Peer review process
Not revised: This Reviewed Preprint includes the authors’ original preprint (without revision), an eLife assessment, public reviews, and a provisional response from the authors.
Read more about eLife’s peer review process.Editors
- Reviewing EditorRio SugimuraThe University of Hong Kong, Pok Fu Lam, Hong Kong
- Senior EditorKathryn CheahUniversity of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
In this study from Zhu and colleagues, a clear role for MED26 in mouse and human erythropoiesis is demonstrated that is also mapped to amino acids 88-480 of the human protein. The authors also show the unique expression of MED26 in later-stage erythropoiesis and propose transcriptional pausing and condensate formation mechanisms for MED26's role in promoting erythropoiesis. Despite the author's introductory claim that many questions regarding Pol II pausing in mammalian development remain unanswered, the importance of transcriptional pausing in erythropoiesis has actually already been demonstrated (Martell-Smart, et al. 2023, PMID: 37586368, which the authors notably did not cite in this manuscript). Here, the novelty and strength of this study is MED26 and its unique expression kinetics during erythroid development.
Strengths:
The widespread characterization of kinetics of mediator complex component expression throughout the erythropoietic timeline is excellent and shows the interesting divergence of MED26 expression pattern from many other mediator complex components. The genetic evidence in conditional knockout mice for erythropoiesis requiring MED26 is outstanding. These are completely new models from the investigators and are an impressive amount of work to have both EpoR-driven deletion and inducible deletion. The effect on red cell number is strong in both. The genetic over-expression experiments are also quite impressive, especially the investigators' structure-function mapping in primary cells. Overall the data is quite convincing regarding the genetic requirement for MED26. The authors should be commended for demonstrating this in multiple rigorous ways.
Weaknesses:
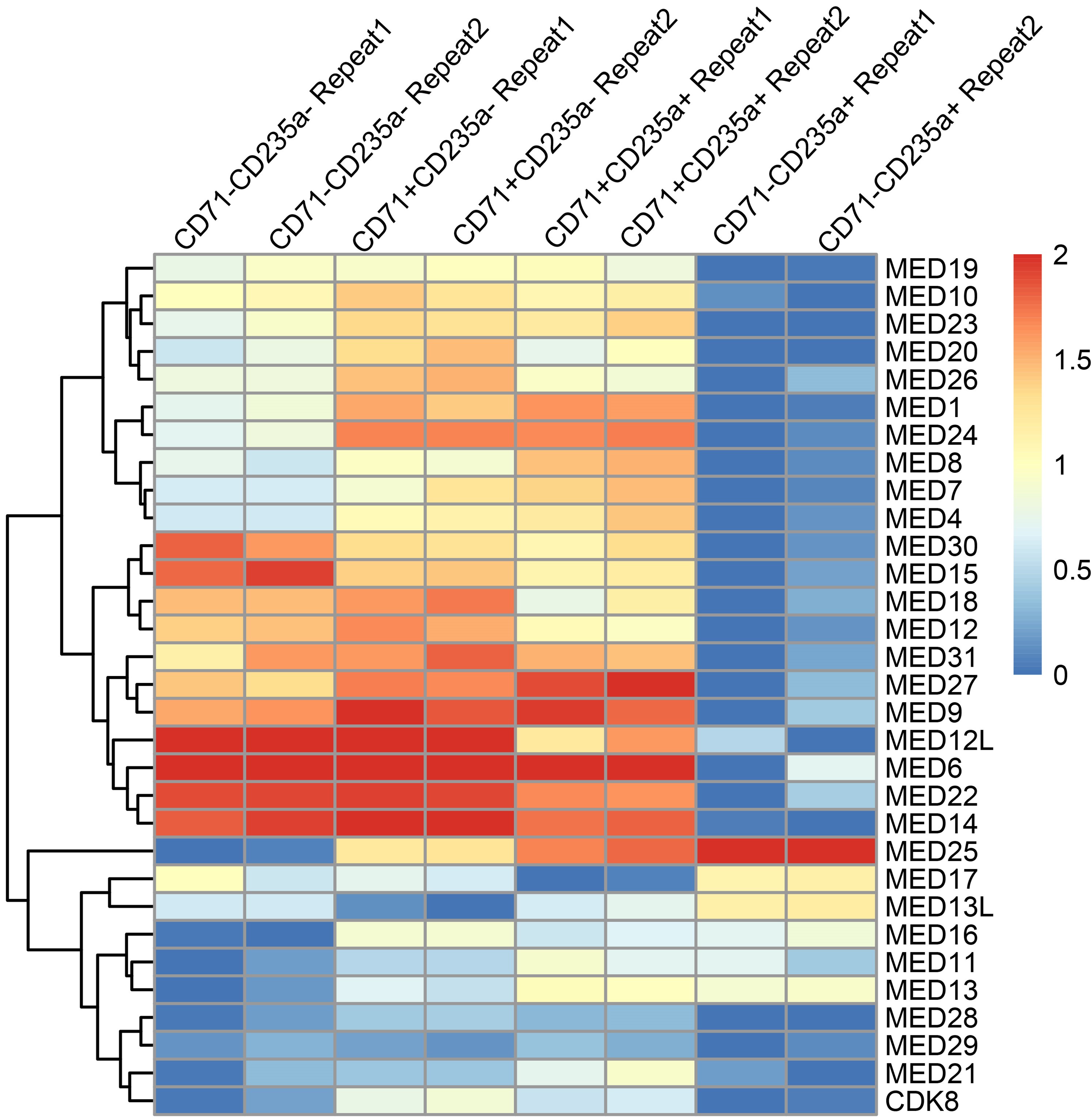
(1) The authors state that MED26 was nominated for study based on RNA-seq analysis of a prior published dataset. They do not however display any of that RNA-seq analysis with regards to Mediator complex subunits. While they do a good job showing protein-level analysis during erythropoiesis for several subunits, the RNA-seq analysis would allow them to show the developmental expression dynamics of all subunit members.
(2) The authors use an EpoR Cre for red cell-specific MED26 deletion. However, other studies have now shown that the EpoR Cre can also lead to recombination in the macrophage lineage, which clouds some of the in vivo conclusions for erythroid specificity. That being said, the in vitro erythropoiesis experiments here are convincing that there is a major erythroid-intrinsic effect.
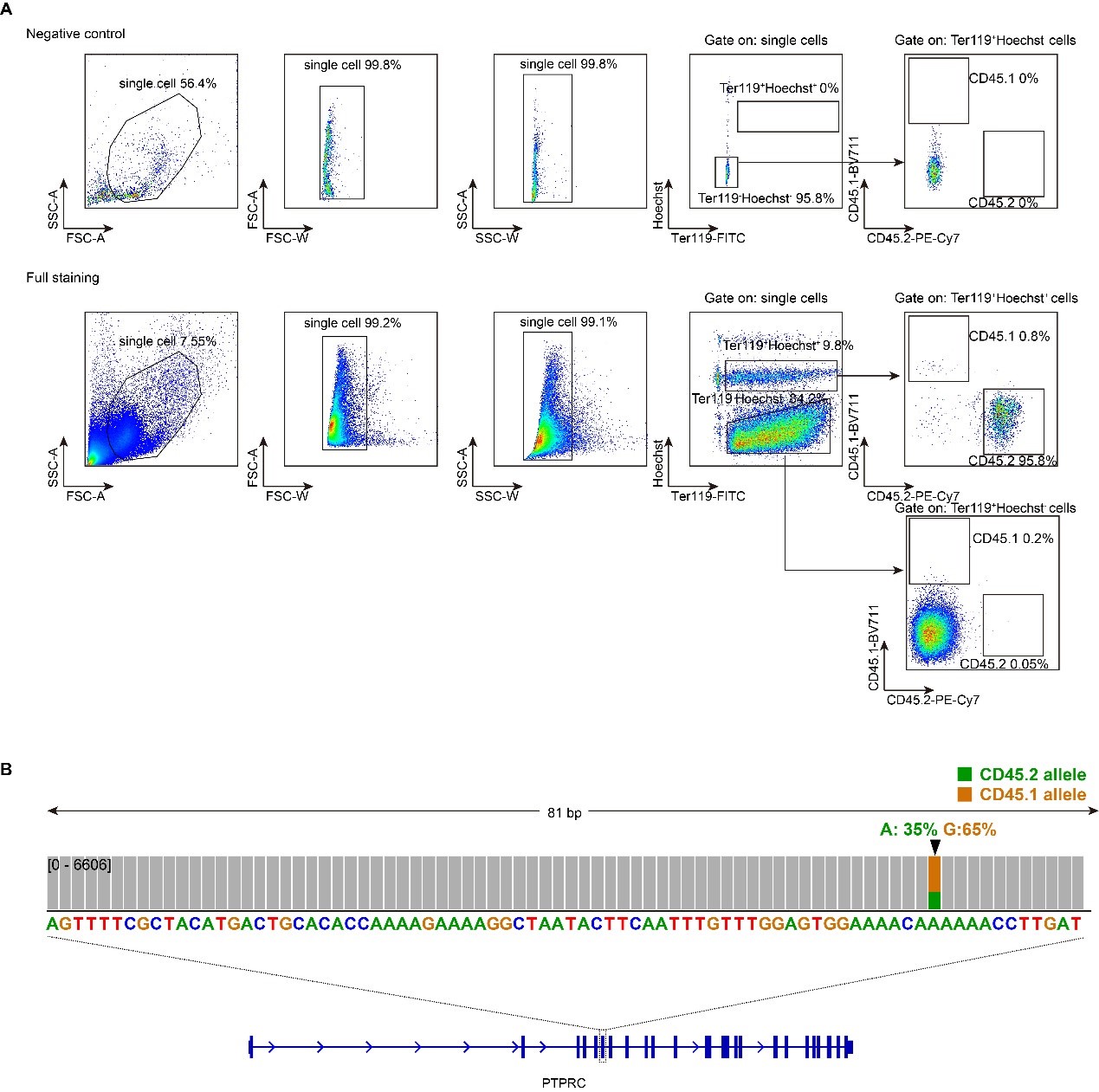
(3) The donor chimerism assessment of mice transplanted with MED26 knockout cells is a bit troubling. First, there are no staining controls shown and the full gating strategy is not shown. Furthermore, the authors use the CD45.1/CD45.2 system to differentiate between donor and recipient cells in erythroblasts. However, CD45 is not expressed from the CD235a+ stage of erythropoiesis onwards, so it is unclear how the authors are detecting essentially zero CD45-negative cells in the erythroblast compartment. This is quite odd and raises questions about the results. That being said, the red cell indices in the mice are the much more convincing data.
(4) The authors make heavy use of defining "erythroid gene" sets and "non-erythroid gene" sets, but it is unclear what those lists of genes actually are. This makes it hard to assess any claims made about erythroid and non-erythroid genes.
(5) Overall the data regarding condensate formation is difficult to interpret and is the weakest part of this paper. It is also unclear how studies of in vitro condensate formation or studies in 293T or K562 cells can truly relate to highly specialized erythroid biology. This does not detract from the major findings regarding genetic requirements of MED26 in erythropoiesis.
(6) For many figures, there are some panels where conclusions are drawn, but no statistical quantification of whether a difference is significant or not.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
The manuscript by Zhu et al describes a novel role for MED26, a subunit of the Mediator complex, in erythroid development. The authors have discovered that MED26 promotes transcriptional pausing of RNA Pol II, by recruiting pausing-related factors.
Strengths:
This is a well-executed study. The authors have employed a range of cutting-edge and appropriate techniques to generate their data, including: CUT&Tag to profile chromatin changes and mediator complex distribution; nuclear run-on sequencing (PRO-seq) to study Pol II dynamics; knockout mice to determine the phenotype of MED26 perturbation in vivo; an ex vivo erythroid differentiation system to perform additional, important, biochemical and perturbation experiments; immunoprecipitation mass spectrometry (IP-MS); and the "optoDroplet" assay to study phase-separation and molecular condensates.
This is a real highlight of the study. The authors have managed to generate a comprehensive picture by employing these multiple techniques. In doing so, they have also managed to provide greater molecular insight into the workings of the MEDIATOR complex, an important multi-protein complex that plays an important role in a range of biological contexts. The insights the authors have uncovered for different subunits in erythropoiesis will very likely have ramifications in many other settings, in both healthy biology and disease contexts.
Weaknesses:
There are almost no discernible weaknesses in the techniques used, nor the interpretation of the data. The IP-MS data was generated in HEK293 cells when it could have been performed in the human CD34+ HSPC system that they employed to generate a number of the other data. This would have been a more natural setting and would have enabled a more like-for-like comparison with the other data.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
The authors aim to explore whether other subunits besides MED1 exert specific functions during the process of terminal erythropoiesis with global gene repression, and finally they demonstrated that MED26-enriched condensates drive erythropoiesis through modulating transcription pausing.
Strengths:
Through both in vitro and in vivo models, the authors showed that while MED1 and MED26 co-occupy a plethora of genes important for cell survival and proliferation at the HSPC stage, MED26 preferentially marks erythroid genes and recruits pausing-related factors for cell fate specification. Gradually, MED26 becomes the dominant factor in shaping the composition of transcription condensates and transforms the chromatin towards a repressive yet permissive state, achieving global transcription repression in erythropoiesis.
Weaknesses:
In the in vitro model, the author only used CD34+ cell-derived erythropoiesis as the validation, which is relatively simple, and more in vitro erythropoiesis models need to be used to strengthen the conclusion.