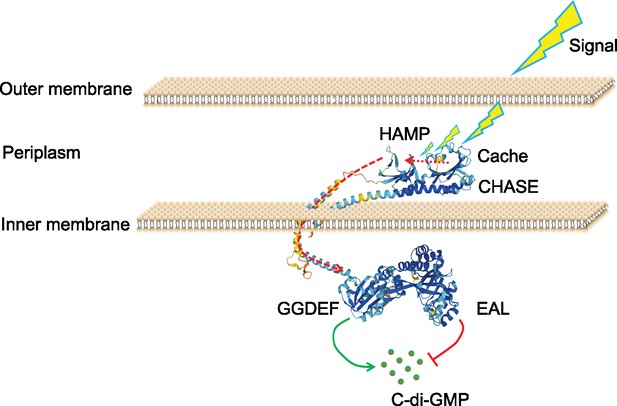
An improved bacterial single-cell RNA-seq reveals biofilm heterogeneity
Figures
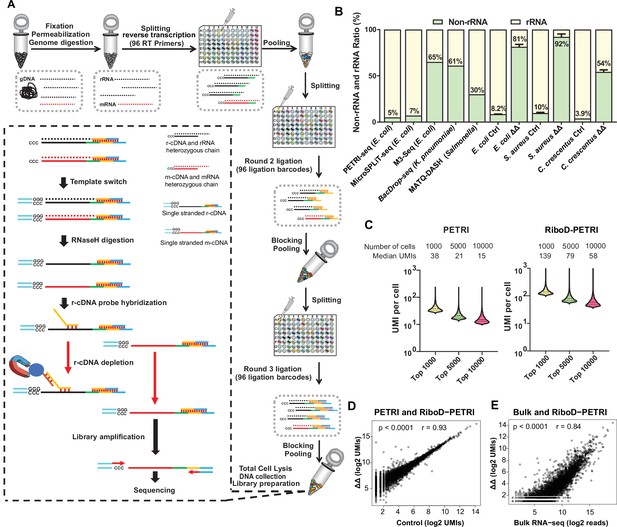
Development of RiboD-PETRI and validation of its technical performance in studying population heterogeneity.
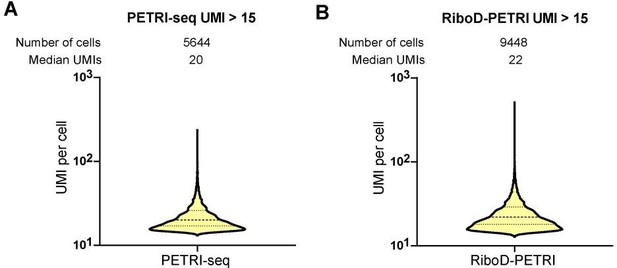
(A) Graphic summary of the RiboD-PETRI method illustrating the incorporation of RiboD after cell pooling and lysis in PETRI-seq. The RiboD protocol is represented by the dashed-line box. In this box, first, we perform template-switching oligonucleotides (TSOs) in the mixture of heterozygous chain, then we remove the RNA strand using RNaseH, at this point the system contains r-cDNA and m-cDNA single-stranded mixture. Then we add the r-cDNA probe, which specifically binds to the r-cDNA. The probes are then bound to magnetic beads, allowing the r-cDNA-probe-bead complexes to be separated from the rest of the library. And then we remove the r-cDNA that is attached to the probe by Streptavidin magnetic beads. We then performed amplification of the libraries and sent them for sequencing. We designed separate probe sets for Escherichia coli, Caulobacter crescentus, and Staphylococcus aureus. Each set was specifically constructed to be reverse complementary to the r-cDNA sequences of its respective bacterial species. This species-specific approach ensures high efficiency and specificity in rRNA depletion for each organism. (B) Comparison of non-rRNA (tRNA, mRNA, and other non-rRNA) and rRNA unique molecular identifier (UMI) counts ratio among different bacterial scRNA-seq methods. Data from PETRI-seq (E. coli), MicroSPLIT-seq (E. coli), M3-seq (E. coli) cited from previous studies. Error bars represent standard deviations of biological replicates. The ‘ΔΔ’ label represents the RiboD-PETRI protocol. The ‘Ctrl’ label represents the classic PETRI-seq protocol we performed. (C) Comparison of UMI counts per cell between RiboD-PETRI (Supplementary file 7) and PETRI (Supplementary file 8) at the same unsaturated sequencing depth. (D) Assessment of the effect of rRNA depletion on transcriptional profiles. The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) of UMI counts per gene (log2 UMIs) between RiboD-PETRI (Supplementary file 7) and PETRI (Supplementary file 9) was calculated for 3790 out of 4141 total genes, excluding those with zero counts in either library. Each point represents a gene. (E) Evaluation of the correlation between RiboD-PETRI (Supplementary file 7) data and bulk RNA-seq (Supplementary file 10) results. The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) of UMI counts per gene (log2 UMIs) among RiboD-PETRI data and the reads per gene (log2 reads) of bulk RNA-seq data was calculated for 3814 out of 4141 total genes, excluding those with zero counts in either library. Each point represents a gene. All data presented in C, D, E were from our own sequencing experiments.
-
Figure 1—source code 1
Related to Figure 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig1-code1-v1.zip
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Related to Figure 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig1-data1-v1.xls
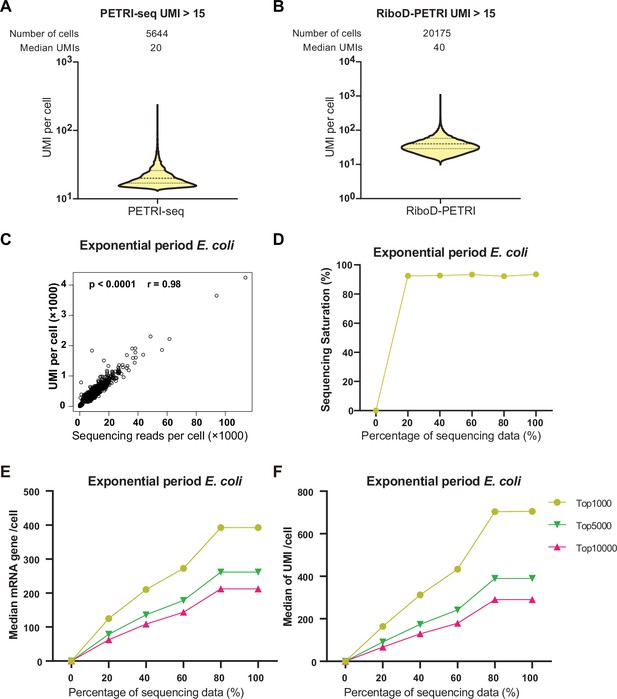
Supplementary analysis of exponential phase E. coli sequencing data.
(A, B) The number of unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) detected per cell in recovered cells in different samples (≥15 UMIs/cell): (A) PETRI, (B) RiboD-PETRI at the same unsaturated sequencing depth. The cells are ranked from highest to lowest based on the number of detected UMIs, and cells with ≥15 UMIs are selected for plotting. The median number of UMIs is calculated for these selected cells. (C) Scatterplot illustrating the relationship between reads per cell and counts of UMIs per cell detected from exponential phase E. coli data. Each dot represents a cell. (D) Sequencing saturation of data of exponential period E. coli (3 hr). We extracted 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100% of the data and further tested their saturation using the saturation calculation method of 10x Genomics. (E and F) Sequencing saturation analysis. We took 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100% of the sequencing data for single-cell analysis and counted the number of genes and UMIs for each cell in these data. The cells were then sorted from largest to smallest values, and cells were taken to count the median number of genes (E) and UMIs (F).
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source code 1
Related to Figure 1—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig1-figsupp1-code1-v1.zip
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Related to Figure 1—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.xls
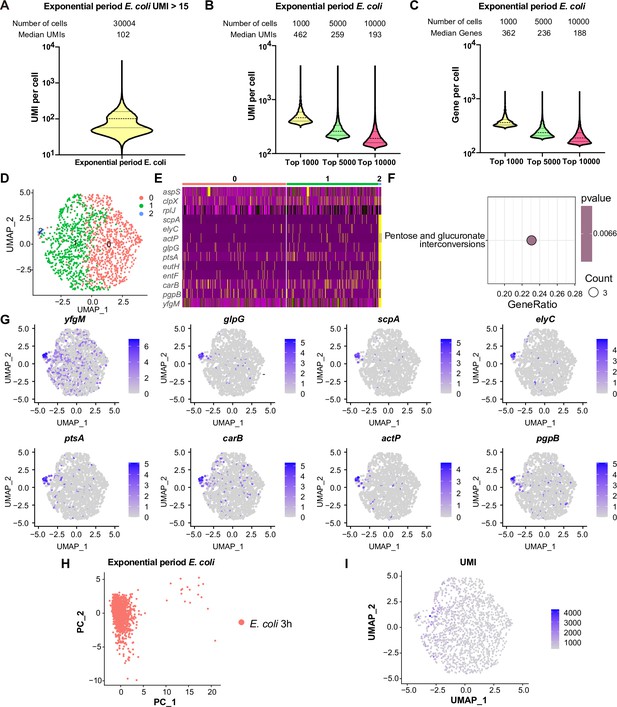
Comprehensive analysis of single-cell mRNA transcriptomic profiles in exponential phase E. coli using RiboD-PETRI.
(A) The number of unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) detected per cell in recovered cells in exponential period E. coli (≥15 UMIs/cell). The cells are ranked from highest to lowest based on the number of detected UMIs, and cells with ≥15 UMIs are selected for plotting. The median number of UMIs is calculated for these selected cells. (B) Distribution of mRNA UMIs captured per cell in RiboD-PETRI data of exponential period E. coli, presented as violin plots showing the upper quartile, median, and lower quartile lines. The cells are ranked from highest to lowest based on the number of UMIs detected. Then, specific numbers of cells (indicated above the panel) are selected for plotting. The median number of UMIs is calculated for these selected cells. (C) The number of genes detected per cell in exponential period E. coli. The cells are ranked from highest to lowest based on the number of genes detected. Then, specific numbers of cells (indicated above the panel) are selected for plotting. The median number of genes is calculated for these selected cells. (D) Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) visualization of E. coli bacteria during the exponential phase. Data were filtered for cells with UMIs between 200 and 5000, resulting in 1464 cells. Each dot represents a cell. (E) Heatmap illustrating the normalized gene expression levels of marker genes in different clusters of exponential period E. coli. Marker genes with relatively high expression levels are depicted in yellow, while lower expression levels are shown in purple. Each row represents a gene, and each column represents a cell. (F) Functional enrichment analysis of marker genes of exponential period E. coli in cluster 2. Marker genes were selected based on screening criteria of p-value <0.001 and log2 fold change (FC)>0.2. The color blocks in these figures represent the p-values of the data points. The color scale ranges from red to blue. Red colors indicate smaller p-values, suggesting higher statistical significance and more reliable results. Blue colors indicate larger p-values, suggesting lower statistical significance and less reliable results. Count is the number of genes enriched into this pathway. (G) Expression levels of marker genes in cluster 2 during the 3 hr exponential period of E. coli overlaid on the UMAP plot. Cells with high expression levels are depicted in blue. Marker genes were selected based on a p-value greater than 0.001 and a log2 FC greater than 3. (H) Principal component analysis (PCA) performed on screened data of exponential phase E. coli. The resulting scatterplots show heterogeneity among the populations, with each point representing a cell. (I) Distribution of UMIs on the UMAP results for exponential phase E. coli. UMAP results reveal heterogeneity among populations, with each point representing a cell and color shading indicating UMI counts (Supplementary file 11).
-
Figure 2—source code 1
Source code for Figure 2 and Figure 2—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig2-code1-v1.zip
-
Figure 2—source code 2
Source code for Figure 2—figure supplement 1, Figure 2—figure supplement 3 and Figure 2—figure supplement 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig2-code2-v1.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Related to Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig2-data1-v1.xls
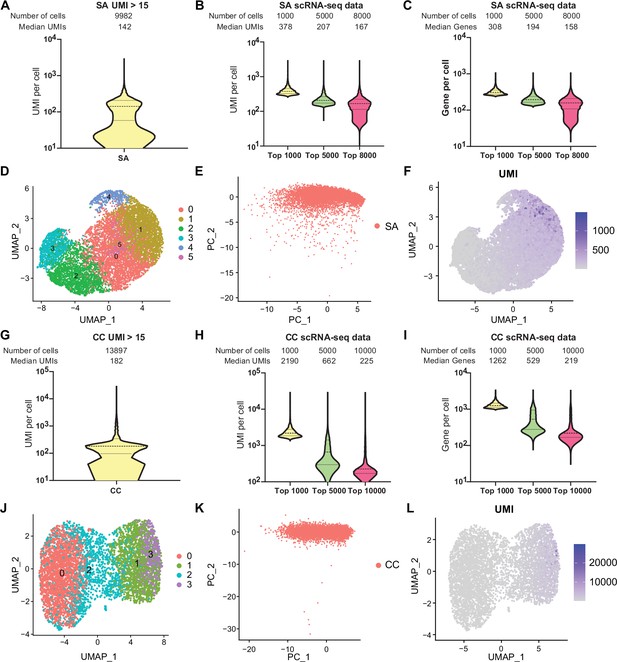
Comprehensive single-cell transcriptomic analysis of S. aureus and C. crescentus using RiboD-PETRI.
Technical application of RiboD-PETRI in S. aureus (SA) (A–F), cultured for 9 hr in Mueller-Hinton Broth (MHB) medium at 37°C (Supplementary file 14) and C. crescentus (CC) (G–L), incubated at 37°C for 3 hr (Supplementary file 15). (A, G) The number of unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) detected per cell in different samples (≥15 UMIs/cell): (A) S. aureus (SA) and (G) C. crescentus (CC). (B, H) Distribution of mRNA UMIs captured per cell in RiboD-PETRI data of (B) S. aureus (SA) and (H) C. crescentus (CC), presented as violin plots showing the upper quartile, median, and lower quartile lines. The cells are ranked from highest to lowest based on the number of UMIs detected. Then, specific numbers of cells (indicated above the panel) are selected for plotting. The median number of UMIs is calculated for these selected cells. (C, I) The number of genes detected per cell in different samples (C) S. aureus and (I) C. crescentus. The cells are ranked from highest to lowest based on the number of genes detected. Then, specific numbers of cells (indicated above the panel) are selected for plotting. The median number of genes is calculated for these selected cells. ‘SA’ denotes S. aureus, and ‘CC’ denotes C. crescentus. (D, J) UMAP visualization of (D) S. aureus and (J) C. crescentus, demonstrating the ability of RiboD-PETRI to distinguish population heterogeneity. (E, K) Normalized and principal component analysis (PCA) performed on screened data of (E) S. aureus and (K) C. crescentus. The resulting scatterplots show heterogeneity among the populations, with each point representing a cell. (F, L) Distribution of UMIs on the UMAP results for (F) S. aureus and (L) C. crescentus. UMAP results reveal heterogeneity among populations, with each point representing a cell and color shading indicating UMI counts.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Related to Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v1.xls
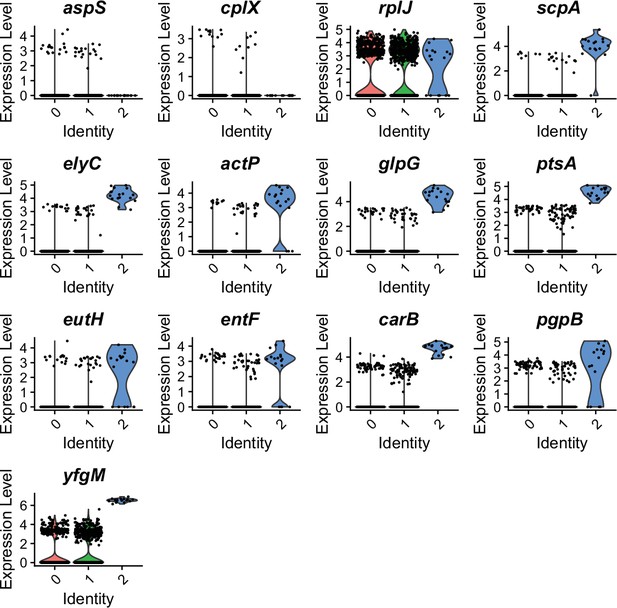
Profiling of marker genes in exponential phase E. coli culture by RiboD-PETRI.
Expression levels of diverse marker genes across distinct clusters in exponential phase E. coli culture, visualized through violin plots. Each individual dot represents a single cell, demonstrating the high-resolution, single-cell nature of the RiboD-PETRI analysis.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source code 1
Related to Figure 2—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig2-figsupp2-code1-v1.zip
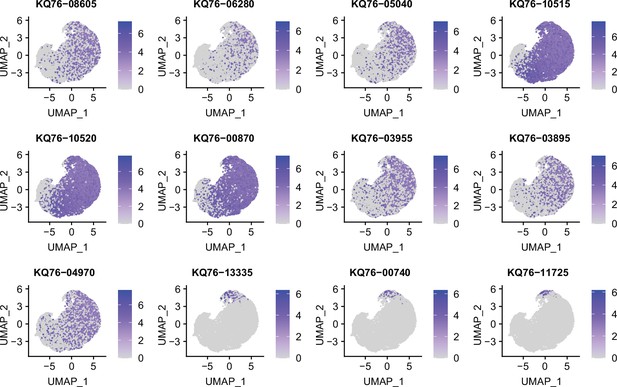
Marker genes identified in stationary phase S. aureus culture by RiboD-PETRI.
Expression levels of different marker genes across different clusters in stationary phase S. aureus culture overlaid on the Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) plot. Marker genes were selected based on a p-value greater than 0.001 and a log2 fold change (FC) greater than 0.2. Each dot represents a cell and color shading indicating unique molecular identifier (UMI) counts.
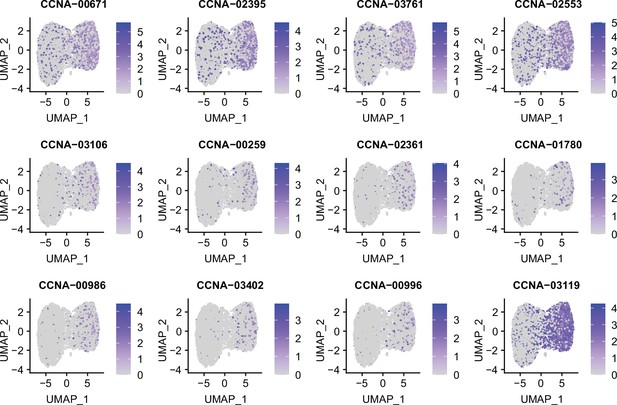
Marker genes identified in exponential phase C. crescentus culture by RiboD-PETRI.
Expression levels of different marker genes across different clusters in exponential phase C. crescentus culture overlaid on the Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) plot. Marker genes were selected based on a p-value greater than 0.001 and a log2 fold change (FC) greater than 0.2. Each dot represents a cell and color shading indicating unique molecular identifier (UMI) counts.
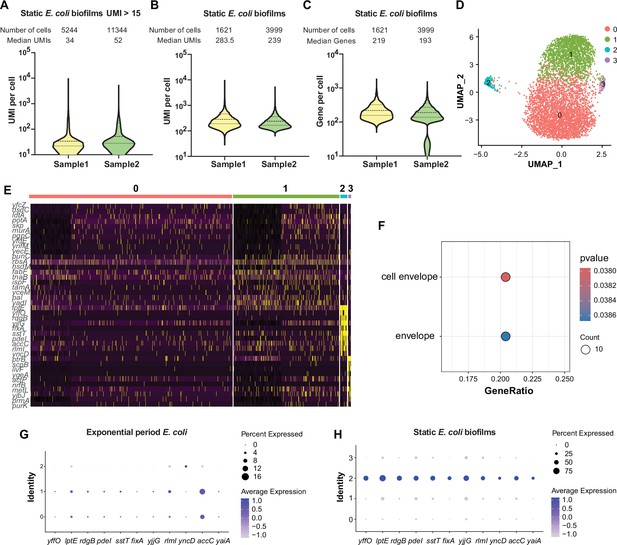
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis and characterization of static E. coli biofilm using RiboD-PETRI.
(A–F, H) RiboD-PETRI data from static E. coli biofilm (E. coli 24 hr static culture) (Supplementary files 12 and 13). RiboD-PETRI data of static E. coli biofilm were screened for cells with unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) between 100 and 2000, resulting in 1621 and 3999 cells. (A) The number of UMIs detected per cell in recovered cells in Static E. coli biofilms (≥15 UMIs/cell). The cells are ranked from highest to lowest based on the number of detected UMIs, and cells with ≥15 UMIs are selected for plotting. (B) Distribution of mRNA UMIs captured per cell in RiboD-PETRI data of static E. coli biofilm. (C) The number of genes detected per cell in static E. coli biofilm. (D) UMAP visualization of static E. coli biofilm, revealing two small populations of heterogeneous cells in clusters 2 and 3. (E) Inferred expression levels of marker genes from static E. coli biofilm of E. coli across different clusters. (F) Enrichment pathways for marker genes of static E. coli biofilm data in cluster 2, selected based on screening criteria of p-value<0.001 and log2 fold change (FC)>0.2. The color blocks in these figures represent the p-values of the data points. (G and H) Dot plot displaying scaled expression levels of marker genes in different clusters of E. coli in exponential phase (G) and E. coli in static E. coli biofilm (H). These genes were markers of static E. coli biofilms in cluster 2, identified with screening criteria of p-value<0.001 and log2 FC>3. Dot size represents the percentage expression of the gene in the cluster, while color indicates the average expression level normalized from 0 to 1 across all clusters for each gene.
-
Figure 3—source code 1
Source code for Figure 3, Figure 3—figure supplement 1 and Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig3-code1-v1.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Related to Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig3-data1-v1.xls
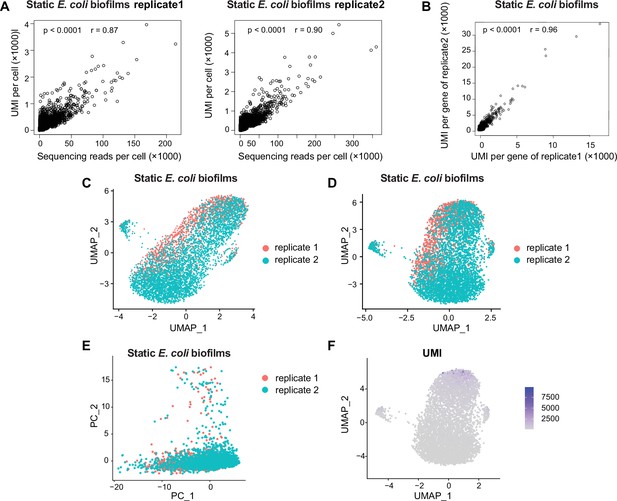
Evaluation of transcriptomic consistency and batch effect analysis in static biofilm E. coli samples.
(A) Scatterplot demonstrating the relationship between reads per cell and counts of unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) per cell detected from static biofilm E. coli data. Two replicates of the sample are included. (B) Calculation of the Pearson correlation coefficient (r) of UMI counts per gene between replicate 1 and replicate 2 of static biofilm E. coli. The analysis involved 4062 out of 4141 total genes, with a significant correlation (p-value<0.0001, r = 0.96), indicating good replication between samples. Each dot represents a gene. (C) Before batch effects were removed, UMAP plot based on the original identity of static biofilm E. coli samples (replicate 1 and replicate 2). Each dot represents a cell, with red indicating replicate 1 and green indicating replicate 2. (D) After batch effects were removed using Harmony, UMAP plot based on the original identity of static biofilm E. coli samples (replicate 1 and replicate 2). (E) Principal component analysis (PCA) performed on screened data of two replicates of static biofilm E. coli. The resulting scatterplots show heterogeneity among the populations, with each point representing a cell. (F) Distribution of UMIs on the UMAP results for two replicates of static biofilm E. coli. UMAP results reveal heterogeneity among populations, with each point representing a cell and color shading indicating UMI counts.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Related to Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v1.xls
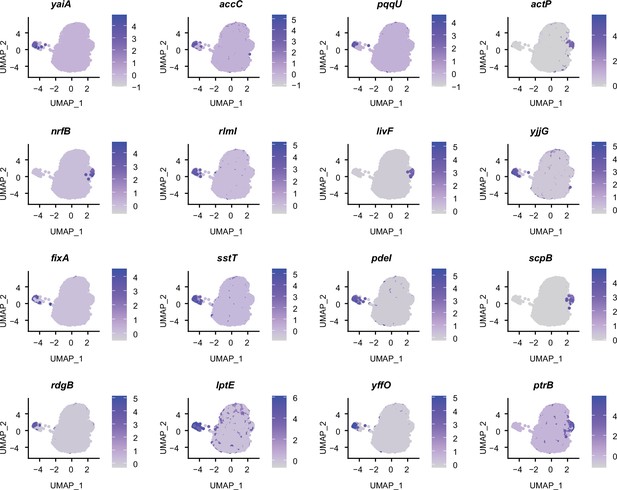
Marker genes identified in static E. coli biofilms by RiboD-PETRI.
Expression levels of different marker genes across different clusters in static E. coli biofilms overlaid on the Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) plot. Marker genes were selected based on a p-value greater than 0.001 and a log2 fold change (FC) greater than 3. Each dot represents a cell and color shading indicating unique molecular identifiers (UMI) counts.
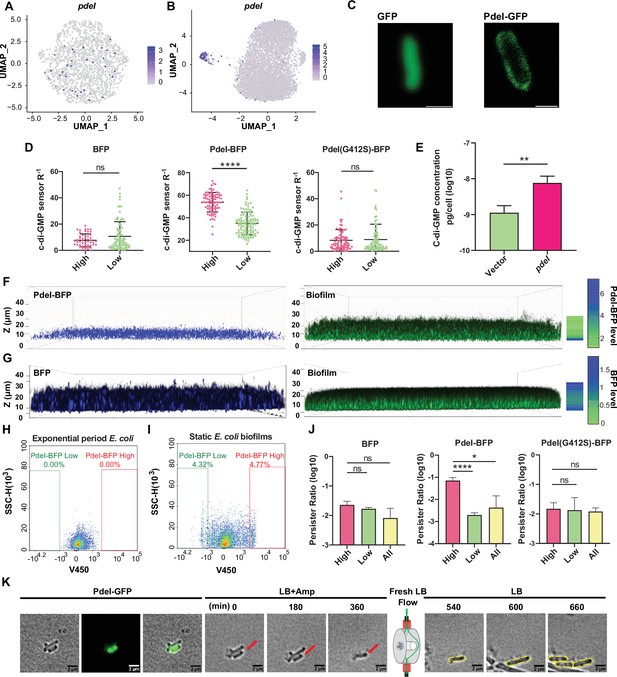
Functional investigation of marker gene pdeI in static E. coli biofilm.
(A, B) Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) plots showing the distribution of pdeI in single-cell data of exponential period E. coli (A) and static E. coli biofilm (B). Each dot represents a cell colored by normalized expression levels of genes. (C) Subcellular localization of PdeI-GFP and GFP. Scale bar, 1 μm. (D) c-di-GMP levels (R–1 score) in E. coli cells with different BFP, PdeI-BFP, PdeI(G412S)-BFP expression levels (low or high), under the control of the pdeI native promoter, in static E. coli biofilm. c-di-GMP levels are measured using the c-di-GMP sensor system integrated into E. coli cells. R–1 score was determined using the fluorescent intensity of mVenusNB and mScarlet-I in the system. The fluorescent intensity is measured by flow cytometry (n>50). (E) Determination of cellular concentrations of c-di-GMP by high-pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) in cells overexpressing PdeI under the control of arabinose promoter, with 0.002% arabinose induction for 2 hr (n=3). (F, G) Localization of PdeI-high cells in the biofilm matrix. Cells expressing PdeI-BFP under the control of the pdeI native promoter were grown in a glass-bottom cell culture dish and stained with SYTO 24 for bacterial DNA. Cells expressing BFP under the control of arabinose promoter, with 0.00001% arabinose induction for 24 hr in a glass-bottom cell culture dish and stained with SYTO 24 for bacterial DNA. (H, I) Heterogeneous expression of PdeI in single-cell data of exponential period E. coli (H) and E. coli in static E. coli biofilm (E. coli 24 hr static culture) (I). Biofilm cells with high or low expression levels of PdeI-BFP were sorted by flow cytometry. (J) Persister counting assay using 150 μg/ml ampicillin on cells with high or low expression levels of BFP, PdeI-BFP, and PdeI(G412S)-BFP from static E. coli biofilm, sorted by flow cytometry (n=3). These strains were under the control of the pdeI native promoter. (K) Time-lapse images of the persister assay observed under a microscope. Static biofilm cells of the PdeI-GFP strain were spotted on a gel pad and treated with 150 μg/ml ampicillin in Luria broth (LB). Images were captured over 6 hr at 37°C, followed by the replacement of fresh LB to allow persister cell resuscitation. Scale bar, 2 μm. Error bars represent standard deviations of biological replicates. Significance was ascertained by unpaired Student’s t-test. Statistical significance is denoted as *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Related to Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-fig4-data1-v1.xls

The proportion of persister cells in the partially maker genes and empty vector control groups.
Following induction of expression with 0.002% arabinose for 2 hours, a persister counting assay was conducted on the strains using 150 μg/ml ampicillin.
Videos
Time-lapse images of the persister assay using cells with different PdeI-BFP.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 | Yale Genetic Stock Center | CGSC#6300 | |
| Strain, strain background (Caulobacter crescentus) | NA1000 | Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences | NCBI accession number CP001340 | |
| Strain, strain background (Staphylococcus aureus) | ATCC 25923 | ATCC | ATCC 25923 | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 pBAD::gfp | This paper | Figure legends and Materials and methods section | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 p(pdeI promoter)::pdeI-gfp | This paper | Figure legends and Materials and methods section | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 p(pdeI promoter)::pdeI-bfp | This paper | Figure legends and Materials and methods section | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 Δara pBAD::pdeI | This paper | Figure legends and Materials and methods section | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 Δara pBAD::vector | This paper | Figure legends and Materials and methods section | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 p(pdeI promoter)::bfp | This paper | Figure legends and Materials and methods section | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 p(pdeI promoter)::pdeI(G412S)-bfp | This paper | Figure legends and Materials and methods section | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 p(pdeI promoter)::bfp p15A::c-di-GMP-sensor | This paper | Figure legends and Materials and methods section | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 p(pdeI promoter)::pdeI-bfp p15A::c-di-GMP-sensor | This paper | Figure legends and Materials and methods section | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 p(pdeI promoter)::pdeI(G412S)-bfp p15A::c-di-GMP-sensor | This paper | Figure legends and Materials and methods section | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | MG1655 Δara pBAD::bfp | This paper | Figure legends and Materials and methods section | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p15A::c-di-GMP-sensor | This paper | p15A ori | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pBAD::vector | This paper | Arabinose-induction | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pBAD::gfp | This paper | Arabinose-induction | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pBAD::bfp | This paper | Arabinose-induction | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p(pdeI promoter)::bfp | This paper | pdeI native promoter induction | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p(pdeI promoter)::pdeI-bfp | This paper | pdeI native promoter induction | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p(pdeI promoter)::pdeI(G412S)-bfp | This paper | pdeI native promoter induction | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p(pdeI promoter)::pdeI-gfp | This paper | pdeI native promoter induction | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p(pdeI promoter)::pdeI | This paper | pdeI native promoter induction | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pBAD::pdeI-gfp | This paper | Arabinose-induction | |
| Sequence-based reagent | P-pdeI-F | This paper | PCR primers | AATTGTCTGATTCGTTACCAACTGACCGTACTGGCGTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | P-pdeI-R | This paper | PCR primers | TTGCTGCTGCCTCGGCTTCTAGCTCTTTTACTAATTTTCCACTTTTATCCCAGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | pdeI-F | This paper | PCR primers | GGCTAACAGGAGGAATTAACCATGCTGAGTTTATACGAAAAGATAAAGATAAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | pdeI-R | This paper | PCR primers | GCTGGAGACCGTTTAAACTCACTACTCTTTTACTAATTTTCCACTTTTATCCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | pBAD-R | This paper | PCR primers | TTGGTAACGAATCAGACAATTGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | pBAD-F | This paper | PCR primers | TGAGTTTAAACGGTCTCCAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | pBAD-R2 | This paper | PCR primers | GGTTAATTCCTCCTGTTAGCCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Bfp-F | This paper | PCR primers | CGAGGCAGCAGCAAAGGCCCTAGAAGGTGGATCCGGCGGTTCTAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gfp-F | This paper | PCR primers | CTAGAAGCCGAGGCAGCAGCAAAGGCCCTAGAAATGAGTAAAGGAGAAGAACTTTTCAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | G412S-F | This paper | PCR primers | GAAGCGGTGTTTAGTGTTGATG |
| Sequence-based reagent | G412S-R | This paper | PCR primers | CATCAACACTAAACACCGCTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | P-bfp-R | This paper | PCR primers | GTTAATACATTTAACAAAATAACTATCTGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | P-bfp-F | This paper | PCR primers | ATAGTTATTTTGTTAAATGTATTAACGGTGGATCCGGCGGTTCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | UP-F | This paper | PCR primers | CATGAATTCTGGCGACGATTTCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | UP-R | This paper | PCR primers | GTTAATACATTTAACAAAATAACTATCTGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | ccdB-F | This paper | PCR primers | CACAGCGTTCAGATAGTTATTTTGTTAAATGTATTAACTCTAGAGCGACGCCAGACG |
| Sequence-based reagent | ccdB-R | This paper | PCR primers | CTGTAAGTACGAACTTATTGATTCTGGACATACGTAAATTACGCCCCGCCCTGCCAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Down-F | This paper | PCR primers | TTTACGTATGTCCAGAATCAATAAGTTCGTACTTAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Down-R | This paper | PCR primers | ATCTTCGTCAAAGGATTTTCTGCCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | UP2-R | This paper | PCR primers | ATCTTTTCGTATAAACTCAGCATGTTAATACATTTAACAAAATAACTATCTGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | pdeI-G412S-F | This paper | PCR primers | ATGCTGAGTTTATACGAAAAGATAAAGAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | pdeI-G412S-R | This paper | PCR primers | CTTATTGATTCTGGACATACGTAAACTACTCTTTTACTAATTTTCCACT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Down2-F | This paper | PCR primers | TTTACGTATGTCCAGAATCAATAAGTTCGTACTTAC |
| Commercial assay or kit | KAPA HIFI hotStart ReadyMix PCR Kits | KAPA | Cat#2602 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | VAHTS Universal DNA Library Prep Kit | Vazyme | Cat#NR603 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Bacteria RNA Extraction Kit | Vazyme | Cat#R403-01 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Ribo-off rRNA Depletion Kit (Bacteria) | Vazyme | Cat#N407 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | 2× MultiF Seamless Assembly Mix | ABclonal | Cat#RK21020 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | VAHTS Universal DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina V3 | Vazyme | Cat#ND607 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | ABScript III RT Master Mix for qPCR with gDNA Remover | ABclonal | Cat#RK20429 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SUPERase-In RNase Inhibitor | Invitrogen | Cat#AM2696 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Streptavidin Magnetic Beads | Thermo Fisher | Cat#88816 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Syto 24 dye | Invitrogen | Cat#S7559 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Arabinose | Sigma | Cat#V900920 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ampicillin | Sangon Biotech | Cat#A610028 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Chloramphenicol | Sangon Biotech | Cat#A600118 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Kanamycin | Sangon Biotech | Cat#A600286 | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | GitHub | https://fiji.sc/; RRID:SCR_002285 | |
| Software, algorithm | FlowJo | Treestar, Inc | https://www.flowjo.com/ |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Primers used in this study.
Related to RiboD-PETRI library construction.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp1-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 2
Multiplet frequency.
The specific calculation process for multiplet frequency.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp2-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 3
rRNA and mRNA expression of PETRI-seq and RiboD-PETRI.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp3-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 4
Various methods in rRNA depletion.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp4-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 5
Sequencing information.
The detailed information of RiboD-PETRI libraries.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp5-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 6
The cost of RiboD-PETRI.
The detailed cost breakdown of RiboD-PETRI.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp6-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 7
Matrix_of_E. coli_3h_data_by_RiboD-PETRI_in_Figure 1C–E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp7-v1.zip
-
Supplementary file 8
Matrix_of_E. coli_data_by_PETRI-seq_in_Figure 1C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp8-v1.zip
-
Supplementary file 9
Matrix_of_E. coli_data_by_PETRI-seq_in_Figure 1D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp9-v1.zip
-
Supplementary file 10
E. coli RNA-seq data.
The result of bulk RNA-seq of exponential period E. coli sample in Figure 1E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp10-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 11
Matrix_of_Exponential_period_E. coli_data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp11-v1.zip
-
Supplementary file 12
Matrix_of_Static_E. coli_biofilm-1_data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp12-v1.zip
-
Supplementary file 13
Matrix_of_Static_E. coli_biofilm-2_data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp13-v1.zip
-
Supplementary file 14
Matrix_of_SA_data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp14-v1.zip
-
Supplementary file 15
Matrix_of_CC_data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-supp15-v1.zip
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/97543/elife-97543-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx