Interneuron FGF13 regulates seizure susceptibility via a sodium channel-independent mechanism
Figures
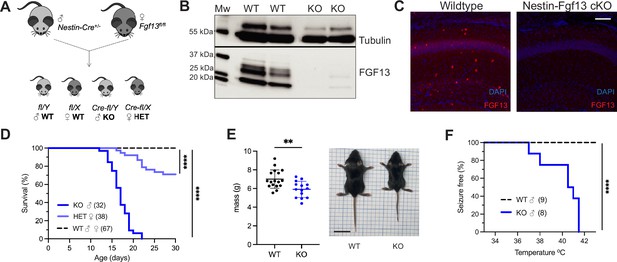
Whole brain knockout of Fgf13 results in premature death and seizure susceptibility.
(A) Breeding scheme to generate Nestin-Fgf13 cKO, Nestin-Fgf13 Het, and wildtype littermates. (B) Western blots of whole brain Nestin-Fgf13 cKO (KO) and wildtype (WT) littermates at P2 validates Fgf13 knockout. Tubulin used as a loading control. (C) Fluorescent immunohistochemistry of hippocampal tissue validates Fgf13 knockout (scale bar, 100 μm). (D) Survival curve of Nestin-Fgf13 cKO mutant mice shows decreased survival at 1 month of age (log-rank test, ****, p<0.0001). (E) Body mass at P14 shows Nestin-Fgf13 cKO are smaller in size (t-test, **, p<0.01). (F) Nestin-Fgf13 cKO are susceptible to hyperthermia-induced seizures (log-rank test, ****, p<0.0001), unlike wildtype littermates.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Original TIFF files saved from BioRad Gel doc system for gels shown in Figure 1B, together with a PDF file identifying the respective portions displayed.Figure 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98661/elife-98661-fig1-data1-v1.zip
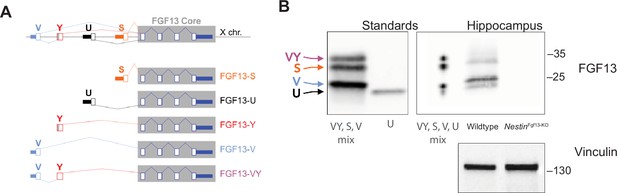
Fgf13 splice variants are differentially expressed in hippocampal cell types.
(A) Fgf13 generates five alternatively spliced variants. (B) Knockout of in Fgf13 in Nestin neurons eliminates all isoforms, while knockout of Fgf13 in Emx excitatory neurons eliminates the S and U isoforms. Vinculin used as a loading control for brain samples.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original TIFF files saved from BioRad Gel doc system for gels shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 1B, together with a PDF file identifying the respective portions displayed.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98661/elife-98661-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
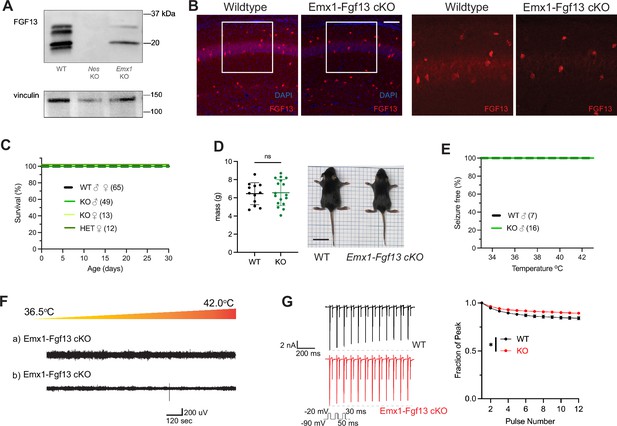
Excitatory neuronal knockout of Fgf13 does not result in premature death and seizure susceptibility.
(A) Western blot shows partial loss of Fgf13 from Emx1-Fgf13 cKO hippocampal tissue, compared to full knockout in Nestin-Fgf13 cKO hippocampus. Vinculin used as a loading control. (B) Fluorescent immunohistochemistry of hippocampal tissue validates Fgf13 knockout (scale bar, 100 μm). (C) Emx1-Fgf13 cKO mutant mice survive past 1 month of age (log-rank test, p=ns). (D). Body mass at postnatal day 14 (P14) shows that Emx1-Fgf13 cKO are not different in size (scale bar, 2 cm) (t-test, p=ns). (E) Emx1-Fgf13 cKO are not susceptible to hyperthermia induced seizures (log-rank test, p=ns). (F) EEG recordings during hyperthermia protocol show Emx1-Fgf13 cKO do not exhibit heat-induced seizures. (G) Emx1-Fgf13 cKO neurons exhibit diminished long-term inactivation (two-way ANOVA, *, p<0.05), though the deficit is not sufficient to cause seizures (WT, N=2, n=15; KO, N=2, n=15). Example traces for WT and Emx1-Fgf13 cKO neurons are shown on the left.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Original TIFF files saved from Bio-Rad Gel doc system for gels shown in Figure 2A, together with a PDF file identifying the respective portions displayed.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98661/elife-98661-fig2-data1-v1.zip
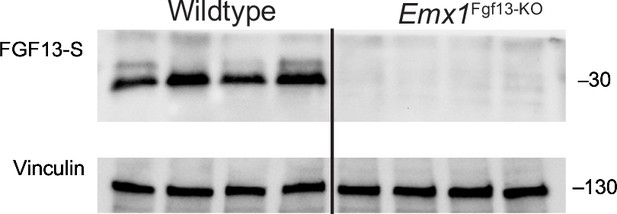
Excitatory neuronal knockout of Fgf13 results in loss of FGF13-S.
Western blot performed with FGF13-S-specific antibody. Vinculin used as a loading control.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original TIFF files saved from Bio-Rad Gel doc system for gels shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1, together with a PDF file identifying the respective portions displayed.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98661/elife-98661-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
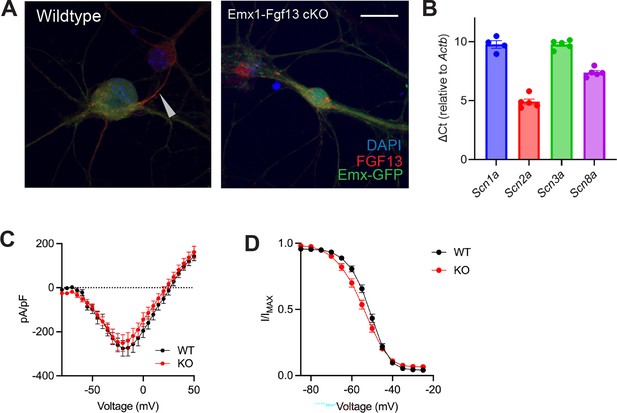
Excitatory neuronal knockout of Fgf13 does not result in sodium current deficits.
(A) Primary hippocampal neuron cultures were generated from Emx1-Cre wildtype (left) or Emx1-Fgf13 cKO male mice, and Emx1 +excitatory cells were labeled by infection with a Cre-dependent AAV8-DIO-GFP virus. Immunocytochemistry was performed with a pan-FGF13 antibody (scale bar, 20 μm). Arrow indicates FGF13 in the axon initial segment, absent in the Emx1-Fgf13 cKO neurons. (B) Reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction of neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels shows levels of expression for specific channels relative to Actb (N=4–5 mice). (C) Emx1-Fgf13 cKO neurons do not exhibit differences in macroscopic sodium currents (two-way ANOVA, p=ns). Peak current-voltage (I–V) curves shown; WT N=3 mice, n=18 cells; KO N=4 mice, n=18 cells. (D) Emx1-Fgf13 cKO neurons do not have a significant difference in steady-state inactivation (V1/2 WT=−52.04 [95% CI, −53.60 to -50.47]; V1/2 KO = –54.47 [95% CI, –56.4––52.54]). WT N=3 n=21; KO N=4 n=37.
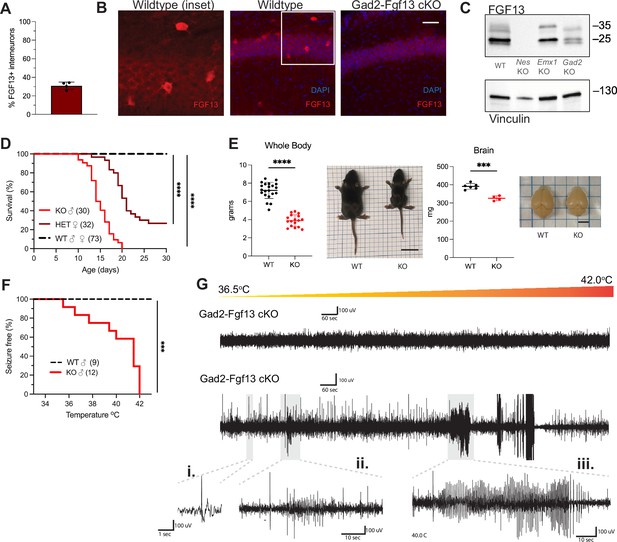
Inhibitory neuronal knockout of Fgf13 recapitulates premature death and seizure susceptibility.
(A) Quantification of hippocampal interneuron histology reveals 31% of Gad2+ interneurons co-express FGF13. (B) Fluorescent immunohistochemistry of hippocampal tissue validates Fgf13 knockout in sparse inhibitory interneurons (scale bar, 50 μm). (C) Western blot validates partial loss of Fgf13 from Emx1-Fgf13 cKO and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO hippocampal tissue, and full knockout in Nestin-Fgf13 cKO mice. Vinculin used as a loading control. (D) Gad2-Fgf13 cKO mutant mice have survival deficits around 1 month of age (log-rank test, ****, p<0.0001). (E) Body mass at P14 shows Gad2-Fgf13 cKO are smaller in size than wildtype littermates (t-test, ****, p<0.001; scale bar, 2 cm) and brains from Gad2-Fgf13 cKO mice are smaller (t-test, ***, p<0.001; scale bar, 0.5 cm). (F) Gad2-Fgf13 cKO mice are susceptible to hyperthermia induced seizures (log-rank test, ***, p<0.001). (G) Example EEG recording of wildtype and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO mice during hyperthermia protocol. Insets show (i) example interictal spike, (ii) and (iii) tonic-clonic seizures.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Original TIFF files saved from Bio-Rad Gel doc system for gels shown in Figure 3C and PDF, together with a identifying the respective portions displayed.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98661/elife-98661-fig3-data1-v1.zip
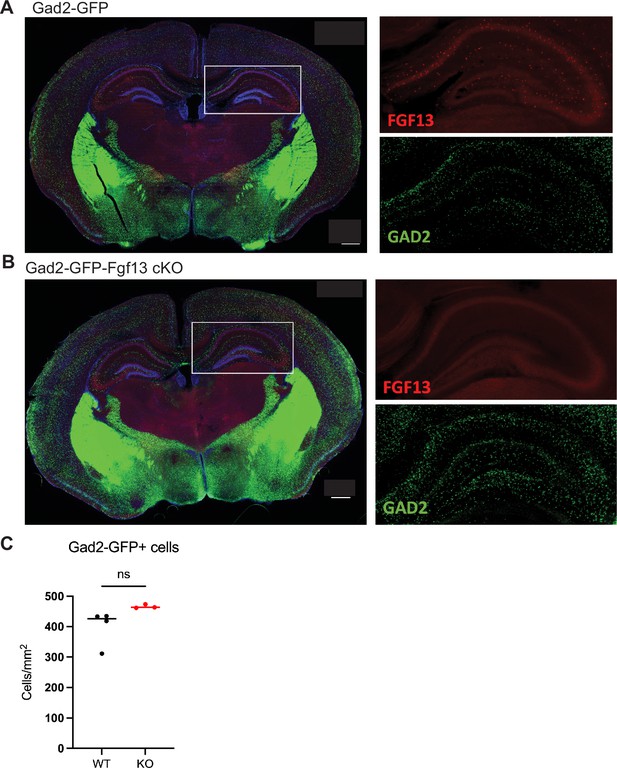
Characterization of FGF13 abundance in hippocampus of Gad2-Fgf13 cKO mice.
(A) Fluorescent immunohistochemistry with a pan-FGF13 antibody on hippocampal tissue in Gad2-GFP reporter mice. (B) Immunohistochemistry of hippocampal tissue in Gad2-GFP-Fgf13 cKO shows loss of FGF13 but not loss of Gad2-GFP+ interneurons (scale bar, 500 μm) and no gross morphological changes. (C) Gad2-Fgf13 cKO mice do not have a significant change in the density of hippocampal GABAergic interneurons, despite decreased brain and body size relative to wildtype littermates (t-test, p=ns), WT N=4 mice, KO N=3 mice.
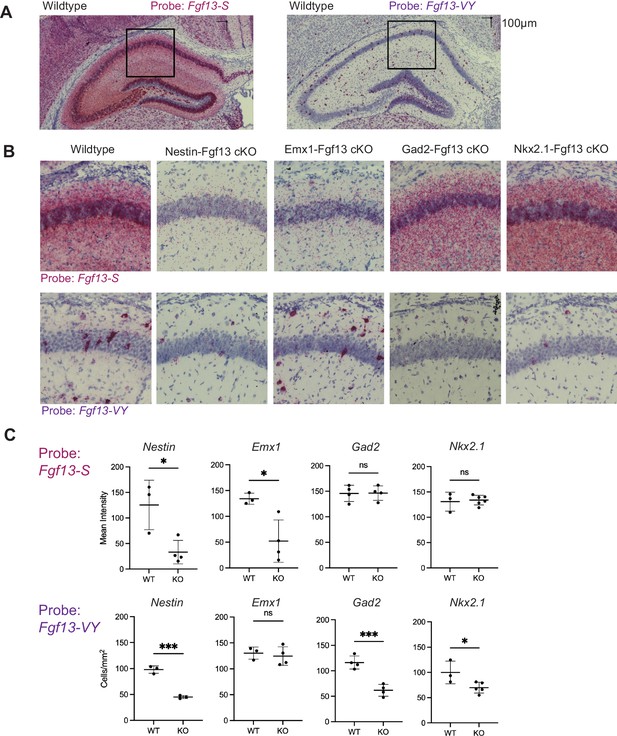
Fgf13 splice variants are differentially expressed in hippocampal cell types.
(A)Fgf13-S and -VY exhibit distinct expression in the hippocampus of wildtype and cell-type-specific knockouts. (B) Example images showing decreased Fgf13-S expression from Nestin-Fgf13 cKO and Emx1-Fgf13 cKO hippocampus or decreased Fgf13-VY expression from Nestin-Fgf13 cKO, Gad2-Fgf13 cKO, and Nkx2.1-Fgf13 cKO hippocampus. (C) Quantification of BASEscope in situ hybridization reveals that Fgf13-S expression is decreased in Nestin-Fgf13 cKO and Emx1-Fgf13 cKO hippocampus, while Fgf13-VY expressing cells are decreased in Nestin-Fgf13 cKO, Gad2-Fgf13 cKO, and Nkx2.1-Fgf13 cKO hippocampus. (t-test, *, p<0.05; ***, p<0.001) N=3–6 mice each.
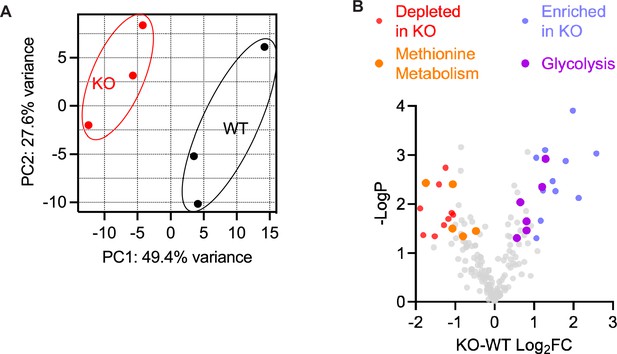
An unbiased metabolomic analysis on whole brain lysate from Gad2-Fgf13 cKO and wildtype mice reveals marked differences between genotypes.
(A) PCA plot showing three WT and three Gad2-Fgf13 cKO mice. (B) Volcano plot of measured metabolites. Colored data show metabolites with p<0.05 and Log2FC >1 or Log2FC <1 (KO v WT). N=3 mice each.
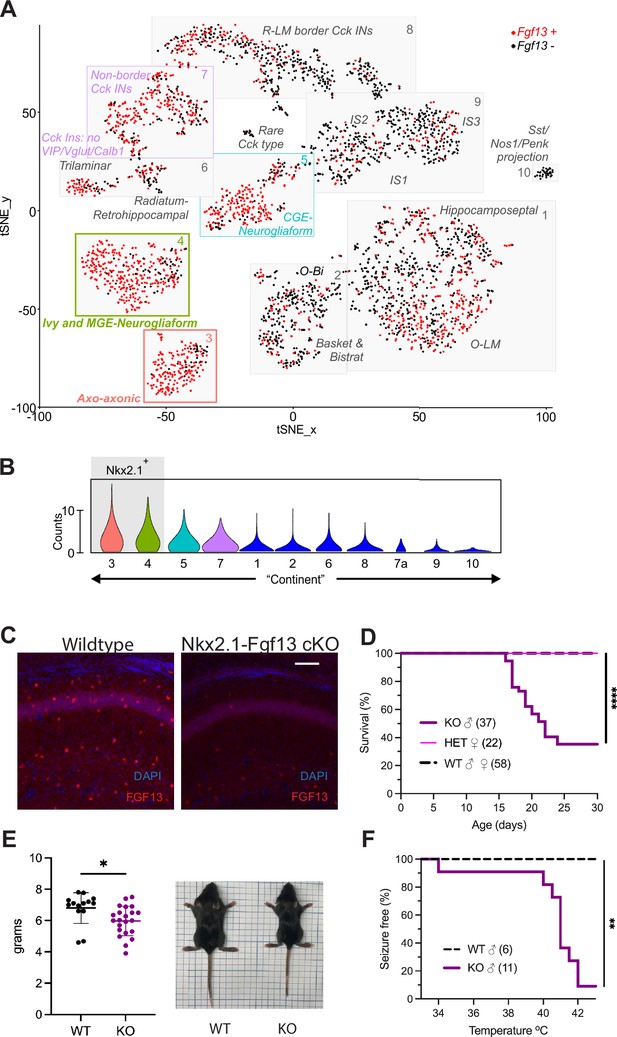
Knockout of Fgf13 from MGE-derived interneurons recapitulates premature death and seizure susceptibility.
(A) Re-analysis of single-cell RNA-seq data (1) reveals that Fgf13 is expressed in MGE-derived interneurons such as the axo-axonic and MGE-derived neurogliaform cell types, as well as CGE-derived interneurons. (B) Violin plots show that cell type continents with the highest expression of Fgf13+ cells are Nkx2.1+. (C) Fluorescent immunohistochemistry of hippocampal tissue validates Fgf13 knockout (scale bar, 100 μm). (D) Nkx2.1-Fgf13 cKO mice have survival deficits around 1 month of age (log-rank test, ****, p<0.0001). (E) Body mass at postnatal day 14 (P14) shows Nkx2.1-Fgf13 cKO are smaller in size (t-test, *, p<0.05). Scale, 2 cm. (F) Nkx2.1-Fgf13 cKO mice are susceptible to hyperthermia induced seizures (log-rank test, **, p<0.01).
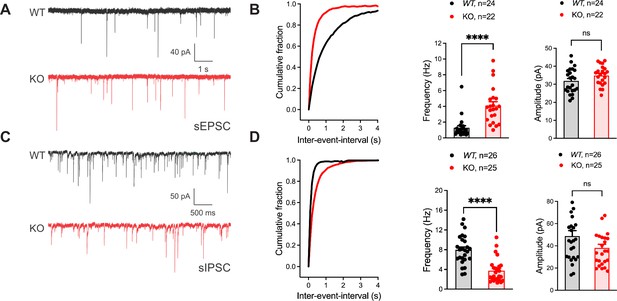
Inhibitory neuronal knockout of Fgf13 results in deficits of synaptic transmission.
(A) Example traces from spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs). (B) Cumulative fraction (Kolmogorov Smirnov test, ****, p<0.0001) frequency, and current amplitude for sEPSCs (t-test, ****, p<0.0001, WT N=7, n=24; KO N=4, n=22.) (C) Example traces from spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs). (D) Cumulative fraction (Kolmogorov Smirnov test, ****, p<0.0001), frequency, and current amplitude for sIPSCs (t-test, ****, p<0.0001, WT N=3, n=26; KO N=4, n=25).
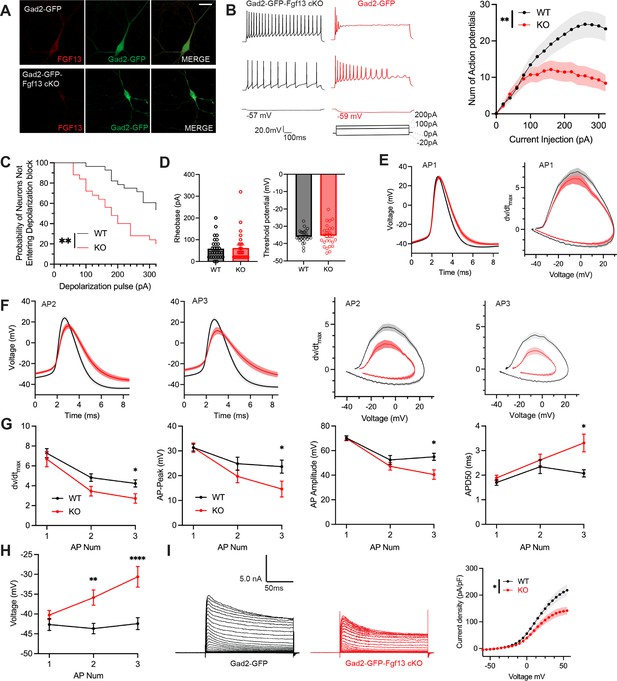
Inhibitory neuronal knockout of Fgf13 results in deficits of interneuron excitability.
(A) Examples of FGF13-stained neurons from primary hippocampal neuron cultures generated from Gad2-Cre wildtype (top) and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO (bottom) male mice (scale bar, 20 μm). (B) Example traces of AP spike trains from wildtype (left) and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons. Input-output curve shows decreased firing of evoked action potentials from Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons (two-way ANOVA, **, p<0.01, WT N=4, n=28; KO N=4, n=26). (C) Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons enter depolarization block at earlier current injections than wildtype interneurons (log-rank test, **, p<0.01). (D) Resting membrane potential, rheobase, and threshold potential for cultured wildtype and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons. (E) Action potential wave forms and phase plots (mean ± s.e.m.) for the first elicited action potential of the spike train for wildtype and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons. (F) Action potential wave forms and phase plots for the second and third action potentials of the spike train of wildtype and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons. (G) Analysis of the first three action potentials in the spike train show a decrease in the dV/dt max, a decrease in action potential (AP) peak, a decrease in AP amplitude, and an increase in APD50 by the third AP of Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons (two-way ANOVA, *, p<0.05). (H) Analysis of the first three action potentials in the spike train show an increase in membrane potential at the end of the AP for Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons (two-way ANOVA, **, p<0.01, ****, p<0.0001). (I) Example traces of K+ currents from wildtype and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons (left). I-V curve for K+ currents (right), (two-way ANOVA, *, p<0.05, WT N=3, n=26; KO N=5, n=29).
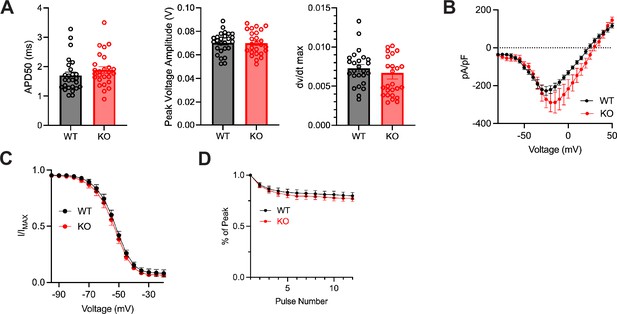
Inhibitory neuronal knockout of Fgf13 does not result in sodium current deficits.
(A) Wildtype and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons have no significant difference in APD50, peak voltage amplitude, and dV/dt max values for the first action potential in each spike train. (B) Wildtype and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons have no difference in macroscopic sodium currents (two-way ANOVA, p=ns). Peak current-voltage curves shown for WT and KO, WT N=3 n=25; KO N=3 n=18. (C) Wildtype and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons have no difference in steady-state inactivation V1/2 WT=−52.98 [95% CI, −55.32 to -50.63]; V1/2 KO = –54.19 [95% CI, –57.28 to –51.10], p=ns. N(WT)=3 n=21, N(KO)=3 n=17. (D). Wildtype and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons show no difference in long-term inactivation, WT N=3 n=15; KO N=3 n=14, p=ns.

AAV-mediated expression of FGF13 isoforms rescues excitability deficits in Gad2-Fgf13 cKO neurons.
(A) Examples of FGF13-stained neurons from primary hippocampal neuron cultures generated from Gad2-Fgf13 cKO male mice transduced with AAV8-DIO-GFP only, AAV8-DIO-GFP and AAV8-DIO-Fgf13-S, or AAV8-DIO-GFP and AAV8-DIO-Fgf13-VY (scale bar, 20 μm). (B) Gad2-Fgf13 cKO neurons expressing FGF13-VY or FGF13-S were not different in terms of threshold potential or rheobase, and were not different from wildtype (black line, from Figure 5) and Gad2-Fgf13 cKO neurons (red line, from Figure 5) (t-test, p=ns, KO +VY N=3, n=14; KO +S N=3 n=17). (C) Evoked action potential traces from Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons expressing FGF13-VY or FGF13-S. Input-output curve shows increased firing of evoked action potentials from the FGF13-VY or FGF13-S expressing interneurons, relative to Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons (red line, from Figure 5; black line = wild type, from Figure 5) (two-way ANOVA, *, p<0.05). (D) Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons expressing FGF13-VY and FGF13-S do not enter depolarization block as early as Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons (Red line [Gad2-Fgf13 cKO] and black line [wild type] are from Figure 5) (log-rank test, *, p<0.05). (E) Action potential wave forms and phase plots for the initial three action potentials of the spike train for FGF13-VY and FGF13-S rescued Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons. The black and red lines are from Figure 5. (F) For the first three action potentials in the spike train, Gad2-Fgf13 cKO neurons re-expressed with FGF13-VY show no difference from Gad2-Fgf13 cKO neurons in terms of dV/dt max, AP peak, and AP amplitude, and AP50. Gad2-Fgf13 cKO neurons re-expressed with FGF13-S show difference from Gad2-Fgf13 cKO neurons only for the first action potential for AP peak and AP amplitude, but not dV/dt max or AP50. (two-way ANOVA, ***, p<0.001, KO +S vs. KO; **, p<0.01, KO +S vs. KO). (G) FGF13-S rescued neurons show a significant decrease in membrane voltage from Gad2-Fgf13 cKO neurons by the third action potential in the spike train (two-way ANOVA, *, p<0.05, KO +S vs. KO). (H) Example traces of K+ currents from Gad2-Fgf13 cKO neurons expressing FGF13-VY and FGF13-S. K+ currents are rescued by expression of FGF13-S in Gad2-Fgf13 cKO interneurons (two-way ANOVA, *, p<0.05, KO +VY N=5, n=21, KO +S N=5, n=21).
Videos
Nestin-Fgf13 cKO male mice suffered spontaneous seizures in their home cage.
Example spontaneous seizure activity is shown.
Tables
Mutant mice are born in Mendelian ratios.
| Mouse strain | Probability density function |
|---|---|
| Nestin-Fgf13 | 0.23 |
| Gad2-Fgf13 | 0.22 |
| Nkx2.1-Fgf13 | 0.24 |
| Emx1-Fgf13 | 0.21 |
-
Mutant mice were born in expected Mendelian ratios. Despite embryonic targeted deletion of Fgf13, mutant suffered no prenatal mortality related to developmental deficits.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Primers used for real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
Forward and reverse primer pair sequences and, where relevant, the PrimerBank ID.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98661/elife-98661-supp1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Metabolite set enrichment analysis in Gad2-Fgf13 cKO vs. WT.
Unbiased metabolites identified by mass spectometery in Gad2-Fgf13 cKO vs. WT.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98661/elife-98661-supp2-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/98661/elife-98661-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx





