Bacteria: Exploring new horizons
Historically, bacteria have been thought of as simple cells whose only aim is to replicate. However, research over the past two decades has revealed that many types of bacteria are able to develop into communities that contain several types of cells, with different cell types performing particular roles (Kuchina et al., 2011). These communities are of interest in scientific fields as diverse as petroleum engineering and bacterial pathogenesis.
Streptomyces were perhaps the first bacteria to be recognized as having a multicellular lifestyle (Waksman and Henrici, 1943). In fact, this lifestyle led to them being classified as fungi when they were first isolated from soil at the beginning of the last century (Hopwood, 2007). This case of mistaken identity stemmed from the fuzzy texture of Streptomyces colonies (see Figure 1A), which resembles many of the fungi we see growing on bread and other natural surfaces (Waksman, 1954).
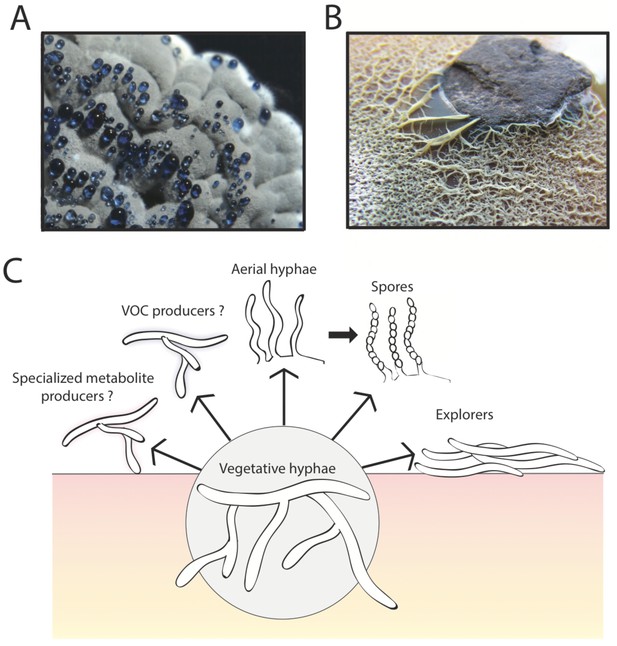
The multicellular lifestyle of Streptomyces.
Streptomyces bacteria form colonies that contain several different types of specialized cells: vegetative hyphae, aerial hyphae, spores and the "explorer" cells discovered by Jones et al. (A) A Streptomyces coelicolor colony exhibiting aerial hyphae (white) and spores (gray). The blue droplets contain compounds that are naturally produced by S. coelicolor including antibiotics. (B) Streptomyces venezuelae explorer cells spreading on a rock. (C) In addition to these four types of cells, it is possible that Streptomyces colonies might contain other cell types that produce specialized metabolites, such as antibiotics, signaling molecules or volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Image credits: panel A and C Vineetha Zacharia; panel B Jones et al. (2016)
The first stage in the life of a Streptomyces colony is the growth of so-called vegetative cells, which form networks of branched filaments that penetrate the surfaces of food sources. The fuzzy appearance of Streptomyces colonies is the result of the vegetative cells producing another type of cell called aerial hyphae that grow upwards into the air (McCormick and Flärdh, 2012; Flärdh and Buttner 2009). Subsequently, cells of a third type (spores) form long chains on the ends of these aerial hyphae. These spores are resistant to drying out and likely allow Streptomyces to passively spread to new environments through the action of water or air movement (McCormick and Flärdh, 2012). Now, in eLife, Marie Elliot at McMaster University and colleagues – including Stephanie Jones as first author – report a new form of growth in Streptomyces termed “exploratory growth” (Jones et al., 2016).
In the initial experiments, Jones et al. – who are based at McMaster University, the University of Toronto and Dartmouth College – grew Streptomyces venezuelae bacteria alone, or close to a yeast called Saccharomyces cerevisiae, on solid agar for two weeks. During this time, the bacteria grown alone formed a normal sized colony typical of Streptomyces. However, in the presence of the yeast, the S. venezuelae colonies expanded rapidly and colonized the entire surface of the growth dish, engulfing the nearby yeast colony. In subsequent experiments, the cells produced during exploratory growth (dubbed “explorer” cells) showed the ability to spread over abiotic surfaces including rocks (Figure 1B) and polystyrene barriers. Scanning electron microscopy revealed that, unlike vegetative cells, these explorer cells did not form branches and more closely resembled simple aerial hyphae.
Previous studies have identified many genes that regulate the development of Streptomyces colonies including the bld genes, which are involved in the formation of aerial hyphae, and the whi genes, which are required to make spores (McCormick and Flärdh, 2012). Jones et al. found that neither of these sets of genes are required for exploratory growth of S. venezuelae in the presence of the yeast. This suggests that the explorer cell type is distinct from the previously known developmental pathways in Streptomyces. Furthermore, Jones et al. found that multiple Streptomyces species were capable of exploratory growth and that various fungal microbes had the ability to trigger this behavior.
Further experiments using libraries of mutant yeast indicated that glucose and pH may be involved in triggering the formation of explorer cells. Jones et al. demonstrated that Streptomyces displays exploratory growth in response to shortages of glucose (caused by the presence of the yeast) and to an increased pH in the surrounding environment. The bacteria trigger this pH change themselves by releasing a volatile organic compound called trimethylamine, which is able to stimulate exploratory growth in Streptomyces over considerable distances. Trimethylamine also inhibits the growth of other bacteria that might compete with S. venezuelae in natural environments.
The work of Jones et al. opens up the possibility that there may be additional types of specialized cells within Streptomyces colonies. Streptomyces are important for medicine because they produce many different chemical compounds, including antibiotics and immunosuppressant drugs, and one might imagine that specific groups of cells within a colony are responsible for making these compounds (Figure 1C). Perhaps other cell types might be dedicated to directing the activities of different cells within the colony (as happens in other bacteria with multicellular lifestyles; Lopez et al., 2009; Baker, 1994), perhaps by producing trimethylamine or other volatile organic compounds.
For decades, researchers have described Streptomyces colonies in terms of vegetative cells, aerial hyphae and spores. The explorer cells identified by Jones et al. offer Streptomyces an alternative means of escape from their normal life cycle and local environment in the face of competition. This makes intuitive sense, given that Streptomyces lack the ability to move (“motility”) in the traditional sense (for example, by swimming, gliding or twitching). Taken together, the work of Jones et al. demonstrates a surprisingly dynamic strategy in which a ‘non-motile’ bacterium can use cues from other microbes, long-range signaling, and multicellularity to make a graceful exit when times get tough.
References
-
Streptomyces morphogenetics: dissecting differentiation in a filamentous bacteriumNature Reviews Microbiology 7:36–49.https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1968
-
BookStreptomyces in Nature and Medicine: The Antibiotic MakersOxford, New York: Oxford University Press.
-
Temporal competition between differentiation programs determines cell fate choiceMolecular Systems Biology 7:557.https://doi.org/10.1038/msb.2011.88
-
Paracrine signaling in a bacteriumGenes & Development 23:1631–1638.https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1813709
-
Signals and regulators that govern Streptomyces developmentFEMS Microbiology Reviews 36:206–231.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00317.x
-
The nomenclature and classification of the ActinomycetesJournal of Bacteriology 46:337–341.
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
Copyright
© 2017, Zacharia et al.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 2,043
- views
-
- 263
- downloads
-
- 2
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Citations by DOI
-
- 2
- citations for umbrella DOI https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.23624





