Researchers have provided new insight on how two proteins help influenza A virus particles fight their way to human cells.
The findings, published today in the open-access journal eLife, further explain how influenza A is able to penetrate defensive mucus barriers in the airways and cause infection. This could lead to new opportunities for therapeutic interventions that disrupt this activity.
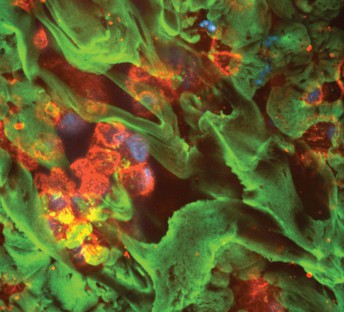
Cells in the airway (indicated in red and blue) are protected by a layer of secreted mucus (in green). Credit: Michael Vahey and Daniel Fletcher.
Mucosal barriers are the body’s first line of defense against influenza A infection, containing sialic acid decoys that bind the virus. To infect cells without getting stuck in the mucus, influenza A relies on a balance between two proteins on the surface of its viral particles: the receptor-binding protein hemagglutinin (HA) and the cleaving protein neuraminidase (NA). But until now, little was known about how these proteins are organised on the particles and how this may contribute to a virus’ ability to penetrate host mucus.
“We reasoned that the shape of a virus particle, together with the packaging and organisation of HA and NA, could influence the balance of attachment and detachment in ways that allow the virus to effectively penetrate mucus barriers,” says first author Michael Vahey, formerly a postdoctoral scholar at the University of California, Berkeley, US, and now Assistant Professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
To explore this, Vahey and his colleague Daniel Fletcher, also at the University of California, Berkeley, and Faculty Scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, used fluorescent labelling and super-resolution microscopy to study the organisation of HA and NA on influenza A. Their work revealed that the proteins are distributed asymmetrically in such a way that the binding and cleaving leads to persistent directional motion.
“The virus appears to operate like a Brownian ratchet, with the proteins’ organisation biasing its thermally-driven motion to move through host mucus,” explains Fletcher. “This resolves the virus’s conflicting needs to both penetrate mucus and attach stably to the underlying cells.”
More work is now needed to understand if these characteristics of influenza A organisation are related to its infectivity in individuals and during host-to-host transmission. Fletcher adds that this concept may be at work in other viruses and could be a target for disruption by future treatments.
Media contacts
Emily Packer
eLife
e.packer@elifesciences.org
+441223855373Kara Manke
University of California, Berkeley
kjmanke@berkeley.edu
+15106437741
About
eLife is a non-profit organisation inspired by research funders and led by scientists. Our mission is to help scientists accelerate discovery by operating a platform for research communication that encourages and recognises the most responsible behaviours in science. We publish important research in all areas of the life and biomedical sciences, including Microbiology and Infectious Disease, and the Physics of Living Systems, which is selected and evaluated by working scientists and made freely available online without delay. eLife also invests in innovation through open-source tool development to accelerate research communication and discovery. Our work is guided by the communities we serve. eLife is supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Max Planck Society, the Wellcome Trust and the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation. Learn more at https://elifesciences.org/about.
To read the latest Microbiology and Infectious Disease research published in eLife, visit https://elifesciences.org/subjects/microbiology-infectious-disease.
And for the latest in the Physics of Living Systems, see https://elifesciences.org/subjects/physics-living-systems.




