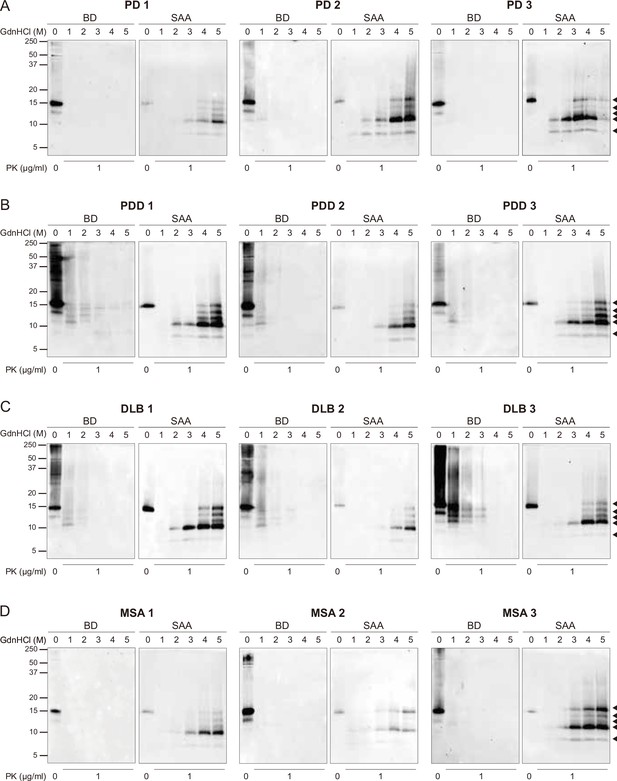
The full biochemical profiles of the brain-derived and SAA alpha-synuclein (αSyn) fibrils from all the cases.
The brain-derived (BD) and SAA αSyn fibrils from all three cases of (A) Parkinson’s disease (PD), (B) Parkinson’s disease with dementia (PDD), (C) dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and (D) multiple system atrophy (MSA) were treated with GdnHCl (0-5 M) and PK (1 μg/ml). The antibody clone 42 (BD Biosciences) was used to reveal the PK-resistant peptides. Black arrows mark the five PK-resistant peptides revealed in the SAA fibrils. The molecular weights of the protein standards are shown in kilodaltons (kDa). SAA, seeding amplification assay; GndHCl, guanidine-hydrochloride; PK, proteinase-K.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Unedited western blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Labelled unedited western blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-fig3-figsupp1-data2-v1.zip
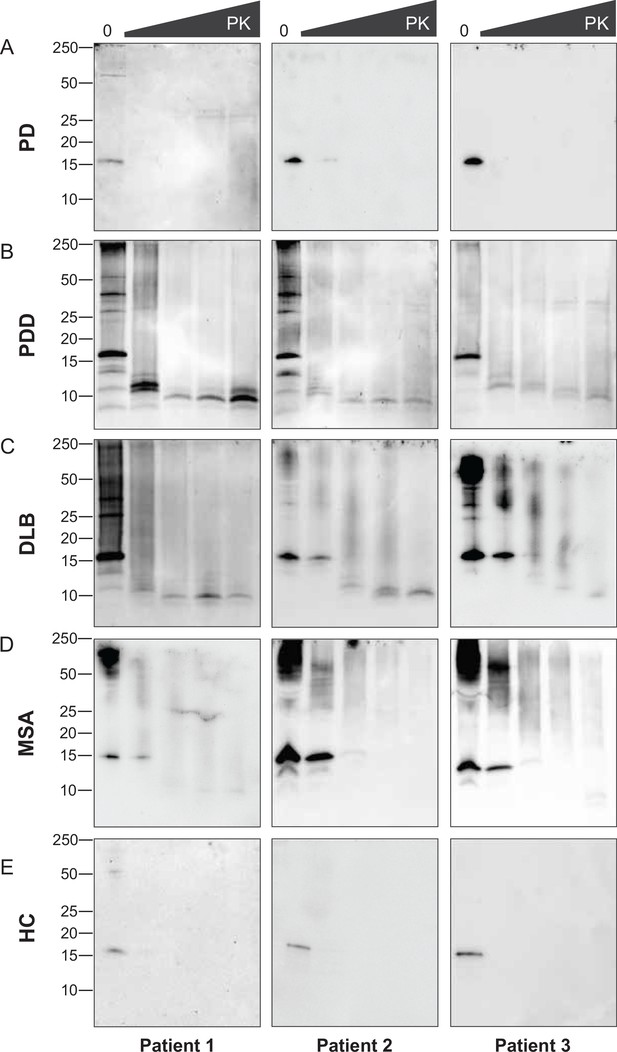
Proteinase-K degradation patterns of the brain-derived alpha-synuclein (αSyn) fibrils.
The brain-derived αSyn fibrils from (A) Parkinson’s disease (PD), (B) Parkinson’s disease with dementia (PDD), (C) dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), (D) multiple system atrophy (MSA), and (E) HC were subjected to increasing concentrations of proteinase-K (PK) at 0, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, and 1 mg/ml, represented by the escalating triangular bar. Western blot was performed using the antibody clone 42 (BD Biosciences). The molecular weights of the protein standards are shown in kilodaltons (kDa).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Unedited western blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-fig4-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Labelled unedited western blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-fig4-data2-v1.zip
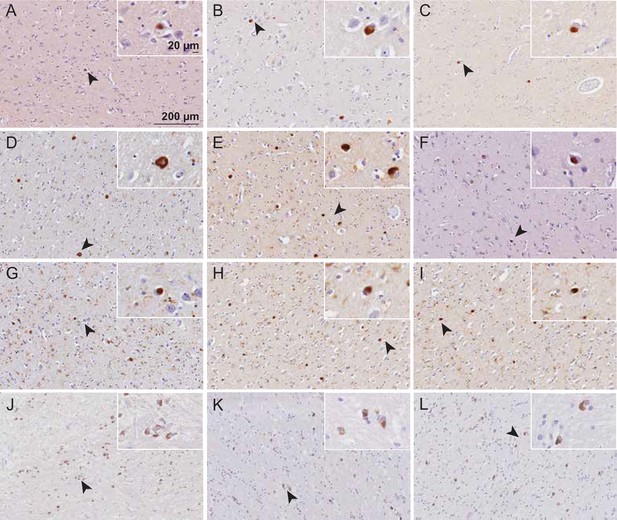
Immunohistochemical detection of alpha-synuclein (αSyn) in Parkinson’s disease (PD), Parkinson’s disease with dementia (PDD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA) brains.
The entorhinal cortex (PD, PDD, DLB) and striatum (MSA) were stained with total αSyn using antibody clone 42 (BD Biosciences). (A–C) PD cases 1–3. (D–F) PDD cases 1–3. (G–I) DLB cases 1-3. (J–L) MSA cases 1–3. Arrows indicate magnified areas. Scale bars = 20 μm and 200 μm.
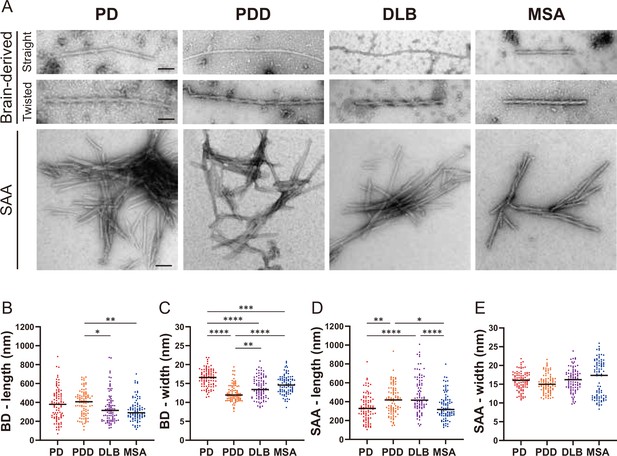
Transmission electron microscopy revealed different structures of brain-derived and seeding amplification assay (SAA) alpha-synuclein (αSyn) fibrils.
(A) Electron microscope image of negatively stained brain-derived (BD) and SAA fibrils from Parkinson’s disease (PD), Parkinson’s disease with dementia (PDD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA) brains. (B, C) The lengths and widths of brain-derived fibrils. (D, E) The lengths and width of SAA fibrils. MSA SAA fibrils were twisted with alternating widths, resulting in two clusters of measurements. A total of 30 fibrils from each case were measured and plotted (n=90). Scale bar = 50 nm. *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ****p≤0.001.
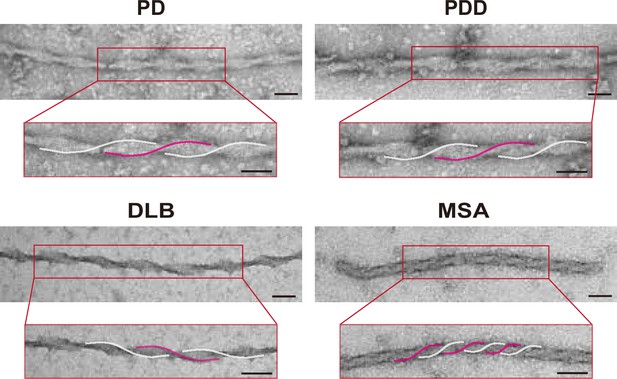
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of the twisted brain-derived alpha-synuclein (αSyn) fibrils.
Parkinson’s disease (PD), Parkinson’s disease with dementia (PDD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA) brain-derived fibrils displayed intertwined fibrils with twists. Helical twists are highlighted in pink and white. Scale bar = 50 μm.
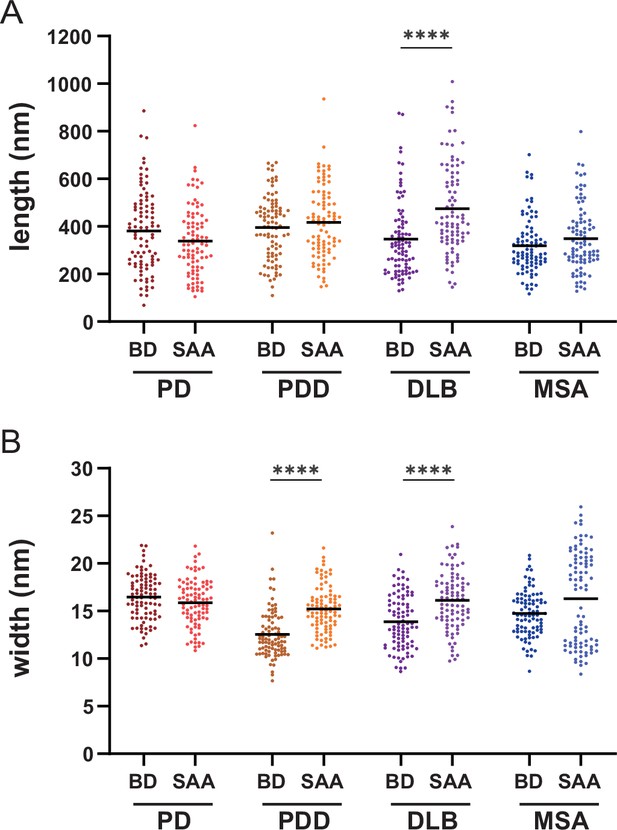
Comparison of the length and width of the brain-derived and SAA alpha-synuclein (αSyn) fibrils.
Comparison of the (A) lengths and the (B) widths of the brain-derived and SAA αSyn fibrils. Thirty fibrils were counted for each case. Thus, a total of 90 data points were plotted (n=90). The black bold line indicates an average. BD, brain-derived; SAA, seeding amplification assay. ****p≤0.001.
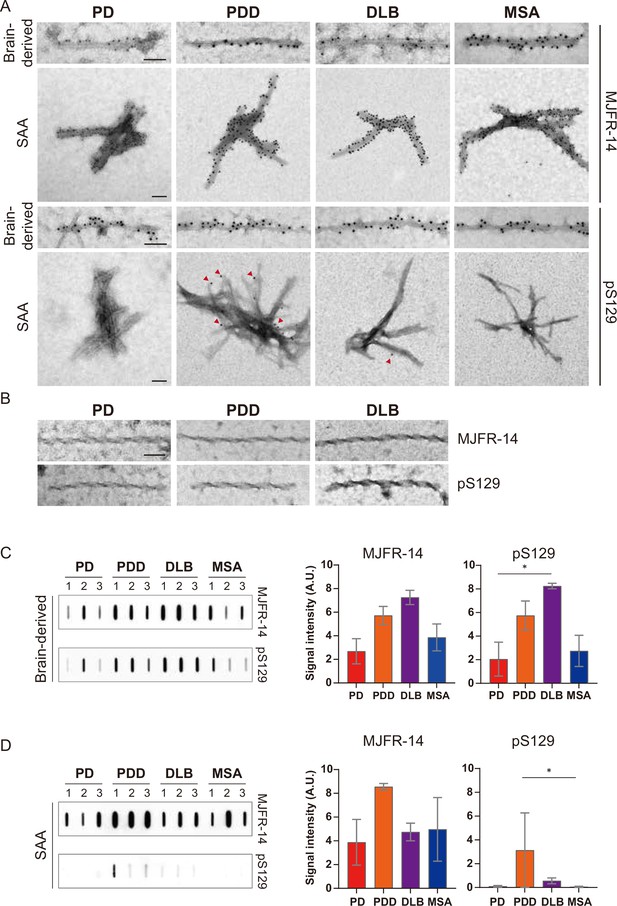
Brain-derived and seeding amplification assay (SAA) alpha-synuclein (αSyn) fibrils showed distinct phosphorylation patterns.
(A) Electron microscope image of brain-derived and SAA αSyn fibrils from Parkinson’s disease (PD), Parkinson’s disease with dementia (PDD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA) brains labeled with fibril conformation-specific (MJFR-14) and anti-pαSyn (pS129) antibodies. (B) The twisted αSyn fibrils from PD, PDD, and DLB brains were not labeled for MJFR-14 and pS129. Scale bar = 50 nm. (C,D) Semi-quantification of αSyn fibrils and pαSyn confirm the different patterns of αSyn phosphorylation between brain-derived and SAA αSyn fibrils. The amount of αSyn fibrils and pαSyn in (C) brain-derived and (D) SAA fibrils was determined using a slot blot. Two μg of proteins were filtered on a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with MJFR-14 and pS129 antibodies. The semi-quantitative measurement was done by averaging the measurements of three cases from each disease. Error bars indicate ± one standard deviation (SD). *p≤0.05.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Unedited slot blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-fig6-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Labelled unedited slot blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-fig6-data2-v1.zip
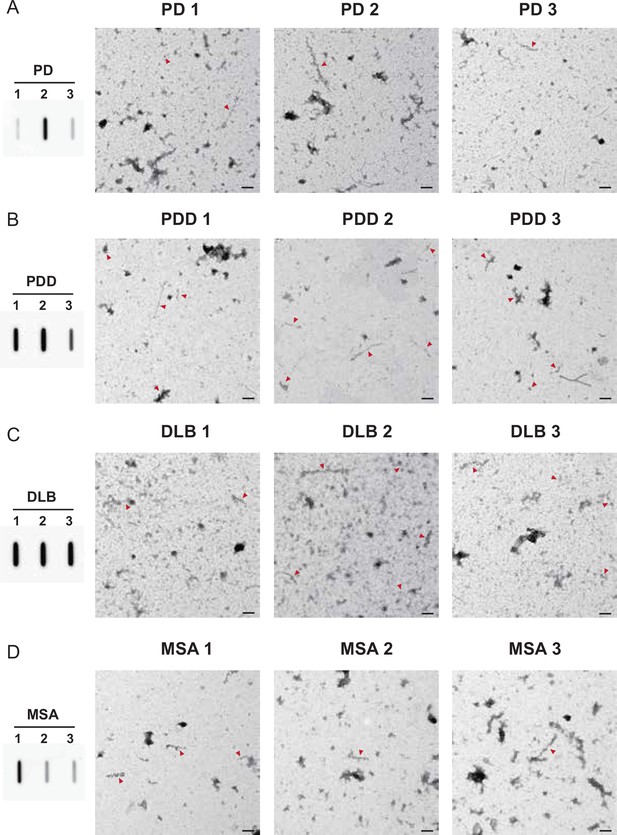
pS129 immunogold transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of the brain-derived alpha-synuclein (αSyn) fibrils.
The brain-derived αSyn fibrils were labeled with anti-pαSyn (pS129) and imaged at low magnification to compare the relative quantities of the pαSyn fibrils between the diseases. All three cases were imaged for each disease (A) Parkinson’s disease (PD), (B) Parkinson’s disease with dementia (PDD), (C) dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and (D) multiple system atrophy (MSA). The amount of pαSyn fibrils was examined using slot blots. Red arrows indicate labeled fibrils. Scale bar = 200 μm.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Unedited slot blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Labelled unedited slot blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-fig6-figsupp1-data2-v1.zip
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Clinicopathological summary of the patients included in this study.
The table summarizes the clinical and pathological reports of the patients included in this study. PD, Parkinson’s disease; PDD, Parkinson’s disease with dementia; DLB, dementia with Lewy body; MSA, multiple system atrophy; HC, healthy control; ECtx, entorhinal cortex; BG, basal ganglia; M, male; F, female; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; CVD, cardiovascular disease; and alpha-synuclein (αSyn).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-supp1-v1.pdf
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92775/elife-92775-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx





