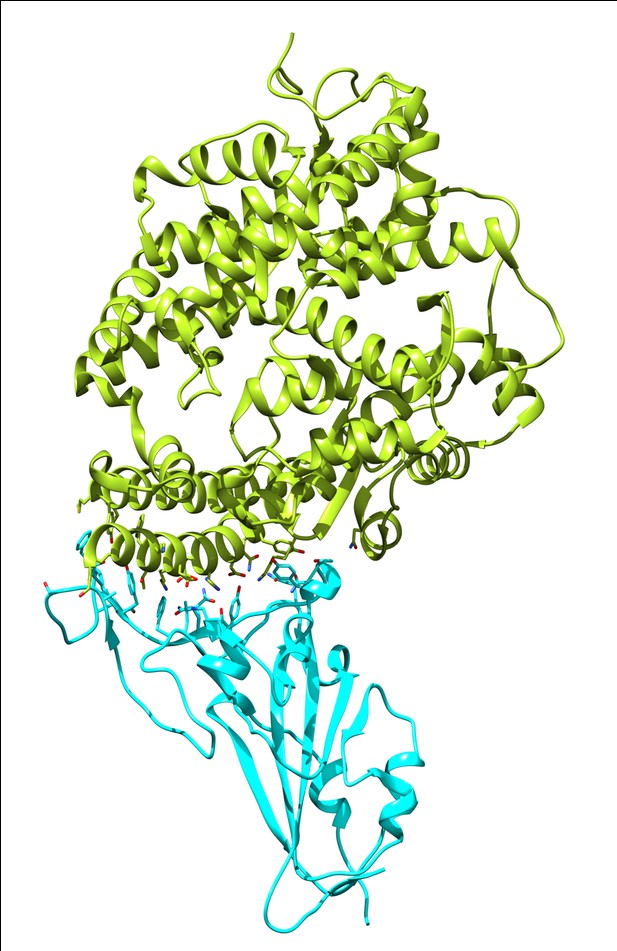
The structure of human ACE2 (green) in complex with SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD (cyan). Image credit: Stuart MacGowan (CC BY 4.0)
As the COVID-19 pandemic has progressed, new variants of the virus SARS-CoV-2 have emerged that are more infectious than the original form. The variants known as Alpha, Beta and Gamma have mutations in a protein on the virus’s surface that is vital for attaching to cells and infecting them. This protein, called Spike, carries out its role by binding to ACE2, a protein on the surface of human cells. Mutations on Spike are found on the region where it binds to ACE2.
The interaction between these two proteins appears to be important to the behaviour of SARS-CoV-2, but the impact of individual mutations in Spike is unknown. In addition, some people have different variants of ACE2 with mutations in the region that interacts with Spike, but it is not known whether this affects these people’s risk of contracting COVID-19.
To answer these questions, Barton et al. measured the precise effect of mutations in Spike and ACE2 on the strength of the interaction between the two proteins. The experiments showed that three of the five common Spike mutations in the Alpha, Beta and Gamma SARS-CoV-2 variants strengthened binding to ACE2. The two mutations that weakened binding were only found together with other mutations that strengthened binding. This meant that the Spike proteins in all three of these SARS-CoV-2 variants bind to ACE2 more strongly than the original form. The experiments also showed that two common variants of ACE2 also increased the strength of binding to Spike. Interestingly, one of these ACE2 variants reversed the effect of a specific SARS-CoV-2 mutation, suggesting that carriers would be resistant to SARS-CoV-2 variants with this mutation.
Identifying the precise effects of Spike mutations on ACE2 binding helps understand why new variants of SARS-CoV-2 spread more rapidly. This could help to identify concerning new variants before they spread widely and inform the response by health authorities. The finding that two common ACE2 variants bind more strongly to Spike suggests that people with these mutations could be more susceptible to SARS-CoV-2.




