A robust brain network for sustained attention from adolescence to adulthood that predicts later substance use
Figures
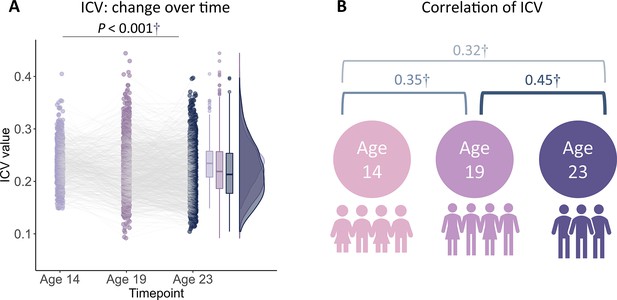
Intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) changes over time.
(A) ICV changes over time. (B) Correlation of ICV between timepoints within participants. †, p<0.001.
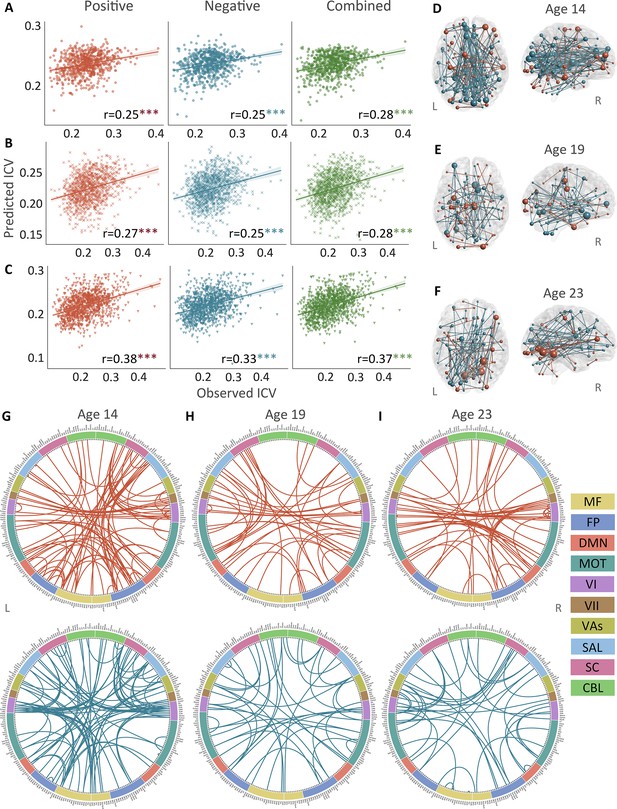
The predictive performances and networks of intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) per timepoint derived from Go trials.
Correlation between observed and predicted ICV in positive, negative, and combined networks at (A) age 14, (B) age 19, and (C) age 23. Predictive networks for ICV are at (D) age 14, (E) age 19, and (F) age 23. Connectome of positive and negative networks of ICV at (G) age 14, (H) age 19, and (I) age 23. The edges depicted above are those selected in at least 95% of cross-validation folds. Red, blue, and green spheres/lines/scatters represent positive, negative, and combined networks respectively. MF, medial frontal; FP, frontoparietal; DMN, default mode; MOT, motor; VI, visual I; VII, visual II; VAs, visual association; SAL, salience; SC, subcortical; CBL, cerebellar. R/L, right/left hemisphere. ***, p<0.001.
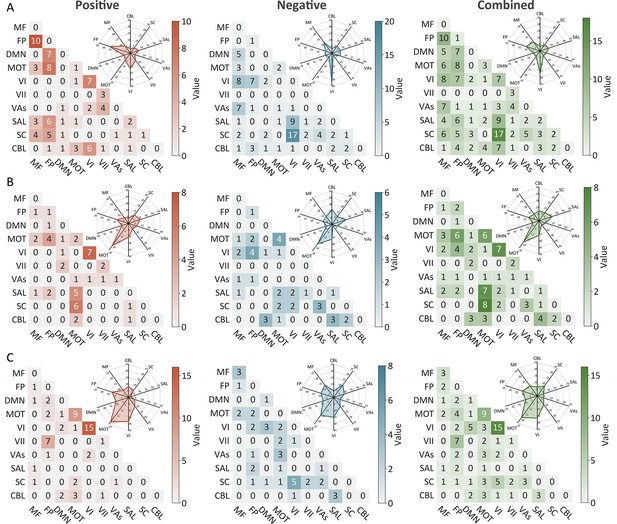
The predictive networks predicting intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) per timepoint derived from Go trials.
The heatmaps show predictive networks with non-zero values at (A) age 14, (B) age 19, (C) age 23. Each heatmap cell shows the number of edges between or within functional networks. Radar plots show the proportion of the functional networks involved in predictive networks. The edges depicted above are those selected in at least 95% of cross-validation folds. Red, blue, and green represent positive, negative, and combined networks respectively. MF, medial frontal; FP, frontoparietal; DMN, default mode; MOT, motor; VI, visual I network; VII, visual II network; VAs, visual association network; SAL, salience; SC, subcortical; CBL, cerebellar. R/L, right/left hemisphere.
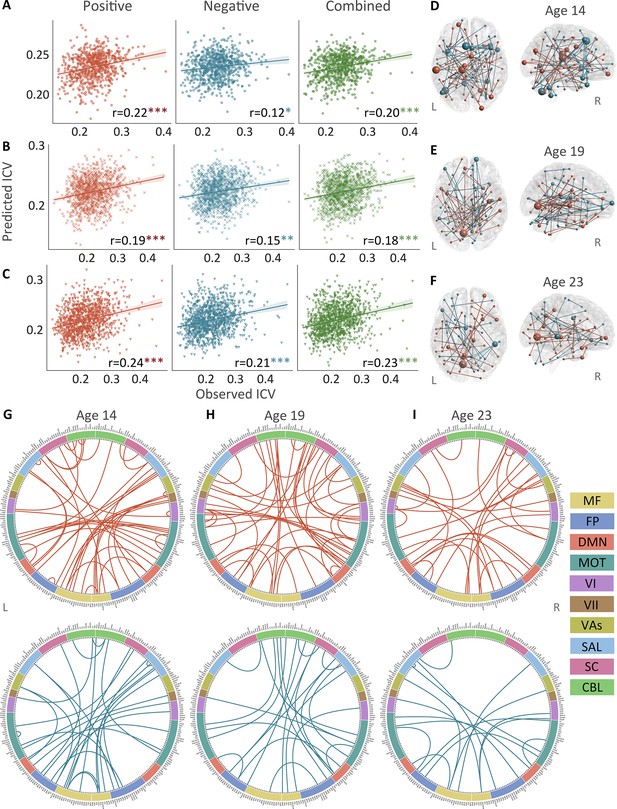
The predictive performances and networks of intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) per timepoint derived from Successful stop trials.
Correlation between observed and predicted ICV in positive, negative, and combined networks at (A) age 14, (B) age 19, and (C) age 23. Predictive networks for ICV are at (D) age 14, (E) age 19, and (F) age 23. Connectome of positive and negative networks of ICV at (G) age 14, (H) age 19, and (I) age 23. The edges depicted above are those selected in at least 95% of cross-validation folds. Red, blue, and green spheres/lines/scatters represent positive, negative, and combined networks respectively. MF, medial frontal; FP, frontoparietal; DMN, default mode; MOT, motor; VI, visual I; VII, visual II; VAs, visual association; SAL, salience; SC, subcortical; CBL, cerebellar. R/L, right/left hemisphere. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001.
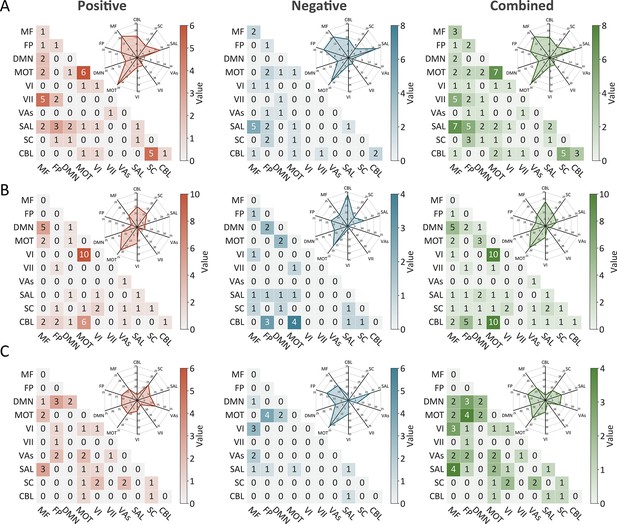
The predictive networks predicting intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) per timepoint derived from Successful stop trials.
The heatmaps show predictive networks with non-zero values at (A) age 14, (B) age 19, and (C) age 23. Each heatmap cell shows the number of edges between or within functional networks. Radar plots show the proportion of the functional networks involved in predictive networks. The edges depicted above are those selected in at least 95% of cross-validation folds. Red, blue, and green represent positive, negative, and combined networks respectively. MF, medial frontal; FP, frontoparietal; DMN, default mode; MOT, motor; VI, visual I network; VII, visual II network; VAs, visual association network; SAL, salience; SC, subcortical; CBL, cerebellar. R/L, right/left hemisphere.
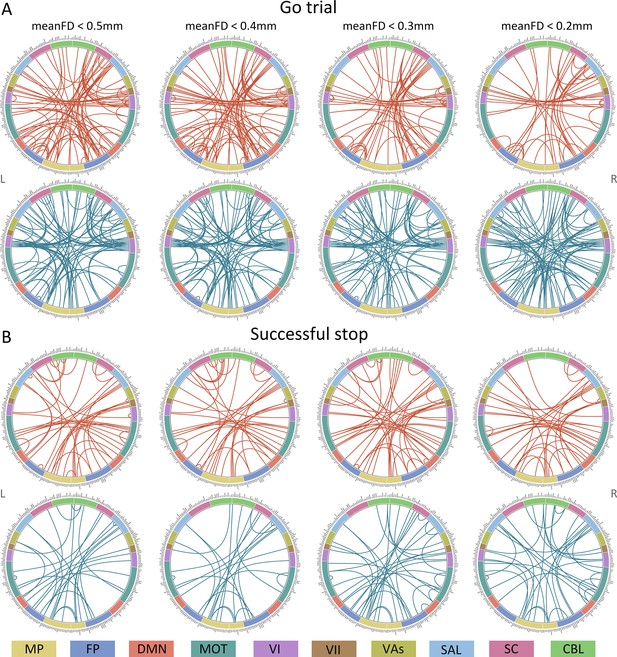
Connectome of positive and negative networks predicting intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) at age 14 with mean framewise displacement (meanFD) from 0.2 mm to 0.5 mm.
Red and blue lines represent positive and negative networks respectively. MF, medial frontal; FP, frontoparietal; DMN, default mode; MOT, motor; VI, visual I; VII, visual II; VAs, visual association; SAL, salience; SC, subcortical; CBL, cerebellar. R/L, right/left hemisphere.
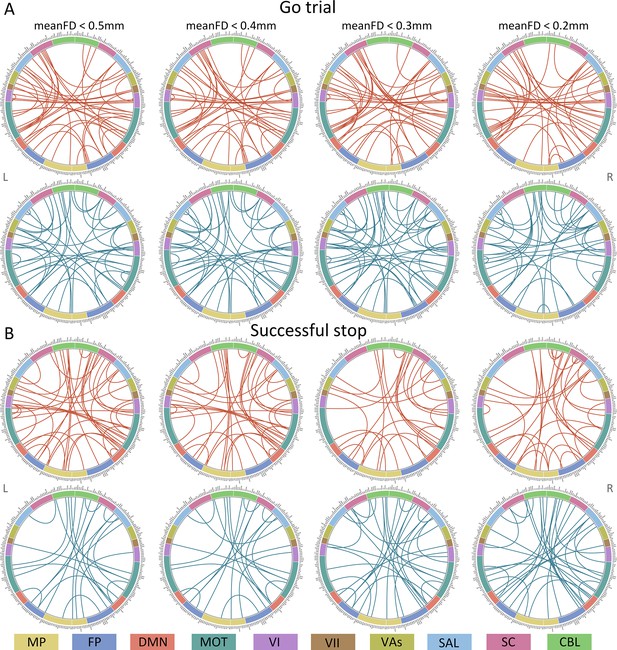
Connectome of positive and negative networks predicting intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) at age 19 with mean framewise displacement (meanFD) from 0.2 mm to 0.5 mm.
Red and blue lines represent positive and negative networks respectively. MF, medial frontal; FP, frontoparietal; DMN, default mode; MOT, motor; VI, visual I; VII, visual II; VAs, visual association; SAL, salience; SC, subcortical; CBL, cerebellar. R/L, right/left hemisphere.
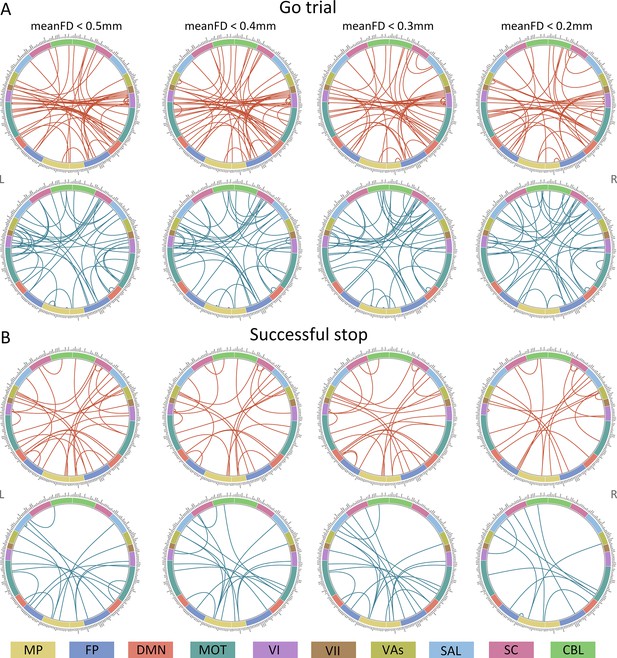
Connectome of positive and negative networks predicting intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) at age 23 with mean framewise displacement (meanFD) from 0.2 mm to 0.5 mm.
Red and blue lines represent positive and negative networks respectively. MF, medial frontal; FP, frontoparietal; DMN, default mode; MOT, motor; VI, visual I; VII, visual II; VAs, visual association; SAL, salience; SC, subcortical; CBL, cerebellar. R/L, right/left hemisphere.
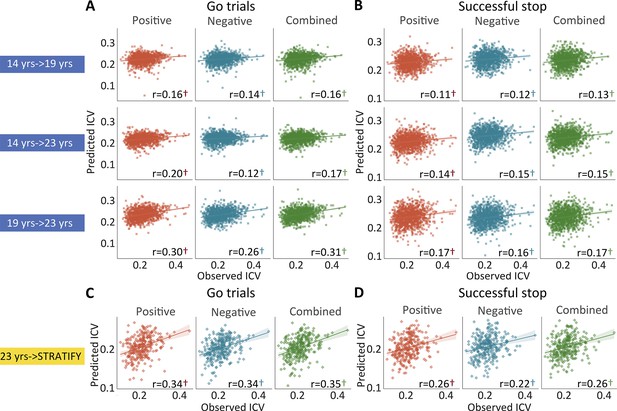
The predictive performances of intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) across timepoints and generalization in STRATIFY.
Predictive performances of ICV (A) derived from Go trials and (B) derived from Successful stop trials. The top, middle, and bottom rows of (A) and (B) panels show the predictive performance: using models defined at age 14 to predict age 19 (i.e. 14 years → 19 years), using models defined at age 14 to predict age 23 (i.e. 14 years → 23 years), and using models defined at age 19 to predict age 23 (i.e. 19 years → 23 years) respectively. Generalization of predictive networks predicting ICV defined at age 23 in STRATIFY (i.e. 23 years → STRATIFY) derived from (C) Go trials and (D) Successful stop trials. The red, blue, and green scatter represent positive, negative, and combined networks. †, p<0.001.
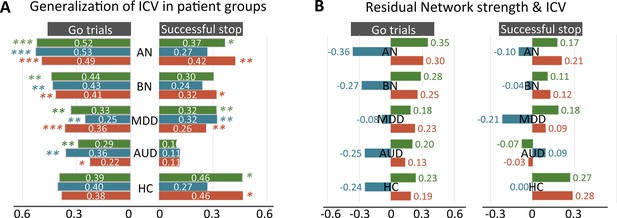
Generalization in subgroups in STRATIFY.
(A) Predictive performance in distinct patient groups in STRATIFY derived from Go and Successful stop trials. (B) The correlation between network strength and intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) across patient cohorts in STRATIFY derived from Go and Successful stop trials. AUD, alcohol use disorder; MDD, major depression disorder; BN, bulimia nervosa; AN, anorexia nervosa; HC, healthy controls. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001.
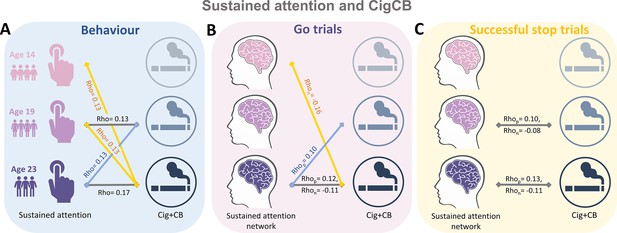
Significant correlations between sustained attention and substance use across timepoints (false discovery rate [FDR] correction, q<0.05).
(A) Correlations between the intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) and cigarette and cannabis use (Cig+CB) across timepoints. Correlations between sustained attention network strength and Cig+CB across timepoints (B) derived from Go trials and (C) derived from Successful stop trials. Rhop: r value between network strength of the positive network. Rhon: r value between network strength of the negative network.
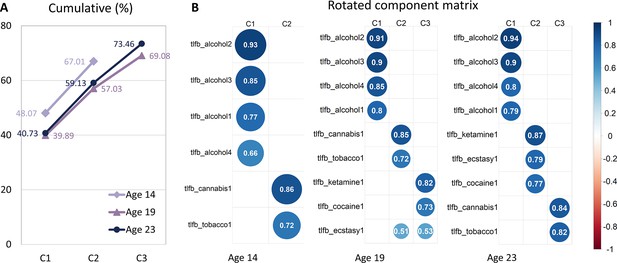
Exploratory factor analysis of Timeline Followback (TLFB) at each timepoint.
(A) Total variance explained for exploratory factor analysis of TLFB items. (B) Rotated component matrix for exploratory factor analysis. Extraction method: Principal component analysis. Rotation method: Varimax with Kaiser normalization.
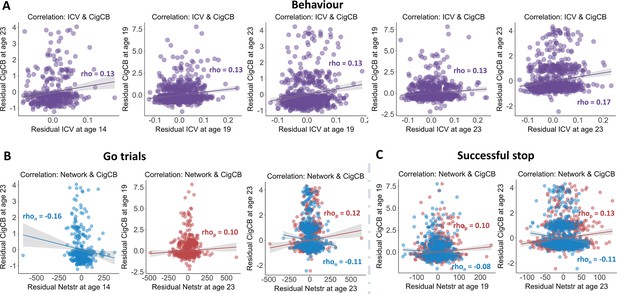
Significant correlations between sustained attention and substance use across timepoints (false discovery rate [FDR] correction, q<0.05).
(A) Correlations between the intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV) and cigarette and cannabis use (Cig+CB) across timepoints. Correlations between sustained attention network strength and Cig+CB across timepoints (B) derived from Go trials and (C) derived from Successful stop trials. Rhop: r value between network strength of the positive network. Rhon: r value between network strength of the negative network.
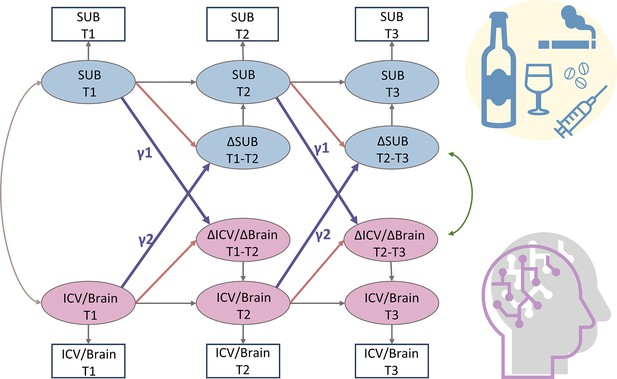
A simplified bivariate latent change score model for substance use and ICV/brain activity.
SUB, substance use (alcohol, cigarette, and cannabis use); Brain, brain network strength of positive/negative network of sustained attention derived from Go trials/Successful stop trials. ICV, intra-individual coefficient of variation. T1, timepoint 1 (age 14); T2, timepoint 2 (age 19); T3, timepoint 3 (age 23). γ1, lagged effects of substance use on ICV or brain activity. γ2, lagged effects of ICV or brain activity on substance use. The square/circle represents the observation/true score in the model.
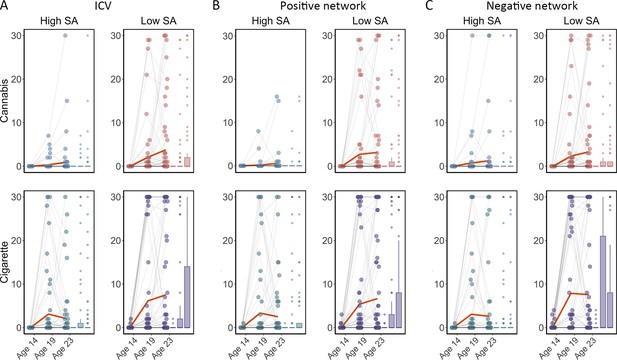
Cigarette and cannabis score in Timeline Followback changes in individuals with high sustained attention (High SA) and low sustained attention (Low SA) from ages 14 to 23.
Participants were categorized into five equal groups based on the intra-individual coefficient of variation (ICV), strength of positive network, and strength of negative network at age 14. (A) Top ICV (Low SA) and bottom ICV (High SA) groups. (B) The top strength of the positive network (Low SA) and bottom strength of the positive network (High SA) groups derived from Go trials. (C) The top strength of the negative network (High SA) and bottom strength of the negative network (Low SA) groups derived from Go trials. Note that the higher strength of the negative network reflects lower ICV and higher sustained attention.
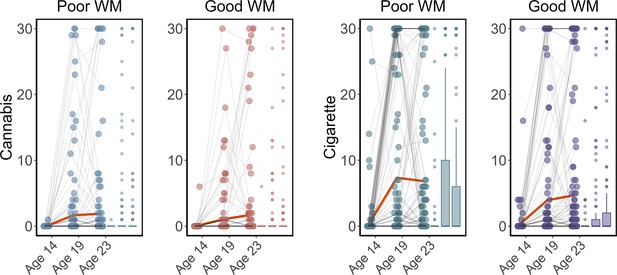
Cigarette and cannabis score in Timeline Followback change in individuals with good working memory (Good WM) and poor working memory (Poor WM) from ages 14 to 23.
Participants were categorized into five equal groups based on the performance of strategy working memory task at age 14.
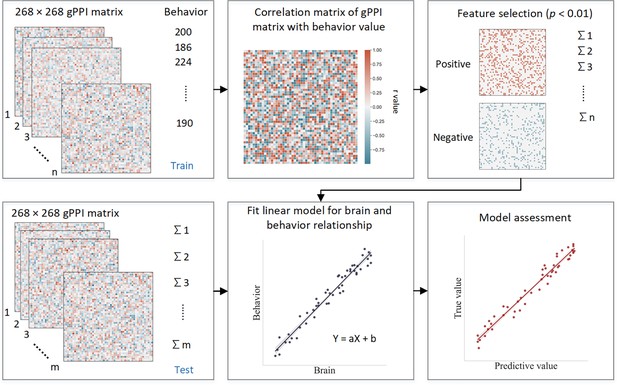
Schematic of connectome-based predictive modeling.
(i) Feature selection. The correlation between each edge in the generalized psychophysiological interaction (gPPI) matrix and the behavioral phenotype is calculated while controlling for several covariates in the training set. These covariates include age, gender, mean framewise displacement (mean FD), scan sites, and mode-centered PDS (only for age 14). The r value with the associated p value for each edge is obtained using partial correlation, and a threshold of p=0.01 is used to select the edges. Positively or negatively correlated edges are regarded as positive or negative networks. Network strength is then calculated by summing the selected edges in the gPPI matrix for both positive and negative networks, as well as by subtracting the strength of the negative network from the strength of the positive network to obtain the combined network strength. (ii) Model building. Linear models are constructed between the network strength of the positive, negative, combined network, and behavioral phenotype in the training set. The network strength is then calculated for each participants in the testing set and input into the predictive model along with covariates to yield a predicted behavioral phenotype (e.g. predicted intra-individual coefficient of variation [ICV]) for each network. (iii) Model validation. The predictive performance is evaluated by calculating the correlation between predicted and observed values.
Tables
Demographic information of adolescents in the linear mixed model across three timepoints.
| Age 14 | Age 19 | Age 23 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (three timepoints) | 2148 | ||
| Sex (M/F) | 1055/1093 | ||
| Age (years) | 14.4±0.4 | 19±0.7 | 22.6±0.7 |
| Mean FD (mm) | 0.28±0.32 | 0.18±0.17 | 0.18±0.12 |
| GO RT (ms) | 466.6±80 | 400.7±71.8 | 403.9±73.8 |
| ICV | 0.234±0.038 | 0.224±0.051 | 0.217±0.052 |
| Stop RT (ms) | 461.5±114.8 | 360±82.4 | 363.6±78.2 |
| SSD (ms) | 319.3±148.1 | 188.1±132.4 | 190±158.4 |
| SSRT (ms) | 217.8±37.2 | 213.3±43.3 | 216.2±42.6 |
| pOmission (%) | 4.4±10.5 | 2.6±8.6 | 3.7±11.1 |
| pChoiceError (%) | 4.7±6.6 | 4.8±4.7 | 5.2±7.6 |
| pCommission (%) | 47.9±6.3 | 47.5±6 | 47.2±6.9 |
-
Note: These data pertain to the participants included in the behavioural analyses. N, number of subjects; FD, framewise displacement of MR images; ICV, intra-individual coefficient of variation (assay for sustained attention); SSRT, stop signal reaction time; GO RT, reaction time in Go trials; Stop RT, reaction time in stop fail trials; SSD, stop signal delay; pOmisssion, probability of go omissions (no response); pChoiceError, probability of choice errors on Go trials; pCommission, probability of commission on Stop trials.
Bivariate latent change score model showing the bidirectional association between substance use and ICV/brain networks (false discovery rate corrected).
| Cig+CB | Alcohol use | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lagged effects of Cig+CB (γ1) | Lagged effects of ICV/brain networks (γ2) | Lagged effects of alcohol use (γ1) | Lagged effects of ICV/brain networks (γ2) | |
| Std. β (SE) | Std. β (SE) | Std. β (SE) | Std. β (SE) | |
| ICV | 0.017 (0.039) | 0.117 (0.031)*** | 0.005 (0.029) | 0.057 (0.030) |
| SA GT PosNet | –0.026 (0.030) | 0.087 (0.032)** | 0.025 (0.030) | 0.022 (0.036) |
| SA GT NegNet | 0.012 (0.026) | –0.094 (0.035)** | –0.012 (0.030) | –0.059 (0.034) |
| SA SS PosNet | 0.005 (0.025) | 0.070 (0.036) | 0.101 (0.040) | 0.046 (0.039) |
| SA SS NegNet | 0.038 (0.028) | –0.061 (0.031) | –0.003 (0.035) | –0.069 (0.031) |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Participants' demographic information.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97150/elife-97150-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97150/elife-97150-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx





