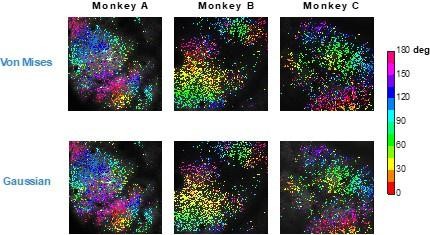
Ocular dominance-dependent binocular combination of monocular neuronal responses in macaque V1
Figures
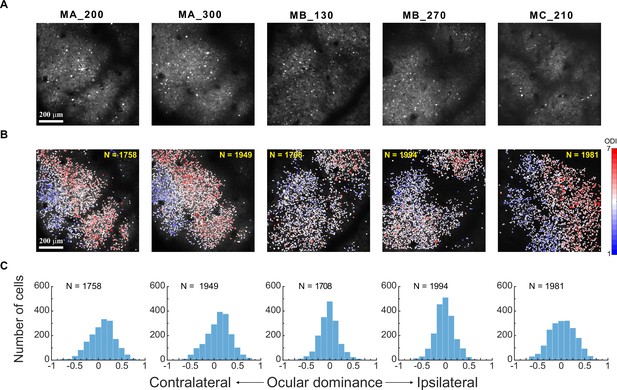
Eye preferences of V1 superficial-layer neurons in three macaques.
(A) Two-photon imaging. Average two-photon images over a recording session for each response FOV. MA_200: Monkey A at a 200 μm cortical depth. (B) Ocular dominance functional maps of each FOV/depth at single-neuron resolution. (C) Frequency distributions of neurons of each FOV/depth as a function of ocular dominance index. Relevant data are provided in the source data file: Figure 1—source data 1.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source data of Figure 1B-C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92839/elife-92839-fig1-data1-v1.mat
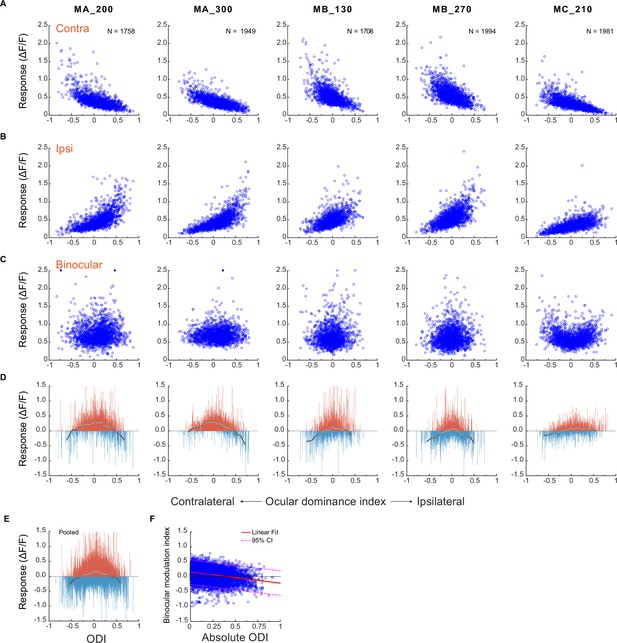
A comparison of neuronal responses to monocular and binocular stimulations.
(A) Responses of individual neurons against their ocular dominance indices with contralateral stimulation. (B) Responses of the same neurons against their ocular dominance indices with ipsilateral stimulation. (C) Binocular responses of the same neurons. (D) The difference between binocular and monocular responses (Rb – max(Ri, Rc)). Each vertical line represents one neuron. To summarize the results, neurons of each FOV/depth are evenly divided into 60 bins in the order of the ocular dominance index. White dots represent the median responses of respective bins and are connected with a black line. (E) The differences between binocular and monocular responses of individual neurons pooled over five FOVs/depths. (F) Binocular modulation index as a function of absolute ODI and the linear fit. The binocular modulation index of each neuron was defined as (Rb – max (Ri, Rc))/(Rb +max (Ri, Rc)). Relevant data are provided in the source data file: Figure 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source data of Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92839/elife-92839-fig2-data1-v1.mat
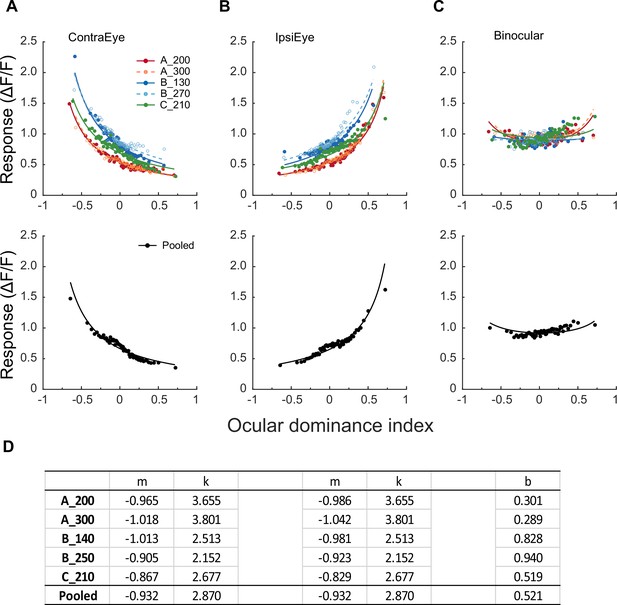
Modeling monocular and binocular responses.
(A, B) Median neuronal responses to contralateral and ipsilateral stimulations as a function of ocular dominance index and respective data fitting with Equation 2. Neurons are evenly divided into 60 bins in the order of the ocular dominance index, with each bin containing 29–33 neurons that varied among different FOVs/depths (156 neurons for the pooled data). Each datum represents the median response of a bin. Free parameter k was kept equal during contralateral and ipsilateral data fitting. (C) Binocular responses as a function of ocular dominance index and data fitting with Equation 3 for the same bins of neurons. During binocular data fitting, parameters k, mi, and mc were inherited from monocular data fitting, and only b was a free-changing parameter. (D) The values of free parameters from monocular and binocular data fitting.
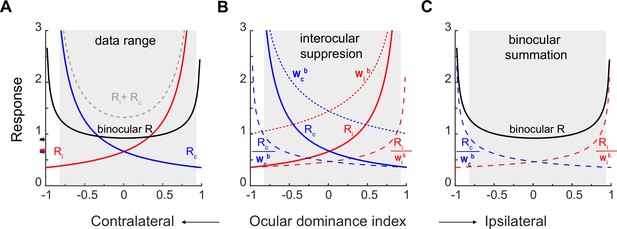
Monocular and binocular responses modeled with binocular suppression and binocular summation.
(A) The solid blue, red, and black curves are respectively simulations of the contralateral, ipsilateral, and binocular responses on the basis of fitting of pooled data (Figure 3D). The grey dashed curve simulates binocular responses as the arithmetic sum of contralateral and ipsilateral responses. The higher branches of contralateral and ipsilateral response functions represent monocular responses with preferred eye stimulation. The black, blue, and red arrows indicate the median binocular, contralateral, and ipsilateral responses, respectively, from pooled data. The shadowed area indicates the region where actual neurons existed on the basis of the ocular dominance index. (B) Interocular suppression. The contralateral and ipsilateral responses (Rc & Ri) are divided by respective interocular suppression factors Wcb and Wib to produce interocular-suppressed responses Rc/wcb and Ri/wib. (C) Binocular summation. Rc/wcb and Ri/wib are summed to produce the final binocular responses Rb.
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92839/elife-92839-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf
-
Source code 1
Source code for removing motion artifacts.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92839/elife-92839-code1-v1.zip