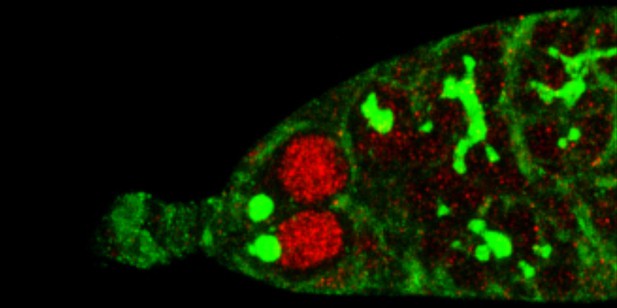
Microscopy image of the part of a Drosophila ovary where eggs are produced showing the nuclei of germline stem cells (red circles), spectrosomes (green circles) and germline cyst fusomes (green shapes on the right-hand side) which are important for the production of egg cells.
Most animals are made up of two cell types: germline stem cells, which give rise to reproductive cells (egg and sperm) and pass their DNA to the next generation, and somatic cells, which make up the rest of the body.
Transposable elements – fragments of DNA that can copy themselves and integrate into different parts of the genome – can greatly disrupt the integrity of the germ cell genome. Systems involving small RNAs and DNA methylation, which respectively modify the sequence and structure of the genome, can protect germ cells from the activity of transposable elements. While these systems have been studied extensively in late germ cells, less is known about how they work in germ cells generated early on in development.
To investigate, Pang et al. studied the germline stem cells that give rise to eggs in female fruit flies. Techniques that measure DNA modifications showed that these germline stem cells and the cells they give rise to early on are better protected against transposable elements. This is likely due to the unusual cell cycle of early germ cells, which display a very short initial growth phase and special DNA replication timing during the synthesis phase. Until now, the purpose of these long-known cell cycle differences between early and late germ cells was not understood.
Experiments also showed known transposable element defences are upregulated before the cell division that produces reproductive cells. DNA becomes more densely packed and germ cells connect with one another, forming germline ‘cysts’ that allow them to share small RNAs that can suppress transposable elements. Pang et al. propose that these changes compensate for the loss of enhanced repression that occurs in the earlier stem cell stage. Very similar changes also take place in the cells generated from fertilized eggs and in mammalian reproductive cells.
Further experiments investigated how these changes impact the transition from stem cell to egg cell, revealing that germline stem cells express a wide diversity of genes, including most genes whose transcripts will be stored in the mature egg later on. Another type of cell produced by germline stem cells known as nurse cells, which synthesize most of the contents of the egg, dramatically upregulate genes supporting growth. Meanwhile, 25% of genes initially expressed in germline stem cells are switched off during the transition, partly due to a mechanism called Polycomb-mediated repression.
The findings advance fundamental knowledge of how germline stem cells become egg cells, and could lead to important findings in developmental biology. Furthermore, understanding that for practical applications germline stem cells do not need to retain transposable element controls designed for evolutionary time scales means that removing them may make it easier to obtain and manipulate new stem cell lines and to develop new medical therapies.




