Sleep need driven oscillation of glutamate synaptic phenotype
Figures
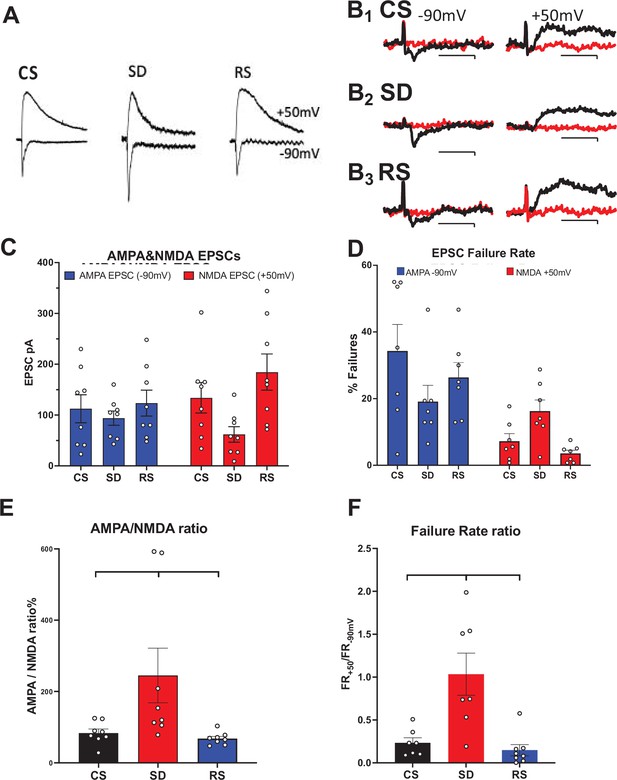
Sleep need-dependent responses of AMPA/NMDA ratio and silent synapses in the motor cortex.
(A) Examples of AMPA currents at –90 mV holding potential and NMDA currents at +50 mV holding potential are shown for: control sleep (CS), 6 hr of sleep deprivation (SD), and 4 hr of sleep deprivation followed by 2 hr of recovery sleep (RS). Traces (100 ms duration) are scaled to the NMDA current for comparison (NMDA current measured @ 40 ms after AMPA peak current). (B) Examples of successes (black) and failures (red) at –90 mV (left, AMPA) and +50 mV (right, NMDA) after minimal stimulation of excitatory inputs to motor cortex pyramidal neurons are shown; Top row: CS sleep, middle row: SD and bottom row: RS (Cal. 10pAX20ms). Rate of failures (% of all stimuli delivered) for AMPA EPSCs (blue) and NMDA EPSCs (red) in the three conditions (+/-sem). (C, D) Average (+/-sem) AMPAR and NMDAR EPSC responses (unmatched) and failure rates, respectively, for each sleep condition. (E), (F) Matched AMPA/NMDA EPSC response and AMPA/NMDA failure rate ratios, respectively, are shown for the three conditions (N=1 cell/slice, 2–3 slice/animal, 3 animals/condition).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
EPSC subtype amplitudes (Tab 1); statistics for EPSC amplitudes X conditions (Tab2 & 3); failure rate data (Tab4); statistics for failure rate data (Tab5); and statistics ratios of failure rate data (Tab6).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98280/elife-98280-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
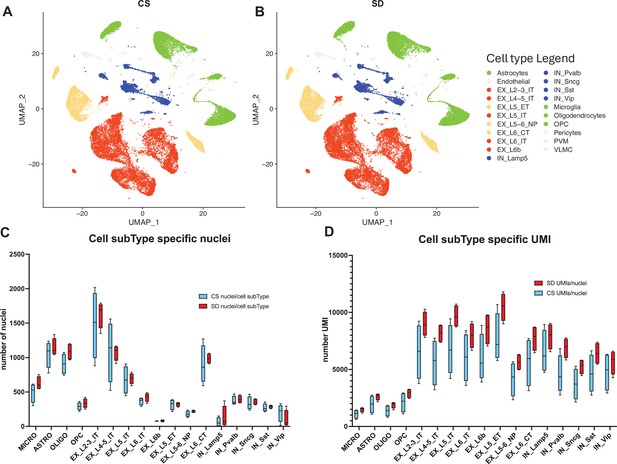
snRNAseq data shows cell type and sub-type based on gene expression patterns are unaffected by sleep needs.
(A) Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) projection of cell-type gene expression pattern following 6 hr ad lib sleep (control sleep, CS) at ZT = 6 hr. (B) As in (A) except after 6 hr of sleep deprivation (SD), ZT = 6 hr. (C) The distribution of cell numbers across subtypes is unaffected by sleep needs. (D) The median number of UMIs/cell is significantly increased by sleep need across all cell subtypes (see_Figure 2—source data 1 and text for statistics).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Table of cell-type specific #'s of cells, genes and UMI's (Tab1); statistics for cell-type specific #'s of nuclei X condition (Tab 2); and statistics for cell-type specific # of UMI's X condition (Tab3).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98280/elife-98280-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
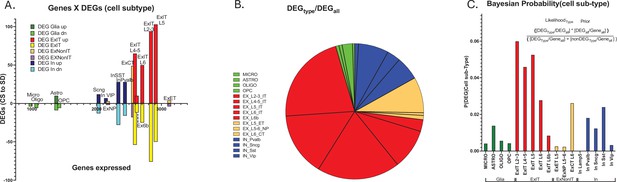
Cell type-specific differential gene expression in response to 6 hr of sleep deprivation (SD).
(A) An XY bar plot of cell type specific differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (both up and down-regulated) organized by cell-type-specific number of expressed genes (X axis) shows the greatest number of DEGs are found in excitatory pyramidal neurons that project within the telencephalon (ExIT). (B) A pie chart of the distribution of DEGs amongst different cell types illustrates that the majority of sleep DEGs are expressed by ExIT neurons. (C) An analysis of the cell type-specific DEG occurrence shows the greatest probability of significant sleep loss gene response is found in ExIT cells by more than threefold compared to all other cell types.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Table of cell-type and condition specific #'s of genes and DEGs (Tab 1); and cell-type specific distribution of DEGs (Tab 2).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98280/elife-98280-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
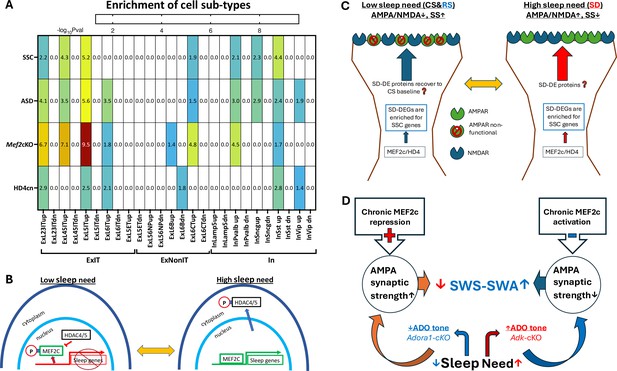
Differentially expressed gene (DEG) enrichment of cell types in response to sleep deprivation (SD) by autism risk genes, synaptic shaping component genes, and DEGs from MEF2c loss of function or constitutive HD4 repression of MEF2c.
(A) Heat map for cell type DEG enrichment by autism spectrum disorder (ASD) risk genes, Synaptic Shaping Component genes, MEF2c-cKO DEGs, and cnHD4 DEGs. (B) Model for the control of sleep DEGs by HD4 repression of MEF2c and by pMEF2c during low sleep need (left). During high sleep need, MEF2c is de-repressed by sequestration of pHD4 to the cytoplasm and dephosphorylation of MEF2c. Both these events facilitate the expression of sleep genes. (C) It is proposed that SSC gene expression induced by prolonged waking or SD can, once asleep, decrease the AMPA/NMDA ratio and increase silent synapses (SS) during sleep. This may bias glutamate synapses towards decreased strength but increased potential for long-term plasticity (LTP) in preparation for the active phase, when sleep need is low. Conversely, as the active phase progresses, the AMPA/NMDA ratio increases (as does synaptic strength), and silent synapses are replaced by active synapses in association with increased expression of SSC genes to complete the cycle of glutamate, synapse, and phenotype oscillation. (D) An illustration of the slow wave activity during slow wave sleep (SWS-SWA) response to chronic MEF2c repression or activation. Chronic activation of MEF2c facilitated transcription leads to decreased AMPAR-mediated synaptic strength mimicking the effect of increased Ado tone, that will inhibit cortical-thalamic, glutamate synaptic activity to increase SWS-SWA. Chronic repression of MEF2c does the opposite, mimicking loss of Ado A1 receptors (ADORA1) function and tone, to decrease SWS-SWA.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Cell-type specific DEGs from CS to SD, corresponding log2 fold change, and FDR (Tabs 1-4); and curated gene lists and the cell-type specific DEGs (>23% change of expression & FDR < 0.05) that overlapped with one of the curated lists (Tab5).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98280/elife-98280-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx





