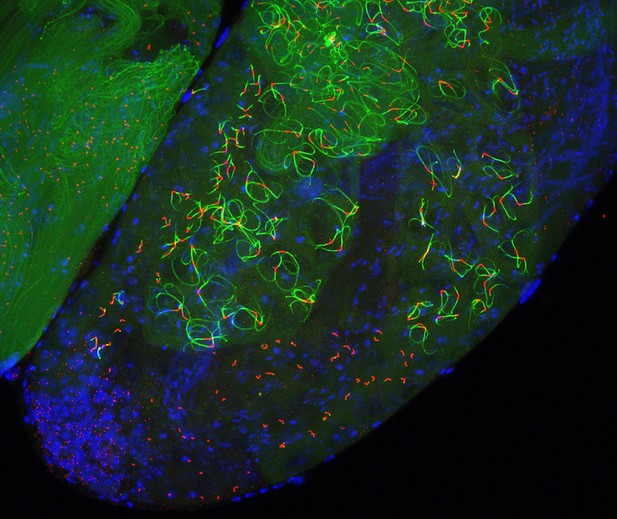
Testes of fruit flies that lack the core transition zone protein Cep290 show uncontrolled cilia formation: DNA (blue), centriole/basal body (red) and cilia (green). Image credit: Jean-André Lapart and Christophe Machu (CC BY 4.0)
Many animal cells have hair-like structures called cilia on their surface, which help them to sense and interact with their surroundings. The cilia are supported by protein filaments and must assemble correctly because faulty cilia can lead to several life-threatening diseases. Problems in an area at the base of the cilia, known as the ‘transition zone’, account for the most severe forms of these diseases in humans.
The transition zone is responsible for selecting which proteins are allowed in and out of the cilia. The transition zone itself is made up of many proteins that work together to determine the cilia composition. But not all of these proteins are known, and it is unclear how those that are known affect cilia structure.
One protein found in transition zones of several animals, including fruit flies and mice, is called Cby. Lapart et al. set out to understand which other proteins interact with Cby in fruit flies to better understand what this protein does in the transition zone. A series of experiments showed that Cby interacts with two proteins called Dzip1 and Fam92 to regulate the assembly of transition zones. Together these three proteins constrain a core component of the transition zone, a fourth protein called Cep290, to the base of the cilia.
Fruit flies only have cilia on cells in their sensory organs and testes and, in both types of tissue, cilia could only form properly when Dzip1 and Fam92 were present. Lapart et al. also showed that, in the fruit fly testes, Dzip1 and Fam92 helped to anchor the newly forming cilia to the cell surface. This anchoring role was particularly important for the fruit flies’ sperm to grow their characteristic whip-like tails, which are a specialized type of cilia that allow sperm cells to move.
Overall, the findings show how some transition zone proteins work together and that they can have different effects in different tissues. Understanding the mechanisms behind healthy cilia assembly will likely be key to tackling cilia-related diseases.




