Peer review process
Not revised: This Reviewed Preprint includes the authors’ original preprint (without revision), an eLife assessment, public reviews, and a provisional response from the authors.
Read more about eLife’s peer review process.Editors
- Reviewing EditorLaura ColginUniversity of Texas at Austin, Austin, United States of America
- Senior EditorLaura ColginUniversity of Texas at Austin, Austin, United States of America
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript by Joshi and colleagues demonstrates that the precise theta-phase timing of spikes is causal for CA1 hippocampal theta sequences during locomotion on a linear track and is necessary for learning the cognitively demanding outbound component of a hippocampus-dependent alternation task (W-maze), independently of replay during immobility. To reach these conclusions, the authors developed a theta-phase-specific, closed-loop manipulation that used optogenetic activation of medial septal parvalbumin (PV) interneurons at the ascending phase of theta during locomotion. This protocol preserved immobility periods, allowing a clean and elegant dissociation from SWR-associated replay.
The manuscript is well written and was a pleasure to read. The work described is of high quality and introduces several notable advances to the field:
(a) It extends prior studies that manipulated theta oscillations by examining precise temporal structure (specifically theta sequences) rather than only LFP features.
(b) The closed-loop manipulation enabled dissociation between deficits in theta sequences during a behavioural task and SWR-associated replay activity.
(c) As controls, the authors included rats with suboptimal viral transduction or optic-fibre placement, and, within subjects, both stimulation-on (stim-on) and stimulation-off (stim-off) trials. Notably, sequence disruption persisted into stim-off periods within the same session.
Overall, this is a strong manuscript that will provide valuable insights to the field. I have only minor comments:
(1) As the authors note, it is striking that both behavioural performance and spike patterns are altered during stim-off trials. They propose that "disruption of theta sequences during the initial experience in an environment is sufficient to have lasting effects," implying that rapid, experience-dependent plasticity is driven by sequential firing. Does this imply that if rats were previously trained on the task, subsequent stim-on and stim-off trials would yield different outcomes, with stim-off trials showing improved performance and intact theta sequences? For example, if the sequence of one-third stim-on, one-third stim-off, one-third stim-on were inverted to off-on-off, would theta sequences be expected to emerge, disappear, and potentially re-emerge? While I am not asking for additional experiments, I think the discussion could be extended in this aspect.
Alternatively, could the number of stim-off trials (one third of the total) be insufficient to support learning/induce plasticity? In the controls, ~50-100 trials appear necessary to achieve high performance.
(2) In line with the point above, the authors characterise the behavioural changes induced by MS optogenetic stimulation specifically as a "learning deficit," as rats failed to improve across 300 trials in an initially novel environment (W-maze). While they present this as complementary to prior demonstrations of impaired performance on previously learned tasks (Zutshi et al., 2018; Quirk et al., 2021; Etter et al., 2023; Petersen et al., 2020), an alternative interpretation is a working-memory deficit. This would produce the same behavioural pattern, with reference memory (the less cognitively demanding trials) remaining intact despite stimulation and concomitant changes in theta sequences. This interpretation would also be consistent with work in certain disease models, where reduced synaptic plasticity and working-memory deficits co-occur with preserved place coding despite impaired theta sequences (e.g., Viana da Silva et al., 2024; Donahue et al., 2025).
(3) It was not immediately clear whether SWR-associated activity was derived from the interleaved ~15-min rest sessions in a rest box, or from periods of immobility or reward consumption in the maze (aSWR, as in Jadhav et al 2012). Regardless, it would be informative to compare aSWR events within the maze to rest-box SWRs that may occur during more prolonged slow-wave episodes (even if not full sleep). This contrasts with Liu et al. (2024), who analysed replay during ~1.5-h sleep sessions.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
The authors of this study developed a closed-loop optogenetic stimulation system with high temporal precision in rats to examine the effect of medial septum (MS) stimulation on the disruption of hippocampal activity at both behavioral and compressed time scales. They found that this manipulation preserved hippocampus single-cell-level spatial coding but affected theta sequences and performance during a spatial alternation task. The performance deficits were observed during the more cognitively demanding component of the task and even persisted after the stimulation was turned off. However, the effects of this disruption were confined to locomotor periods and did not impact waking rest replay, even during the early phase of stimulation-on. Their conclusion is consistent with previous findings from the Pastalkova lab, where MS disruption (using different methods) affected theta sequences and task performance but spared replay (Wang et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2016). However, it differs from a recent study in which optogenetic disruption of EC inputs during running affected both theta sequences and replay (Liu et al., 2023).
Strengths:
The experiments were well designed and controlled, and the results were generally well presented.
Weaknesses:
Major concerns are primarily technical but also conceptual. To further increase the impact of this study by contrasting findings from different disruptions, it is necessary to better align the analysis and detection methods.
Major concerns:
(1) To show that MS disruption does not affect spatial tuning, the authors computed the KL divergence of tuning curves between stimulation-on and stimulation-off conditions. I have two main questions about this analysis:
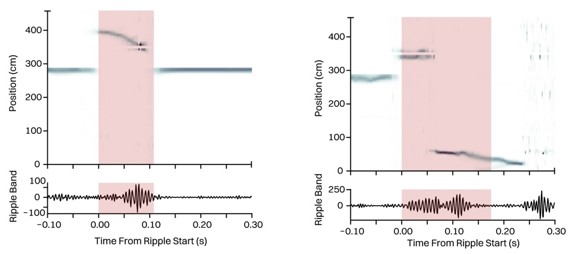
(1.1) The authors seem to impose stringent inclusion criteria requiring a large number of spikes and a strong concentration of tuning curves. These criteria may have selected strongly spatially tuned cells, which are typically more stable and potentially less vulnerable to perturbations. Based on the Figure 2 caption, it seems that fewer than 10% of cells were included in the KL divergence analysis, which is lower than the usual proportion of place cells reported in the literature. What is the rationale for using such strict inclusion criteria? What happens to the cells that are not as strongly tuned but are still identified as significant place cells?
(1.2) The KL divergence was computed between stimulation-on and stimulation-off conditions within the same animal group. However, the authors also showed that MS stimulation had lasting effects on theta sequences and performance even during stimulation-off periods. Would that lasting effect also influence spatial tuning? Based on these questions, the authors should perform additional analyses that directly measure spatial tuning quality and compare results across control and experimental groups - for example, spatial information of spikes (Skaggs et al., 1996), tuning stability, field length, and decoding error during running.
(2) The authors compared their results with those from Liu et al. (2023) and proposed that the different outcomes could be explained by different sites of disruption. However, the detection and quantification methods for theta sequences and replay differ substantially between the two studies, emphasizing different aspects of the phenomenon. I am not suggesting that either method is superior, but providing additional analyses using aligned detection methods would better support the authors' interpretations and benefit the field by enabling clearer comparisons across studies. In the current analysis, the power spectrum of the decoded ahead/behind distance only indicates that there is a rhythmic pattern, without specifying the decoding features at different theta phases. Moreover, the continuous non-local representations during ripples could include stationary representations of a location or zigzag representations that do not exhibit a linear sequential trace. Given that, the authors should show averaged decoding results corrected by the animal's actual position within theta cycles and compute a quadrant ratio. For replay analysis, they could use a linear fit (as in Liu et al., 2023) and report the proportion of significant replay events.
(3) The finding that theta sequences and performance were impaired even during stimulation-off periods is particularly interesting and warrants deeper exploration. In the Discussion, the authors claim that this may arise from "the rapid plasticity engaged during early learning." However, this explanation does not fully account for the observation. Previous studies have shown that theta sequences can develop very rapidly (Feng et al., Foster lab, 2015; Zhou et al., Dragoi lab, 2025). If the authors hypothesize that rapid plasticity during early stimulation-on disrupts the theta sequence, then the plasticity window must also be short and terminate during the subsequent stimulation-off period. Otherwise, why can't animals redevelop theta sequences during stimulation-off? The authors should conduct additional analyses during the stimulation-off periods of the W-maze task. For example:
(3.1) What is the spike-theta phase relationship? Do the phases return to normal or remain altered as during stimulation-on?
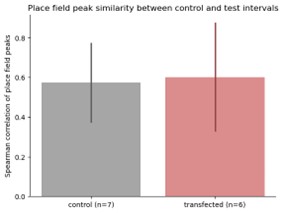
(3.2) Is there a significant place-field remapping from stimulation-on to stimulation-off? (Supplementary Figure 3F includes only a small subset of cells; what if population vector correlations are computed across all cells, or Bayesian decoding of stimulation-on spikes is performed using stimulation-off tuning curves?)
(3.3) The authors should also discuss why the stimulation-off epochs were not sufficient to support learning, and if the stimulation-off place cell sequences could have supported replay.
(4) Citations and/or discussion of key studies relevant to the current work are missing: Wang et al. in Pastalkova lab 2015-2016 studies for disruption of theta sequence (but not place cell sequence) disrupting learning but not replay, Drieu et al. in Zugaro lab 2018 study on disruption of theta sequence affecting sleep replay, Farooq and Dragoi 2019 for association between a lack of theta sequence and presence of waking rest replay during postnatal development, etc. The authors should discuss what the conceptually new findings in the current study are, given the findings of the previous literature above.
(5) The assessment of theta sequence is not state-of-the-art:
(5.1) Detecting the peak of cross-correlograms between neurons (CCG) relates to behavioral timescale CCG, not the theta sequence one; for the theta sequence, the closest to zero local peak should be used instead.
(5.2) How were other methods of detecting theta sequences performing on the stimulation-on/stimulation-off data: Bayesian decoding, firing sequences?
(5.3) How was phase precession during stimulation-on/stimulation-off?
(6) It would be important to calculate additional variables in the replay part of the study to compare the quality of replay across the 2 groups:
(6.1) Proportion of significant replay events out of the detected multiunit events.
(6.2) The average extent of trajectory depicted by the significant replay events in the targeted compared to the control, stimulation-on/stimulation-off.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Joshi et al. present an elegant and technically rigorous study examining how the temporal structure of hippocampal spiking during locomotion contributes to spatial learning. Using a closed-loop, theta phase-specific optogenetic manipulation of medial septal parvalbumin-expressing neurons in rats, the authors demonstrate that disrupting theta-timescale coordination impairs performance on the cognitively demanding component outbound trajectory of a spatial alternation task, while sparing hippocampal replay, place coding, and the simpler inbound learning. The work aims to dissociate the role of theta-associated temporal organization during navigation from sharp-wave ripple-associated replay during subsequent rest periods, providing a mechanistic link between theta sequences and learning. The findings have important implications for models of septo-hippocampal coordination and the functional segregation between online (theta) and offline (SWR) network states. That said, there are a few conceptual and methodological issues that need to be addressed.
One concern is the overall novelty of this work; the dissociation between online temporal sequence and offline replay events following memory deficits has previously been shown by Wang et al., 2016 elife. While the authors discuss Lui et al., 2023, which demonstrates MEC activation of inhibitory neurons at gamma frequencies during locomotion disrupts theta sequences, subsequent replay and learning (line 65-66), they do not reference Wang et al., 2016 who performed a very similar study with MS pharmacological inactivation, and report large decreases in theta power, attenuated theta frequencies together with behavioural deficits but SWR replay persisted. Given strong similarities in the manipulation and findings, this study should be discussed.
Along the same lines, it should be noted that Brandon et al. (2014, Neuron) demonstrated that hippocampal place codes can still form in novel environments despite MS inactivation and loss of theta, indicating that spatial representations can emerge without intact septal drive. Referencing this study would strengthen the discussion of how temporal coordination, rather than spatial coding per se, underlies the learning deficits observed here.
The conclusion that disrupting "theta microstructure" impairs learning relies on the assumption that the observed behavioral deficits arise from altered temporal coding from within hippocampal CA1 only. However, optogenetic modulation of medial septal PV neurons influences multiple downstream regions (entorhinal cortex, retrosplenial cortex) via widespread GABAergic projections. While the authors do touch on this, their discussion should expand to include the network-level consequences of entorhinal grid-cell disruption and how this could affect temporal coding both online and offline.
The finding that replay content, rate, and duration are unchanged is critical to the paper's claim of dissociation. However, the analysis is restricted to immobility on the track. Given evidence for distinct awake vs. sleep replay, confirming that off-track rest and post-session sleep replays are similarly unaffected would confirm the conclusions of the paper. If these data are unavailable, the limitation should be acknowledged explicitly. Moreover, statistical power for detecting subtle differences in replay organization or spatial bias should be added to the supplement (n of events per animal, variability across sessions).
The exact protocol for optogenetic stimulation is a bit confusing. For the task, the first and final third (66%) of trials were disrupted and were only stimulated when away from the reward well and only when the animal was moving. What proportion of time within "stimulated" trials remained unstimulated? Why were only 66% of trials stimulated?