A novel role for lipid droplets in the organismal antibacterial response
Figures
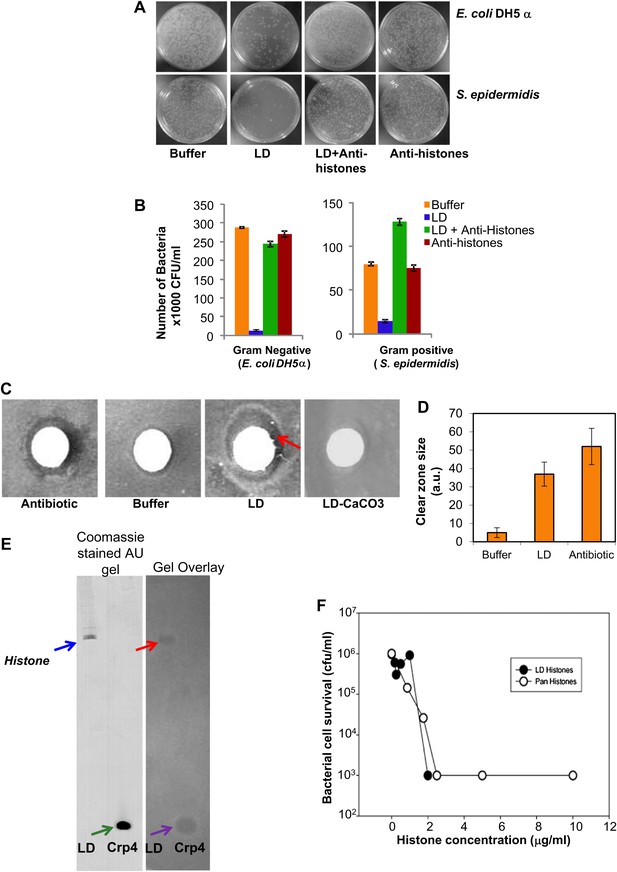
LDs kill bacteria via droplet bound histones.
(A). Representative plates in a colony forming assay, showing growth of Gram-negative (Escherichia coli DH5α, top) and Gram-positive (Staphylococcus epidermidis, bottom) bacteria, where a known amount of bacteria were incubated at 37°C either in buffer alone, or with LDs pre-treated with or without anti-histone antibodies. In buffer (left, ‘Buffer’), many colonies (white spots) were observed, but in the presence of LDs (LD), the observed number of colonies was greatly decreased, demonstrating an antibacterial effect of the LDs. Pre-treatment of the droplets with anti-histone antibodies abolished this effect (LD + Anti-histones). (B). Quantification of colony forming assay in A. Each bar represents the mean number of observed colonies, in three independent trials, presented with the standard error. (C). Disc diffusion assay over a lawn of E. coli DH5α. A potential antibacterial agent is placed on a small sterile piece of filter paper (white circle); a cleared area (darker region) indicates antibacterial activity. Positive control: the antibiotic kanamycin (Antibiotic); growth inhibition region indicated by the red arrow. Negative control: buffer (Buffer). LDs isolated in the presence (LD-CaCO3) or absence (LD) of alkaline carbonate were spotted on sterile discs; bacterial inhibition was observed in the untreated droplets (LD) but not in the carbonate-treated droplets (LD-CaCO3). The filter papers are 7 mm in diameter. (D). Quantification of the size of the clear zone in the disc diffusion assay from C. Fifteen independent disc diffusion assays were performed with purified LDs from Drosophila embryos, the antibiotic kanamycin, or buffer. Antimicrobial activity of compounds was quantified as the diameter of the clear zones surrounding the filter papers after subtraction of filter papers diameter (1 A.U. = 0.1 mm). (E). Use of a gel-overlay assay to determine the identity of the anti-bacterial protein(s) on the LDs. Proteins extracted from LDs (LD, left lane) were run in duplicate on an AU-gel; murine cryptdin 4 (Crp 4, right lane) served as positive control. After electrophoresis, the gel was split. One half (left) was stained by Coomassie Blue; the histone bands are indicated by a blue arrow and the crp 4 control is indicated by the green arrow. The other half (right) was used in a gel overlay assay (see ‘Materials and methods’) to reveal regions of the gel able to inhibit bacterial growth (inhibition by LD is indicated by the red arrow and that by crp 4 control is indicated by the violet arrow). Inhibition of bacterial growth due to proteins on the LDs was only observed in a single region, corresponding to the histones (red arrow). Consistent with this, mass spectrometry of proteins cut from the Coomassie gel corresponding to the killing region identified predominantly histones H2A and H2B (see ‘LDs have antimicrobial activity’). (F). E. coli ML35 cultures were transiently (∼1 hr) exposed to commercial calf thymus pan-histone proteins (Sigma) or gel-extracted LD-histones (from the gel-overlay assay). Both preparations show similar potency for bacterial killing.
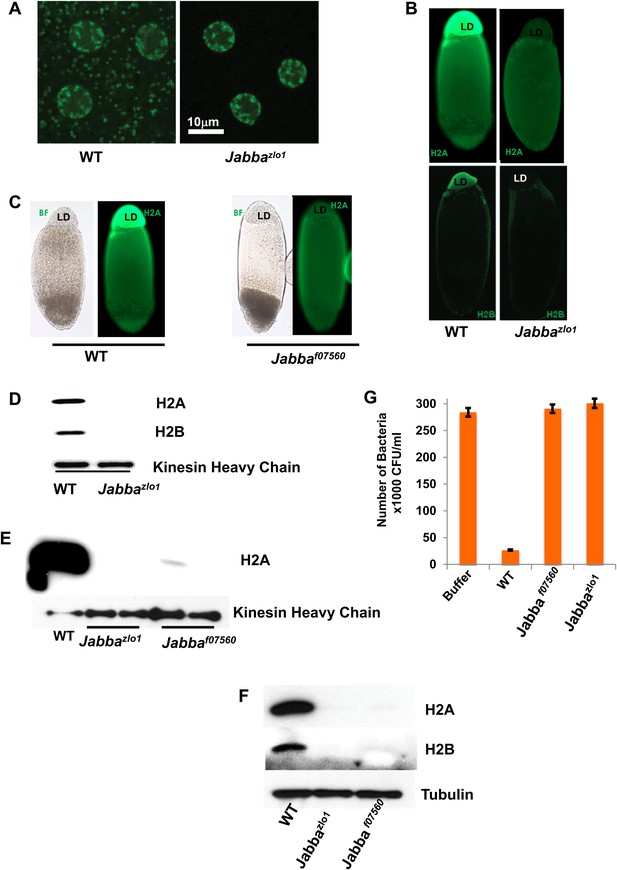
Presence of extranuclear histones depends on the Jabba protein.
(A) Histone H2Av GFP is not detectable in cytoplasmic puncta of Jabbazl01 embryos. Both genotypes show strong signal in nuclei. (B). By immunostaining, endogenous H2A and H2B are absent from the lipid droplet layer (LD) of centrifuged Jabbazl01 embryos. (C). Histone H2A is absent from the lipid droplet layer in centrifuged Jabbaf07560 embryos. BF is the bright field image and LD is the lipid droplet layer. (D). Equal amounts of proteins from purified LDs were compared by Western analysis. Droplets from Jabbazl01 embryos lack histones H2A and H2B. The droplet-bound Khc protein serves as loading control. (E). When compared side by side, similar reductions in droplet-bound histones were found for both the independently isolated Jabba alleles Jabbaf07560 and Jabbazlo1. (F). Western blot of equal numbers of unfertilized wild-type and Jabba mutant embryos. Overall levels of histone H2A and H2B are significantly reduced in the Jabba mutants. (G). LDs purified from embryos of two independently isolated Jabba mutants revealed no bacterial killing activity in antibacterial plate assays, with bacterial growth comparable to buffer alone, in contrast to droplets purified from wild-type embryos which dramatically decreased bacterial growth.
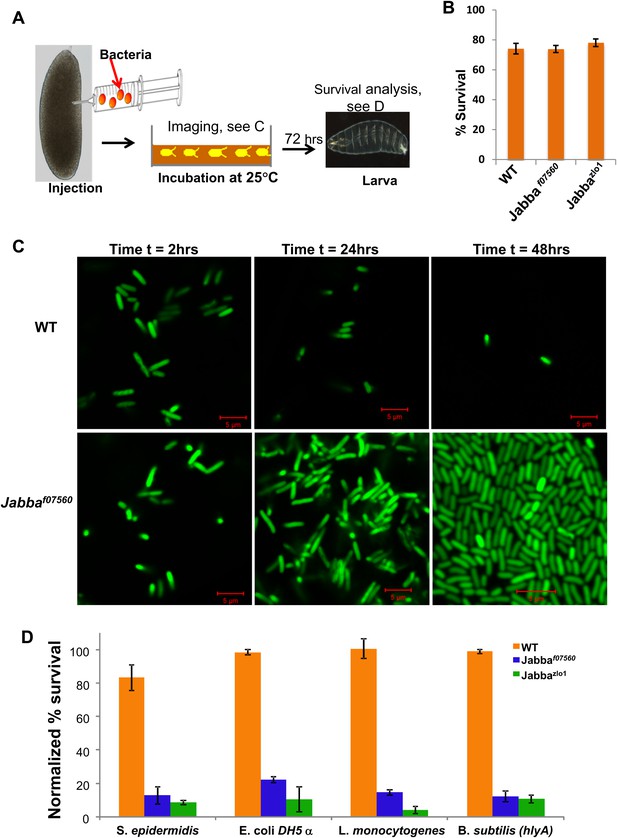
LD bound histones can kill bacteria in vivo.
(A) Schematic representation of embryo microinjection. Early embryos collected within half an hour of laying were injected with a bacterial suspension, as detailed in ‘Materials and methods’. (B). Wild-type and Jabba mutant embryos show similar survival when injected with buffer alone. Wild-type and Jabba mutants (Jabbaf07560, Jabbazl01) embryos were injected with microinjection buffer (no bacteria) and the percentage survival was scored 72 hr post injection. (C) Bacteria grow only in embryos lacking droplet-bound histones. Approximately equal numbers of GFP labeled bacteria (E. coli strain YD133) were injected into wild-type and Jabba mutant embryos (Jabbaf07560) and the growth of bacteria inside embryos was monitored at various times post injection. (D). Drosophila embryos lacking droplet-bound histones have reduced survival due to bacterial infection. Approximately equal numbers of bacteria were injected into wild-type and Jabba mutant (Jabbazl0 and Jabbaf07560) embryos and embryo survival after 72 hr was normalized to the buffer-only injected embryos (in B). The bacterial strains used were Staphylococcus epidermidis (Gram-positive); E. coli DH 5α (Gram- negative); Listeria monocytogenes (Gram-positive and intracellular); and Bacillus subtilis (hlyA), modified Bacillus subtilis expressing listeria hemolysin-A protein (Gram-positive and intracelluar).
2 hr: Additional images of wild-type and Jabba mutant embryos with fluorescent bacteria, 2 hr after bacterial injection.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00003.006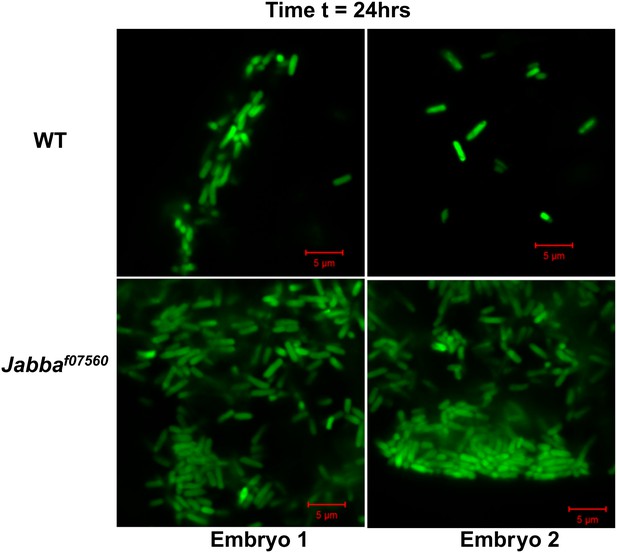
24 hr: Additional images of wild-type and Jabba mutant embryos with fluorescent bacteria, 24 hr after bacterial injection.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00003.007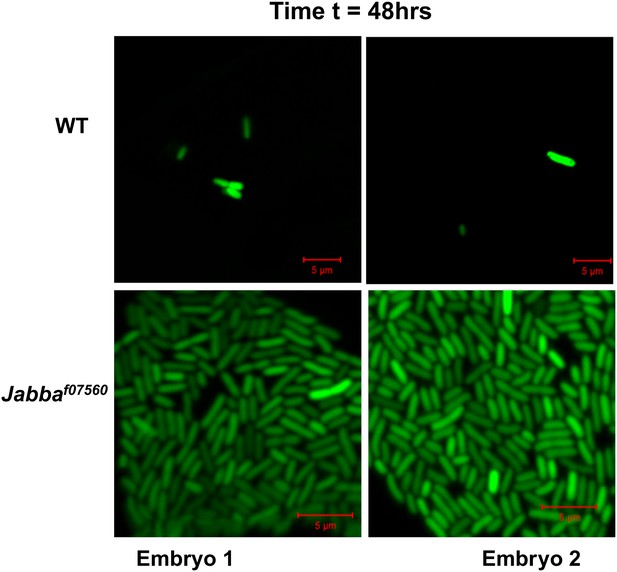
48 hr: Additional images of wild-type and Jabba mutant embryos with fluorescent bacteria, 48 hr after bacterial injection.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00003.008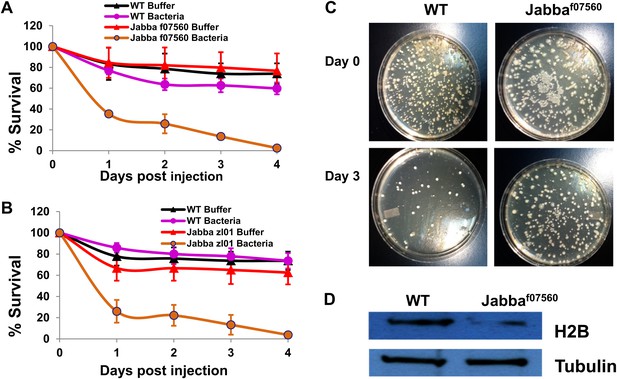
The Jabba protein contributes to improved survival for adult flies.
(A and B) Adult Drosophila lacking Jabba (A: Jabbaf07560; B: Jabbazl01) have reduced survival when challenged by bacteria. Wild-type and Jabba mutant (Jabbazl0 and Jabbaf07560) adult flies were infected with Listeria monocytogenes as detailed in ‘Materials and methods’, and fly survival was monitored over the course of 4 days. (C). Representative plates in a colony forming assay, showing bacterial colonies on agar plates streaked with cytosolic extract from bacteria infected adult flies. (D) Western blots of histone H2B from equal amounts of cytosolic extracts from wild type and Jabba mutant adult flies, showing that overall levels of H2B were significantly reduced in the Jabba mutants.
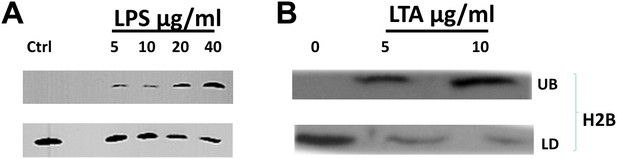
Bacterial cell wall components release droplet bounds histones in a dose dependent manner.
(A). Increasing concentrations of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the buffer releases droplet bound histones from purified LDs. (B). Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) causes the dose dependent release of histones from purified droplets. LDs were purified from wild-type Drosophila embryos, re-suspended in buffer, and incubated for 2 hr at room temperature with different concentrations of LPS or LTA. LDs (LD) were then separated from the under-layer buffer (UB) and both were processed for SDS-PAGE. Western Blot analysis was carried out with H2B histone antibodies.
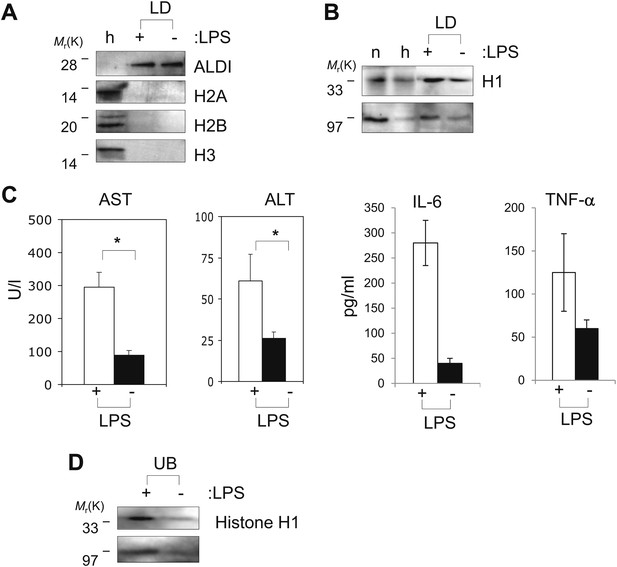
Histones are on mammalian LDs and respond to LPS.
(A). Western blot analysis of LDs (LD) purified from hepatocytes of mice injected with (+) or without (−) LPS. Antibodies against ALDI, histones H2A, H2B and H3 were used. Whole liver homogenate (h) was used for comparison and as a control. (B) The presence of histone H1 (H1) on LDs (LD) purified from hepatocytes of mice injected with (+) or without (−) LPS was detected by immunoblot, and more H1 was present on droplets purified from LPS-treated animals. Equal total proteins from the nuclear fraction (n) and from whole liver homogenate (h) were used as comparison. (C). Mice were injected intraperitoneally with (+) or without (−) LPS, and transaminase levels (AST and ALT) and cytokine levels (IL-6 and TNFα) were quantified in units/l or units/ml in the serum; asterisk indicates statistical significance (p=0.05), confirming that LPS injection provoked the expected biological response. (D). Western blot analysis of histone H1 released into the buffer (UB) when purified LDs, from the liver of infection induced mice, were treated with LPS (+). Histone H1 is either minimally detected or not at all detected in the buffer in the absence of LPS (−). The band at 97 kDa in C and D represents histone H1 oligomers.





