Structural assembly of the bacterial essential interactome
Figures

Analysis of essential binary complexes predicted by AlphaFold2 (AF2).
(a) Representation of protein-protein interactions (PPIs) based on their essentiality. This study focuses on interactions between essential proteins, highlighted by a green rectangle. (b) Pipeline used to construct the essential interactomes. (c) Cumulative distribution function of ipTM scores in selected (orange) and randomly generated PPIs (cyan). A two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was performed to assess the statistical significance of the difference between the two distributions. (d) Histograms displaying ipTM scores in selected complexes compared to random PPIs. Chi-square test p-values: <0.05*, <0.01**, <0.001***. (e) Accessible surface area of AF2 binary complexes grouped by ipTM score. (f) Conservation score comparison between interface and surface residues. Wilcoxon test p-values: <0.05*, <0.01**, <0.001***. (g) Network representation of side-chain residue contacts in high-accuracy binary models. Nodes represent residue types, and edges indicate interactions between residues. The color of the edges reflects the number of occurrences.

Correlation between the ipTM score with pDockQ of high-accuracy AlphaFold2 (AF2) protein binary complexes (ipTM>0.6).
The scatter plot includes 146 high-accuracy protein-protein interactions (PPIs), with each dot representing a specific interaction. The red line in the plot represents the average line of the values, and the obtained R-value of 0.328 indicates a low correlation.
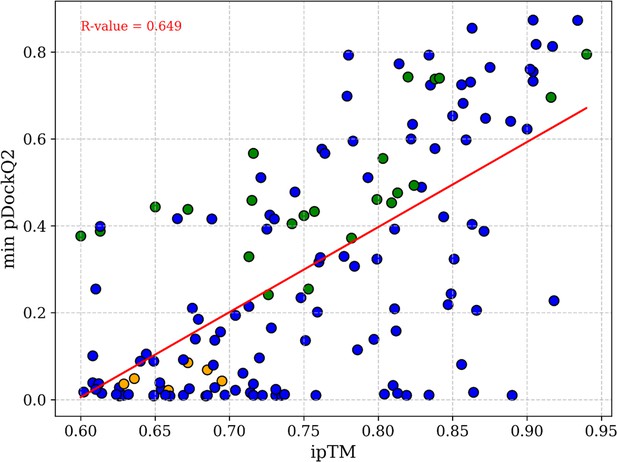
Correlation between the ipTM score with pDockQ2 of high-accuracy AlphaFold2 (AF2) protein binary complexes (ipTM>0.6).
The same 146 high-accuracy protein-protein interactions (PPIs) are represented in the scatter plot. Green points represent protein binary complexes discussed in this study with pDockQ2 values exceeding 0.23, whereas orange dots denote the binary complexes discussed with pDockQ2 scores below 0.23. Complexes labeled in orange however exhibit higher scores when modeled with additional accessory proteins, improving their pDockQ2 score above 0.23. The red line in the plot represents the average line of the values, and the obtained R-value of 0.649 indicates a stronger correlation.

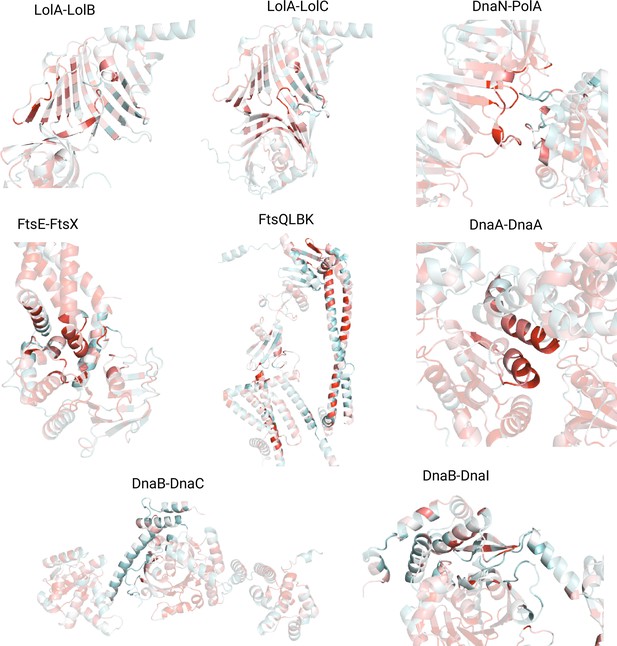
AlphaFold2 (AF2) predicted interfaces colored by residue conservation.
Conservation scores were computed using VESPA and range from 0 (not conserved, cyan) to 9 (highly conserved, red). The interface residues are highlighted while the rest of the protein is set to higher transparency to improve contrast.
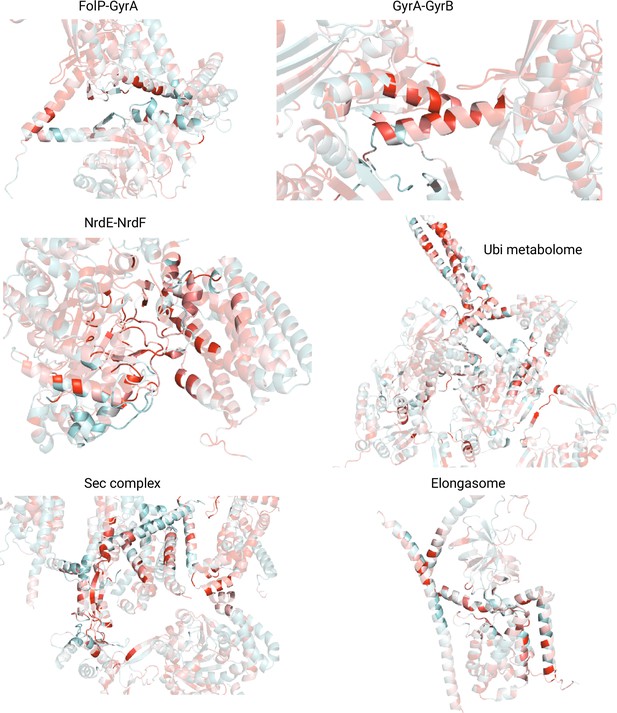
AlphaFold2 (AF2) predicted interfaces colored by residue conservation.
Conservation scores were computed using VESPA and range from 0 (not conserved, cyan) to 9 (highly conserved, red). The interface residues are highlighted while the rest of the protein is set to higher transparency to improve contrast.
AlphaFold2 (AF2) predicted interfaces colored by residue conservation.
Conservation scores were computed using VESPA and range from 0 (not conserved, cyan) to 9 (highly conserved, red). The interface residues are highlighted while the rest of the protein is set to higher transparency to improve contrast.
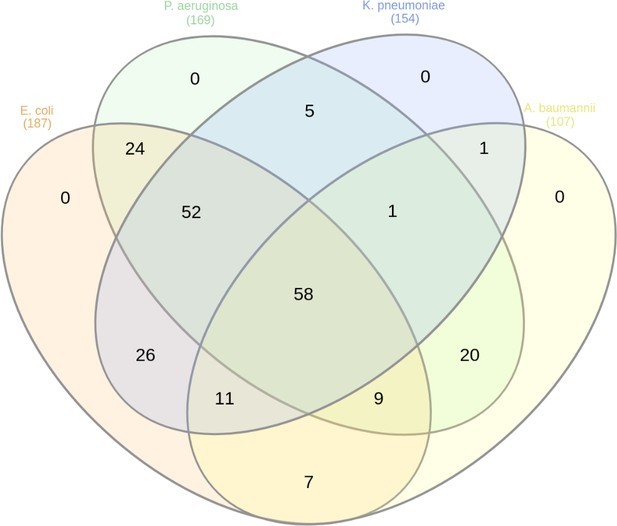
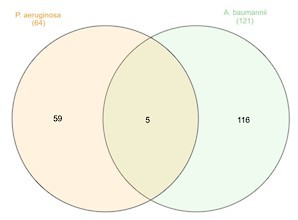
Venn diagram representing the number of essential proteins shared among the Gram-negative species.
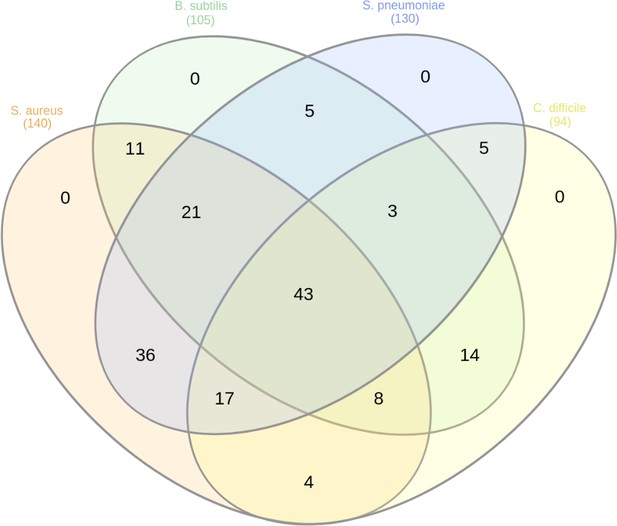
Venn diagram representing the number of essential proteins shared among the Gram-positive species.

Essential interactomes.
(a) Gram-negative essential interactome; (b) Gram-positive essential interactome. Nodes represent essential proteins, and edges indicate interactions between them. The color of the edges reflects the ipTM score as calculated by AlphaFold2 (AF2). The most representative biological processes are highlighted in the figure.

AlphaFold2 (AF2) predicted interfaces discussed in this work aligned with experimentally solved structures.
Experimentally derived structures are showed in light gray and the PDB codes are highlighted.

Core enzymes in fatty acid (FA) synthesis.
(a) FA synthesis pathway. (b) Proposed structural rearrangements in the BirA-AccB complex. Initially, the yellow arginine-rich loop and the green loop encapsulate the substrate in BirA pocket (closed state, left). (1) Upon interaction, Lys122 in AccB repels the arginine-rich loop in BirA (open state, right), (2) facilitating the covalent binding of the substrate to Lys122. The brown thumb loop likely interacts with the arginine-rich loop, contributing to complex stabilization. (c) Proposed mechanism of AccB shuttle in the Acc complex. Initially, the C-terminal domain of holo-AccB exhibits stronger affinity for AccC. Once the biotinyl group of AccB is carboxylated, the same domain may shuttle to AccA, facilitating the transfer of the carboxyl group to an acetyl-CoA molecule. The dotted line represents the flexible loop of AccB that would allow it to shuttle between AccA and AccC. All represented protein structures are AlphaFold2 (AF2) models. Uniprot codes used for AF2: AccA: P0ABD5, AccB: P0ABD8, AccC: P24182, AccD: P0A9Q5, and birA: P06709.
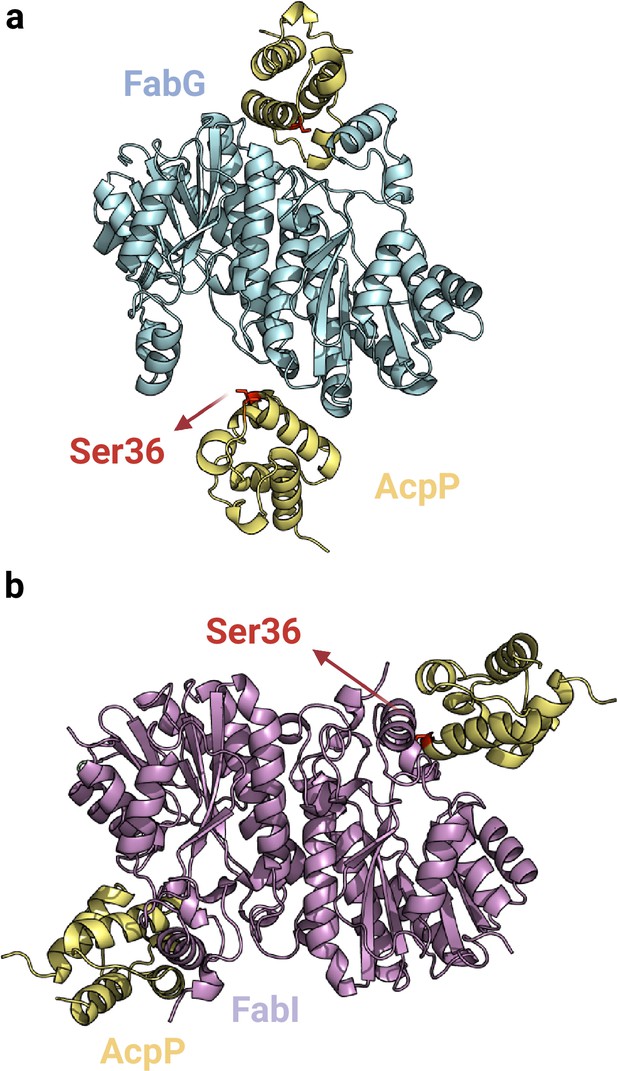
Predicted interfaces of FabG2-AcpP2 (a) and FabI2-AcpP2 (b).
The experimentally solved FabI-AcpP structure 2FHS is aligned with the AlphaFold2 (AF2) predicted model. While these AF2 complexes show substantial structural similarity, there is a significant difference in the AcpP conformation. Only in the predicted models, the central AcpP catalytic residue Ser36 (highlighted in red) is positioned toward the binding pockets of both FabG and FabI. Uniprot codes used for AF2: AcpP: P0A6A8, fabG: P0AEK2, fabI: P0AEK4.

Common mechanism in initial steps of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) synthesis pathway.
(a) Simplified Raetz pathway. (b) Top view (left), front view (center), and magnified interface (right) of GlmU-AcpP, LpxA-AcpP, and LpxD-AcpP predicted AlphaFold2 (AF2) models. GlmU contains an N-terminal uridyltransferase domain (UDT, yellow) while LpxA incorporates a C-terminal acetyltransferase domain (ACT, cyan) forming a collapsed helix that does not interact with the other LpxA monomers. LpxD incorporates a uridine-binding domain (UBD, green) and a C-terminal acetyltransferase domain forming a 3-helix bundle. The common left-handed β-helix domain is colored in pink, the extruding loop is highlighted in blue, AcpP in orange, and AcpP’s Ser36 in red. Uniprot codes used for AF2: GlmU: P0ACC7, LpxA: P0A722, LpxD: P21645, AcpP: P0A6A8.
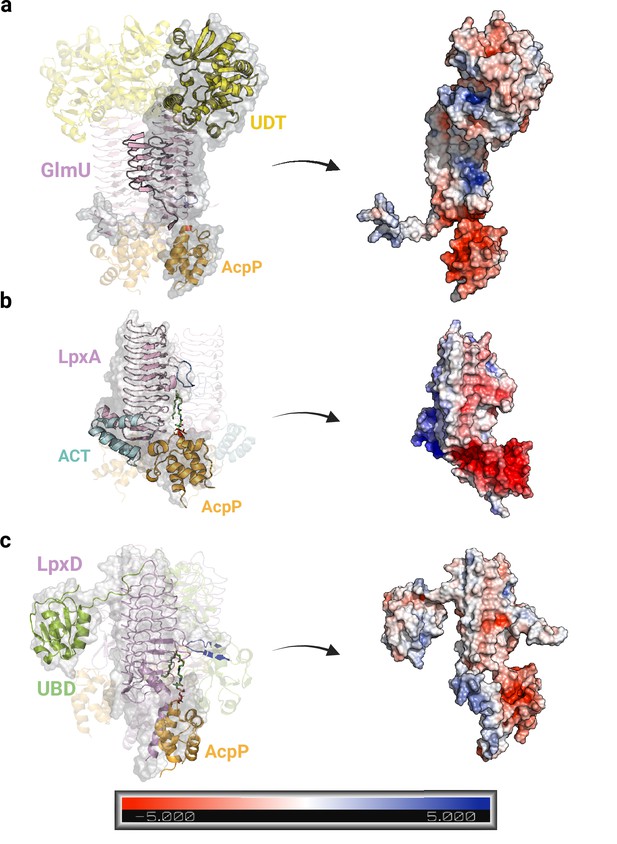
Electrostatic potentials of AlphaFold2 (AF2) predicted models for the GlmU-AcpP (a), LpxA-AcpP, (b), and LpxD-AcpP (c) complexes.
In all three complexes, the ligands are primarily accommodated in non-polar binding sites, while the remaining protein structure exhibits charged potentials. The color-coded representation in the legend at the bottom of the figure indicates the electrostatic potential of the molecular surface. Uniprot codes used for AF2: GlmU: P0ACC7, LpxA: P0A722, LpxD: P21645, AcpP: P0A6A8.
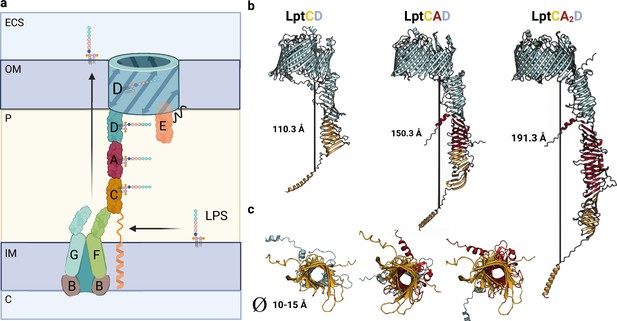
Model of Lpt bridge.
(a) Schematic representation of the Lpt complex. Initially, the LptB2FGC complex extracts the LPS from the inner membrane (IM). The LPS molecule then moves from the hydrophobic pocket of LptFG to LptC. The LptCAD periplasmic bridge shields the LPS molecule and facilitates its insertion into the outer membrane (OM) by LptDE. Key compartments include the IM, OM, periplasm (P), cytoplasm (C), and extracellular space (ECS). LPS refers to lipopolysaccharide. (b) AlphaFold2 (AF2) models of Lpt bridges with varying LptA stoichiometries are depicted, with each LptA subunit approximately measuring 40 Å in length. (c) A view of the interior of the Lpt bridge reveals a hole with a diameter ranging from 10 to 15 Å in all three cases. The structures are presented in the same order as in the previous model: LptCD, LptCAD, and LptCA2D. Uniprot codes used for AF2: LptA: P0ADV1, LptC: P0ADV9, LptD: P31554.
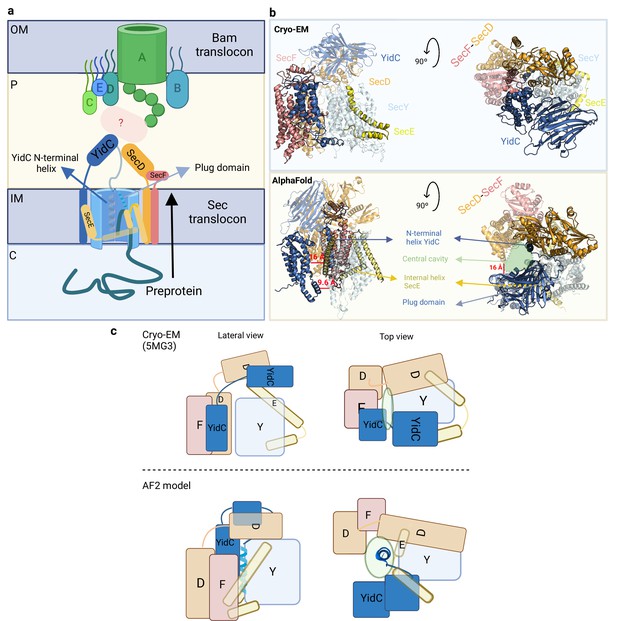
Organization of the Sec translocon.
(a) Schematic representation of the Sec translocon and its crosstalk with the Bam translocon. During protein translocation, the preprotein engages with the central cavity of SecY, where the N-terminal helix of YidC is accommodated. Subsequently, the plug domain is displaced, allowing the preprotein to be released into the periplasm through the lateral gate. Crosstalk between the Sec and Bam translocons may occur via indirect interactions facilitated by periplasmic chaperones. Key compartments include the inner membrane (IM), outer membrane (OM), periplasm (P), and cytoplasm (C). (b) Front and top views of the cryo-EM structure (top) and the AlphaFold2 (AF2) model (bottom), providing different perspectives on the Sec translocon organization. (c) Schematic representation of the Sec translocon showing the relative orientation of the corresponding subunits in the cryo-EM structure (top) and our AF2 model (bottom). Uniprot codes used for AF2: secD: P0AG90, secE: P0AG96, secF: P0AG93, secY: P0AGA2, YidC; P25714.
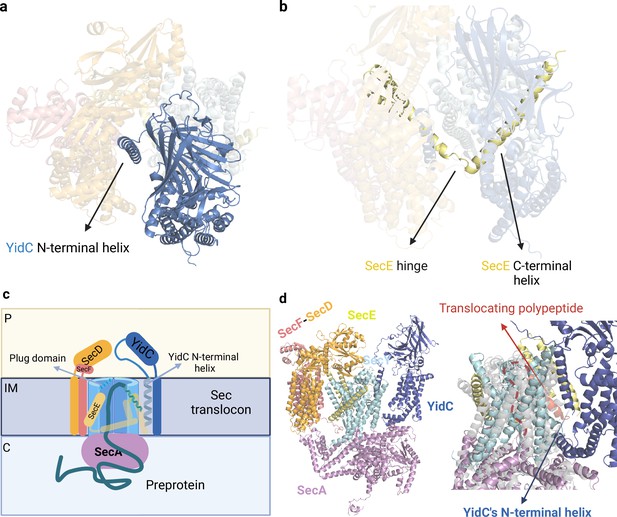
Sec translocon bound to SecA.
(a) Detailed view of the AlphaFold2 (AF2) model of the Sec translocon. The N-terminal helix of YidC is accommodated inside the central cavity of the Sec translocon. (b) SecE’s hinge is facing the central cavity and the C-terminal helix is interacting with the YidC’s transmembrane (TM) domain. (c) Schematic representation of the architecture of the Sec translocon bound to SecA-preprotein. C: cytoplasm, IM: inner membrane, P: periplasm. (d) Sec translocon complex predicted by AF2 (left). Predicted model superimposed with the crystal structure of SecY-SecA translocating a polypeptide (PDB ID: 5EUL, right). The crystal structure is colored in gray and the translocating polypeptide in red, the red dashed line represents the unfolded region of the polypeptide inside SecY. The polypeptide is located in the SecY’s exit lateral gate and it is bound to YidC’s N-terminal helix. Uniprot codes used for AF2: secA: P10408, secD: P0AG90, secE: P0AG96, secF: P0AG93, secY: P0AGA2, YidC; P25714.
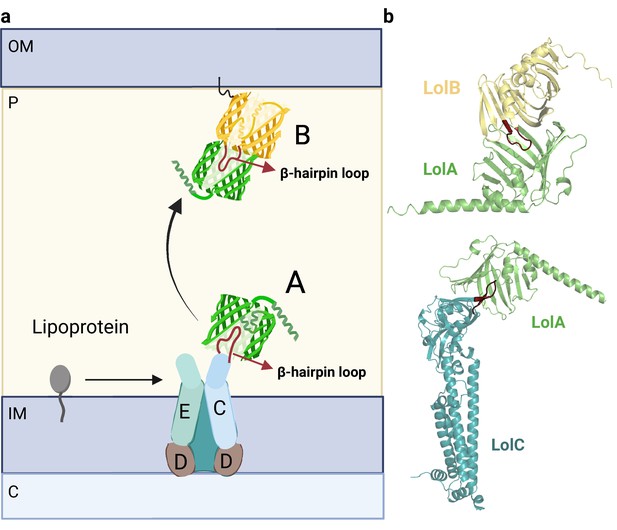
Organization of the Lol complex.
(a) Schematic depiction of the Lol complex. The outer membrane (OM), inner membrane (IM), periplasm (P), and cytoplasm (C) are highlighted in the figure. The structures of LolA and LolB are shown in green and yellow, respectively. The LolCD2E complex and the lipoprotein are represented in a schematic manner. (b) Predicted AF2 models of LolAB and LolAC. The protruding loops of LolB and LolC are highlighted in red for clarity. Uniprot codes used for AF2: lolA: P61316, lolB: P61320, lolC: P0ADC3.
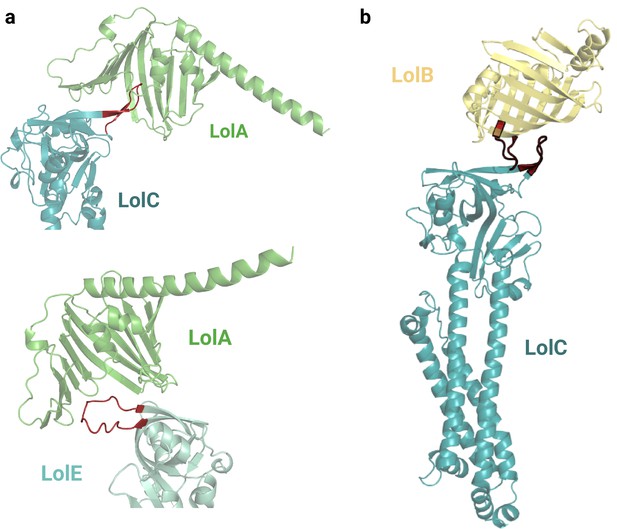
Predicted interfaces of LolA with LolC and LolE.
(a) This LolAC model displays a high level of confidence, indicating successful accommodation of the protruding β-hairpin loop within LolA. The LolAC crystal structure 6F3Z is aligned to the AlphaFold2 (AF2) model in Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Conversely, the interaction between LolAE is deemed unlikely based on the AF2 prediction, as the protruding loop of LolE cannot be positioned within LolA. This discrepancy may be attributed to the specific amino acid composition of the loop. (b) Low accuracy binary complex LolBC predicted by AF2. The AF2 prediction suggests a weak interface between the β-hairpin loops of LolB and LolC in this complex. Uniprot codes used for AF2: lolA: P61316, lolB: P61320, lolC: P0ADC3.
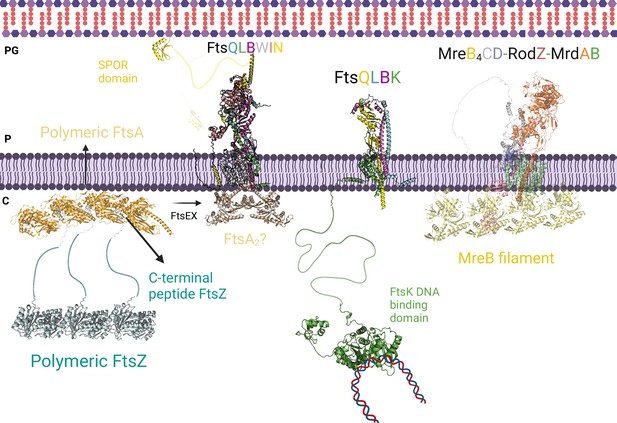
Divisome and elongasome predicted complexes.
The initial step of cell division involves the binding of the polymer FtsZ to inner membrane proteins FtsA. FtsEX assists in converting the polymer form of FtsA to its individual subunit form, which promotes the recruitment of FtsK, FtsQLB, FtsWI, and FtsN. On the left side, the AlphaFold2 (AF2) model shows the interaction between FtsQLBWIN and FtsA2. Previous research suggested that the monomeric form of FtsA is responsible for recruiting the divisome proteins, while the AF2 model indicates that the dimeric form of FtsA could also play a role in this recruitment. In the center, the interactions between the transmembrane domains of FtsK and FtsQLB are shown, along with FtsK’s long linker and the DNA binding domain. This interaction likely occurs before the recruitment of FtsN to prevent DNA entrapment during division. On the right side, the AF2 predicted elongasome complex is displayed. For a more detailed depiction of the divisome and elongasome complexes, please refer to Figure 8—figure supplement 2 and Figure 8—figure supplement 3, respectively. Notations: PG refers to peptidoglycan, P refers to periplasm, and C refers to cytoplasm. All represented protein structures are AF2 predictions. Uniprot codes used for AF2: ftsA: Q02KT7, ftsB: A0A0H2ZE93, ftsE: A0A0H2ZGN1, ftsH: A0A0H2ZC79, ftsI: A0A0H2ZFM0, ftsK: P46889, ftsQ: A0A0H2ZGP2, ftsN: P29131, ftsW: A0A0H2ZGG8, ftsY: A0A0H2ZKT5, ftsZ: A0A0H2ZM25. mrdA: P0AD65, mrdB: P0ABG7, mreB: P0A9X4, mreC: P16926, mreD: P0ABH4, rodZ: P27434.
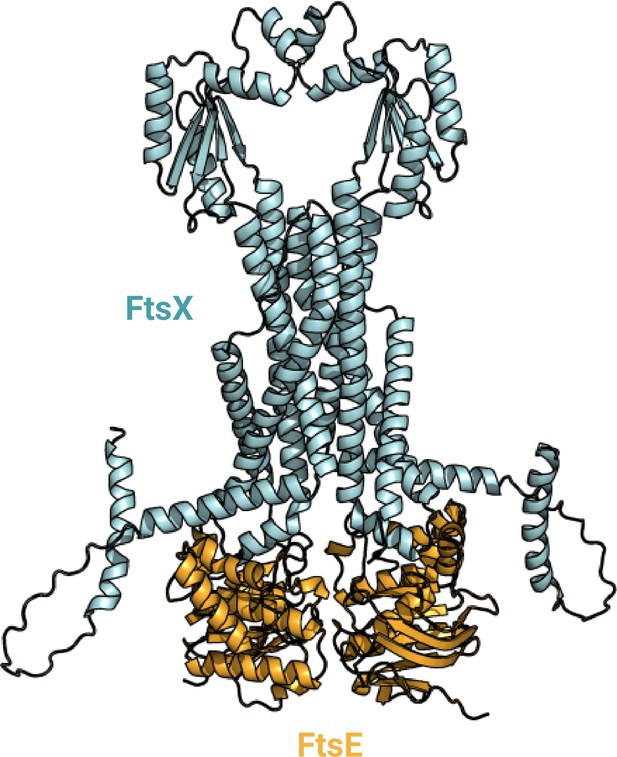
AlphaFold2 (AF2) model of the FtsE2X2 complex.
FtsEX is a type of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter that has a role in regulating the breakdown of peptidoglycan (PG) and the divisome. FtsE is a component that binds to ATP and is found in the cytoplasm, while FtsX consists of four transmembrane (TM) helices and a periplasmic domain. Together, this complex helps convert the polymeric form of FtsA into monomeric units, which then recruits other proteins involved in cell division and starts the constriction of the cell membrane. Although the process doesn't require the hydrolysis of ATP, it is necessary to activate and regulate the synthesis of PG. Uniprot codes used for AF2: ftsE: P0A9R7, ftsX: P0AC30.
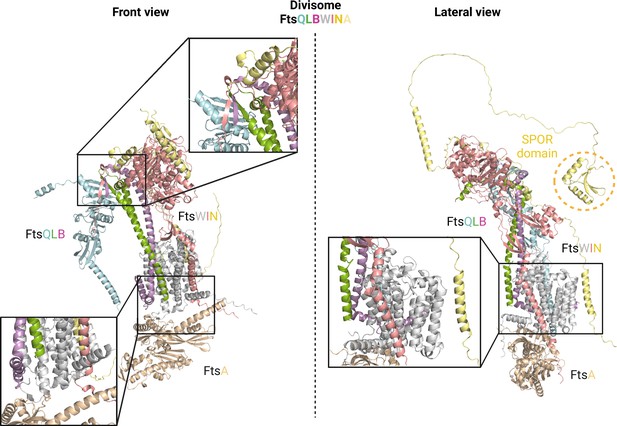
Detailed view of AlphaFold2 (AF2) divisome model.
FtsL and FtsB proteins interact with each other, forming a coiled-coil structure. Furthermore, the C-terminal domains of FtsLB engage in an antiparallel β-sheet structure with FtsQ and FtsI (top-left magnified view). Interactions between the flexible linkers of FtsN and FtsWI are also depicted. FtsA primarily interacts with the transmembrane (TM) domain of FtsW, as shown in the zoomed view on the bottom-left. The TM domains of all the divisome proteins exhibit tight interactions with each other, with FtsW being prominently involved in most of these interactions (as observed in the magnified view on the bottom-right). It is important to note that the SPOR domain of FtsN does not participate in any protein-protein interactions; instead, it would interact with peptidoglycan. Uniprot codes used for AF2: ftsA: Q02KT7, ftsB: A0A0H2ZE93, ftsE: A0A0H2ZGN1, ftsH: A0A0H2ZC79, ftsI: A0A0H2ZFM0, ftsK: P46889, ftsQ: A0A0H2ZGP2, ftsN: P29131, ftsW: A0A0H2ZGG8, ftsY: A0A0H2ZKT5, ftsZ: A0A0H2ZM25.
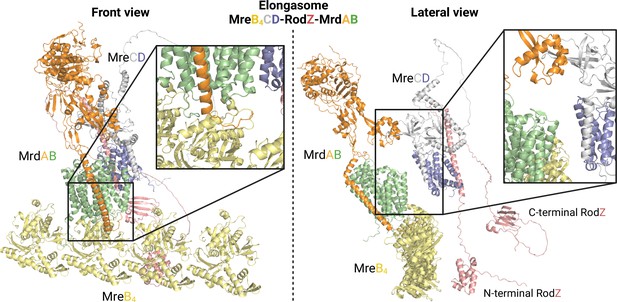
Detailed view of AlphaFold2 (AF2) elongasome model.
The figure presents two views of the elongasome model: a front view on the left and a lateral view on the right. In the front view, the interface region between MrdAB and MreB is magnified. It highlights the contact between the cytoplasmic loops of MrdAB and MrdB. The lateral view provides insights into potential interactions between MreCD and MrdA, as well as between the N-terminal domain of RodZ and MreB. It is worth noting that while the C-terminal domain of RodZ is likely a periplasmic domain, it appears to be positioned in the cytoplasm due to the absence of other periplasmic proteins and the presence of a highly flexible linker. Uniprot codes used for AF2: mrdA: P0AD65, mrdB: P0ABG7, mreB: P0A9X4, mreC: P16926, mreD: P0ABH4, rodZ: P27434.
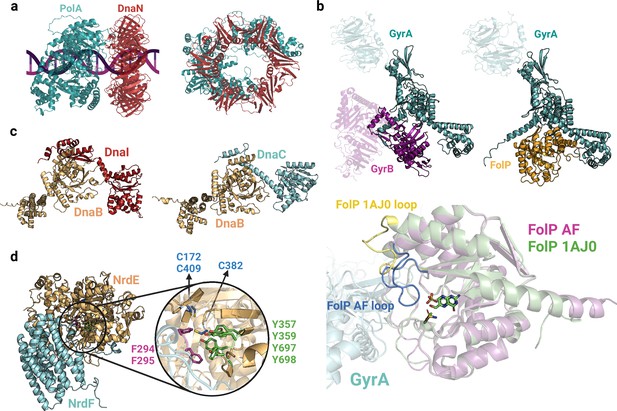
Complexes involved in DNA replication and synthesis.
(a) Predicted interface between DNA polymerase I (PolA) and DnaN2. (b) Models of GyrAB and GyrA-FolP (top). Close-up view of the GyrA-FolP interface and comparison with the crystal structure of FolP (bottom;1AJ0). The notable difference between the two structures is the loop region spanning residues 22–36, indicated in yellow/blue. (c) Predicted binary complexes DnaBI and DnaBC. The DnaBC predicted model is aligned to the solved crystal structure 6KZA (Figure 2—figure supplement 1). (d) Close-up view of the AlphaFold2 (AF2) predicted interface between NrdE and NrdF, highlighting important aromatic residues and cysteines involved in nucleotide reduction. Uniprot codes used for AF2: DnaB (DnaBI): A0A062WMW9, DnaB (DnaBC): P0ACB0, DnaC: P0AEF0, DnaI: Q8CWP7, DnaN: P0A988, GyrA: P0AES4, GyrB: P0AES6, FolP: P0AC13, NrdE: A0A0B7LYQ0, NrdF: A0A062WM39.

AlphaFold2 (AF2) prediction for DnaA4 complex.
DnaA is composed of four domains: domains I, II, III, and IV. Among these, domains III (violet) and IV (green) have been more extensively studied and characterized. Domain III of DnaA is responsible for binding and hydrolyzing ADP/ATP. It also enables ATP-dependent self-oligomerization of DnaA in a head-to-tail manner. Domain IV contains a helix-turn-helix motif that is inserted into the major groove of DnaA boxes. This motif plays a crucial role in DNA binding and recognition. Uniprot codes used for AF2: DnaA: P03004.
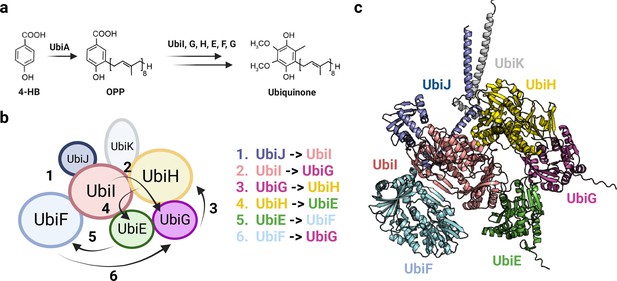
Organization of the Ubi metabolon.
(a) Simplified ubiquinone synthesis pathway from 4-HB. 4-HB: 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, OPP: octaprenyl diphosphate. (b) Architecture of the Ubi metabolon. The numbers indicate the six reactions carried out by the Ubi metabolon, and the arrows depict the path followed by the lipid intermediate transported by UbiJ. In the first step, UbiJ shields the lipid intermediate and binds to UbiI, catalyzing the first reaction. In the following steps, the flexible UbiJ transport the biosynthetic intermediates to the next enzyme. (c) AlphaFold2 (AF2) model of the Ubi metabolon. Uniprot codes used for AF2: ubiA: P0AGK1, ubiE: P0A887, ubiF: P75728, ubiG: P17993, ubiH: P25534, ubiI: P25535, ubiJ: P0ADP7, ubiK: Q46868.
Tables
Protein complexes discussed in this work.
The ipTM score is shown along with the PDB accessions for the cases where the structure has already been solved. The AlphaFold2 (AF2) predictions are structurally aligned with the experimental structures in Figure 2—figure supplement 1 except for SecYEDF-YidC, which is discussed in Figure 6.
| Protein | ipTM | PDB* | ModelArchive ID | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AccB-BirA | 0.841 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-02 | Fatty acid synthesis |
| AccABCD | 0.809 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-01 | Fatty acid synthesis |
| AcpP-FabG | 0.757 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-06 | Fatty acid synthesis |
| AcpP-FabI | 0.753 | 2FHS | ma-sysbio-bei-07 | Fatty acid synthesis |
| AcpP3-GlmU3 | 0.908 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-03 | Lipopolysaccharide synthesis |
| AcpP3-LpxA3 | 0.940 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-04 | Lipopolysaccharide synthesis |
| AcpP3-LpxD3 | 0.957 | 4IHF | ma-sysbio-bei-05 | Lipopolysaccharide synthesis |
| LptC-LptD | 0.695 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-24 | Lipopolysaccharide transport |
| LptCAD | 0.600 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-23 | Lipopolysaccharide transport |
| SecYEDF-YidC | 0.642 | 5MG3 | ma-sysbio-bei-27 | Outer membrane protein transport |
| SecYEDFA-YidC | 0.632 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-26 | Outer membrane protein transport |
| LolA-LolC | 0.809 | 6F3Z | ma-sysbio-bei-22 | Lipoprotein transport |
| LolA-LolB | 0.838 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-21 | Lipoprotein transport |
| FtsA3 | 0.761 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-13 | Cell division |
| FtsZ3 | 0.614 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-18 | Cell division |
| FtsA3-FtsZ3 | 0.542 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-14 | Cell division |
| FtsQLBWIN | 0.727 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-17 | Cell division |
| FtsQLBK | 0.572 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-16 | Cell division |
| FtsE2-FtsX2 | 0.856 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-15 | Cell division |
| MreB4CD-RodZ-MrdAB | 0.764 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-12 | Cell division |
| DnaA4 | 0.545 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-08 | DNA replication |
| DnaN-PolA | 0.813 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-11 | DNA replication |
| DnaB-DnaI | 0.750 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-10 | DNA replication |
| DnaB-DnaC | 0.650 | 6KZA | ma-sysbio-bei-09 | DNA replication |
| NrdE-NrdF | 0.856 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-25 | DNA replication |
| GyrA-GyrB | 0.715 | 6RKU | ma-sysbio-bei-20 | DNA replication |
| GyrA-FolP | 0.847 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-19 | DNA replication |
| UbiEFGHIJK | 0.806 | – | ma-sysbio-bei-28 | Ubiquinone synthesis |
-
*
Complexes FtsA3-FtsZ3 and FtsQLBK have an ipTM score <0.6 because they contain large intrinsically disordered segments that, despite not participating in the interaction, contribute to decrease the global ipTM score.
Performance of state-of-the-art PPI prediction methods (Huang et al., 2023).
| Methods | AUPRC* |
|---|---|
| SGPPI | 0.422 |
| Profppikernel | 0.359 |
| PIPR | 0.342 |
| PIPE2 | 0.220 |
| SigProd | 0.264 |
-
*
AUPRC denotes the average AUPRC value of 10-fold cross-validation.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of validated bacterial complexes.
The listed complexes were not included in the training dataset of AF and share <30% sequence identity with all models deposited in the PDB.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/94919/elife-94919-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/94919/elife-94919-mdarchecklist1-v2.pdf
-
Source data 1
Essential protein annotations and protein-protein interactions (PPIs) scores provided by AlphaFold2 (AF2).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/94919/elife-94919-data1-v2.xlsx