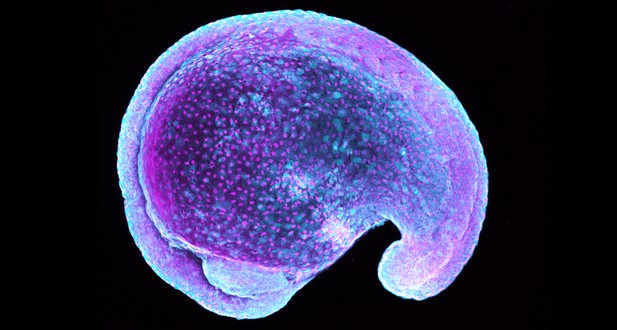
A zebrafish embryo lacking Hai1, shows increased levels of RSK (shown in turquoise) in the surface of the skin (magenta). Image credit: Jiajia Ma (CC BY 4.0)
Cancer occurs when normal processes in the cell become corrupted or unregulated. Many proteins can contribute, including one enzyme called Matriptase that cuts other proteins at specific sites. Matriptase activity is tightly controlled by a protein called Hai1. In mice and zebrafish, when Hai1 cannot adequately control Matriptase activity, invasive cancers with severe inflammation develop. However, it is unclear how unregulated Matriptase leads to both inflammation and cancer invasion.
One outcome of Matriptase activity is removal of proteins called Cadherins from the cell surface. These proteins have a role in cell adhesion: they act like glue to stick cells together. Without them, cells can dissociate from a tissue and move away, a critical step in cancer cells invading other organs. However, it is unknown exactly how Matriptase triggers the removal of Cadherins from the cell surface to promote invasion.
Previous work has shown that Matriptase switches on a receptor called Proteinase-activated receptor 2, or Par2 for short, which is known to activate many enzymes, including one called phospholipase C. When activated, this enzyme releases two signals into the cell: a sugar called inositol triphosphate, IP3; and a lipid or fat called diacylglycerol, DAG. It is possible that these two signals have a role to play in how Matriptase removes Cadherins from the cell surface.
To find out, Ma et al. mapped the effects of Matriptase in zebrafish lacking the Hai1 protein. This revealed that Matriptase increases IP3 and DAG levels, which initiate both inflammation and invasion. IP3 promotes inflammation by switching on pro-inflammatory signals inside the cell such as the chemical hydrogen peroxide. At the same time, DAG promotes cell invasion by activating a well-known cancer signalling pathway called MAPK. This pathway activates a protein called RSK. Ma et al. show that this protein is required to remove Cadherins from the surface of cells, thus connecting Matriptase’s activation of phospholipase C with its role in disrupting cell adhesion.
An increase in the ratio of Matriptase to HAI-1 (the human equivalent of Hai1) is present in many cancers. For this reason, the signal cascades described by Ma et al. may be of interest in developing treatments for these cancers. Understanding how these signals work together could lead to more direct targeted anti-cancer approaches in the future.




