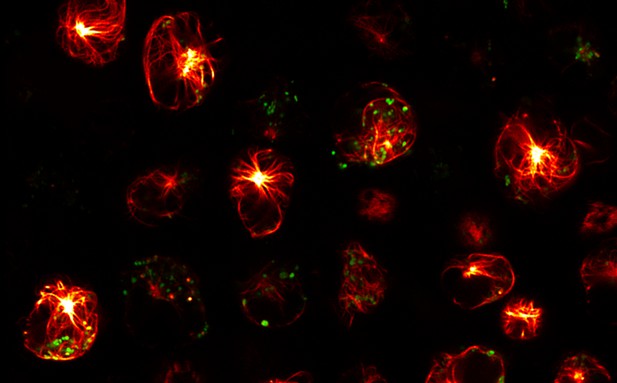
Living T cells collected from a genetically modified mouse, with the cytotoxic granules labeled in green and the microtubular network that supports the cells labeled with fire colors. Image credit: Chitirala, Chang et al. (CC BY 4.0)
Cytotoxic, or killer, T cells are a key part of the immune system. They carry a lethal mixture of toxic chemicals, stored in packages called cytotoxic granules. Killer T cells inject the contents of these granules into infected, cancerous or otherwise foreign cells, forcing them to safely self-destruct. In test tubes, T cells are highly efficient serial killers, moving from one infected cell to the next at high speed. But, inside the body, their killing rate slows down. Researchers think that this has something to do with how killer T cells interact with other immune cells, but the details remain unclear.
To get to grips with how killer T cells work in their natural environment, researchers need a way to follow them inside the body. One approach could be to use genetic engineering to attach a fluorescent tag to a protein found inside killer T cells. That tag then acts as a beacon, lighting the cells up and allowing researchers to track their movements. Tagging a protein inside the cytotoxic granules would allow close monitoring of T cells as they encounter, recognize and kill their targets. But fluorescent tags are bulky, and they can stop certain proteins from working as they should.
To find out whether it is possible to track killer T cells with fluorescent tags, Chitirala, Chang et al. developed a new type of genetically modified mouse. The modification added a teal-colored tag to a protein inside the granules of the killer T cells. Chitirala, Chang et al. then used a combination of microscopy techniques inside and outside of the body to find out if the T cells still worked. This analysis showed that, not only were the tagged T cells able to kill diseased cells as normal, the tags made it possible to watch it happening in real time. Super-resolution microscopy outside of the body allowed Chitirala, Chang et al. to watch the killer T cells release their toxic granule content. It was also possible to follow individual T cells as they moved into, and destroyed, foreign tissue that had been transplanted inside the mice.
These new mice provide a tool to understand how killer T cells really work. They could allow study not only of the cells themselves, but also their interactions with other immune cells inside the body. This could help to answer open questions in T cell research, such as why T cells seem to be so much more efficient at killing in test tubes than they are inside the body. Understanding this better could support the development of new treatments for viruses and cancer.




