A component of the mir-17-92 polycistronic oncomir promotes oncogene-dependent apoptosis
Figures
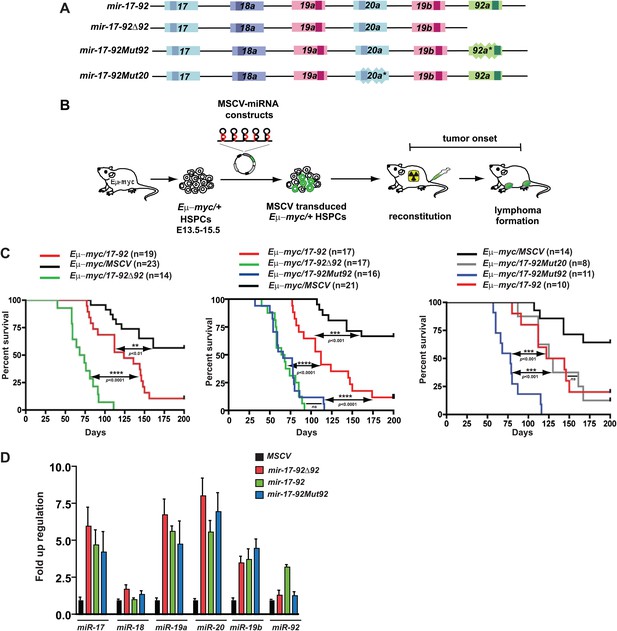
miR-92 negatively regulates the mir-17-92 oncogenic activity in the Eμ-myc B-lymphoma model.
(A) The gene structure of the mir-17-92 polycistron and its mutated derivatives. Light colored boxes, pre-miRNAs; dark colored boxes, mature miRNAs. Homologous miRNA components are indicated by the same color. (B) Schematic representation of the adoptive transfer protocol using Eμ-myc hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). Eμ-myc/+ HSPCs were extracted from E13.5–E15.5 mouse embryos, infected with MSCV retroviral vectors overexpressing mir-17-92 and its derivatives, and finally transplanted into lethally irradiated recipient mice. Lymphoma onset of the adoptive transferred mice was monitored to evaluate the oncogenic collaboration between c-Myc and a specific miRNA. (C) miR-92 deficiency specifically accelerates the oncogenic activity of mir-17-92 in the Eμ-myc model. Using the Eμ-myc adoptive transfer model, we compared the oncogenic effects between mir-17-92 and mir-17-92Δ92 and observed a significant acceleration of tumor onset in Eμ-myc/mir-17-92Δ92 mice (p<0.0001, left). When the oncogenic effects of mir-17-92, mir-17-92Δ92 and mir-17-92Mut92 were compared in the same adoptive transfer model, mir-17-92Δ92 and mir-17-92Mut92 similarly accelerated Eμ-myc-induced lymphomagenesis compared to mir-17-92 (p<0.0001 for both comparisons, middle). Deficiency of miR-20 failed to affect the oncogenic cooperation between mir-17-92 and Eμ-myc, having minimal effects on tumor onset (right). (D) The mutation of miR-92 has minimal effects on the levels of the remaining mir-17-92 components. Eμ-myc B-lymphoma cells were infected with MSCV retrovirus overexpressing mir-17-92, mir-17-92Δ92 and mir-17-92Mut92 at an MOI (multiplicity of infection) of 1. Expression levels of miR-17, 18a, 19a, 20a, 19b and 92 were subsequently determined using Taqman miRNA assays. Error bars indicate standard deviation (n = 3). **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
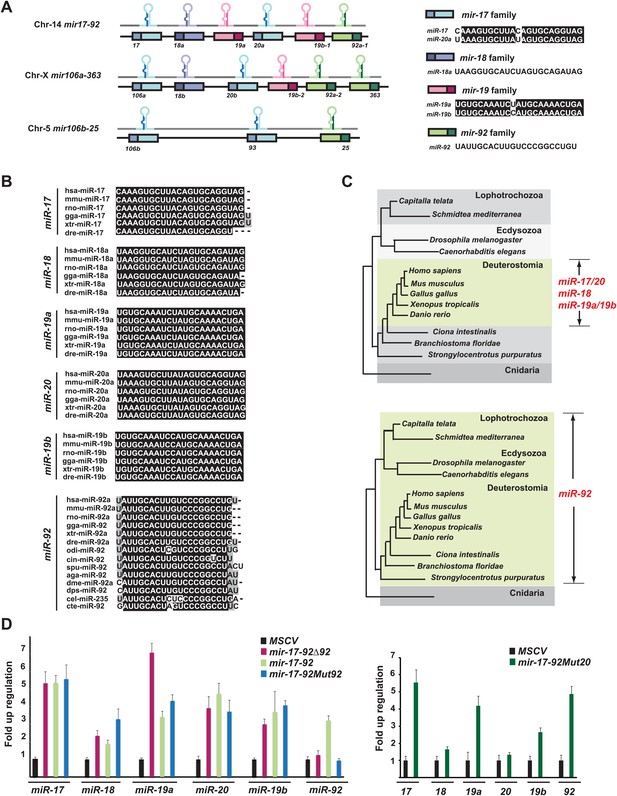
Gene structure and evolutionary conservation of mir-17-92.
(A) A diagram represents the gene structure of mir-17-92 and its two mammalian homologs. The six mir-17-92 components are classified into four distinct miRNA families based on the seed sequence conservation. (B and C) miR-92 has a more ancient evolutionary history compared to the rest of mir-17-92 components. miR-92 is evolutionarily conserved in Deuterostome, Ecdysozoa and Lophotrochozoa, yet the remaining mir-17-92 components only have vertebrate homologs. (D) The mutation of miR-92 or miR-20 in the mir-17-92 retroviral construct has minimal effects on the expression levels of the remaining mir-17-92 components. 3T3 cells were infected with MSCV retrovirus at an MOI (multiplicity of infection) of 1 to overexpress mir-17-92, mir-17-92Δ92 and mir-17-92Mut92 (left), or overexpress mir-17-92Mut20 (right). Expression levels of miR-17, 18a, 19a, 20a, 19b and 92 were each determined using Taqman miRNA assays. Error bars indicate standard deviation (n = 3).
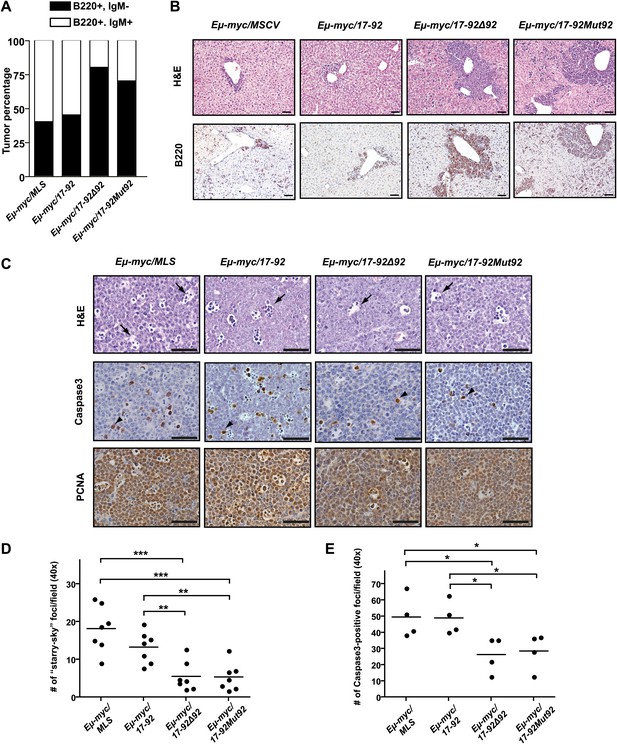
The miR-92 deficient mir-17-92 cooperates with c-Myc to promote highly aggressive B-lymphomas.
(A) The percentage of IgM positive and IgM negative B-lymphomas was calculated for each genotype (Eμ-myc/MSCV, n = 10; Eμ-myc/17-92, n = 9; Eμ-myc/17-92Δ92, n = 10; Eμ-myc/17-92Mut92, n = 10). (B) The Eμ-myc/17-92Mut92 and Eμ-myc/17-92Δ92 mice developed high grade B-lymphomas that were frequently disseminated into the liver. When compared to Eμ-myc/MSCV and Eμ-myc/17-92 mice, Eμ-myc/17-92Mut92 and Eμ-myc/17-92Δ92 lymphomas gave rise to more liver dissemination, as indicated by H&E and B220 staining. (C) Eμ-myc/17-92Mut92 and Eμ-myc/17-92Δ92 lymphomas exhibited a decreased apoptosis compared to Eμ-myc/MSCV or Eμ-myc/17-92 lymphomas. Representative lymphomas were stained for H&E, cleaved caspase-3 and PCNA. Arrow, ‘starry sky’ feature of apoptotic lymphoma cells; arrowhead, apoptotic cells with positive staining for cleaved caspase-3; scale bar, 50 μm. (D and E) Apoptosis was quantitatively measured in representative lymphomas of each genotype using the ‘starry sky’ features (D) and cleaved caspase-3 staining (E). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
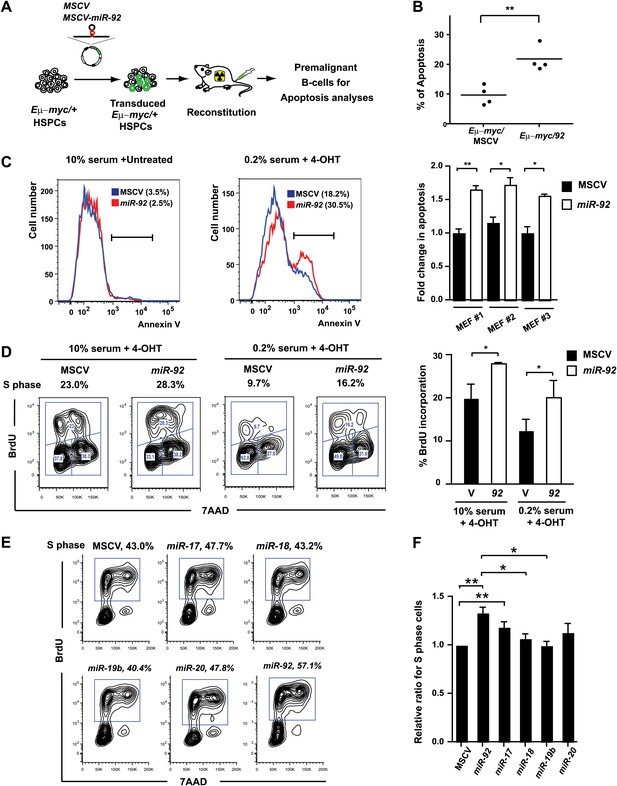
miR-92 enhances both c-Myc-induced apoptosis and c-Myc-induced proliferation.
(A) The schematic representation of the adoptive transfer model to evaluate the miR-92 effects on the Eμ-myc premalignant B-cells in vivo. (B) miR-92 overexpression enhances the apoptotic response in the premalignant Eμ-myc B-cells in vivo. Using the Eμ-myc adoptive transfer model, we generated well-controlled Eμ-myc/MSCV and Eμ-myc/92 mice reconstituted from donor matched Eμ-myc HSPCs. Premalignant Eμ-myc splenic B-cells were isolated from the Eμ-myc/MSCV and Eμ-myc/92 mice 6 weeks after reconstitution. The in vivo apoptosis was measured by the level of caspase activation using Red-VAD-FMK, a fluorescently labeled caspase inhibitor that specifically bound to cleaved caspases. The percentage of Eμ-myc B-cells positive for cleaved caspases was shown for four independent experiments. (C) Enforced miR-92 expression in R26MER/MER MEFs significantly enhanced c-Myc-induced apoptosis. miR-92 overexpressing and the control R26MER/MER MEFs were serum starved, and the MycERT2 transgene was activated by 4-OHT treatment. The level of apoptosis of each MEF was measured using Annexin V staining before (left) and after (middle) 4-OHT treatment and serum starvation. Quantification of c-Myc-induced apoptosis was performed in three independent MEF lines that overexpressed MSCV or miR-92 (right panel, error bars represent SEM). (D) Enforced miR-92 expression in R26MER/MER MEFs significantly enhanced c-Myc-induced proliferation. Proliferative effects of miR-92 was measured by BrdU incorporation in MycERT2 activated R26MER/MER MEFs. miR-92 cooperated with c-Myc to promote BrdU incorporation in both 10% (left) and 0.2% (middle) serum culture conditions. Quantification of BrdU incorporation was performed in two independent experiments (right). (E) miR-92 is a potent mir-17-92 component to promote primary B-cell proliferation. The proliferative effects of all mir-17-92 miRNAs were measured individually in primary B-cells using BrdU incorporation. (F) The quantification of BrdU incorporation in experiments described in (E) was performed in four independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviation, *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
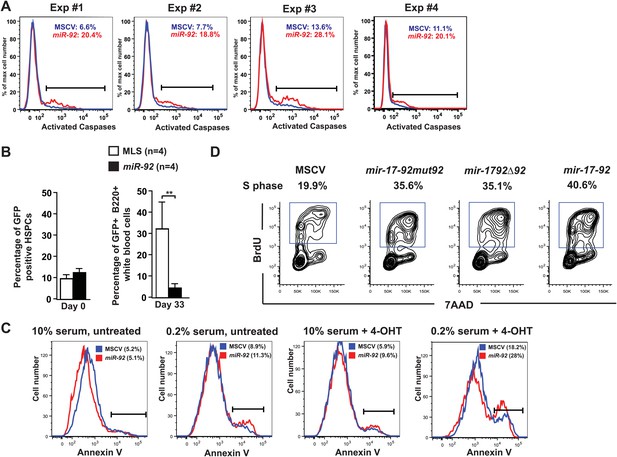
miR-92 enhances c-Myc-induced apoptosis both in vitro and in vivo.
(A) miR-92 enhances the apoptotic response in the premalignant Eμ-myc B-cells in vivo. Using the Eμ-myc adoptive transfer model, we generated well-controlled Eμ-myc/MSCV and Eμ-myc/92 mice that were reconstituted from the same Eμ-myc HSPCs. The in vivo apoptosis was measured by the level of caspase activation 6 weeks after the transplantation. The percentage of Eμ-myc B-cells positive for cleaved caspases was shown for four independent experiments. (B) miR-92 infected, premalignant Eμ-myc B-cells is significantly depleted in the Eμ-myc adoptive transfer model. We generated well-controlled Eμ-myc/MSCV and Eμ-myc/92 mice reconstituted from the same Eμ-myc HSPCs. We measured the percentage of retrovirally infected cells (GFP+) before reconstitution (left), and demonstrated similar infection efficiency in Eμ-myc/MSCV and Eμ-myc/92 mice. At day 33 post adoptive transfer, we isolated white blood cells from the peripheral blood of these mice, and measured the percentage of retrovirally infected, Eμ-myc B-cells (B-220-positive; GFP-positive cells) using FACS. Error bars indicate standard deviation, n = 4, **p<0.01. (C) Enforced miR-92 expression in R26MER/MER MEFs significantly enhanced c-Myc-induced apoptosis. The miR-92 effect was most evident when the infected R26MER/MER MEFs were serum starved and treated with 4-OHT. (D) miR-92 is required for the potent proliferative effect of mir-17-92 in primary B-cells. miR-92 deficient mir-17-92 miRNA polycistrons exhibited a reduced BrdU incorporation in primary B-cell culture in vitro.
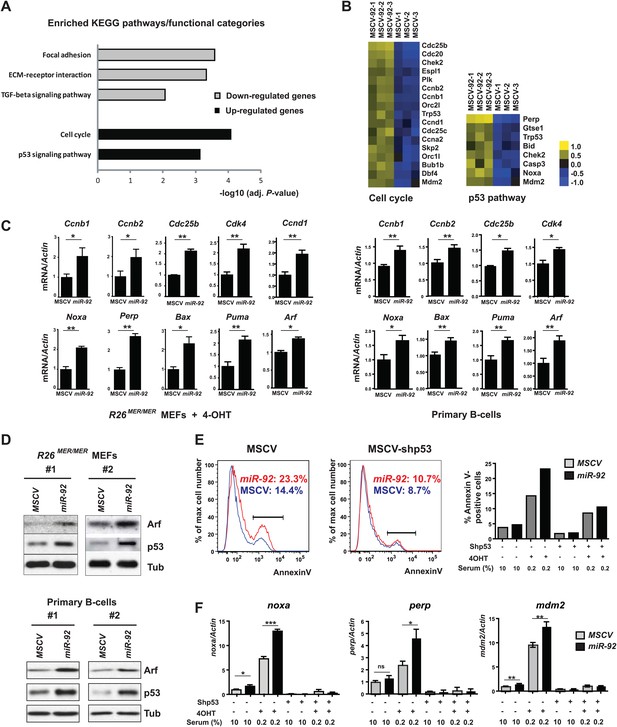
miR-92 induces apoptosis through the activation of the p53 pathway.
(A) The genes upregulated by miR-92 were enriched for the cell cycle pathway and the p53 pathway. Microarray analyses compared gene expression profiles of serum starved and 4-OHT treated R26MER/MER MEFs overexpressing either miR-92 or a control MSCV vector (n = 3). The differentially expressed genes were defined as those with at least 1.5-fold expression level change using SAM (Significance analysis of microarrays, false discovery rate <1%). Pathway analyses were performed on upregulated and downregulated genes using the KEGG database. (B) The heatmaps of the miR-92 upregulated genes enriched for the cell cycle and p53 pathways. (C) Components of the cell cycle and p53 pathways were upregulated upon miR-92 overexpression in both MEFs (left) and primary B-cells (right). The quantitation of gene expression was performed using real time PCR. (D) miR-92 overexpression induces the accumulation of Arf and p53 proteins in MEFs and primary B-cells from bone marrow. Western analyses were performed on the R26MER/MER MEFs (left) and primary B-cells (right) that overexpressed miR-92 or a control MSCV vector in two independent experiments. The infected R26MER/MER MEFs were assayed at 6 hr after serum starvation and 4-OHT treatment; the infected primary B-cells were collected 72 hr post infection. (E) The apoptotic effect of miR-92 requires an intact p53 pathway. We infected R26MER/MER MEFs with two MSCV retrovirus, MSCV-p53shRNA and MSCV-92, to obtain doubly infected cells. Knocking down p53 in R26MER/MER MEFs abolished the ability of miR-92 to enhance c-Myc-induced apoptosis, as measured by Annexin V staining (two left panels). The percentage of apoptotic MEFs of each experimental condition was quantitatively measured (right). (F) The induction of the p53 pathway components by miR-92 is dependent on an intact p53. Knocking down p53 in R26MER/MER MEFs abolished the ability of miR-92 to induce pro-apoptotic p53 targets and other canonical p53 targets, including noxa, perp and mdm2. Error bars represent standard deviation, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
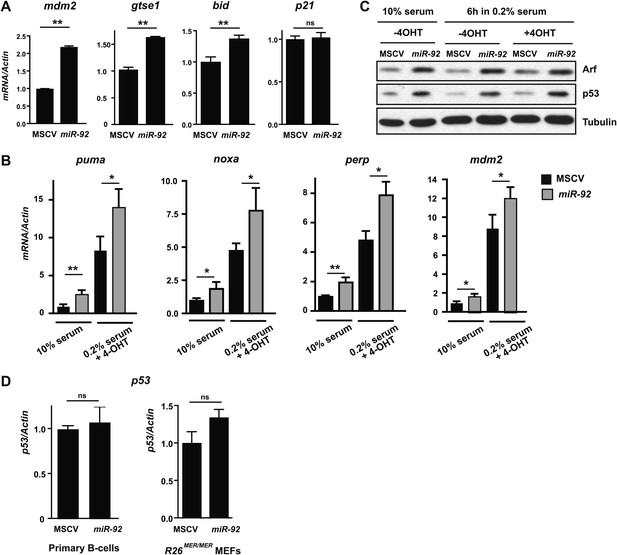
miR-92 overexpression triggers the activation of the p53 pathway.
(A) miR-92 overexpression in R26MER/MER MEFs induced several p53 target genes in addition to those described in Figure 3C, including mdm2, Gtse1 and Bid, but not p21. (B) Induction of p53 targets by miR-92 in R26MER/MER MEFs with and without MycERT2 activation. (C) miR-92 overexpression alone enhanced Arf and p53 protein level in R26MER/MER MEFs with and without 4-OHT treatment. (D) miR-92 overexpression did not affect p53 mRNA levels in either primary B-cells or in R26MER/MER MEFs. Error bars indicate standard deviation, n = 3, *p<0.05; **p<0.01.
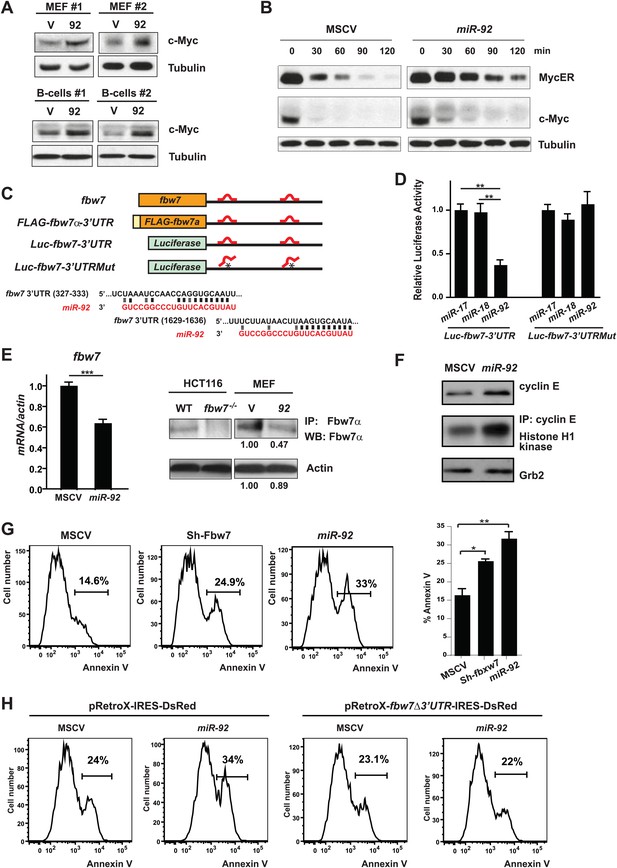
miR-92 promotes the accumulation of c-Myc protein through repressing Fbw7.
(A) miR-92 enhances the accumulation of c-Myc protein in synchronized R26MER/MER MEFs (upper), as well as primary B-cells (lower). The miR-92 overexpression and the control R26MER/MER MEFs were synchronized by serum starvation and were collected 12 hr after being released into serum culture conditions to determine the c-Myc protein level. This synchronization approach in R26MER/MER MEFs has provided us with the most consistent measurement for c-Myc protein level, because it is regulated in a cell-cycle-dependent manner. (B) miR-92 overexpression decreases the turnover of c-Myc protein. Serum-synchronized R26MER/MER MEFs that overexpress either miR-92 or the control MSCV vector were released into the serum for 6 hr, treated with cycloheximide, collected at the indicated time points, then analyzed by western blot to determine the levels of MycER and the endogenous c-Myc protein. (C) Schematic representation of the two miR-92 binding sites in the murine fbw7 3′UTR. Additionally, a luciferase reporter and a FLAG tagged fbw7 ORF were each placed upstream of a wild-type fbw7 3′UTR, or a mutated fbw7 3′UTR that abolished the predicted miR-92 binding. (D) The expression of Luc-fbw7-3′UTR was specifically repressed by miR-92 in Dicer−/− HCT116, while mutations of the two putative miR-92 binding sites within the fbw7-3′UTR (Luc-fbw7-3′UTRMut) abolished this repression. (E) The endogenous fbw7 gene was downregulated by miR-92 post-transcriptionally. Both the endogenous fbw7 mRNA (left) and the endogenous Fbw7 protein (right) were repressed upon miR-92 overexpression in R26MER/MER MEFs. Due to the lack of a proper antibody to detect endogenous Fbw7 in regular western analysis, we demonstrated the downregulation of endogenous Fbw7 by miR-92 using immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting with a polyclonal anti-Fbw7 antibody. (F) miR-92 enhances the accumulation of Cyclin E protein. Overexpression of miR-92 increased the accumulation of Cyclin E protein, which was further confirmed by the increased Cyclin E-dependent kinase activity. (G) The knockdown of fbw7 resembles the effect of miR-92 to enhance c-Myc-induced apoptosis. Knocking down fbw7 in R26MER/MER MEFs enhanced c-Myc-induced apoptosis, partially recapitulating the phenotype caused by miR-92 overexpression. Apoptosis was quantitatively measured by Annexin V staining in two independent lines of R26MER/MER MEFs upon serum starvation and 4-OHT treatment. (H) Overexpression of fbw7 abolished the apoptotic effects of miR-92 in R26MER/MER MEFs. R26MER/MER MEFs were doubly infected by pRetro-fbw7αΔ3′UTR-IRES-dsRed and MSCV-miR-92. The c-Myc-induced apoptosis was quantitatively measured by Annexin V staining in doubly infected R26MER/MER MEFs upon serum starvation and 4-OHT treatment. Error bars represent standard deviation). *p<0.05; **p<0.01.
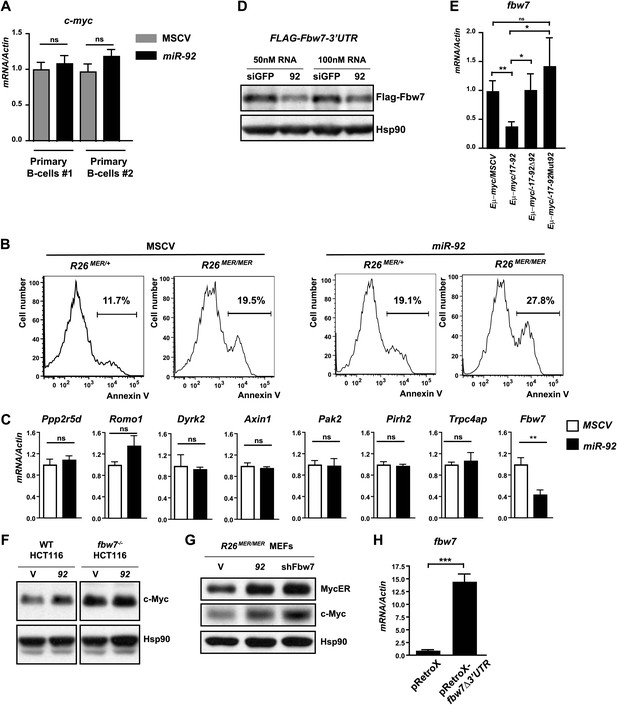
miR-92 overexpression enhances c-Myc protein level by repressing Fbw7.
(A) miR-92 overexpression did not affect c-myc mRNA levels in two independent primary B-cells. (B) The c-Myc dosage determines the degree of c-Myc-induced apoptosis in R26MER/MER MEFs. When R26MER/MER MEFs were compared with R26MER/+ MEFs, a twofold increase in the MycERT2 dosage significantly enhanced the c-Myc-induced apoptotic response upon serum starvation. This effect was observed in R26MER/MER MEFs either with or without miR-92 overexpression. (C) Negative regulators of c-Myc that contain a putative miR-92 binding site(s) were screened for miR-92-mediated repression in R26MER/MER MEFs that overexpress miR-92 or a control MSCV vector. Only fbw7 exhibited a miR-92–mediated repression. (Error bars indicate standard deviation, n = 3, **p<0.01). (D) The expression of FLAG-fbw7-3′UTR was significantly repressed by miR-92 in Dicer−/− HCT116 cells. (E) fbw7 is downregulated in Eμ-myc lymphomas that overexpress miR-92. A panel of Eμ-myc/MSCV (n = 9), Eμ-myc/17-92 (n = 7), Eμ-myc/17-92Δ92 (n = 6) and Eμ-myc/17-92Mut92 (n = 5) lymphomas were compared for their expression level of endogenous fbw7. Eμ-myc/17–92 lymphomas exhibited a specific decrease of fbw7 compared to the other genotypes, possibly due to the miR-92 overexpression. (F) The c-MYC upregulation by miR-92 requires an intact fbw7. The effect of miR-92 to upregulate c-MYC protein level was observed in wild-type Hct116 cells, but largely absent in FBW7−/− Hct116 cells. (G) fbw7 knockdown by RNAi in R26MER/MER MEFs recapitulated the c-Myc upregulation by miR-92. (H) fbw7 expression level in R26MER/MER MEFs infected with pRetroX-fbw7-IRES-DsRedExpress. Error bars indicate standard deviation, *p<0.05; **p<0.01.
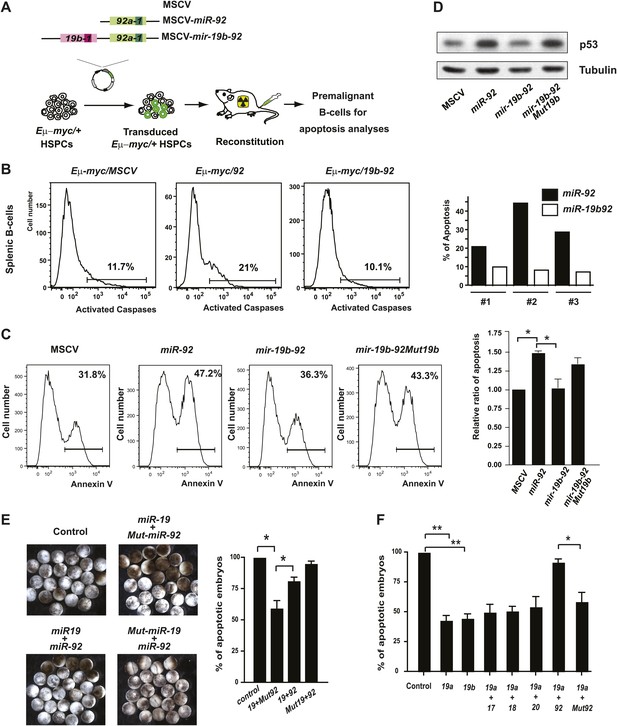
The antagonistic interaction between miR-19 and miR-92 regulates the balance between proliferation and apoptosis.
(A) The schematic representation of the Eμ-myc adoptive transfer model to evaluate the functional interaction between miR-92 and miR-19 in vivo. Light colored boxes, pre-miRNAs; dark colored boxes, mature miRNAs. (B) miR-19 antagonizes the apoptotic effects of miR-92 in vivo. miR-92 overexpression in the Eμ-myc adoptive transfer model enhanced apoptosis in premalignant Eμ-myc splenic B-cells, while the mir-19b-92 dicistron expression abolished this apoptotic effect (left three panels). A quantitative analysis of apoptosis by FACS was shown for three independent, well-controlled experiments (right). (C) miR-19b dampens the miR-92-induced apoptosis in MycERT2 activated R26MER/MER MEFs. R26MER/MER MEFs were infected by miR-92, mir-19b-92, mir-19b-92Mut19b and the MSCV control vector, and were subsequently serum starved and treated with 4-OHT to activate MycERT2. Apoptosis in these samples was measured quantitatively using Annexin V staining (left four panels). The extent of apoptosis induced by MSCV, miR-92, mir-19b-92, mir-19b-92Mut19b was normalized to that of MSCV infected R26MER/MER MEFs and then averaged from four independent experiments (right). (D) miR-19b dampens the miR-92-induced p53 activation. R26MER/MER MEFs that overexpress the indicated constructs (miR-92, mir-19b-92Mut19b and mir-19b-92) were collected 48 hr after infection and then analyzed by western blot to determine the level of p53 protein. (E) miR-92 and miR-19 exhibit antagonistic effects to regulate hydroxyurea (HU)-induced cell death in Xenopus embryos. Representative images of HU-treated Xenopus embryos that were co-injected with human Ago2 and the indicated miRNA mimics (left). Co-injection of miR-92 dampened the cell survival effects of miR-19 on HU-induced apoptosis (right, n = 3, with >20 embryos in each group). (F) miR-92 exhibits a specific antagonistic interaction with miR-19. Injection of miR-19a or miR-19b rescued HU-induced apoptosis in Xenopus embryos. Co-injection of miR-92, but not a mutated miR-92, or other mir-17-92 components, dampened the cell survival effect of miR-19 (n = 3, with >20 embryos in each group). Error bars represent standard deviation, *p<0.05; **p<0.01.
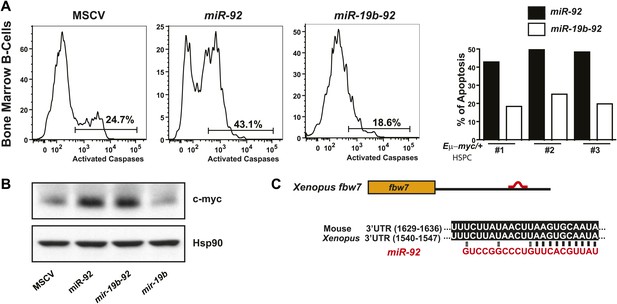
Functional antagonism between miR-19:miR-92 regulates the balance between proliferation and apoptosis.
(A) miR-19 antagonizes the apoptotic effects of miR-92 in vivo. miR-92 overexpression enhanced apoptosis in premalignant Eμ-myc bone marrow B-cells in vivo, while co-expression of miR-19 and miR-92 as a dicistron (mir-19b-92) abolished this apoptotic effect (left three panels). A quantitative analysis of apoptosis by FACS was shown for three independent experiments (right). (B) miR-19 has no effects on the level of c-Myc protein. While miR-92 overexpression significantly enhanced the level of c-Myc in R26MER/MER MEFs, co-expression of miR-19b and miR-92 did not reverse the increase in c-Myc expression. In addition, miR-19b expression alone did not impact the dosage of c-Myc protein. (C) Xenopus fbw7 contains one predicted target site for miR-92. This predicted miR-92 binding site is conserved between Xenopus and mouse.
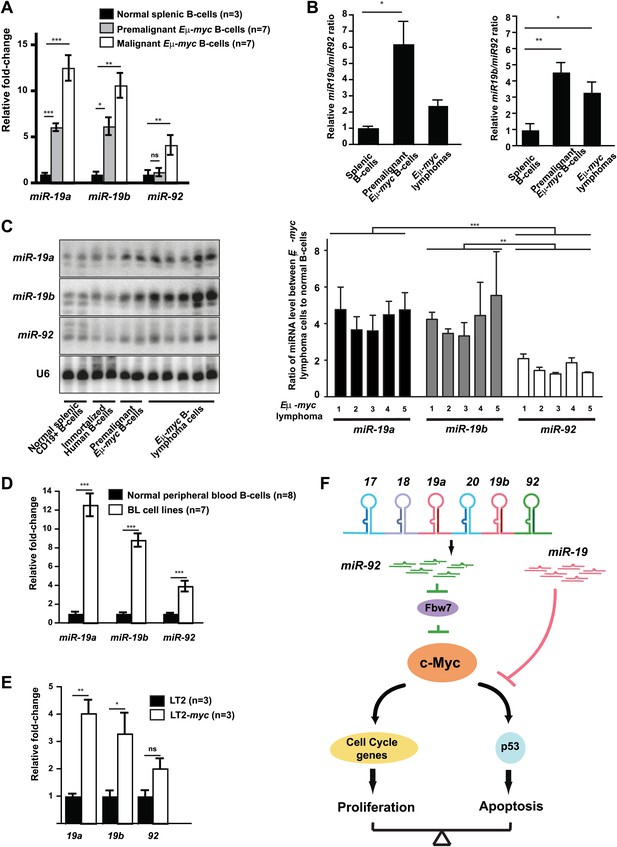
The miR-19:miR-92 antagonism is disrupted during malignant transformation.
(A and B) Compared to normal splenic B-cells, premalignant and malignant Eμ-myc B-cells favored a greater increase in mature miR-19 (miR-19a and miR-19b) than miR-92. The purified normal splenic B-cells, premalignant Eμ-myc bone marrow B-cells and malignant Eμ-myc B-lymphoma cells were subjected to Taqman miRNA assays to determine the expression level of miR-19a, miR-19b and miR-92. Comparing premalignant/malignant Eμ-myc B-cells vs normal splenic B-cells, all three miRNAs exhibited an increased level, although the increase in miR-19a or miR-19b was significantly higher than that of miR-92 (A). In the same experiment, the relative ratios for miR-19a:miR-92 and miR-19b:miR-92 were measured for all normal splenic B-cells and Eμ-myc B-cells (B). (C) Mature miR-19 and miR-92 are differentially expressed in normal splenic B-cells and Eμ-myc B-lymphoma cells. The normal splenic B-cells, immortalized human B-cells, premalignant Eμ-myc/+ B-cells, and Eμ-myc/+ B-lymphoma cells were subjected to Northern analysis. Compared to normal splenic B-cells, both malignant and premalignant Eμ-myc/+ B-cells favored a greater increase of miR-19 than miR-92. (D) Compared to normal B-cells isolated from peripheral blood, human Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines favor a greater increase in mature miR-19 than miR-92. (E) Compared to normal livers (LT2), mouse hepatocellular carcinomas caused by the inducible c-Myc over-expression (LT2-myc) favor a greater increase in mature miR-19 than miR-92. (F) A diagram describes our proposed model to explain the functional interactions between miR-92 and miR-19 in c-Myc-induced B-lymphomagenesis. Aberrant c-Myc expression couples rapid proliferation and p53-dependent apoptosis. miR-92 overexpression further increases c-Myc dosage to strengthen this coupling, at least in part by repressing Fbw7. This miR-92 effect ensures a potent mechanism to eliminate premalignant c-Myc overexpressing cells. Interestingly, miR-92 and can be antagonized by the survival effects of the miR-19 miRNAs encoded by the same mir-17-92 miRNA polycistron. Taken together, while miR-19 miRNAs repressed c-Myc-induced apoptosis to promote the oncogenic cooperation between mir-17-92 and c-Myc, miR-92 exhibits a negative regulation. Thus, the antagonistic interactions between miR-92 and miR-19 confer an intricate crosstalk between proliferation and apoptosis. Error bars represent standard deviation, *p<0.05; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
Tables
Flow cytometric immunophenotyping of Eμ-myc lymphomas with enforced expression of different mir-17-92 derivatives
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00822.006| Genotype | n | Percentage (%) | Immunotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eμ-myc/MSCV | 4 | 40 | B220+, IgM−, CD19+, CD4−, CD8− |
| 6 | 60 | B220+, IgM+, CD19+, CD4−, CD8− * | |
| Eμ-myc/17–92 | 4 | 40 | B220+, IgM−, CD19+, CD4−, CD8− |
| 5 | 50 | B220+, IgM+, CD19+, CD4−, CD8− † | |
| 1 | 10 | B220−, IgM−, CD19−, CD4+, CD8+ | |
| Eμ-myc/17–92Mut92 | 7 | 70 | B220+, IgM−, CD19+, CD4−, CD8− |
| 3 | 30 | B220+, IgM+, CD19+, CD4−, CD8− ‡ | |
| Eμ-myc/1792Δ92 | 8 | 80 | B220+, IgM−, CD19+, CD4−, CD8− |
| 2 | 20 | B220+, IgM+, CD19+, CD4−, CD8− § |
-
*
1 out of 6 samples predominantly contains IgM+ cells, with a small percentage of IgM− cells.
-
†
3 out of 5 samples predominantly contain IgM+ cells, with a small percentage of IgM− cells.
-
‡
1 out of 3 samples predominantly contains IgM+ cells, with a small percentage of IgM− cells.
-
§
1 out of 2 samples predominantly contains IgM+ cells, with a small percentage of IgM− cells.





